GOF(八)-组合模式【推荐】
组合模式(Composite Pattern)
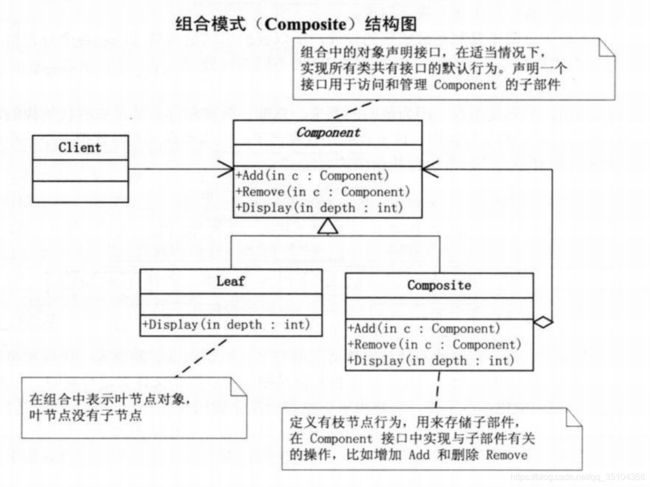
组合模式(又叫部分整体模式):根据树形结构来组合对象,用来表示部分及整体的层次,所以是结构型
组合模式让单个对象和组合对象的使用具有一致性,用户不需要关心自己处理的是单个对象还是整个组合结构,而且不用因为加入新的对象而修改代码。
UML的相关知识,可以访问我的另外一篇博文
组合模式有两种实现方式:透明式的组合模式、安全式的组合模式,至于二者的区别,请大家观察代码体会:
透明式:
由于Component被聚合,所以我习惯先编写此类
【名称与UML图名称一致,不多解释】
public abstract class Component {
public abstract int totalPrice();
public abstract void add(Component component);
public abstract void remove(Component component);
}
编写Component的两个实现类
Composite【相当于树干】(树干可以有叶子、也可以有其他 “子”树干 )
/**
* @description:
* 树干,可以有叶子,或者其他更小的 子树干
*/
public class Composite extends Component {
private String name;
private int price;
// 聚合抽象类
private List<Component> childs = new ArrayList<>();
public Composite() {
}
public Composite(String name, int price) {
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public int getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(int price) {
this.price = price;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public int totalPrice() {
int num = this.price;
// 使用stream流计算总价
num += childs.stream().mapToInt(Component::totalPrice).sum();
// 普通方式计算总价:遍历子节点,计算总价钱
// for (Component c : childs) {
// num += c.totalPrice();
// }
return num;
}
// 添加子节点,其实就是向list中加入Component类型的值
@Override
public void add(Component component) {
childs.add(component);
}
// 删除子节点,其实就是向list中移除Component类型的值
@Override
public void remove(Component component) {
childs.remove(component);
}
}
Leaf【相当于叶子】
/**
* @description:
* 叶子节点,无法进行添加和删除操作
* 透明式的组合模式:叶子节点中的添加和删除操作用不到,但是必须要有
*/
public class Leaf extends Component {
private String name;
private int price;
public Leaf(String name, int price) {
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(int price) {
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public int totalPrice() {
return this.price;
}
@Override
public void add(Component component) {
try {
throw new Exception("leaf 不具有add功能");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public void remove(Component component) {
try {
throw new Exception("leaf 不具有remove功能");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
由此可以看出,之所以可以add和remove,主要是Composite【树干】聚合了Component【即:List 】,对List进行操作(这里只是举例为List,实际使用时,可以根据情况修改为其他数据类型)
代码实现组合的树形结构:
root
|___computerCase(机箱)【树干】
| |
| |____mainBoard(主板)【叶子】
| |____cpu【叶子】
| |____gpu(显卡)【叶子】
|
|___keyboard(键盘)【叶子】
|
|___screen(显示屏)【叶子】
测试代码:
// 透明式的组合模式:new 的时候不需要区分是叶子还是树干
public static void main(String[] args) {
Component root = new Composite();
Component computerCase = new Composite("机箱", 500);
Component mainBoard = new Composite("主板",1000);
// 不管是不是叶子,都统一使用树干创建
Component gpu = new Composite("显卡",2000);
Component cpu = new Composite("cpu",1200);
// 不管是不是叶子,都统一使用树干创建
Component keyboard = new Composite("键盘", 200);
Component screen = new Composite("显示屏", 400);
// 在主板上安装cpu和显卡
mainBoard.add(cpu);
mainBoard.add(gpu);
// 在机箱中安装集成后的主板
computerCase.add(mainBoard);
// 加入根结点
root.add(computerCase);
root.add(screen);
root.add(keyboard);
/* 组装的先后顺序没有强制要求,先从根结点开始组装也是可以的 */
// 输出总价格
System.out.println(root.totalPrice());
}
测试结果:
5300
安全式代码如下:
Component:
public abstract class Component {
public abstract int totalPrice();
public void add(Component component){};
public void remove(Component component){};
}
Composite【树干】:和透明式相比没有什么变化
/**
* @description:
* 树干,可以有叶子,或者其他更小的 子树干
*/
public class Composite extends Component {
private String name;
private int price;
// 聚合抽象类
private List<Component> childs = new ArrayList<>();
public Composite() {
}
public Composite(String name, int price) {
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public int getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(int price) {
this.price = price;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public int totalPrice() {
int num = this.price;
// 使用stream流计算总价
num += childs.stream().mapToInt(Component::totalPrice).sum();
// 普通方式计算总价:遍历子节点,计算总价钱
// for (Component c : childs) {
// num += c.totalPrice();
// }
return num;
}
// 添加子节点,其实就是向list中加入Component类型的值
@Override
public void add(Component component) {
childs.add(component);
}
// 删除子节点,其实就是向list中移除Component类型的值
@Override
public void remove(Component component) {
childs.remove(component);
}
}
Leaf:这里我选择了删除它的add和remove方法
/**
* @description:
* 叶子节点,无法进行添加和删除操作
* 安全式的组合模式:叶子节点中的添加和删除操作用不到,我选择了删除
*/
public class Leaf extends Component {
private String name;
private int price;
public Leaf(String name, int price) {
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(int price) {
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public int totalPrice() {
return this.price;
}
}
测试代码:
// 安全式的组合模式:需要指明是叶子还是树干
public static void main(String[] args) {
Component root = new Composite();
Component computerCase = new Composite("机箱", 500);
Component mainBoard = new Composite("主板",1000);
// 显卡和cpu不可再分,所以创建为叶子节点
Component gpu = new Leaf("显卡",2000);
Component cpu = new Leaf("cpu",1200);
// 键盘和显示屏不可再分,所以创建为叶子节点
Component keyboard = new Leaf("键盘", 200);
Component screen = new Leaf("显示屏", 400);
// 在主板上安装cpu和显卡
mainBoard.add(cpu);
mainBoard.add(gpu);
// 在机箱中安装集成后的主板
computerCase.add(mainBoard);
// 加入根结点
root.add(computerCase);
root.add(screen);
root.add(keyboard);
/* 组装的先后顺序没有强制要求,先从根结点开始组装也是可以的 */
// 输出总价格
System.out.println(root.totalPrice());
}
测试结果:
5300
总结:
- 组合模式其实是一种
树形结构。 透明式:我不区分叶子还是树干,创建方式相同,简化创建,但是对叶子节点可能会出现非法操作。安全式:创建需要指明是叶子还是树干,但是不会出现非法访问的情况。
代码已经上传到Git:请点击访问
如果大家对于组合模式还有更多的使用技巧和使用心得,欢迎评论并在评论中分享自己的链接!