Netty拾遗(二)——Java NIO的三个组件(Buffer,Channel,Selector)
前言
关于Java的NIO与BIO在上一篇博客中已经简单总结,这里开始梳理NIO的三个组件——buffer,channel与selector
Buffer
从名字来看其实就是一个用于缓存数据的类,Buffer类是一个抽象类,具体的实现在NIO中有8种缓冲区类,分别如下:ByteBuffer,CharBuffer,DoubleBuffer,FloatBuffer,IntBuffer,LongBuffer,ShortBuffer,MappedByteBuffer 前7种其实就对应的Java中的基本类型,第八种数据类型是专门用于内存映射的一种ByteBuffer类型。
三个关键的属性
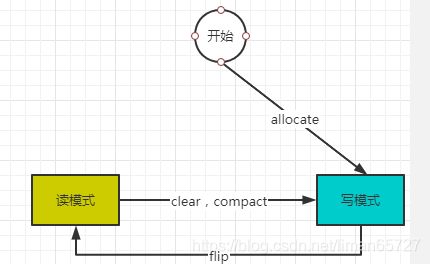
Buffer内部维护了三个关键的属性,一个是capacity,一个是position,一个是limit,同时Buffer存在两种不同的模式,可读模式和可写模式。
capacity
这个表示Buffer的容量大小,写入对象的数量最多不能超过capacity,该属性一旦被分配,就不会改变。
Buffer的创建是通过调用之类的allocate方法来分配。
position
这个表示当前的位置,但是position的值与Buffer的读写模式有关,在不同的模式下,position属性的值是不同的。当Buffer进行读写模式的切换的时候position会进行调整。
几个方法的调用都会触发Buffer的读写模式的切换,后续会总结这个
limit
limit表示读写的最大上限。这个也与Buffer的读写模式有关,不同的模式limit的值不同。
写模式下:limit表示写入的数据最大上限,在Buffer刚进入到写模式下,limit属性值被设置为缓冲区的capacity容量。
读模式下:limit表示最多能从Buffer中读到多少数据。
下面以IntBuffer为例来说明
Buffer的容量分配
打印Buffer相关属性的方法
/**
* 打印出buffer各个属性的位置
* @param buffer
*/
public static void printBufferPropertiesInfo(Buffer buffer){
int position = buffer.position();
int limit = buffer.limit();
int capacity = buffer.capacity();
log.info("================= print buffer info start =================");
log.info("position:{}",position);
log.info("limit:{}",limit);
log.info("capacity:{}",capacity);
log.info("================= print buffer info end =================");
}
通过allocate进行容量的分配
/**
* buffer分配空间,buffer创建之后,默认进入写模式
*/
public static void allocateBuffer(){
//Buffer.allocate,分配指定空间的buffer
intBuffer = IntBuffer.allocate(20);
log.info("buffer allocate finished");
log.info("buffer mode : {}",intBuffer.isReadOnly());
intBuffer.flip();
log.info("buffer mode : {}",intBuffer.isReadOnly());
printBufferPropertiesInfo(intBuffer);
}
运行结果如下:
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - buffer allocate finished
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - ================= print buffer info start =================
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - position:0
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - limit:20
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - capacity:20
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - ================= print buffer info end =================
Buffer的写入
Buffer只要分配了内存空间,就是可写入模式,写入数据需要调用Buffer中的put方法,如下实例
/**
* 往buffer中写入数据
* @param buffer
* @param count
*/
public static void writeBuffer(IntBuffer buffer,int count){
int i = 0;
while(i<count){
buffer.put(i+1);
i++;
}
printBufferPropertiesInfo(buffer);
}
写入指定数据之后,相关变量的变化如下
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - ================= print buffer info start =================
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - position:6
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - limit:20
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - capacity:20
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - ================= print buffer info end =================
可以看到position变成了6,表示写入了6个元素,limit表示可写入20个元素
Buffer的读取
向缓冲区中写入数据之后,并不能直接从Buffer中读取数据,需要进行一个模式的切换,需要调用Buffer的flip方法完成模式的切换。
/**
* 从buffer中读取,从写入模式切换到读取模式,需要调用buffer的flip方法
* @param buffer
*/
public static void readBuffer(IntBuffer buffer){
//由写入模式切换成读取模式
buffer.flip();
int index = 0;
printBufferPropertiesInfo(buffer);
while(index<buffer.limit()){
//利用get()方法从Buffer中读取数据
log.info("read info {}",buffer.get());
index++;
}
log.info("after read print buffer info");
printBufferPropertiesInfo(buffer);
}
运行读取数据之后的日志
# 可以看到由写入模式切换成读取模式之后。position置为0,limit置成了可读取的个数
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - ================= print buffer info start =================
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - position:0
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - limit:6
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - capacity:20
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - ================= print buffer info end =================
# 开始读取数据
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - read info 1
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - read info 2
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - read info 3
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - read info 4
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - read info 5
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - read info 6
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - after read print buffer info
# 读取完成之后,position指向当前读取到的元素位置,limit依旧为可读取的个数。
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - ================= print buffer info start =================
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - position:6
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - limit:6
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - capacity:20
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - ================= print buffer info end =================
倒带,标记读取
倒带读取
已经读完的数据,如果需要再读一遍,需要调用rewind方法,position的位置会被重新置为0,然后可以重新读取缓存中的数据
/**
* 倒带读取
* @param buffer
*/
public static void readWind(IntBuffer buffer){
log.info("after rewind");
buffer.rewind();//倒带的操作
printBufferPropertiesInfo(buffer);
log.info("rewind read buffer info");
int index = 0;
while(index<buffer.limit()){
log.info("buffer item : {}",buffer.get(index++));
}
}
运行日志如下:
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - after rewind
# 倒带之后的position和limit的值
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - ================= print buffer info start =================
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - position:0
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - limit:6
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - capacity:20
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - ================= print buffer info end =================
# 倒带之后读取的数据
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - rewind read buffer info
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - buffer item : 1
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - buffer item : 2
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - buffer item : 3
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - buffer item : 4
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - buffer item : 5
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - buffer item : 6
标记读取
可以通过mark方法,暂存需要读取的位置。然后reset方法之后,position可以置回mark方法记录的位置,之后从mark标记的位置开始读取
代码如下所示:
/**
* 测试mark和reset的操作
* @param buffer
*/
public static void markAndResetRead(IntBuffer buffer){
buffer.flip();
int i = 0;
log.info("normal read");
printBufferPropertiesInfo(buffer);
while(i<buffer.limit()){
if(i==2){
log.info("mark index");
buffer.mark();//这里标记的一个位置
}
log.info("mark read item:{}",buffer.get());
i++;
}
printBufferPropertiesInfo(buffer);
log.info("reset read");
buffer.reset();//回退到上一次mark的位置
printBufferPropertiesInfo(buffer);
while(buffer.position()<buffer.limit()){
log.info("after reset read item:{}",buffer.get());
}
}
运行结果
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - normal read
# 正常读取的position等相关属性
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - ================= print buffer info start =================
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - position:0
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - limit:6
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - capacity:20
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - ================= print buffer info end =================
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - mark read item:1
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - mark read item:2
## 这里是标志位
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - mark index
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - mark read item:3
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - mark read item:4
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - mark read item:5
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - mark read item:6
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - ================= print buffer info start =================
##正常读取完成之后的 position等相关属性
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - position:6
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - limit:6
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - capacity:20
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - ================= print buffer info end =================
##reset标记为
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - reset read
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - ================= print buffer info start =================
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - position:2
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - limit:6
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - capacity:20
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - ================= print buffer info end =================
##从第3个元素开始读取
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - after reset read item:3
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - after reset read item:4
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - after reset read item:5
[main] INFO com.learn.netty.component.buffer.BufferDemo - after reset read item:6
清空
clear方法会清空Buffer中的数据,同时Buffer会切换入写入模式
小结
关于Buffer的模式切换,这里做一个简单的总结
Channel
在NIO中一个连接就是一个channel,如果熟悉Linux的话,其实一个channel就是对应一个文件描述符。在Java NIO中对应不同的网络传输协议,对应不同的channel。几种常用的channel实现类如下:FileChannel,SocketChannel,ServerSocketChannel,DatagramChannel。NIO中的读取数据,都会通过channel与Buffer进行交互。
FileChannel是文件通道,SocketChannel是套接字通道,ServerSocketChannel是服务套接字通道,DatagramChannel是数据报通道。下面我们重点通过实例说明FileChannel,SocketChannel和ServerSocketChannel。
FileChannel
获取FileChannel
通常来讲获取FileChannel有两种方式,一种是根据文件输入输出流进行获取,另一种是根据文件随机访问类进行获取。需要说明的是FileChannel没有非阻塞模式,都是阻塞模式。
1、根据文件输入输出流获取文件channel
需要注意的是根据输入文件流获取的channel对文件只有读取的权限,没有写入的权限。
//1.构建文件输入流
FileInputStream fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(new File(fileName));
//2.获取文件channel
FileChannel fileChannel = fileInputStream.getChannel();
//1.构建文件输出流
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(new File(fileName));
//2.获取文件channel
FileChannel fileChannel = fileInputStream.getChannel();
2、通过RandomAccessFile获取FileChannel
如果需要channel对文件进行可读写,则需要指定rw访问权限。
//这里的targetFileName是文件的绝对路径
RandomAccessFile randomAccessFile = new RandomAccessFile(targetFileName,"rw");
//通过RandomAccessFile获取FileChannel
FileChannel fileChannel = randomAccessFile.getChannel();
通过FileChannel读取文件内容
调用指定的read方法,将文件中的内容读取到buffer中即可
//,因此我们每次在读取文件内容的时候,需要先分配一个Buffer缓冲区。
fileChannel.read(buffer)
通过FileChannel写入文件内容
在将channel中的内容写入到磁盘的时候,需要将buffer变成读模式。
//将buffer中的内容读取出来,写入到FileChannel指定的文件中,因此在读取之前,需要将buffer变成可读模式
buffer.flip();
fileChannel.write(buffer)
实例
可以通过以下实例来熟悉FileChannel。下述代码的读取和写入都是用的同一个buffer
/**
* 先读取文件内容,然后将简单的一句话附加到文件末尾
*/
public static void simpleAppendInfo2File(){
String targetFileName = "F:\\git_learn\\index_newName_bak.html";
FileInputStream fileInputStream=null;
FileChannel fileChannel = null;
try{
//1、创建FileChannel
RandomAccessFile randomAccessFile = new RandomAccessFile(targetFileName,"rw");
fileChannel = randomAccessFile.getChannel();
//2.实例化Buffer缓冲区
ByteBuffer fileBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);//文件缓冲区
//3、文件内容的读取
while(fileChannel.read(fileBuffer)!=-1){
fileBuffer.flip();//fileBuffer变成可读模式
//读取buffer中的内容
while(fileBuffer.position()<fileBuffer.limit()){
System.out.print((char)fileBuffer.get());
}
//清空缓冲区
fileBuffer.clear();
}
//4、在文件的末尾附加内容,依旧可以用同一个buffer操作
fileBuffer.put("\nthis is append coment".getBytes("UTF-8"));
fileBuffer.flip();//这里需要切换成可读模式
fileChannel.write(fileBuffer);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
fileChannel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
ServerSocketChannel和SocketChannel
NIO中涉及到网络的通道有两个,一个是ServerSocketChannel,一个是SocketChannel。前者负责连接的监听,后者负责连接的传输。ServerSocketChannel位于服务端,而SocketChannel则位于两端。需要说明的是这两者有阻塞和非阻塞两种模式,但是接下来的代码实例我们只介绍阻塞模式下二者的操作。这里还是采用一个简单的网络通信实例
客户端代码:
/**
* autor:liman
* createtime:2020/8/26
* comment:SocketChannel的实例
*/
@Slf4j
public class SocketChannelSelf {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SocketChannel socketChannel = null;
try {
socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1",8899));
//这里实例化了两个buffer,一个用于从channel中读取数据,一个用于往channel中写入数据。
ByteBuffer writeBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
ByteBuffer readBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
String clientMessage = "i am client ";
writeBuffer.put(clientMessage.getBytes("UTF-8"));
writeBuffer.flip();//变成读模式
socketChannel.write(writeBuffer);//将客户端的数据发送到服务端的SocketChannel
readBuffer.clear();//clear操作之后,buffer会变成写模式
String serverInfo = readInfoFromBuffer(socketChannel,readBuffer);
log.info("从服务端接受到的消息:{}",serverInfo);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
socketChannel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
* 从buffer读取相关内容
* @param socketChannel
* @param buffer
* @return
* @throws IOException
*/
public static String readInfoFromBuffer(SocketChannel socketChannel,ByteBuffer buffer) throws IOException {
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
socketChannel.read(buffer);//这里的buffer是可写模式,可以直接read
buffer.flip();//将buffer变成可读模式
while(buffer.hasRemaining()){
while(buffer.position()<buffer.limit()) {
stringBuilder.append((char) buffer.get());
}
}
return stringBuilder.toString();
}
}
服务端代码:
/**
* autor:liman
* createtime:2020/8/26
* comment:ServerSocketChannel的实例
*/
@Slf4j
public class ServerSocketChannelSelf {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = null;
SocketChannel socketChannel = null;
try {
serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1",8899));
socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
ByteBuffer writeBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
ByteBuffer readBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
writeBuffer.put("hello this is Server,I'm listening in port 8899".getBytes("UTF-8"));
writeBuffer.flip();
socketChannel.write(writeBuffer);
//读取数据
String messageFromClient = readInfoFromClient(socketChannel, readBuffer);
log.info("从客户端读取到的信息为:{}",messageFromClient);
System.in.read();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
try {
socketChannel.close();
serverSocketChannel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
从buffer中读取数据
*/
public static String readInfoFromClient(SocketChannel socketChannel,ByteBuffer buffer) throws IOException {
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
socketChannel.read(buffer);
buffer.flip();
while(buffer.hasRemaining()){
while(buffer.position()<buffer.limit()) {
stringBuilder.append((char) buffer.get());
}
}
return stringBuilder.toString();
}
}
二者其实差异不大,只需要注意buffer的操作即可,同时需要注意SocketChannel与ServerSocketChannel的构建即可。
Selector
Selector是完成IO多路复用的关键组件,通过上面的Channel实例我们可以看出,其实一个channel可以代表一条连接通道,但是通过一个Selector就可以同时监控多个通道的网络IO操作。
通道和选择器的关系通过注册完成,注册到选择器的通道,必须处于非阻塞模式,这也意味着FileChannel无法注册到选择器。同时只有继承了SelectableChannel的通道才能注册到选择器上 关于Selector的实例需要详细参考其他资料。
选择器实例的获取
通过Selector的静态open方法来获取Selector实例。
Selector selector = Selector.open()
通道注册到Selector
如果将通道注册到Selector,需要提前准备好对应的channel,相关代码如下所示
selector = Selector.open();
serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
//注册到选择器的通道必须是非阻塞模式
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(port), 1024);
//将serverSocketChannel注册到selector上
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
遍历Selector中的事件
try {
selector.select(1000);
Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> keysIterator = selectionKeys.iterator();
SelectionKey key = null;
while (keysIterator.hasNext()) {
key = keysIterator.next();
try {
//TODO:处理相关事件
// ......
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("通道出现异常,异常信息为:{}",e);
if(key!=null){
key.cancel();
if(key.channel()!=null){
key.channel().close();
}
}
}
keysIterator.remove();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
Selector更多的东西需要多多领悟,有时候通过文字似乎不好表述。还是直接上实例(该实例参照《Netty 权威指南》)。
实例
服务端代码
/**
* autor:liman
* createtime:2020/8/12
* comment:
*/
@Slf4j
public class MultiplexerTimeServer implements Runnable {
private Selector selector;
private ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel;
private volatile boolean stop;
public MultiplexerTimeServer(int port) {
//构造方法中将ServerSocketChannel注册到Selector
try {
selector = Selector.open();
serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
//注册到选择器的通道必须是非阻塞模式
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
serverSocketChannel.socket().bind(new InetSocketAddress(port), 1024);
//将serverSocketChannel注册到selector上
serverSocketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
log.info("The time server is start in port : {}", port);
} catch (IOException e) {
log.error("服务启动出行异常,异常信息为:{}", e);
System.exit(1);
}
}
public void stop() {
this.stop = true;
}
/**
开辟线程处理Selector上注册的事件
*/
@Override
public void run() {
while (!stop) {
try {
selector.select(1000);
Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> keysIterator = selectionKeys.iterator();
SelectionKey key = null;
while (keysIterator.hasNext()) {
key = keysIterator.next();
try {
handleInput(key);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("通道出现异常,异常信息为:{}",e);
if(key!=null){
key.cancel();
if(key.channel()!=null){
key.channel().close();
}
}
}
keysIterator.remove();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
}
}
if (selector != null) {
try {
selector.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
/**
* 处理Selector上的注册事件
* @param key
* @throws IOException
*/
private void handleInput(SelectionKey key) throws IOException {
String currentTime = null;
if (key.isValid()) {
//处理服务端ServerSocketChannel的Accept事件。
if(key.isAcceptable()){
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = (ServerSocketChannel) key.channel();
//将与ServerSocketChannel建立连接的SocketChannel注册到selector,并注册READ事件
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
socketChannel.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}
//处理ServerSocketChannel的可读事件,读取SocketChannel中的数据
if (key.isReadable()) {
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
ByteBuffer readBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int readBytes = socketChannel.read(readBuffer);
if (readBytes > 0) {
readBuffer.flip();
byte[] bytes = new byte[readBuffer.remaining()];
readBuffer.get(bytes);
String body = new String(bytes, "UTF-8");
log.info("the time server receive order:{}", body);
if ("QUERY TIME".equalsIgnoreCase(body)) {
currentTime = LocalDateTime.now().toString();
} else {
currentTime = "BAD ORDER";
}
doWrite(socketChannel, currentTime);
} else if (readBytes < 0) {
key.channel();
}
socketChannel.close();
}
}
}
/*
将SocketChannel中的内容写入到buffer中
*/
private void doWrite(SocketChannel socketChannel, String response) throws IOException {
if (response != null && response.trim().length() > 0) {
byte[] bytes = response.getBytes();
ByteBuffer writeBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(bytes.length);
writeBuffer.put(bytes);
writeBuffer.flip();
socketChannel.write(writeBuffer);
}
}
}
启动服务端的代码
/**
* autor:liman
* createtime:2020/8/12
* comment:时间回显服务端启动
*/
@Slf4j
public class TimeServer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int port = 8999;
MultiplexerTimeServer timeServer = new MultiplexerTimeServer(port);
new Thread(timeServer,"NIO-Time-HandlerServer-001").start();
}
}
客户端代码
客户端的线程代码
/**
* autor:liman
* createtime:2020/8/12
* comment:
*/
@Slf4j
public class TimeClientHandler implements Runnable {
private String host;
private int port;
private Selector selector;
private SocketChannel socketChannel;
private volatile boolean stop;
public TimeClientHandler(String host, int port) {
this.host = host;
this.port = port;
try {
//构造方法中,将SocketChannel注册到selector
selector = Selector.open();
socketChannel = SocketChannel.open();
socketChannel.configureBlocking(false);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("客户端初始化异常,异常信息为:{}",e);
}
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
doConnect();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
while(!stop){
try {
selector.select(1000);
Set<SelectionKey> selectionKeys = selector.selectedKeys();
Iterator<SelectionKey> selectorKeyIterator = selectionKeys.iterator();
SelectionKey key = null;
while(selectorKeyIterator.hasNext()){
key = selectorKeyIterator.next();
try{
handleInput(key);
}catch (Exception e){
if(key!=null){
key.cancel();
if(key.channel()!=null){
key.channel().close();
}
}
}
selectorKeyIterator.remove();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(selector!=null){
try{
selector.close();
}catch (Exception e){
log.error("流关闭异常,异常信息为:{}",e);
}
}
}
private void handleInput(SelectionKey key) throws IOException {
if (key.isValid()) {
SocketChannel socketChannel = (SocketChannel) key.channel();
if (key.isConnectable()) {
//如果可连接,则继续注册可读事件。
if (socketChannel.finishConnect()) {
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
log.info("client connect to server ,client time is {}", LocalDateTime.now().toString());
doWrite(socketChannel);
} else {
System.exit(1);
}
}
if (key.isReadable()) {
//可读事件
ByteBuffer readBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int readBytes = socketChannel.read(readBuffer);
if (readBytes > 0) {
readBuffer.flip();
byte[] bytes = new byte[readBuffer.remaining()];
readBuffer.get(bytes);
String body = new String(bytes,"UTF-8");
log.info("receive server message,Now is : {}",body);
this.stop = true;
}else if(readBytes < 0){
key.cancel();
}
socketChannel.close();
}
}
}
/**
将客户端的连接事件注册到Selector上
这里只注册了CONNECT和READ事件。
*/
private void doConnect() throws IOException {
if (socketChannel.connect(new InetSocketAddress(host, port))) {
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
doWrite(socketChannel);
} else {
socketChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_CONNECT);
}
}
/**
将指定的发送命令写入到SocketChannel
*/
private void doWrite(SocketChannel socketChannel) throws IOException {
byte[] req = "QUERY TIME".getBytes();
ByteBuffer writeBuffer = ByteBuffer.allocate(req.length);
writeBuffer.put(req);
writeBuffer.flip();
socketChannel.write(writeBuffer);
if (!writeBuffer.hasRemaining()) {
log.info("send order 2 server succeed.");
}
}
}
注册事件
关于注册事件,主要有以下四种
| 可读事件 | OP_READ |
|---|---|
| 可写事件 | OP_WRITE |
| 连接事件 | OP_CONNECT |
| 接收事件 | OP_ACCEPT |
但每一个通道,其实并不需要关注所有的事件,比如ServerSocketChannel,仅仅支持接收事件。SocketChannel支持接收事件,可读与可写事件,并不支持接收事件。
总结
本篇博客简单总结了一下Java NIO中的三个核心组件,大部分参考了《Netty、Redis、Zookeeper高并发实战》与《Netty权威指南》两本书。