基于N源码的AccountManagerService简单认识和账户添加流程分析
AccountManagerService负责管理手机中用户的在线账户,主要的工作涉及账户的添加、删除和AuthToken的获取和更新。
下面看下AccountManagerService的初始化,进入SystemServer中的startOtherServices方法看到如下代码:
mSystemServiceManager.startService(ACCOUNT_SERVICE_CLASS);其中ACCOUNT_SERVICE_CLASS为com.android.server.accounts.AccountManagerService$Lifecycle,SystemServiceManager的startService里面会通过反射创建AccountManagerService.Lifecycle对象,并调用其onStart方法:
public void onStart() {
mService = new AccountManagerService(getContext());
publishBinderService(Context.ACCOUNT_SERVICE, mService);
}可以看到创建AccountManagerService对象,并发布到服务总管里面。下面看下AccountManagerService构造函数:
public AccountManagerService(Context context) {
this(context, context.getPackageManager(), new AccountAuthenticatorCache(context));
}
public AccountManagerService(Context context, PackageManager packageManager,
IAccountAuthenticatorCache authenticatorCache) {
mContext = context;
mPackageManager = packageManager;
mAppOpsManager = mContext.getSystemService(AppOpsManager.class);
mMessageHandler = new MessageHandler(FgThread.get().getLooper());
mAuthenticatorCache = authenticatorCache;
mAuthenticatorCache.setListener(this, null /* Handler */);这里又创建了AccountAuthenticatorCache对象并设置监听器,AccountAuthenticatorCache是android平台中账户验证服务(AAS)的管理中心,AAS是应用程序中定义的服务,对它的定义有一定的要求,后面会看到。接着看下AccountAuthenticatorCache的构造函数:
/* package private */ class AccountAuthenticatorCache
extends RegisteredServicesCache
public AccountAuthenticatorCache(Context context) {
super(context, AccountManager.ACTION_AUTHENTICATOR_INTENT,
AccountManager.AUTHENTICATOR_META_DATA_NAME,
AccountManager.AUTHENTICATOR_ATTRIBUTES_NAME, sSerializer);
} 这里又调用父类RegisteredServicesCache构造函数,传递的参数如下定义:
public static final String ACTION_AUTHENTICATOR_INTENT =
"android.accounts.AccountAuthenticator";
public static final String AUTHENTICATOR_META_DATA_NAME =
"android.accounts.AccountAuthenticator";
public static final String AUTHENTICATOR_ATTRIBUTES_NAME = "account-authenticator";后面解析XML要用到,所以AAS的配置文件也需要符合这个要求。
public RegisteredServicesCache(Context context, String interfaceName, String metaDataName,
String attributeName, XmlSerializerAndParser serializerAndParser) {
mContext = context;
mInterfaceName = interfaceName;
mMetaDataName = metaDataName;
mAttributesName = attributeName;
mSerializerAndParser = serializerAndParser;
migrateIfNecessaryLocked();
IntentFilter intentFilter = new IntentFilter();
intentFilter.addAction(Intent.ACTION_PACKAGE_ADDED);
intentFilter.addAction(Intent.ACTION_PACKAGE_CHANGED);
intentFilter.addAction(Intent.ACTION_PACKAGE_REMOVED);
intentFilter.addDataScheme("package");
mContext.registerReceiverAsUser(mPackageReceiver, UserHandle.ALL, intentFilter, null, null); 简单看下RegisteredServicesCache构造函数,其中migrateIfNecessaryLocked用户在系统目录下创建文件:
File systemDir = new File(getDataDirectory(), "system");
File syncDir = new File(systemDir, REGISTERED_SERVICES_DIR);
AtomicFile oldFile = new AtomicFile(new File(syncDir, mInterfaceName + ".xml"));接着注册了包添加删除广播。猜测应用安装或卸载会在这里进行账户信息添加和删除。下面看下这个广播接收器:
private final BroadcastReceiver mPackageReceiver = new BroadcastReceiver() {
@Override
public void onReceive(Context context, Intent intent) {
final int uid = intent.getIntExtra(Intent.EXTRA_UID, -1);
if (uid != -1) {
handlePackageEvent(intent, UserHandle.getUserId(uid));
}
}
};接着进入handlePackageEvent:
private final void handlePackageEvent(Intent intent, int userId) {
// Don't regenerate the services map when the package is removed or its
// ASEC container unmounted as a step in replacement. The subsequent
// _ADDED / _AVAILABLE call will regenerate the map in the final state.
final String action = intent.getAction();
// it's a new-component action if it isn't some sort of removal
final boolean isRemoval = Intent.ACTION_PACKAGE_REMOVED.equals(action)
|| Intent.ACTION_EXTERNAL_APPLICATIONS_UNAVAILABLE.equals(action);
// if it's a removal, is it part of an update-in-place step?
final boolean replacing = intent.getBooleanExtra(Intent.EXTRA_REPLACING, false);
if (isRemoval && replacing) {
// package is going away, but it's the middle of an upgrade: keep the current
// state and do nothing here. This clause is intentionally empty.
} else {
int[] uids = null;
// either we're adding/changing, or it's a removal without replacement, so
// we need to update the set of available services
if (Intent.ACTION_EXTERNAL_APPLICATIONS_AVAILABLE.equals(action)
|| Intent.ACTION_EXTERNAL_APPLICATIONS_UNAVAILABLE.equals(action)) {
uids = intent.getIntArrayExtra(Intent.EXTRA_CHANGED_UID_LIST);
} else {
int uid = intent.getIntExtra(Intent.EXTRA_UID, -1);
if (uid > 0) {
uids = new int[] { uid };
}
}
generateServicesMap(uids, userId);
}当包正在删除且部分在更新情况不做任何处理,接着进入generateServicesMap:
private void generateServicesMap(int[] changedUids, int userId) {
if (DEBUG) {
Slog.d(TAG, "generateServicesMap() for " + userId + ", changed UIDs = " + changedUids);
}
final ArrayList> serviceInfos = new ArrayList>();
final List resolveInfos = queryIntentServices(userId);
for (ResolveInfo resolveInfo : resolveInfos) {
try {
ServiceInfo info = parseServiceInfo(resolveInfo);
if (info == null) {
Log.w(TAG, "Unable to load service info " + resolveInfo.toString());
continue;
}
serviceInfos.add(info);
} catch (XmlPullParserException|IOException e) {
Log.w(TAG, "Unable to load service info " + resolveInfo.toString(), e);
}
} 首先传递userid通过PMS查询应用包服务信息。接着通过parseServiceInfo解析服务信息:
protected ServiceInfo parseServiceInfo(ResolveInfo service)
throws XmlPullParserException, IOException {
android.content.pm.ServiceInfo si = service.serviceInfo;
ComponentName componentName = new ComponentName(si.packageName, si.name);
PackageManager pm = mContext.getPackageManager();
XmlResourceParser parser = null;
parser = si.loadXmlMetaData(pm, mMetaDataName);
AttributeSet attrs = Xml.asAttributeSet(parser);
V v = parseServiceAttributes(pm.getResourcesForApplication(si.applicationInfo),
si.packageName, attrs);
if (v == null) {
return null;
}
final android.content.pm.ServiceInfo serviceInfo = service.serviceInfo;
return new ServiceInfo(v, serviceInfo, componentName);
} 解析MetaData信息,接着调用子类parseServiceAttributes来解析MetaData中的resource信息。
public AuthenticatorDescription parseServiceAttributes(Resources res,
String packageName, AttributeSet attrs) {
TypedArray sa = res.obtainAttributes(attrs,
com.android.internal.R.styleable.AccountAuthenticator);
try {
final String accountType =
sa.getString(com.android.internal.R.styleable.AccountAuthenticator_accountType);
final int labelId = sa.getResourceId(
com.android.internal.R.styleable.AccountAuthenticator_label, 0);
final int iconId = sa.getResourceId(
com.android.internal.R.styleable.AccountAuthenticator_icon, 0);
final int smallIconId = sa.getResourceId(
com.android.internal.R.styleable.AccountAuthenticator_smallIcon, 0);
final int prefId = sa.getResourceId(
com.android.internal.R.styleable.AccountAuthenticator_accountPreferences, 0);
final boolean customTokens = sa.getBoolean(
com.android.internal.R.styleable.AccountAuthenticator_customTokens, false);
if (TextUtils.isEmpty(accountType)) {
return null;
}
return new AuthenticatorDescription(accountType, packageName, labelId, iconId,
smallIconId, prefId, customTokens);
} finally {
sa.recycle();
}
}MetaData的resource一般是xml文件,下面举例SimContact模块中的AAS(SimAuthenticateService),看下它的配置文件和MetaDta的resource:
sim_authenticator.xml文件如下
上面xml文件中的accountType标签用于指定账户类型,icon、smallIcon、label等用于界面显示。最终将sim_authenticator文件解析封装到AuthenticatorDescription对象中返回。
关于AccountManagerService的认识就先了解到这,下面重点分析下添加账户的过程。一般默认添加账户都是在设置里面添加,应用程序也可以自己添加。添加账户入口在AccountManager类的addAccount:
public AccountManagerFuture addAccount(final String accountType,
final String authTokenType, final String[] requiredFeatures,
final Bundle addAccountOptions,
final Activity activity, AccountManagerCallback callback, Handler handler) {
return new AmsTask(activity, handler, callback) {
@Override
public void doWork() throws RemoteException {
mService.addAccount(mResponse, accountType, authTokenType,
requiredFeatures, activity != null, optionsIn);
}
}.start();
} 这里返回AmsTask对象,这是什么鬼?
private abstract class AmsTask extends FutureTask implements AccountManagerFuture {
final IAccountManagerResponse mResponse;
final Handler mHandler;
final AccountManagerCallback mCallback;
final Activity mActivity;
public AmsTask(Activity activity, Handler handler, AccountManagerCallback callback) {
super(new Callable() {
@Override
public Bundle call() throws Exception {
throw new IllegalStateException("this should never be called");
}
});
mHandler = handler;
mCallback = callback;
mActivity = activity;
mResponse = new Response();
}
public final AccountManagerFuture start() {
try {
doWork();
} catch (RemoteException e) {
setException(e);
}
return this;
}
public abstract void doWork() throws RemoteException;
private class Response extends IAccountManagerResponse.Stub {
@Override
public void onResult(Bundle bundle) {
Intent intent = bundle.getParcelable(KEY_INTENT);
mActivity.startActivity(intent);
}
@Override
public void onError(int code, String message) {
}
} 它继承FutureTask实现AccountManagerFuture,关于FutureTask介绍可查看链接 FutureTask 深度解析 ,构造函数里面还创建了Response对象,它继承IAccountManagerResponse.Stub,根据经验它是服务的实现者,用于响应AccountManagerService的回调。接着调用start-》dowork()进入到AccountManagerService中的addAccount:
public void addAccount(final IAccountManagerResponse response, final String accountType,
final String authTokenType, final String[] requiredFeatures,
final boolean expectActivityLaunch, final Bundle optionsIn) {
UserAccounts accounts = getUserAccounts(usrId);
logRecordWithUid(
accounts, DebugDbHelper.ACTION_CALLED_ACCOUNT_ADD, TABLE_ACCOUNTS, uid);
new Session(accounts, response, accountType, expectActivityLaunch,
true /* stripAuthTokenFromResult */, null /* accountName */,
false /* authDetailsRequired */, true /* updateLastAuthenticationTime */) {
@Override
public void run() throws RemoteException {
mAuthenticator.addAccount(this, mAccountType, authTokenType, requiredFeatures,
options);
}
@Override
protected String toDebugString(long now) {
return super.toDebugString(now) + ", addAccount"
+ ", accountType " + accountType
+ ", requiredFeatures "
+ (requiredFeatures != null
? TextUtils.join(",", requiredFeatures)
: null);
}
}.bind();
}这里创建了一个Session对象,这又是什么鬼?
private abstract class Session extends IAccountAuthenticatorResponse.Stub
implements IBinder.DeathRecipient, ServiceConnection {
IAccountManagerResponse mResponse;
IAccountAuthenticator mAuthenticator = null;
public Session(UserAccounts accounts, IAccountManagerResponse response, String accountType,
boolean expectActivityLaunch, boolean stripAuthTokenFromResult, String accountName,
boolean authDetailsRequired, boolean updateLastAuthenticatedTime) {
super();
mAccounts = accounts;
mResponse = response;
mAccountType = accountType;
mAccountName = accountName;
synchronized (mSessions) {
mSessions.put(toString(), this);
}
}
void bind() {
if (!bindToAuthenticator(mAccountType)) {
}
}
public void onServiceConnected(ComponentName name, IBinder service) {
mAuthenticator = IAccountAuthenticator.Stub.asInterface(service);
run();
}
public abstract void run() throws RemoteException;
public void onResult(Bundle result) {
}
private boolean bindToAuthenticator(String authenticatorType) {
final AccountAuthenticatorCache.ServiceInfo authenticatorInfo;
authenticatorInfo = mAuthenticatorCache.getServiceInfo(
AuthenticatorDescription.newKey(authenticatorType), mAccounts.userId);
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setAction(AccountManager.ACTION_AUTHENTICATOR_INTENT);
intent.setComponent(authenticatorInfo.componentName);
if (Log.isLoggable(TAG, Log.VERBOSE)) {
Log.v(TAG, "performing bindService to " + authenticatorInfo.componentName);
}
if (!mContext.bindServiceAsUser(intent, this, Context.BIND_AUTO_CREATE,
UserHandle.of(mAccounts.userId))) {
}
return true;
}
}
它继承IAccountAuthenticatorResponse.Stub,是服务的实现者,跟谁通信?后面再看,又实现ServiceConnection,感觉在绑定服务的时候见过。接着调用bind()-》bindToAuthenticator,这里通过mAuthenticatorCache获取服务信息,mAuthenticatorCache在前面认识AccountManagerService介绍过。获取到ServiceInfo信息就开始绑定服务。这里以SimAuthenticateService为例,bindServiceAsUser调用后就会调用它的onBind方法:

这里的SimAuthenticator继承AbstractAccountAuthenticator,返回它的getIBinder(),其实是AbstractAccountAuthenticator中的内部类Transport对象的binder对象:
private Transport mTransport = new Transport();
/**
* @return the IBinder for the AccountAuthenticator
*/
public final IBinder getIBinder() {
return mTransport.asBinder();
} private class Transport extends IAccountAuthenticator.Stub {
@Override
public void addAccount(IAccountAuthenticatorResponse response, String accountType,可见Transport又是服务的实现者,猜测在AccountManagerService会调用。
回到上面AccountManagerService中的添加服务流程中,刚才走到绑定服务,绑定成功会调用onServiceConnected函数,该函数中获取服务代理对象:
mAuthenticator = IAccountAuthenticator.Stub.asInterface(service);
接着run:
public void run() throws RemoteException {
mAuthenticator.addAccount(this, mAccountType, authTokenType, requiredFeatures,
options);
}
mAuthenticator为本地代理对象,调用addAccount会根据binder机制进入服务的实现者,也就是AbstractAccountAuthenticator中的内部类Transport:
final Bundle result = AbstractAccountAuthenticator.this.addAccount(
new AccountAuthenticatorResponse(response) if (result != null) {
response.onResult(result);
}
这里调用AbstractAccountAuthenticator的子类,也就是上面举例的SimAuthenticator,注意上面传递的IAccountAuthenticatorResponse 的binder对象response,它的真正实现者在AccountManagerService内部类Session(private abstract class Session extends IAccountAuthenticatorResponse.Stub),也就是说这里调用response.onResult(result);又回到了Session中:
public void onResult(Bundle result) {
IAccountManagerResponse response;
response = mResponse;
if (response != null) {
response.onResult(result);
}
}这里的response又是个binder对象。额,已经晕了。仔细回忆,它是在AccountManager的addAccount传递进来的,它是AmsTask的内部类Response:
private class Response extends IAccountManagerResponse.Stub {
@Override
public void onResult(Bundle bundle) {
Intent intent = bundle.getParcelable(KEY_INTENT);
if (intent != null && mActivity != null) {
// since the user provided an Activity we will silently start intents
// that we see
mActivity.startActivity(intent);
整个流程差不多介绍完了。最后看下SimAuthenticator是如何添加服务的,它调用AccountManager的addAccountExplicitly:
public boolean addAccountExplicitly(Account account, String password, Bundle userdata) {
if (account == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("account is null");
try {
return mService.addAccountExplicitly(account, password, userdata);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();
}
}
直接进入AccountManagerService的addAccountExplicitly:
public boolean addAccountExplicitly(Account account, String password, Bundle extras) {
UserAccounts accounts = getUserAccounts(userId);
return addAccountInternal(accounts, account, password, extras, callingUid);
}进入addAccountInternal:
private boolean addAccountInternal(UserAccounts accounts, Account account, String password,
Bundle extras, int callingUid) {
final SQLiteDatabase db = accounts.openHelper.getWritableDatabaseUserIsUnlocked();
db.beginTransaction();
ContentValues values = new ContentValues();
values.put(ACCOUNTS_NAME, account.name);
values.put(ACCOUNTS_TYPE, account.type);
values.put(ACCOUNTS_PASSWORD, password);
long accountId = db.insert(CE_TABLE_ACCOUNTS, ACCOUNTS_NAME, values);
values = new ContentValues();
values.put(ACCOUNTS_ID, accountId);
values.put(ACCOUNTS_NAME, account.name);
values.put(ACCOUNTS_TYPE, account.type);
values.put(ACCOUNTS_LAST_AUTHENTICATE_TIME_EPOCH_MILLIS,
System.currentTimeMillis());
if (db.insert(TABLE_ACCOUNTS, ACCOUNTS_NAME, values) < 0)
db.endTransaction();
}
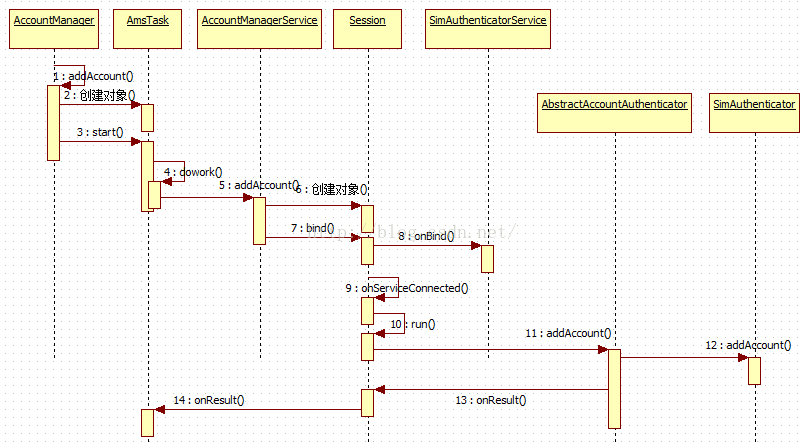
sendAccountsChangedBroadcast(accounts.userId);最后贴一张添加服务的流程图: