matlab(五)图形绘制
目录
- 图形绘制基础
-
- 步骤
- 基本绘图命令
- 二维图形的绘制
图形绘制基础
步骤
- 准备数据和函数, 常用指令如下:
x = 0: 0.1: 10;
y1 = bessel(1, x);
y2 = bessel(2, x);
- 选择图形输出的窗口及位置, 常用指令如下:
figure(1); %打开第一个图形
subplot(m, n, k); %绘制m×n个图形, k表示当前图形的位置
- 调用基本的绘图函数, 常用指令如下:
plot(x, y1, x, y2, x, y3); %绘制y1, y2, y3三条曲线
plot3(x, y, z, ‘r:’);%绘制三维曲线, r表示红色, : 表示曲线
- 设置坐标轴的范围, 标记号和网格线, 常用指令如下:
axis([0, 10, -3, 3]);%x轴范围0到10, y轴范围-3到3
grid on; %加网格
- 用名称, 图例, 坐标名, 文本等对图形进行注释, 常用指令如下:
xlabel(‘x’); %对x轴进行标注, 标注内容为单引号内的内容
titlel(‘图1’);
text(1, 1, ‘y = f(x)’); %在(1, 1)处标注文本
- 打印输出图形, 常用指令如下:
print-dps2;
基本绘图命令
plot(y, 's'); %y是一个向量, 其x坐标是元素序号
plot(x, y, 's');
plot(x1, y1, 's1', x2, y2, 's2');
h = plot(...);
plot3(x, y, z, 's');
loglog; %横纵坐标都是对数形式
semilogx; %x坐标是对数
semilogy; %y坐标是对数
plotyy(x1, y1, x2, y2, '参数1', '参数2'); %同一个图中两套坐标轴, 参数1和参数2可以设置坐标形式, 如'loglog'
二维图形的绘制
同一张图上画两条曲线:
x = 0:0.01:10;
y = sin(x);
y1 = x.*sin(x);
plot(x,y,x,y1);
grid on;
在同一窗口中画三张图:
y2 = exp(2*cos(x));
subplot(2,2,1); plot(x, y);
subplot(2,2,2); plot(x, y1);
subplot(2,2,3); plot(x, y2);
自定义曲线样式:
- 颜色: 红色r, 蓝色b, 绿色g, 黑色k, 白色w
- 线型: ":"表示虚线, "-"表示实线, "–"表示划线, "-."表示点划线
- 特殊点标注: “+, ×, <, >”
plot(x, y, 'r:', x, y1, 'g--', x, y2, 'b-.');
x = 0:0.2:10;
y = sin(x);
y1 = x.*sin(x);
y2 = exp(2*cos(x));
plot(x,y,'r:+',x,y1,'g--d',x,y2,'b-.o')
二维图的标注:
x= -10:0.1:10;
x= x+(x==0)*eps;%使用近似0,防止出现0/0的情况
y= sin(x)./x;
plot(x, y);
xlabel('x轴');
ylabel('y轴');
title('函数的频谱');
plot(x,y);
xlabel('x');
ylabel('y = sin(x)');
text(0,sin(0),'\leftarrowsin(x)=0');%左箭头标注
text(3*pi/4,sin(3*pi/4),'\rightarrowsin(x)=0.707');%右箭头标注
用gtext指令在曲线上取点:
plot(x,y);
xlabel('x');
ylabel('y');
text(0,sin(0),'\rightarrowsin(x)=0');
text(3*pi/4,sin(3*pi/4),'\leftarrowsin(x)=0.707');
legend('y=cos(x)'); %标注函数名, 有几条曲线就有几个参数
grid on;
gtext('No.1')
对数和半对数坐标的绘制:
x = linspace(0,10,100);
y=exp(x);
subplot(1,3,1);
plot(x,y);
subplot(1,3,2);
loglog(x,y);
subplot(1,3,3);
semilogy(x,y)
双y轴图形的绘制(plotyy):
x = 0:1:1000;
a = 1000;b=0.01;c=0.01;
y1 = a*exp(-b*x);
y2 = cos(c*x);
plotyy(x,y1,x,y2,'semilogy','plot');
legend('y1=a×exp(-b×x)','y2 = cos(c×x)')
极坐标绘制:
polar(theta, rho, linespec); 其中theta是极角, rho是极径, linespec用来指定曲线线型, 标记符号和颜色等.
x =0:0.01:2*pi;
polar(x,sin(2*x).*cos(2*x),'r:');
title('八瓣梅花图')
x=[1 2 3];
y = [3 5 2; 4 6 8; 7 5 3];
bar(x,y)
%bar(x,y,'stack'); %画成堆栈形式
x=[1 2 3];
y = [3 5 2; 4 6 8; 7 5 3];
barh(x,y)
二维区域图:
A = [1 2 3 4
2 4 6 8
3 5 7 6
7 5 3 2
6 3 2 1];
area(A);
set(gca,'xtick',1:5);%设置x轴
grid on; %显示网格
set(gca,'layer','top'); %将网格显示在图形之上

矩阵A的每一列构成一条折线, 第一条折线(1, 2, 3, 7, 6)与第二列的值相加到底第二条折线, 以此类推.
二维饼图:



离散图:
枝干图:
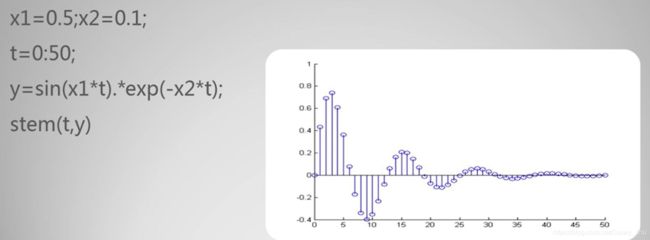
可以设置样式, 如:
stem(t, y,’:dr’, ‘fill’); %虚线, 菱形, 红色, 填充
阶梯图:

二维轮廓图:
将相对于某一平面具有同一高度的点连成一条线, 高度由高度矩阵来反映, 即等高线.

(peaks产生尖峰, 总共画30条线)
