平面最近点对 洛谷1257 分治 c++
题目描述
给定平面上n个点,找出其中的一对点的距离,使得在这n个点的所有点对中,该距离为所有点对中最小的。
输入格式:
第一行:n;2≤n≤10000
接下来n行:每行两个实数:x y,表示一个点的行坐标和列坐标,中间用一个空格隔开。
输出格式:
仅一行,一个实数,表示最短距离,精确到小数点后面4位。
说明
本题爆搜即可
Solution
嗯,这么良心的说明已经少见了
一直想刷的分治题。首先将点图排序、分成左右两半,分别得出左右两半的最近距离
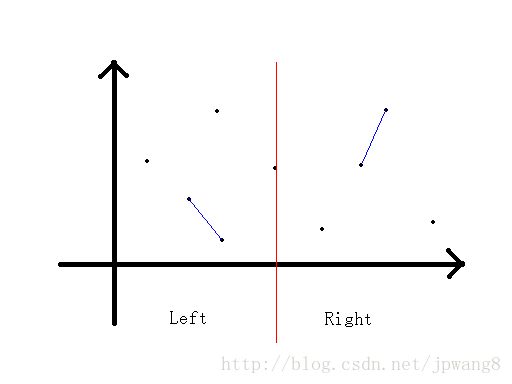
然后可以看出蓝色的线段分别是两部分的最短距离(意思一下)
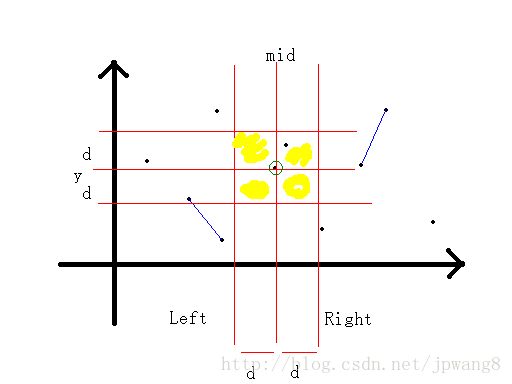
若递归得来的最短距离为d,那么可知合并答案时新的最近点对可能出现在这个区间
我才没有偷偷加点呢哼
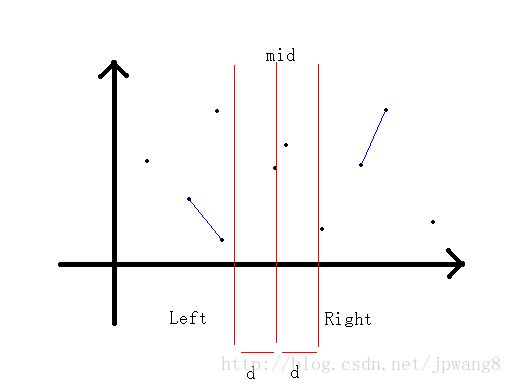
也就是 mid−d 一直到 mid+d 这一段,为什么呢?
显然不证
那么我们可以筛选一批点出来,在这里面找跨越分界线的最近点对
再竖着看,显然对于一个纵坐标为y的点只有 y−mid 到 y+mid 这一段可能有最近点
为什么呢?
显然不证(滑稽
然后根据鸽巢原理,这样符合条件的点是最多只有6个的
然后就A了嗯
还有那道数据加强版过不了是为什么
Code
#include inline int cmp2(const pos &a, const pos &b){
return a.y < b.y;
}
inline double getAns(const int &l, const int &r){
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if (l == r){
return INF;
}
if (l + 1 == r){
return dist(p[l], p[r]);
}
double d = min(getAns(l, mid), getAns(mid + 1, r));
vector