C++深入理解(一)——自定义类中重载运算符返回引用以及连续赋值的机制理解
0. 写作目的
好记性不如烂笔头。
结论:在自定义的类中,运算符重载需要返回类对象的引用。如果返回的是类对象,则在赋值的过程中会调用拷贝构造函数,引起不必要的运算。如果返回的是void,则不能进行连续赋值(如a = b = c)。
(补充:在自定义类的对象连续赋值中a = b = c(a,b,c均为新定义的类的实例),
当运算符重载函数返回的是类对象引用时,其过程为,b = c调用运算符重载函数,返回b的引用,然后a = b调用运算符重载函数,返回a 的引用。
当运算符重载函数返回的是类对象时,其过程为,b = c先调用运算符重载函数,该函数结束后,由于返回的是类对象,因此在a = b = c这行代码中会创建一个临时类对象tem_c,用于接收运算符重载之后的结果,此时会调用拷贝构造函数tem_c( *this ),其中this是运算符重载函数中的。同时a = tem_c调用运算符重载函数,然后在a = b = c创建一个临时类对象tem_a,然后调用拷贝构造函数tem_a( *this ),然后释放tem_a(析构函数),再释放tem_c(析构函数))。
(补充2:自定义的类,C++编译器会自动创建6个函数,其中(默认的move constructor 和 默认的move assignment operator函数是从C++11之后有的,由于平时不采用这两种函数进行赋值,因此不对此进行考虑)。主要关注其余4中默认函数——默认构造函数(default constructor),拷贝构造函数(copy constructor),赋值运算符重载函数(copy assignment operator)和析构函数(Destructor) [1]。)
1. 运算符重载返回对象
#include
#include
using namespace std;
class CStudent
{
public:
CStudent(char *pName) :m_pName(NULL)
{
if (NULL == pName)
{
return;
}
m_pName = new char[strlen(pName) + 1];
strcpy(m_pName, pName);
printf("CStudent: address:0x%08x name:%s\n", this, m_pName);
}
~CStudent()
{
printf("~CStudent: address:0x%08x name:%s\n", this, m_pName);
delete []m_pName;
}
//拷贝构造函数
CStudent(const CStudent &a) :m_pName(NULL)
{
if (NULL == a.m_pName)
{
cout<<"reference"<m_pName = new char[len + 20];
memset(m_pName, 0, len + 20);
strcpy(m_pName, a.m_pName);
strcat(m_pName, "_copy_construct"); // 为了测试
printf("copy construct: address:0x%08x name:%s\n", this, this->m_pName);
}
public:
#if 1
//重载赋值函数 返回对象
CStudent operator=(const CStudent &b)
{
if (&b == this)
{
return *this;
}
if (NULL == b.m_pName)
{
delete []m_pName;
m_pName = NULL;
return *this;
}
delete []m_pName;
int len=strlen(b.m_pName);
m_pName=new char[len+1];
memset(m_pName, 0, len+1);
strcpy(m_pName,b.m_pName);
return *this;
}
#else
//重载赋值函数 返回引用
CStudent& operator=(const CStudent &b)
{
if (&b == this)
{
return *this;
}
if (NULL == b.m_pName)
{
delete []m_pName;
m_pName = NULL;
return *this;
}
delete []m_pName;
int len = strlen(b.m_pName);
m_pName = new char[len + 1];
memset(m_pName, 0, len+1);
strcpy(m_pName, b.m_pName);
return *this;
}
#endif
//或者 我们也可以这样重载赋值运算符 即不返回任何值。如果这样的话,他将不支持客户代码中的链式赋值
//例如a=b=c will be prohibited!
//void operator=(const CStudent &a);
private:
char *m_pName;
};
int main()
{
{
CStudent liubei("liubei");
CStudent guanyu("guanyu");
CStudent zhangfei("zhangfei");
//CStudent dd(NULL);
//CStudent ff(dd);
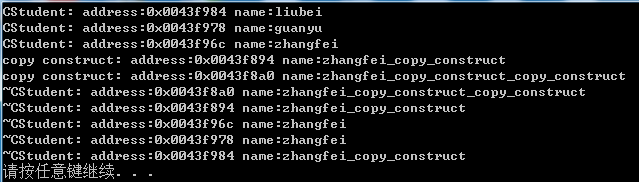
liubei = guanyu = zhangfei;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
这里为了说明问题,在拷贝构造函数中添加了类对象的处理,因此出现了上图结果中最后一行析构函数中出现了zhang_fei_copy_construct的结果。在实际中肯定不会这样做,因此实际在写代码中,返回引用和返回对象的结果都一样,但是由于返回对象的运算符重载函数多了拷贝构造函数的调用, 而且当运算顺序为(a=b)=c时,结果与预想的结果不同,因此建议使用运算符重载函数返回引用。
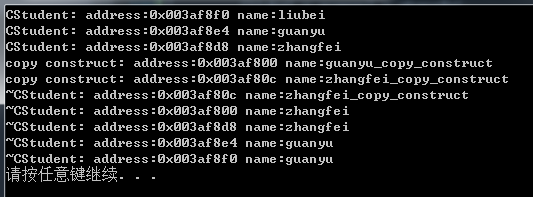
当把上述代码修改为时:
(liubei = guanyu) = zhangfei运行结果为(为什么结果是这样的,由于 liubei = guanyu 先调用运算符重载函数得到结果,产生一个临时对象tem_c,然后调用拷贝构造函数tem_c(*this), *this是运算符重载函数的返回对象,同时tem_c = zhangfei调用了运算符重载函数,得到一个临时对象tem_a,然后调用拷贝构造函数tem_a(*this),因此得到如下结果):
2. 运算符重载函数返回类对象的引用
#include
#include
using namespace std;
class CStudent
{
public:
CStudent(char *pName) :m_pName(NULL)
{
if (NULL == pName)
{
return;
}
m_pName = new char[strlen(pName) + 1];
strcpy(m_pName, pName);
printf("CStudent: address:0x%08x name:%s\n", this, m_pName);
}
~CStudent()
{
printf("~CStudent: address:0x%08x name:%s\n", this, m_pName);
delete []m_pName;
}
//拷贝构造函数
CStudent(const CStudent &a) :m_pName(NULL)
{
if (NULL == a.m_pName)
{
cout<<"reference"<m_pName = new char[len + 20];
memset(m_pName, 0, len + 20);
strcpy(m_pName, a.m_pName);
strcat(m_pName, "_copy_construct"); // 为了测试
printf("copy construct: address:0x%08x name:%s\n", this, this->m_pName);
}
public:
#if 0
//重载赋值函数 返回对象
CStudent operator=(const CStudent &b)
{
if (&b == this)
{
return *this;
}
if (NULL == b.m_pName)
{
delete []m_pName;
m_pName = NULL;
return *this;
}
delete []m_pName;
int len=strlen(b.m_pName);
m_pName=new char[len+1];
memset(m_pName, 0, len+1);
strcpy(m_pName,b.m_pName);
return *this;
}
#else
//重载赋值函数 返回引用
CStudent& operator=(const CStudent &b)
{
if (&b == this)
{
return *this;
}
if (NULL == b.m_pName)
{
delete []m_pName;
m_pName = NULL;
return *this;
}
delete []m_pName;
int len = strlen(b.m_pName);
m_pName = new char[len + 1];
memset(m_pName, 0, len+1);
strcpy(m_pName, b.m_pName);
return *this;
}
#endif
//或者 我们也可以这样重载赋值运算符 即不返回任何值。如果这样的话,他将不支持客户代码中的链式赋值
//例如a=b=c will be prohibited!
//void operator=(const CStudent &a);
private:
char *m_pName;
};
int main()
{
{
CStudent liubei("liubei");
CStudent guanyu("guanyu");
CStudent zhangfei("zhangfei");
//CStudent dd(NULL);
//CStudent ff(dd);
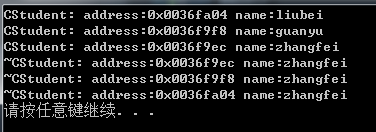
liubei = guanyu = zhangfei;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果:
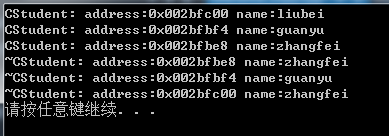
当把上述代码修改为时:
(liubei = guanyu) = zhangfei运行结果为(运行过程为: liubei = guanyu先调用运算符重载函数,由于返回的是liubei的引用,因此进行 liubei = zhangfei调用运算符重载函数):
[Reference]
[1]代码参考:https://blog.csdn.net/miyunhong/article/details/51149376