手把手带你撸一遍vue-loader源码
前言
前面写过两篇webpack实战的文章:
- webpack实战之(手把手教你从0开始搭建一个vue项目)
- 手把手教你从0开始搭建一个vue项目(完结)
强烈建议小伙伴们去看一下前面几个章节的内容,
这一节我们研究一下vue-loader。
介绍
Vue Loader 是什么?
Vue Loader 是一个 webpack 的 loader,它允许你以一种名为单文件组件 (SFCs)的格式撰写 Vue 组件:
Vue Loader 还提供了很多酷炫的特性:
- 允许为 Vue 组件的每个部分使用其它的 webpack loader,例如在 `` 的部分使用 Sass 和在 ` 的部分使用 Pug;
- 允许在一个
.vue文件中使用自定义块,并对其运用自定义的 loader 链;- 使用 webpack loader 将 `` 和 ` 中引用的资源当作模块依赖来处理;
- 为每个组件模拟出 scoped CSS;
- 在开发过程中使用热重载来保持状态。
简而言之,webpack 和 Vue Loader 的结合为你提供了一个现代、灵活且极其强大的前端工作流,来帮助撰写 Vue.js 应用。
以上内容都是vue-loader官网的内容,基础用法大家可以自己去看vue-loader的官网,我就不在这里详细介绍了。
开始
我们还是用之前章节的webpack-vue-demo项目做测试demo,大家可以直接clone。
我们首先看一下demo项目的入口文件src/main.ts:
import Vue from "vue";
// import App from "./app.vue";
import App from "./app.vue";
new Vue({
el: "#app",
render: h => h(App)
});
可以看到,直接引用了一个app.vue组件,
src/app.vue:
{
{ msg }}
代码很简单,就是一个普通的vue组件,然后输出一个“hello world”,大家可以直接在项目根目录执行"npm run dev"命令来运行项目。
ok,然后看一下webpack的配置文件webpack.config.js:
const path = require("path");
const config = new (require("webpack-chain"))();
const isDev = !!process.env.WEBPACK_DEV_SERVER;
config
.context(path.resolve(__dirname, ".")) //webpack上下文目录为项目根目录
.entry("app") //入口文件名称为app
.add("./src/main.ts") //入口文件为./src/main.ts
.end()
.output
.path(path.join(__dirname,"./dist")) //webpack输出的目录为根目录的dist目录
.filename("[name].[hash:8].js")
.end()
.resolve
.extensions
.add(".js").add(".jsx").add(".ts").add(".tsx").add(".vue") //配置以.js等结尾的文件当模块使用的时候都可以省略后缀
.end()
.end()
.module
.rule('js')
.test(/\.m?jsx?$/) //对mjs、mjsx、js、jsx文件进行babel配置
.exclude
.add(filepath => {
// Don't transpile node_modules
return /node_modules/.test(filepath)
})
.end()
.use("babel-loader")
.loader("babel-loader")
.end()
.end()
.rule("type-script")
.test(/\.tsx?$/) //loader加载的条件是ts或tsx后缀的文件
.use("babel-loader")
.loader("babel-loader")
.end()
.use("ts-loader")
.loader("ts-loader")
.options({
//ts-loader相关配置
transpileOnly: true, // disable type checker - we will use it in fork plugin
appendTsSuffixTo: ['\\.vue$']
})
.end()
.end()
.rule("vue")
.test(/\.vue$/)// 匹配.vue文件
.use("vue-loader")
.loader("vue-loader")
.end()
.end()
.rule("sass")
.test( /\.(sass|scss)$/)//sass和scss文件
.use("extract-loader")//提取css样式到单独css文件
.loader(require('mini-css-extract-plugin').loader)
.options({
hmr: isDev //开发环境开启热载
})
.end()
.use("css-loader")//加载css模块
.loader("css-loader")
.end()
.use("postcss-loader")//处理css样式
.loader("postcss-loader")
.options( {
config: {
path: path.resolve(__dirname, "./postcss.config.js")
}
})
.end()
.use("sass-loader")//sass语法转css语法
.loader("sass-loader")
.end()
.end()
.rule('eslint')//添加eslint-loader
.exclude
.add(/node_modules/)//校验的文件除node_modules以外
.end()
.test(/\.(vue|(j|t)sx?)$/)//加载.vue、.js、.jsx、.ts、.tsx文件
.use('eslint-loader')
.loader(require.resolve('eslint-loader'))
.options({
emitWarning: true, //把eslint报错当成webpack警告
emitError: !isDev, //把eslint报错当成webapck的错误
})
.end()
.end()
.end()
.plugin("vue-loader-plugin")//vue-loader必须要添加vue-loader-plugin
.use(require("vue-loader").VueLoaderPlugin,[])
.end()
.plugin("html")// 添加html-webpack-plugin插件
.use(require("html-webpack-plugin"),[{
template: path.resolve(__dirname,"./public/index.html"), //指定模版文件
chunks: ["runtime", "chunk-vendors", "chunk-common", "app"], //指定需要加载的chunks
inject: "body" //指定script脚本注入的位置为body
}])
.end()
.plugin("extract-css")//提取css样式到单独css文件
.use(require('mini-css-extract-plugin'), [{
filename: "css/[name].css",
chunkFilename: "css/[name].css"
}])
.end()
.plugin('fork-ts-checker') //配置fork-ts-checker
.use(require('fork-ts-checker-webpack-plugin'), [{
eslint: {
files: './src/**/*.{ts,tsx,js,jsx,vue}' // required - same as command `eslint ./src/**/*.{ts,tsx,js,jsx} --ext .ts,.tsx,.js,.jsx`
},
typescript: {
extensions: {
vue: {
enabled: true,
compiler: "vue-template-compiler"
},
}
}
}])
.end()
.devServer
.host("0.0.0.0") //为了让外部服务访问
.port(8090) //当前端口号
.hot(true) //热载
.open(true) //开启页面
.overlay({
warnings: false,
errors: true
}) //webpack错误和警告信息显示到页面
config.when(!isDev,()=>{
config.optimization
.minimize(true)
.minimizer("terser")
.use(require("terser-webpack-plugin"),[{
extractComments: false, //去除注释
terserOptions:{
output: {
comments: false //去除注释
}
}
}]);
},()=>{
config.devtool("eval-cheap-module-source-map");
});
config.optimization
.splitChunks({
cacheGroups: {
vendors: {
//分离入口文件引用node_modules的module(vue、@babel/xxx)
name: `chunk-vendors`,
test: /[\\/]node_modules[\\/]/,
priority: -10,
chunks: 'initial'
},
common: {
//分离入口文件引用次数>=2的module
name: `chunk-common`,
minChunks: 2,
priority: -20,
chunks: 'initial',
reuseExistingChunk: true
}
}
})
.runtimeChunk("single"); //分离webpack的一些帮助函数,比如webpackJSONP等等
module.exports = config.toConfig();
每一个配置项前面章节都有详细介绍的,我就不一一解析了,我们继续往下。
SFC
我们直接打开src/app.vue文件:
{
{ msg }}
ok! 那么webpack是怎么加载我们的“.vue”结尾的文件呢?
因为我们在webpack.config.js中配置了loader,也就是说是我们的loader去加载的".vue"文件,那么我们项目中的".vue"文件到底被哪些loader加载了呢?
我们直接利用IDE断点看看,我们直接定位到webpack的“NormalModule”,然后当webpack加载到app.vue模块的时候,
node_modules/webpack/lib/NormalModule.js:
ok! 可以看到,当webpack在加载app.vue模块的时候,webpack使用的loader有(loader执行顺序为从下往上):
- vue-loader
- eslint-loader
我直接知道vue-loader的源码,我这里的版本是“[email protected]”,
node_modules/vue-loader/lib/index.js:
const path = require('path')
const hash = require('hash-sum')
const qs = require('querystring')
const plugin = require('./plugin')
const selectBlock = require('./select')
const loaderUtils = require('loader-utils')
const {
attrsToQuery } = require('./codegen/utils')
const {
parse } = require('@vue/component-compiler-utils')
const genStylesCode = require('./codegen/styleInjection')
const {
genHotReloadCode } = require('./codegen/hotReload')
const genCustomBlocksCode = require('./codegen/customBlocks')
const componentNormalizerPath = require.resolve('./runtime/componentNormalizer')
const {
NS } = require('./plugin')
let errorEmitted = false
function loadTemplateCompiler (loaderContext) {
try {
return require('vue-template-compiler')
} catch (e) {
if (/version mismatch/.test(e.toString())) {
loaderContext.emitError(e)
} else {
loaderContext.emitError(new Error(
`[vue-loader] vue-template-compiler must be installed as a peer dependency, ` +
`or a compatible compiler implementation must be passed via options.`
))
}
}
}
module.exports = function (source) {
const loaderContext = this
if (!errorEmitted && !loaderContext['thread-loader'] && !loaderContext[NS]) {
loaderContext.emitError(new Error(
`vue-loader was used without the corresponding plugin. ` +
`Make sure to include VueLoaderPlugin in your webpack config.`
))
errorEmitted = true
}
const stringifyRequest = r => loaderUtils.stringifyRequest(loaderContext, r)
const {
target,
request,
minimize,
sourceMap,
rootContext,
resourcePath,
resourceQuery
} = loaderContext
const rawQuery = resourceQuery.slice(1)
const inheritQuery = `&${
rawQuery}`
const incomingQuery = qs.parse(rawQuery)
const options = loaderUtils.getOptions(loaderContext) || {
}
const isServer = target === 'node'
const isShadow = !!options.shadowMode
const isProduction = options.productionMode || minimize || process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production'
const filename = path.basename(resourcePath)
const context = rootContext || process.cwd()
const sourceRoot = path.dirname(path.relative(context, resourcePath))
const descriptor = parse({
source,
compiler: options.compiler || loadTemplateCompiler(loaderContext),
filename,
sourceRoot,
needMap: sourceMap
})
// if the query has a type field, this is a language block request
// e.g. foo.vue?type=template&id=xxxxx
// and we will return early
if (incomingQuery.type) {
return selectBlock(
descriptor,
loaderContext,
incomingQuery,
!!options.appendExtension
)
}
// module id for scoped CSS & hot-reload
const rawShortFilePath = path
.relative(context, resourcePath)
.replace(/^(\.\.[\/\\])+/, '')
const shortFilePath = rawShortFilePath.replace(/\\/g, '/') + resourceQuery
const id = hash(
isProduction
? (shortFilePath + '\n' + source)
: shortFilePath
)
// feature information
const hasScoped = descriptor.styles.some(s => s.scoped)
const hasFunctional = descriptor.template && descriptor.template.attrs.functional
const needsHotReload = (
!isServer &&
!isProduction &&
(descriptor.script || descriptor.template) &&
options.hotReload !== false
)
// template
let templateImport = `var render, staticRenderFns`
let templateRequest
if (descriptor.template) {
const src = descriptor.template.src || resourcePath
const idQuery = `&id=${
id}`
const scopedQuery = hasScoped ? `&scoped=true` : ``
const attrsQuery = attrsToQuery(descriptor.template.attrs)
const query = `?vue&type=template${
idQuery}${
scopedQuery}${
attrsQuery}${
inheritQuery}`
const request = templateRequest = stringifyRequest(src + query)
templateImport = `import { render, staticRenderFns } from ${
request}`
}
// script
let scriptImport = `var script = {}`
if (descriptor.script) {
const src = descriptor.script.src || resourcePath
const attrsQuery = attrsToQuery(descriptor.script.attrs, 'js')
const query = `?vue&type=script${
attrsQuery}${
inheritQuery}`
const request = stringifyRequest(src + query)
scriptImport = (
`import script from ${
request}\n` +
`export * from ${
request}` // support named exports
)
}
// styles
let stylesCode = ``
if (descriptor.styles.length) {
stylesCode = genStylesCode(
loaderContext,
descriptor.styles,
id,
resourcePath,
stringifyRequest,
needsHotReload,
isServer || isShadow // needs explicit injection?
)
}
let code = `
${
templateImport}
${
scriptImport}
${
stylesCode}
/* normalize component */
import normalizer from ${
stringifyRequest(`!${
componentNormalizerPath}`)}
var component = normalizer(
script,
render,
staticRenderFns,
${
hasFunctional ? `true` : `false`},
${
/injectStyles/.test(stylesCode) ? `injectStyles` : `null`},
${
hasScoped ? JSON.stringify(id) : `null`},
${
isServer ? JSON.stringify(hash(request)) : `null`}
${
isShadow ? `,true` : ``}
)
`.trim() + `\n`
if (descriptor.customBlocks && descriptor.customBlocks.length) {
code += genCustomBlocksCode(
descriptor.customBlocks,
resourcePath,
resourceQuery,
stringifyRequest
)
}
if (needsHotReload) {
code += `\n` + genHotReloadCode(id, hasFunctional, templateRequest)
}
// Expose filename. This is used by the devtools and Vue runtime warnings.
if (!isProduction) {
// Expose the file's full path in development, so that it can be opened
// from the devtools.
code += `\ncomponent.options.__file = ${
JSON.stringify(rawShortFilePath.replace(/\\/g, '/'))}`
} else if (options.exposeFilename) {
// Libraries can opt-in to expose their components' filenames in production builds.
// For security reasons, only expose the file's basename in production.
code += `\ncomponent.options.__file = ${
JSON.stringify(filename)}`
}
code += `\nexport default component.exports`
return code
}
module.exports.VueLoaderPlugin = plugin
代码有点多,不过不要慌,我们一步一步来,还记得我们之前实战的配置vue-loader的时候,如果不配置VueLoaderPlugin的话,webpack就会直接报错?ok,那我们就看一下VueLoaderPlugin到底干了什么,
node_modules/vue-loader/lib/plugin.js:
const webpack = require('webpack')
let VueLoaderPlugin = null
if (webpack.version && webpack.version[0] > 4) {
// webpack5 and upper
VueLoaderPlugin = require('./plugin-webpack5')
} else {
// webpack4 and lower
VueLoaderPlugin = require('./plugin-webpack4')
}
module.exports = VueLoaderPlugin
我们这里用的webpack版本是"4.44.0",所以我们直接就看“plugin-webpack4”了(其实这里的5.0区别也就是rule的获取不一样罢了,因为webpack5.0添加了depend参数等等),
node_modules/vue-loader/lib/plugin-webpack4.js:
const qs = require('querystring')
const RuleSet = require('webpack/lib/RuleSet')
const id = 'vue-loader-plugin'
const NS = 'vue-loader'
class VueLoaderPlugin {
apply (compiler) {
// add NS marker so that the loader can detect and report missing plugin
if (compiler.hooks) {
// webpack 4
compiler.hooks.compilation.tap(id, compilation => {
const normalModuleLoader = compilation.hooks.normalModuleLoader
normalModuleLoader.tap(id, loaderContext => {
loaderContext[NS] = true
})
})
} else {
// webpack < 4
compiler.plugin('compilation', compilation => {
compilation.plugin('normal-module-loader', loaderContext => {
loaderContext[NS] = true
})
})
}
// use webpack's RuleSet utility to normalize user rules
const rawRules = compiler.options.module.rules
const {
rules } = new RuleSet(rawRules)
// find the rule that applies to vue files
let vueRuleIndex = rawRules.findIndex(createMatcher(`foo.vue`))
if (vueRuleIndex < 0) {
vueRuleIndex = rawRules.findIndex(createMatcher(`foo.vue.html`))
}
const vueRule = rules[vueRuleIndex]
if (!vueRule) {
throw new Error(
`[VueLoaderPlugin Error] No matching rule for .vue files found.\n` +
`Make sure there is at least one root-level rule that matches .vue or .vue.html files.`
)
}
if (vueRule.oneOf) {
throw new Error(
`[VueLoaderPlugin Error] vue-loader 15 currently does not support vue rules with oneOf.`
)
}
// get the normlized "use" for vue files
const vueUse = vueRule.use
// get vue-loader options
const vueLoaderUseIndex = vueUse.findIndex(u => {
return /^vue-loader|(\/|\\|@)vue-loader/.test(u.loader)
})
if (vueLoaderUseIndex < 0) {
throw new Error(
`[VueLoaderPlugin Error] No matching use for vue-loader is found.\n` +
`Make sure the rule matching .vue files include vue-loader in its use.`
)
}
// make sure vue-loader options has a known ident so that we can share
// options by reference in the template-loader by using a ref query like
// template-loader??vue-loader-options
const vueLoaderUse = vueUse[vueLoaderUseIndex]
vueLoaderUse.ident = 'vue-loader-options'
vueLoaderUse.options = vueLoaderUse.options || {
}
// for each user rule (expect the vue rule), create a cloned rule
// that targets the corresponding language blocks in *.vue files.
const clonedRules = rules
.filter(r => r !== vueRule)
.map(cloneRule)
// global pitcher (responsible for injecting template compiler loader & CSS
// post loader)
const pitcher = {
loader: require.resolve('./loaders/pitcher'),
resourceQuery: query => {
const parsed = qs.parse(query.slice(1))
return parsed.vue != null
},
options: {
cacheDirectory: vueLoaderUse.options.cacheDirectory,
cacheIdentifier: vueLoaderUse.options.cacheIdentifier
}
}
// replace original rules
compiler.options.module.rules = [
pitcher,
...clonedRules,
...rules
]
}
}
function createMatcher (fakeFile) {
return (rule, i) => {
// #1201 we need to skip the `include` check when locating the vue rule
const clone = Object.assign({
}, rule)
delete clone.include
const normalized = RuleSet.normalizeRule(clone, {
}, '')
return (
!rule.enforce &&
normalized.resource &&
normalized.resource(fakeFile)
)
}
}
function cloneRule (rule) {
const {
resource, resourceQuery } = rule
// Assuming `test` and `resourceQuery` tests are executed in series and
// synchronously (which is true based on RuleSet's implementation), we can
// save the current resource being matched from `test` so that we can access
// it in `resourceQuery`. This ensures when we use the normalized rule's
// resource check, include/exclude are matched correctly.
let currentResource
const res = Object.assign({
}, rule, {
resource: {
test: resource => {
currentResource = resource
return true
}
},
resourceQuery: query => {
const parsed = qs.parse(query.slice(1))
if (parsed.vue == null) {
return false
}
if (resource && parsed.lang == null) {
return false
}
const fakeResourcePath = `${
currentResource}.${
parsed.lang}`
if (resource && !resource(fakeResourcePath)) {
return false
}
if (resourceQuery && !resourceQuery(query)) {
return false
}
return true
}
})
if (rule.rules) {
res.rules = rule.rules.map(cloneRule)
}
if (rule.oneOf) {
res.oneOf = rule.oneOf.map(cloneRule)
}
return res
}
VueLoaderPlugin.NS = NS
module.exports = VueLoaderPlugin
又是很长一段代码!!
我们直接找到这么一段代码:
class VueLoaderPlugin {
apply (compiler) {
...
// use webpack's RuleSet utility to normalize user rules
const rawRules = compiler.options.module.rules
const {
rules } = new RuleSet(rawRules)
// find the rule that applies to vue files
let vueRuleIndex = rawRules.findIndex(createMatcher(`foo.vue`))
if (vueRuleIndex < 0) {
vueRuleIndex = rawRules.findIndex(createMatcher(`foo.vue.html`))
}
const vueRule = rules[vueRuleIndex]
if (!vueRule) {
throw new Error(
`[VueLoaderPlugin Error] No matching rule for .vue files found.\n` +
`Make sure there is at least one root-level rule that matches .vue or .vue.html files.`
)
}
// get the normlized "use" for vue files
const vueUse = vueRule.use
// get vue-loader options
const vueLoaderUseIndex = vueUse.findIndex(u => {
return /^vue-loader|(\/|\\|@)vue-loader/.test(u.loader)
})// make sure vue-loader options has a known ident so that we can share
// options by reference in the template-loader by using a ref query like
// template-loader??vue-loader-options
const vueLoaderUse = vueUse[vueLoaderUseIndex]
...
首先找到了我们配置在webpack中的vueLoaderUse,也就是我们配置的“vue-loader”,然后给默认webpack的loader配置中添加了一个叫“pitcher”的loader:
...
const vueLoaderUse = vueUse[vueLoaderUseIndex]
vueLoaderUse.ident = 'vue-loader-options'
vueLoaderUse.options = vueLoaderUse.options || {
}
// for each user rule (expect the vue rule), create a cloned rule
// that targets the corresponding language blocks in *.vue files.
const clonedRules = rules
.filter(r => r !== vueRule)
.map(cloneRule)
// global pitcher (responsible for injecting template compiler loader & CSS
// post loader)
const pitcher = {
loader: require.resolve('./loaders/pitcher'),
resourceQuery: query => {
const parsed = qs.parse(query.slice(1))
return parsed.vue != null
},
options: {
cacheDirectory: vueLoaderUse.options.cacheDirectory,
cacheIdentifier: vueLoaderUse.options.cacheIdentifier
}
}
// replace original rules
compiler.options.module.rules = [
pitcher,
...clonedRules,
...rules
]
...
我们看一下“pitcher-loader”干了什么?
我们先看一下默认loader的执行顺序,比如我们的配置是这样的:
odule.exports = {
//...
module: {
rules: [
{
//...
use: [
'a-loader',
'b-loader',
'c-loader'
]
}
]
}
};
然后webpack默认加载顺序是这样的:
|- a-loader `pitch` //如果a-loader有pitch函数就会先加载a-loader的pitch函数
|- b-loader `pitch`
|- c-loader `pitch`
|- requested module is picked up as a dependency
|- c-loader normal execution
|- b-loader normal execution
|- a-loader normal execution
但凡有一个loader是有pitch函数并且pitch函数有返回值的话,顺序又不一样了,比如当a-loader的pitch函数有返回值的时候,
a-loader:
module.exports = function(content) {
return someSyncOperation(content);
};
module.exports.pitch = function(remainingRequest, precedingRequest, data) {
if (someCondition()) {
return 'module.exports = require(' + JSON.stringify('-!' + remainingRequest) + ');';
}
};
执行顺序就变成了:
|- a-loader `pitch`
当a-loader的pitch函数有返回值的时候,就只会执行排在a-loader之后的loader,但是在我们当前配置中a-loader之后已经没有loader了,所以会直接返回:
return 'module.exports = require(' + JSON.stringify('-!' + remainingRequest) + ');';
具体大家可以可以看一下webpack官网,或者可以看看网上的这篇文章[揭秘webpack loader](https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000021657031),借用下他文章的两幅图:
当有pitch返回值的时候,比如loader2的pitch函数有返回值了:
![]()
好吧,我简单的带大家看一下webpack源码~
还记得我们文章一开始的断点吗?
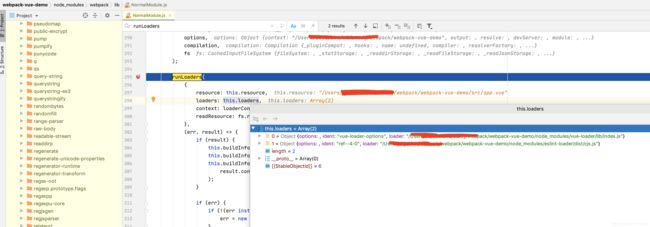
当webpack需要加载某个模块的时候(app.vue),会先执行NormalModule的doBuild方法,
node_modules/webpack/lib/NormalModule.js:
const {
getContext, runLoaders } = require("loader-runner");
...
doBuild(options, compilation, resolver, fs, callback) {
const loaderContext = this.createLoaderContext(
resolver,
options,
compilation,
fs
);
runLoaders(
{
resource: this.resource, //当前app.vue文件位置
loaders: this.loaders, //加载app.vue的所有loader
context: loaderContext, //loader上线文对象
readResource: fs.readFile.bind(fs) //当前webpack文件系统
},
...
ok,可以看到之后就是执行了runLoaders方法,webpack直接把runLoaders方法放到了一个叫“loader-runner”的第三方依赖中,
node_modules/loader-runner/lib/LoaderRunner.js:
...
exports.runLoaders = function runLoaders(options, callback) {
// read options
var resource = options.resource || "";
var loaders = options.loaders || [];
iteratePitchingLoaders(processOptions, loaderContext, function(err, result) {
....
});
...
代码有点多,我们直接看重点,我们看到runLoaders方法中又执行了一个叫iteratePitchingLoaders的方法:
function iteratePitchingLoaders(options, loaderContext, callback) {
// abort after last loader
if(loaderContext.loaderIndex >= loaderContext.loaders.length)
return processResource(options, loaderContext, callback);
var currentLoaderObject = loaderContext.loaders[loaderContext.loaderIndex];
// iterate
if(currentLoaderObject.pitchExecuted) {
loaderContext.loaderIndex++;
return iteratePitchingLoaders(options, loaderContext, callback);
}
// load loader module
loadLoader(currentLoaderObject, function(err) {
if(err) {
loaderContext.cacheable(false);
return callback(err);
}
var fn = currentLoaderObject.pitch;
currentLoaderObject.pitchExecuted = true;
if(!fn) return iteratePitchingLoaders(options, loaderContext, callback);
runSyncOrAsync(
fn,
loaderContext, [loaderContext.remainingRequest, loaderContext.previousRequest, currentLoaderObject.data = {
}],
function(err) {
if(err) return callback(err);
var args = Array.prototype.slice.call(arguments, 1);
if(args.length > 0) {
loaderContext.loaderIndex--;
iterateNormalLoaders(options, loaderContext, args, callback);
} else {
iteratePitchingLoaders(options, loaderContext, callback);
}
}
);
});
}
ok, 这里代码我们就不详细解析了,小伙伴自己去断点跑跑就ok了,还是很容易看懂的,翻译过后的逻辑就是我们前面说的那样:
比如我们的配置是这样的:
odule.exports = {
//...
module: {
rules: [
{
//...
use: [
'a-loader',
'b-loader',
'c-loader'
]
}
]
}
};
然后webpack默认加载顺序是这样的:
|- a-loader `pitch` //如果a-loader有pitch函数就会先加载a-loader的pitch函数
|- b-loader `pitch`
|- c-loader `pitch`
|- requested module is picked up as a dependency
|- c-loader normal execution
|- b-loader normal execution
|- a-loader normal execution
ok!又说了那么多webpack-loader的知识,我们还是回到我们的vue-loader,前面说了vue-loader的VueLoaderPlugin给我们默认loaders上面又添加了一个叫“pitcher-loader”的配置,
node_modules/vue-loader/lib/plugin-webpack4.js:
...
const pitcher = {
loader: require.resolve('./loaders/pitcher'),
resourceQuery: query => {
const parsed = qs.parse(query.slice(1))
return parsed.vue != null
},
options: {
cacheDirectory: vueLoaderUse.options.cacheDirectory,
cacheIdentifier: vueLoaderUse.options.cacheIdentifier
}
}
// replace original rules
compiler.options.module.rules = [
pitcher,
...clonedRules,
...rules
]
...
node_modules/vue-loader/lib/loaders/pitcher.js:
...
module.exports = code => code
// This pitching loader is responsible for intercepting all vue block requests
// and transform it into appropriate requests.
module.exports.pitch = function (remainingRequest) {
const options = loaderUtils.getOptions(this)
const {
cacheDirectory, cacheIdentifier } = options
const query = qs.parse(this.resourceQuery.slice(1))
let loaders = this.loaders
//过滤掉eslint-loader
if (query.type) {
// if this is an inline block, since the whole file itself is being linted,
// remove eslint-loader to avoid duplicate linting.
if (/\.vue$/.test(this.resourcePath)) {
loaders = loaders.filter(l => !isESLintLoader(l))
} else {
// This is a src import. Just make sure there's not more than 1 instance
// of eslint present.
loaders = dedupeESLintLoader(loaders)
}
}
// 过滤掉自己
loaders = loaders.filter(isPitcher)
// 过滤掉一些null-loader
if (loaders.some(isNullLoader)) {
return
}
const genRequest = loaders => {
// Important: dedupe since both the original rule
// and the cloned rule would match a source import request.
// also make sure to dedupe based on loader path.
// assumes you'd probably never want to apply the same loader on the same
// file twice.
// Exception: in Vue CLI we do need two instances of postcss-loader
// for user config and inline minification. So we need to dedupe baesd on
// path AND query to be safe.
const seen = new Map()
const loaderStrings = []
loaders.forEach(loader => {
const identifier = typeof loader === 'string'
? loader
: (loader.path + loader.query)
const request = typeof loader === 'string' ? loader : loader.request
if (!seen.has(identifier)) {
seen.set(identifier, true)
// loader.request contains both the resolved loader path and its options
// query (e.g. ??ref-0)
loaderStrings.push(request)
}
})
return loaderUtils.stringifyRequest(this, '-!' + [
...loaderStrings,
this.resourcePath + this.resourceQuery
].join('!'))
}
// Inject style-post-loader before css-loader for scoped CSS and trimming
if (query.type === `style`) {
const cssLoaderIndex = loaders.findIndex(isCSSLoader)
if (cssLoaderIndex > -1) {
const afterLoaders = loaders.slice(0, cssLoaderIndex + 1)
const beforeLoaders = loaders.slice(cssLoaderIndex + 1)
const request = genRequest([
...afterLoaders,
stylePostLoaderPath,
...beforeLoaders
])
// console.log(request)
return `import mod from ${
request}; export default mod; export * from ${
request}`
}
}
// for templates: inject the template compiler & optional cache
if (query.type === `template`) {
const path = require('path')
const cacheLoader = cacheDirectory && cacheIdentifier
? [`${
require.resolve('cache-loader')}?${
JSON.stringify({
// For some reason, webpack fails to generate consistent hash if we
// use absolute paths here, even though the path is only used in a
// comment. For now we have to ensure cacheDirectory is a relative path.
cacheDirectory: (path.isAbsolute(cacheDirectory)
? path.relative(process.cwd(), cacheDirectory)
: cacheDirectory).replace(/\\/g, '/'),
cacheIdentifier: hash(cacheIdentifier) + '-vue-loader-template'
})}`]
: []
const preLoaders = loaders.filter(isPreLoader)
const postLoaders = loaders.filter(isPostLoader)
const request = genRequest([
...cacheLoader,
...postLoaders,
templateLoaderPath + `??vue-loader-options`,
...preLoaders
])
// console.log(request)
// the template compiler uses esm exports
return `export * from ${
request}`
}
// if a custom block has no other matching loader other than vue-loader itself
// or cache-loader, we should ignore it
if (query.type === `custom` && shouldIgnoreCustomBlock(loaders)) {
return ``
}
// When the user defines a rule that has only resourceQuery but no test,
// both that rule and the cloned rule will match, resulting in duplicated
// loaders. Therefore it is necessary to perform a dedupe here.
const request = genRequest(loaders)
return `import mod from ${
request}; export default mod; export * from ${
request}`
}
ok,我们先放一放这个“pitcher-loader”
在文章一开始的时候还记得我们的断点吗?当webpack在加载app.vue模块的时候,webpack使用的loader有(loader执行顺序为从下往上):
- vue-loader
- eslint-loader
ok,我们先直接看一下当我们的app.vue文件:
<template>
<div class="app-container">{
{
msg }}</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import {
Vue, Component } from "vue-property-decorator";
@Component
export default class App extends Vue {
msg = "hello world";
user = {
name: "yasin"
};
created(): void {
// const name = this.user?.name;
// console.log("name");
}
}
</script>
<style scoped lang="scss">
.app-container {
color: red;
}
</style>
经过vue-loader后变成什么样了?
import {
render, staticRenderFns } from "./app.vue?vue&type=template&id=5ef48958&scoped=true&"
import script from "./app.vue?vue&type=script&lang=ts&"
export * from "./app.vue?vue&type=script&lang=ts&"
import style0 from "./app.vue?vue&type=style&index=0&id=5ef48958&scoped=true&lang=scss&"
/* normalize component */
import normalizer from "!../node_modules/vue-loader/lib/runtime/componentNormalizer.js"
var component = normalizer(
script,
render,
staticRenderFns,
false,
null,
"5ef48958",
null
)
/* hot reload */
if (module.hot) {
var api = require("/Users/ocj1/doc/h5/study/webpack/webpack-vue-demo/node_modules/vue-hot-reload-api/dist/index.js")
api.install(require('vue'))
if (api.compatible) {
module.hot.accept()
if (!api.isRecorded('5ef48958')) {
api.createRecord('5ef48958', component.options)
} else {
api.reload('5ef48958', component.options)
}
module.hot.accept("./app.vue?vue&type=template&id=5ef48958&scoped=true&", function () {
api.rerender('5ef48958', {
render: render,
staticRenderFns: staticRenderFns
})
})
}
}
component.options.__file = "src/app.vue"
export default component.exports
ok, 可以看到,我们的模版代码:
{
{ msg }}
第一次经过vue-loader变成了:
import { render, staticRenderFns } from "./app.vue?vue&type=template&id=5ef48958&scoped=true&"
然后我们的script代码:
第一次经过vue-loader变成了:
import script from "./app.vue?vue&type=script&lang=ts&"
我们的style模块代码:
<style scoped lang="scss">
.app-container {
color: red;
}
</style>
第一次经过vue-loader变成了:
import style0 from "./app.vue?vue&type=style&index=0&id=5ef48958&scoped=true&lang=scss&"
然后这几个的值传给了一个叫“normalizer”的方法:
/* normalize component */
import normalizer from "!../node_modules/vue-loader/lib/runtime/componentNormalizer.js"
var component = normalizer(
script,
render,
staticRenderFns,
false,
null,
"5ef48958",
null
)
最后我们的app.vue经过vue-loader后导出了一个vue组件:
export default component.exports
ok,我们看一下component返回的是不是一个vue组件呢?
我们直接找到“!../node_modules/vue-loader/lib/runtime/componentNormalizer.js”文件:
/* globals __VUE_SSR_CONTEXT__ */
// IMPORTANT: Do NOT use ES2015 features in this file (except for modules).
// This module is a runtime utility for cleaner component module output and will
// be included in the final webpack user bundle.
export default function normalizeComponent (
scriptExports,
render,
staticRenderFns,
functionalTemplate,
injectStyles,
scopeId,
moduleIdentifier, /* server only */
shadowMode /* vue-cli only */
) {
// Vue.extend constructor export interop
var options = typeof scriptExports === 'function'
? scriptExports.options
: scriptExports
// render functions
if (render) {
options.render = render
options.staticRenderFns = staticRenderFns
options._compiled = true
}
// functional template
if (functionalTemplate) {
options.functional = true
}
// scopedId
if (scopeId) {
options._scopeId = 'data-v-' + scopeId
}
var hook
if (moduleIdentifier) {
// server build
hook = function (context) {
// 2.3 injection
context =
context || // cached call
(this.$vnode && this.$vnode.ssrContext) || // stateful
(this.parent && this.parent.$vnode && this.parent.$vnode.ssrContext) // functional
// 2.2 with runInNewContext: true
if (!context && typeof __VUE_SSR_CONTEXT__ !== 'undefined') {
context = __VUE_SSR_CONTEXT__
}
// inject component styles
if (injectStyles) {
injectStyles.call(this, context)
}
// register component module identifier for async chunk inferrence
if (context && context._registeredComponents) {
context._registeredComponents.add(moduleIdentifier)
}
}
// used by ssr in case component is cached and beforeCreate
// never gets called
options._ssrRegister = hook
} else if (injectStyles) {
hook = shadowMode
? function () {
injectStyles.call(
this,
(options.functional ? this.parent : this).$root.$options.shadowRoot
)
}
: injectStyles
}
if (hook) {
if (options.functional) {
// for template-only hot-reload because in that case the render fn doesn't
// go through the normalizer
options._injectStyles = hook
// register for functional component in vue file
var originalRender = options.render
options.render = function renderWithStyleInjection (h, context) {
hook.call(context)
return originalRender(h, context)
}
} else {
// inject component registration as beforeCreate hook
var existing = options.beforeCreate
options.beforeCreate = existing
? [].concat(existing, hook)
: [hook]
}
}
return {
exports: scriptExports,
options: options
}
}
ok,这里代码还是很容易看懂的,以我们app.vue为例,最后componentNormalizer会返回一个:
{
exports: {
render(h){
var _vm = this
var _h = _vm.$createElement
var _c = _vm._self._c || _h
return _c("div", { staticClass: "app-container" }, [_vm._v(_vm._s(_vm.msg))])
},
data:{
msg: "hello world"
},
beforeCreate:[
...
hook
]
},
options: ...
}
我这里只是简单的列了一下哈,后面我们会具体分析到,也就是说componentNormalizer会把我们的app.vue模版文件解析成一个普通的vue组件。
ok,我们的app.vue文件第一次被vue-loader解析后的代码是这样的:
import { render, staticRenderFns } from "./app.vue?vue&type=template&id=5ef48958&scoped=true&"
import script from "./app.vue?vue&type=script&lang=ts&"
export * from "./app.vue?vue&type=script&lang=ts&"
import style0 from "./app.vue?vue&type=style&index=0&id=5ef48958&scoped=true&lang=scss&"
/* normalize component */
import normalizer from "!../node_modules/vue-loader/lib/runtime/componentNormalizer.js"
var component = normalizer(
script,
render,
staticRenderFns,
false,
null,
"5ef48958",
null
)
/* hot reload */
if (module.hot) {
var api = require("/Users/ocj1/doc/h5/study/webpack/webpack-vue-demo/node_modules/vue-hot-reload-api/dist/index.js")
api.install(require('vue'))
if (api.compatible) {
module.hot.accept()
if (!api.isRecorded('5ef48958')) {
api.createRecord('5ef48958', component.options)
} else {
api.reload('5ef48958', component.options)
}
module.hot.accept("./app.vue?vue&type=template&id=5ef48958&scoped=true&", function () {
api.rerender('5ef48958', {
render: render,
staticRenderFns: staticRenderFns
})
})
}
}
component.options.__file = "src/app.vue"
export default component.exports
可以看到,解析完了的vue-loader里面又引用了app.vue文件,比如我们模版转换过后的代码:
import { render, staticRenderFns } from "./app.vue?vue&type=template&id=5ef48958&scoped=true&"
所以当webpack又执行到这一行代码的时候,我们看一下webpack默认又用什么样的loader去加载它呢?
ok, 可以看到,会有三个loader去加载"./app.vue?vue&type=template&id=5ef48958&scoped=true&"模块(从下往上):
- xxx/node_modules/vue-loader/lib/loaders/pitcher.js
- vue-loader
- eslint-loader
ok, 还记得我们前面说的loader执行顺序吗?
|- a-loader `pitch` //如果a-loader有pitch函数就会先加载a-loader的pitch函数
|- b-loader `pitch`
|- c-loader `pitch`
|- requested module is picked up as a dependency
|- c-loader normal execution
|- b-loader normal execution
|- a-loader normal execution
我们这里的顺序为:
|-xxx/node_modules/vue-loader/lib/loaders/pitcher.js `pitch`
|-vue-loader `pitch`
|-eslint-loader `pitch`
|- requested module is picked up as a dependency
|-eslint-loader normal execution
|-vue-loader normal execution
|-xxx/node_modules/vue-loader/lib/loaders/pitcher.js normal execution
ok, 如果当“xxx/node_modules/vue-loader/lib/loaders/pitcher.js”的pitch函数有返回值时,会执行排在pitcher-loader之前的loader,但是我们可以发现,排在pitcher-loader之前已经没有loader了,所以会直接返回pitcher-loader的pitch函数返回的内容,我们来看看“xxx/node_modules/vue-loader/lib/loaders/pitcher.js” loader的pitch方法到底返回了什么?
node_modules/vue-loader/lib/loaders/pitcher.js:
module.exports.pitch = function (remainingRequest) {
...
// for templates: inject the template compiler & optional cache
if (query.type === `template`) {
const path = require('path')
const cacheLoader = cacheDirectory && cacheIdentifier
? [`${require.resolve('cache-loader')}?${JSON.stringify({
// For some reason, webpack fails to generate consistent hash if we
// use absolute paths here, even though the path is only used in a
// comment. For now we have to ensure cacheDirectory is a relative path.
cacheDirectory: (path.isAbsolute(cacheDirectory)
? path.relative(process.cwd(), cacheDirectory)
: cacheDirectory).replace(/\\/g, '/'),
cacheIdentifier: hash(cacheIdentifier) + '-vue-loader-template'
})}`]
: []
const preLoaders = loaders.filter(isPreLoader)
const postLoaders = loaders.filter(isPostLoader)
const request = genRequest([
...cacheLoader,
...postLoaders,
templateLoaderPath + `??vue-loader-options`,
...preLoaders
])
// console.log(request)
// the template compiler uses esm exports
return `export * from ${request}`
}
...
ok,也就是说当我们的这一行代码:
import { render, staticRenderFns } from "./app.vue?vue&type=template&id=5ef48958&scoped=true&"
经过“node_modules/vue-loader/lib/loaders/pitcher.js”后会变成什么样呢?
export * from "-!../node_modules/vue-loader/lib/loaders/templateLoader.js??vue-loader-options!../node_modules/vue-loader/lib/index.js??vue-loader-options!./app.vue?vue&type=template&id=5ef48958&scoped=true&"
ok,可以看到又是直接导入app.vue,然后让:
- …/node_modules/vue-loader/lib/loaders/templateLoader.js
- …/node_modules/vue-loader/lib/index.js
这两个loader去加载app.vue。
这里再说几个webpack中的知识:
loader分为:
- pre: 前置loader
- normal: 普通loader
- inline: 内联loader
- post: 后置loade
执行顺序为:pre > normal > inline > post
内联 loader 可以通过添加不同前缀,跳过其他类型 loader(从右至左)。
- ! 跳过 normal loader。
- -! 跳过 pre 和 normal loader。
- !! 跳过 pre、 normal 和 post loader。
所以针对这里的:
export * from "-!../node_modules/vue-loader/lib/loaders/templateLoader.js??vue-loader-options!../node_modules/vue-loader/lib/index.js??vue-loader-options!./app.vue?vue&type=template&id=5ef48958&scoped=true&"
首先执行的是"…/node_modules/vue-loader/lib/index.js??vue-loader-options!./app.vue?vue&type=template&id=5ef48958&scoped=true&",“??vue-loader-options!./app.vue?vue&type=template&id=5ef48958&scoped=true&”是vue-loader的参数,这次我们看一下vue-loader会把我们的app.vue转成什么样子呢?
node_modules/vue-loader/lib/index.js
module.exports = function (source) {
...
if (incomingQuery.type) {
return selectBlock(
descriptor,
loaderContext,
incomingQuery,
!!options.appendExtension
)
}
可以看到,这一次我们的loader是带有type=template参数的,所以进了vue-loader的selectBlock方法,
node_modules/vue-loader/lib/select.js:
module.exports = function selectBlock (
descriptor,
loaderContext,
query,
appendExtension
) {
// template
if (query.type === `template`) {
if (appendExtension) {
loaderContext.resourcePath += '.' + (descriptor.template.lang || 'html')
}
loaderContext.callback(
null,
descriptor.template.content,
descriptor.template.map
)
return
}
// script
if (query.type === `script`) {
if (appendExtension) {
loaderContext.resourcePath += '.' + (descriptor.script.lang || 'js')
}
loaderContext.callback(
null,
descriptor.script.content,
descriptor.script.map
)
return
}
// styles
if (query.type === `style` && query.index != null) {
const style = descriptor.styles[query.index]
if (appendExtension) {
loaderContext.resourcePath += '.' + (style.lang || 'css')
}
loaderContext.callback(
null,
style.content,
style.map
)
return
}
// custom
if (query.type === 'custom' && query.index != null) {
const block = descriptor.customBlocks[query.index]
loaderContext.callback(
null,
block.content,
block.map
)
return
}
}
最后经过select输出:
{
{ msg }}
ok,然后vue-loader处理完后给到了“…/node_modules/vue-loader/lib/loaders/templateLoader.js”,
/node_modules/vue-loader/lib/loaders/templateLoader.js:
const qs = require('querystring')
const loaderUtils = require('loader-utils')
const {
compileTemplate } = require('@vue/component-compiler-utils')
// Loader that compiles raw template into JavaScript functions.
// This is injected by the global pitcher (../pitch) for template
// selection requests initiated from vue files.
module.exports = function (source) {
const loaderContext = this
const query = qs.parse(this.resourceQuery.slice(1))
// although this is not the main vue-loader, we can get access to the same
// vue-loader options because we've set an ident in the plugin and used that
// ident to create the request for this loader in the pitcher.
const options = loaderUtils.getOptions(loaderContext) || {
}
const {
id } = query
const isServer = loaderContext.target === 'node'
const isProduction = options.productionMode || loaderContext.minimize || process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production'
const isFunctional = query.functional
// allow using custom compiler via options
const compiler = options.compiler || require('vue-template-compiler')
const compilerOptions = Object.assign({
outputSourceRange: true
}, options.compilerOptions, {
scopeId: query.scoped ? `data-v-${
id}` : null,
comments: query.comments
})
// for vue-component-compiler
const finalOptions = {
source,
filename: this.resourcePath,
compiler,
compilerOptions,
// allow customizing behavior of vue-template-es2015-compiler
transpileOptions: options.transpileOptions,
transformAssetUrls: options.transformAssetUrls || true,
isProduction,
isFunctional,
optimizeSSR: isServer && options.optimizeSSR !== false,
prettify: options.prettify
}
const compiled = compileTemplate(finalOptions)
// tips
if (compiled.tips && compiled.tips.length) {
compiled.tips.forEach(tip => {
loaderContext.emitWarning(typeof tip === 'object' ? tip.msg : tip)
})
}
// errors
if (compiled.errors && compiled.errors.length) {
// 2.6 compiler outputs errors as objects with range
if (compiler.generateCodeFrame && finalOptions.compilerOptions.outputSourceRange) {
// TODO account for line offset in case template isn't placed at top
// of the file
loaderContext.emitError(
`\n\n Errors compiling template:\n\n` +
compiled.errors.map(({
msg, start, end }) => {
const frame = compiler.generateCodeFrame(source, start, end)
return ` ${
msg}\n\n${
pad(frame)}`
}).join(`\n\n`) +
'\n'
)
} else {
loaderContext.emitError(
`\n Error compiling template:\n${
pad(compiled.source)}\n` +
compiled.errors.map(e => ` - ${
e}`).join('\n') +
'\n'
)
}
}
const {
code } = compiled
// finish with ESM exports
return code + `\nexport { render, staticRenderFns }`
}
function pad (source) {
return source
.split(/\r?\n/)
.map(line => ` ${
line}`)
.join('\n')
}
我们看一下“/node_modules/vue-loader/lib/loaders/templateLoader.js”处理完后又变成什么样了?
var render = function() {
var _vm = this
var _h = _vm.$createElement
var _c = _vm._self._c || _h
return _c("div", { staticClass: "app-container" }, [_vm._v(_vm._s(_vm.msg))])
}
var staticRenderFns = []
render._withStripped = true
export { render, staticRenderFns}
总结
ok,终于是转完毕了,我们再从新回顾一下整个流程(我这里以app.vue的template为例子)。
首先是我们的app.vue文件template:
{
{ msg }}
然后经过vue-loader后:
import { render, staticRenderFns } from "./app.vue?vue&type=template&id=5ef48958&scoped=true&"
然后是pitcher-loader:
export * from "-!../node_modules/vue-loader/lib/loaders/templateLoader.js??vue-loader-options!../node_modules/vue-loader/lib/index.js??vue-loader-options!./app.vue?vue&type=template&id=5ef48958&scoped=true&"
接着又是vue-loader:
{
{ msg }}
然后是…/node_modules/vue-loader/lib/loaders/templateLoader.js:
var render = function() {
var _vm = this
var _h = _vm.$createElement
var _c = _vm._self._c || _h
return _c("div", { staticClass: "app-container" }, [_vm._v(_vm._s(_vm.msg))])
}
var staticRenderFns = []
render._withStripped = true
export { render, staticRenderFns }
ok, app.vue中的template模块解析过程就是这样的了,还有script跟style,过程都差不多,小伙伴自己结合demo跟断点跑一下哦,我就不演示了!
补充
vue模块热载
webpack中的模块热载集成大家可以看webpack官网:https://webpack.js.org/api/hot-module-replacement/.
当我们的app.vue第一次经过vue-loader后:
import { render, staticRenderFns } from "./app.vue?vue&type=template&id=5ef48958&scoped=true&"
import script from "./app.vue?vue&type=script&lang=ts&"
export * from "./app.vue?vue&type=script&lang=ts&"
import style0 from "./app.vue?vue&type=style&index=0&id=5ef48958&scoped=true&lang=scss&"
/* normalize component */
import normalizer from "!../node_modules/vue-loader/lib/runtime/componentNormalizer.js"
var component = normalizer(
script,
render,
staticRenderFns,
false,
null,
"5ef48958",
null
)
/* hot reload */
if (module.hot) {
//加载vue模块热载代码
var api = require("xxx/node_modules/vue-hot-reload-api/dist/index.js")
api.install(require('vue'))
if (api.compatible) {
module.hot.accept() //把当前模块加入到webpack的热载中(当前模块有变换的时候会通知)
if (!api.isRecorded('5ef48958')) { //第一次的时候记录当前组件
api.createRecord('5ef48958', component.options)
} else { //热载的时候从新渲染当前组件
api.reload('5ef48958', component.options)
}
//模块代码改变的时候也认为可以热载,通知当前组件刷新
module.hot.accept("./app.vue?vue&type=template&id=5ef48958&scoped=true&", function () {
api.rerender('5ef48958', {
render: render,
staticRenderFns: staticRenderFns
})
})
}
}
component.options.__file = "src/app.vue"
export default component.exports
node_modules/vue-hot-reload-api/dist/index.js:
exports.reload = tryWrap(function (id, options) {
...
record.instances.slice().forEach(function (instance) {
if (instance.$vnode && instance.$vnode.context) {
instance.$vnode.context.$forceUpdate() //强制刷新组件
} else {
console.warn(
'Root or manually mounted instance modified. Full reload required.'
)
}
})
})
ok!整个vue-loader流程我们差不多撸了一遍,其实掌握了webpack后这东西感觉也不是很难了对吧?,所以强烈推荐小伙伴看看之前的webpack的文章,觉得不错的也可以关注跟点点赞哦! 也欢迎志同道合的小伙伴一起学习一起交流!!