PCL Lesson5: 直通滤波+空间平面拟合+提供原始点云数据集PCD文件
书接上文。本节做下面一个工作:通过直通滤波过滤一小片平面区域的点云(标定版),通过最小二乘法拟合,并把参数化的平面绘制在原图中。
待修正:拟合平面时离散点的处理。和拟合效果的判别
原始点云的文件这这里:(16线激光雷达,3.2w左右个点)
https://pan.baidu.com/s/1k6JOqbMgIFBJVz54bt3Ekg
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#define random(x1,x2) ((rand()%x2) - x1/2.0)
//Ax+by+cz=D
void cvFitPlane(const CvMat* points, float* plane){
// Estimate geometric centroid.
int nrows = points->rows;
int ncols = points->cols;
int type = points->type;
CvMat* centroid = cvCreateMat(1, ncols, type);
cvSet(centroid, cvScalar(0));
for (int c = 0; c < ncols; c++){ //用地址的形式才能实现先列后行的操作,如果用Mat型只能先行后列
for (int r = 0; r < nrows; r++)
{
centroid->data.fl[c] += points->data.fl[ncols*r + c];
}
centroid->data.fl[c] /= nrows;
}
// Subtract geometric centroid from each point.
CvMat* points2 = cvCreateMat(nrows, ncols, type);
for (int r = 0; r < nrows; r++)
for (int c = 0; c < ncols; c++)
points2->data.fl[ncols*r + c] = points->data.fl[ncols*r + c] - centroid->data.fl[c];
// Evaluate SVD of covariance matrix.
CvMat* A = cvCreateMat(ncols, ncols, type);
CvMat* W = cvCreateMat(ncols, ncols, type);
CvMat* V = cvCreateMat(ncols, ncols, type);
cvGEMM(points2, points, 1, NULL, 0, A, CV_GEMM_A_T); //points也要为CVMat型
cvSVD(A, W, NULL, V, CV_SVD_V_T);
// Assign plane coefficients by singular vector corresponding to smallest singular value.
plane[ncols] = 0;
for (int c = 0; c < ncols; c++){
plane[c] = V->data.fl[ncols*(ncols - 1) + c];
plane[ncols] += plane[c] * centroid->data.fl[c];
}
// Release allocated resources.
cvReleaseMat(¢roid);
cvReleaseMat(&points2);
cvReleaseMat(&A);
cvReleaseMat(&W);
cvReleaseMat(&V);
}
int main()
{
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud2(new pcl::PointCloud); //PointXYZ 数据结构
pcl::PointCloud::Ptr cloud_medium(new pcl::PointCloud);
pcl::PCDReader reader;
reader.read("pcdData//lader3.PCD",*cloud2);
//x
pcl::PassThrough pass_x;
pass_x.setInputCloud(cloud2);
pass_x.setFilterFieldName("x");
pass_x.setFilterLimitsNegative(false);
pass_x.setFilterLimits(5,7);
pass_x.filter(*cloud_medium);
//y
pcl::PassThrough pass_y;
pass_y.setInputCloud(cloud_medium);
pass_y.setFilterFieldName("y");
pass_y.setFilterLimitsNegative(false);
pass_y.setFilterLimits(-1, 1);
pass_y.filter(*cloud_medium);
//z
pcl::PassThrough pass_z;
pass_z.setInputCloud(cloud_medium);
pass_z.setFilterFieldName("z");
pass_z.setFilterLimitsNegative(false);
pass_z.setFilterLimits(-1.5, 1.5);
pass_z.filter(*cloud_medium);
//双视口
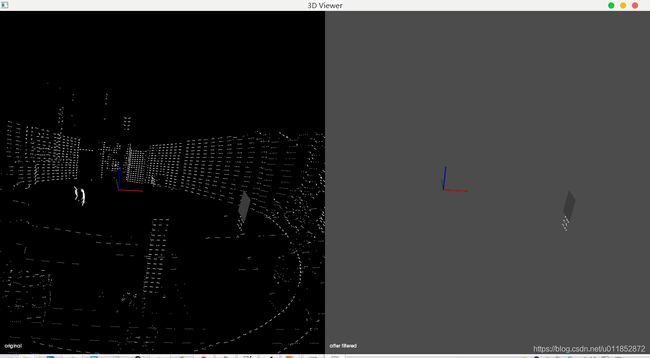
int v1(0), v2(0);
boost::shared_ptr viewer(new pcl::visualization::PCLVisualizer("3D Viewer"));
viewer->createViewPort(0.0, 0.0, 0.5, 1.0, v1);//(Xmin,Ymin,Xmax,Ymax)设置窗口坐标
viewer->setBackgroundColor(0, 0, 0, v1);
viewer->addText("original", 10, 10, "v1 text", v1);//设置视口名称
viewer->addPointCloud(cloud2, "sample cloud1", v1);//添加点云
viewer->createViewPort(0.5, 0.0, 1.0, 1.0, v2);
viewer->setBackgroundColor(0.3, 0.3, 0.3, v2);
viewer->addText("after filtered", 10, 10, "v2 text", v2);
viewer->addPointCloud(cloud_medium, "sample cloud2", v2);
viewer->addCoordinateSystem(1.0,"sample cloud1");
//
CvMat*points_mat = cvCreateMat(cloud_medium->size(), 3, CV_32FC1);//定义用来存储需要拟合点的矩阵
float plane12[4] = { 0 };//定义用来储存平面参数的数组
printf("%d\n", cloud_medium->size());
for (int i = 0; isize();i++)
{
points_mat->data.fl[i * 3 + 0] = cloud_medium->points[i].x;
points_mat->data.fl[i * 3 + 1] = cloud_medium->points[i].y;// Y的坐标值
points_mat->data.fl[i * 3 + 2] = cloud_medium->points[i].z;
}
cvFitPlane(points_mat, plane12);//调用方程
printf("A=%f\nB=%f\nC=%f\nD=%f\n", plane12[0], plane12[1], plane12[2], plane12[3]);
pcl::ModelCoefficients plane_coeff;
plane_coeff.values.resize(4); // We need 4 values
plane_coeff.values[0] = plane12[0];
plane_coeff.values[1] = plane12[1];
plane_coeff.values[2] = plane12[2];
plane_coeff.values[3] = -plane12[3];
viewer->addPlane(plane_coeff);
while (!viewer->wasStopped())
{
viewer->spinOnce();
}
return 0;
}