Java基础——Maven
目录
-
- Maven
-
- 创建Maven项目
- 依赖管理
- Maven执行流程
- 结合命令行使用Maven
- 模块管理
- 网络编程
-
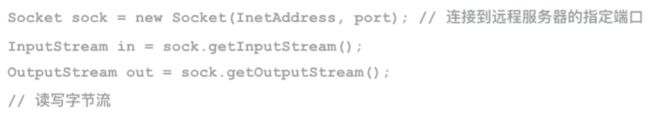
- TCP编程
- TCP多线程编程
- UDP编程
- 邮件收发
-
- 发送邮件
- 接收邮件
- HTTP请求响应协议
- RMI远程调用
- XML&JSON
-
- XML
-
- 解析XML
- JSON
-
- 解析JSON
Maven
- 标准化项目结构
- 标准化构建流程
- 依赖管理等
groupId与artifactId被称为项目坐标,作用就是定位!
groupId一般被设置为包名,而包名一般使用“域名+其他名称”,如org.apache,apache代表公司名
artifactId是唯一的,一般设为模块名;即使项目分为多模块,也能唯一定位子模块
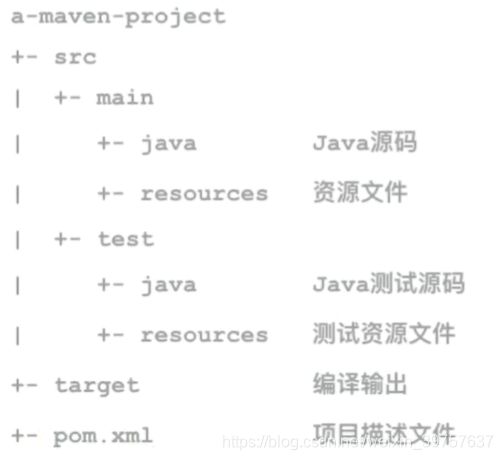
创建Maven项目
- 借助IDEA工具可以创建Maven项目,一般选择quickstart
- 第一次创建会下载一些插件
- 声明一个依赖项,Maven可以自动下载并导入相关jar包
依赖管理
- Maven为我们管理了复杂的依赖包
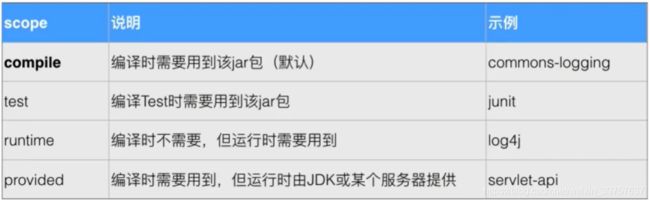
- Maven设置的依赖关系有以下几种:
- Maven从何处下载这些依赖?

- Maven的中央仓库
- 最重要的还是配置文件
pom.xml,包含项目属性、依赖、插件等信息;下面是一个Maven项目的配置文件
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0modelVersion>
<groupId>com.feiyangedu.samplegroupId>
<artifactId>hellodepartifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOTversion>
<packaging>jarpackaging>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8project.build.sourceEncoding>
<java.version>1.8java.version>
<maven.compiler.source>1.8maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>1.8maven.compiler.target>
properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-logginggroupId>
<artifactId>commons-loggingartifactId>
<version>1.2version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4jgroupId>
<artifactId>log4j-jclartifactId>
<version>2.8.2version>
<scope>runtimescope>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4jgroupId>
<artifactId>log4j-coreartifactId>
<version>2.8.2version>
<scope>runtimescope>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junitgroupId>
<artifactId>junitartifactId>
<version>4.12version>
<scope>testscope>
dependency>
dependencies>
project>
Maven执行流程
- Maven的生命周期由一系列阶段(phase)构成

- 使用Maven构建项目就是执行指定的
Phase - 执行一个Phase其实执行了一系列阶段,只不过到此为止,例如:

- 执行一个Phase又会触发绑定的一个或多个
Goal,Goal是最小执行单元
结合命令行使用Maven
- 下载Maven管理工具
- 将bin/目录添加至环境变量,也可以创建
M2_HOME环境变量 - 使用
mvn命令查看是否安装成功 - 接着便可以使用命令行编译和测试项目了
mvn clean compile // 可能需要将JDK的目录设为%JAVA_HOME%并添加至path,上移
mvn test // 执行项目测试
mvn clean package // 最常用,打成jar包 不会打包依赖的jar
- maven-shade-plugin:打包所有依赖包生成可执行jar
- cobertura-maven-plugin:生成单元测试覆盖率报告
- findbugs-maven-plugin:对java源码进行静态分析
- 我们只需要将插件的配置加入到项目配置文件即可,如下所示:
- 打包依赖文件,生成可执行jar包
// 使用maven-shade-plugin,生成可执行jar包
// 网页搜索maven shade plugin executable jar
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-shade-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.2.2</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<phase>package</phase>
<goals>
<goal>shade</goal>
</goals>
<configuration>
<transformers>
<transformer implementation="org.apache.maven.plugins.shade.resource.ManifestResourceTransformer">
<mainClass>org.sonatype.haven.HavenCli</mainClass>
</transformer>
</transformers>
</configuration>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
</plugins>
// 将上面的配置放在 // 网页搜索 cobertura maven plugin usage
// 加入到pom.xml
<plugin>
<groupId>org.codehaus.mojogroupId>
<artifactId>cobertura-maven-pluginartifactId>
<version>2.7version>
plugin>
// 貌似这些东西都放在<build>中才行
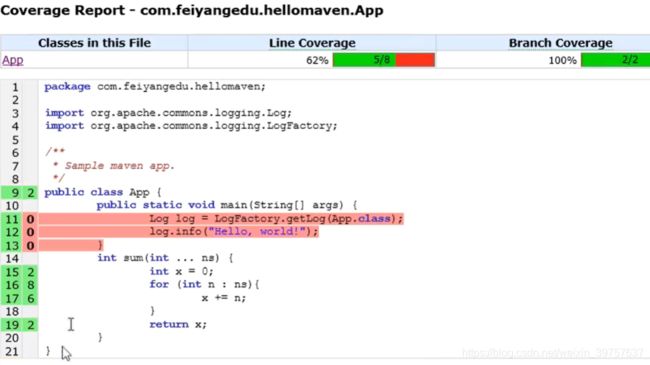
// 编写个除main之外的方法
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Log log = LogFactory.getLog(App.class);
log.info("Hello, world!");
}
public int sum(int ... ns) {
int x = 0;
for (int n:ns){
x += n;
}
return x;
}
}
// 编写测试
import org.junit.Test;
import static org.junit.Assert.*;
public class AppTest {
@Test
public void testApp() {
// assertTrue(true);
// App.main(null); // 未测试到
assertEquals(6,new App().sum(1,2,3));
}
}
// 命令行:mvn cobertura:cobertura
// 这是一个Goal操作,可以直接执行
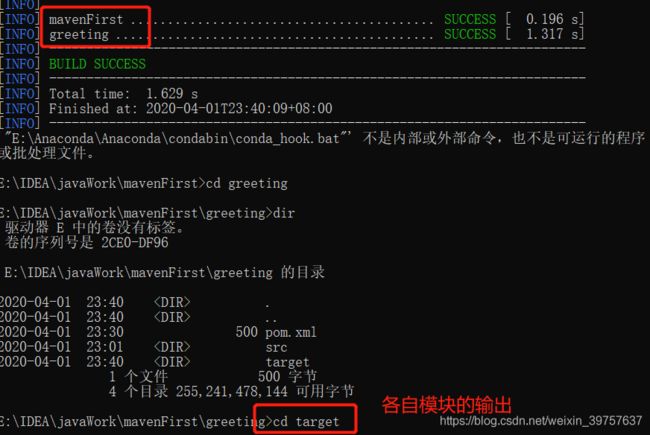
模块管理
- 将一个大项目拆分成模块是降低复杂度的有效方法
- Maven可以有效管理多个模块,IDEA创建多模块:
// 新建Maven项目(基模块)mavenFirst,项目中:New——Module——Maven,填入子模块的标识信息即可
// 也可以通过 File——Project Structure——Modules——New Module创建
// 子模块配置继承父模块:
<parent>
<artifactId>mavenFirstartifactId>
<groupId>xyz.roykungroupId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOTversion>
parent>
// 子模块一般不需再设置groupId,和父模块一致即可!
// 继承父模块后,可以使用其下载好的依赖;也可将公共配置均放置在父模块
// 在父模块中设置<modules>,可以在编译项目的时候自动解析出各模块,生成文件也存放在各自的target
<modules>
<module>greetingmodule>
modules>
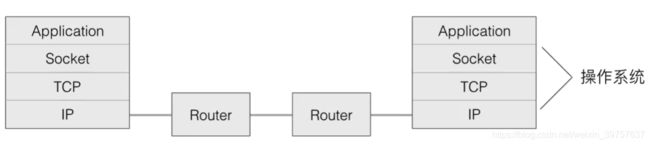
网络编程
- 这部分需要计算机网络的基础知识,包括TCP/IP协议,OSI模型等,这里不介绍
TCP编程
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
/**
* Java网络编程
*/
public class TCPClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
InetAddress addr = InetAddress.getLoopbackAddress(); // "127.0.0.1"
try (Socket sock = new Socket(addr, 9090)) {
// 客户端套接字
try (BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(sock.getInputStream(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8))) {
try (BufferedWriter writer = new BufferedWriter(// Filter包装还记得吗?
new OutputStreamWriter(sock.getOutputStream(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8))) {
writer.write("time\n");
writer.flush(); // 强制输出缓冲区
String resp = reader.readLine(); // 读取服务器返回信息
System.out.println("Response: " + resp);
}
}
}
}
}
- 服务器端
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
public class TCPServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(9090); // 服务器端套接字,监听端口信息
System.out.println("TCP server ready.");
Socket sock = ss.accept(); // 接收连接(套上了)
try (BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(// 这个sock是服务器的
new InputStreamReader(sock.getInputStream(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8))) {
try (BufferedWriter writer = new BufferedWriter(
new OutputStreamWriter(sock.getOutputStream(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8))) {
String cmd = reader.readLine();
if ("time".equals(cmd)) {
writer.write(LocalDateTime.now().toString() + "\n");
writer.flush();
} else {
writer.write("Sorry?\n");
writer.flush();
}
}
}
sock.close();
ss.close();
}
}
- 先启动服务器端程序开启监听,再启动客户端程序即可得到Response
TCP多线程编程
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
public class TCPClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
InetAddress addr = InetAddress.getByName("localhost");
try (Socket sock = new Socket(addr, 9090)) {
try (BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(sock.getInputStream(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8))) {
try (BufferedWriter writer = new BufferedWriter(
new OutputStreamWriter(sock.getOutputStream(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8))) {
writer.write("time\n");
writer.flush();
String resp = reader.readLine();
System.out.println("Response: " + resp);
Thread.sleep(1000);
writer.write("q\n");
writer.flush();
resp = reader.readLine();
System.out.println("Response: " + resp);
}
}
}
}
}
- 服务器端
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.net.ServerSocket;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
public class TCPServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
ServerSocket ss = new ServerSocket(9090);
System.out.println("TCP server ready.");
for (;;) {
Socket sock = ss.accept();
System.out.println("Accept from " + sock.getRemoteSocketAddress());
TimeHandler handler = new TimeHandler(sock);// 开启一个新的线程
handler.start();
}
}
}
class TimeHandler extends Thread {
Socket sock;
TimeHandler(Socket sock) {
this.sock = sock;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try (BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(sock.getInputStream(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8))) {
try (BufferedWriter writer = new BufferedWriter(
new OutputStreamWriter(sock.getOutputStream(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8))) {
for (;;) {
String cmd = reader.readLine();
if ("q".equals(cmd)) {
writer.write("bye!\n");
writer.flush();
break;
} else if ("time".equals(cmd)) {
writer.write(LocalDateTime.now().toString() + "\n");
writer.flush();
} else {
writer.write("Sorry?\n");
writer.flush();
}
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
this.sock.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
- 使用线程池可以提高效率
UDP编程
import java.net.DatagramPacket;
import java.net.DatagramSocket;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
public class UDPClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
InetAddress addr = InetAddress.getLoopbackAddress();
try (DatagramSocket sock = new DatagramSocket()) {
sock.connect(addr, 9090); // 并不建立连接
byte[] data = "time".getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(data, data.length);
sock.send(packet);
System.out.println("Data was sent.");
Thread.sleep(1000);
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
DatagramPacket resp = new DatagramPacket(buffer, buffer.length);
sock.receive(resp);
byte[] respData = resp.getData();
String respText = new String(respData, 0, resp.getLength(), StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
System.out.println("Response: " + respText);
}
}
}
import java.net.DatagramPacket;
import java.net.DatagramSocket;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
public class UDPServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
@SuppressWarnings("resource")
DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket(9090);// 服务器端监听
System.out.println("UDP server ready.");
for (;;) {
// receive:
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(buffer, buffer.length);
ds.receive(packet); // 接收客户端信息
byte[] data = packet.getData();
String s = new String(data, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
System.out.println("Packet received from: " + packet.getSocketAddress() + " " + s);
// send:
String resp = LocalDateTime.now().toString();
packet.setData(resp.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
ds.send(packet); // 发送
}
}
}
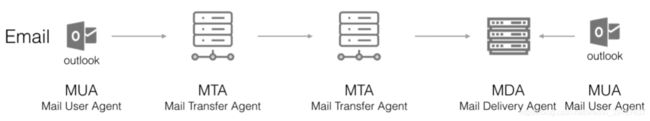
邮件收发
发送邮件
- 使用Maven引入Javamail依赖
- 确定SMTP服务器信息:域名/端口/使用明文/SSL
- 调用API发送(无序关心底层socket连接)
- 设置debug模式可以排查错误
import java.util.Properties;
import javax.mail.Authenticator;
import javax.mail.Message;
import javax.mail.MessagingException;
import javax.mail.PasswordAuthentication;
import javax.mail.Session;
import javax.mail.Transport;
import javax.mail.internet.InternetAddress;
import javax.mail.internet.MimeMessage;
public class SendMail {
final String smtpHost;
final String username;
final String password;
final boolean debug;
public SendMail(String smtpHost, String username, String password) {
// 这里填入你自己的某个邮箱信息
//使用哪个邮箱就用哪个的SMTP服务器,有的服务器可能需要开启一下SMTP服务
this.smtpHost = smtpHost;
this.username = username;
this.password = password;
this.debug = true;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 发送者信息
SendMail sender = new SendMail("smtp.qq.com", "[email protected]", "xxxxxx");
Session session = sender.createTLSSession();
Message message = createTextMessage(session, "[email protected]", "[email protected]", "Java邮件测试",
"Hello, 这是一封javamail测试邮件!");
Transport.send(message);
}
Session createSSLSession() {
Properties props = new Properties();
props.put("mail.smtp.host", this.smtpHost); // SMTP主机名
props.put("mail.smtp.port", "465"); // 主机端口号
props.put("mail.smtp.auth", "true"); // 是否需要用户认证
// 启动SSL:
props.put("mail.smtp.socketFactory.class", "javax.net.ssl.SSLSocketFactory");
props.put("mail.smtp.socketFactory.port", "465");
Session session = Session.getInstance(props, new Authenticator() {
// 用户名+口令认证:
protected PasswordAuthentication getPasswordAuthentication() {
return new PasswordAuthentication(SendMail.this.username, SendMail.this.password);
}
});
session.setDebug(this.debug); // 显示调试信息
return session;
}
Session createTLSSession() {
Properties props = new Properties();
props.put("mail.smtp.host", this.smtpHost); // SMTP主机名
props.put("mail.smtp.port", "587"); // 主机端口号
props.put("mail.smtp.auth", "true"); // 是否需要用户认证
props.put("mail.smtp.starttls.enable", "true"); // 启用TLS加密
Session session = Session.getInstance(props, new Authenticator() {
protected PasswordAuthentication getPasswordAuthentication() {
return new PasswordAuthentication(SendMail.this.username, SendMail.this.password);
}
});
session.setDebug(this.debug); // 显示调试信息
return session;
}
Session createInsecureSession(String host, String username, String password) {
Properties props = new Properties();
props.put("mail.smtp.host", this.smtpHost); // SMTP主机名
props.put("mail.smtp.port", "25"); // 主机端口号
props.put("mail.smtp.auth", "true"); // 是否需要用户认证
Session session = Session.getInstance(props, new Authenticator() {
protected PasswordAuthentication getPasswordAuthentication() {
return new PasswordAuthentication(SendMail.this.username, SendMail.this.password);
}
});
session.setDebug(this.debug); // 显示调试信息
return session;
}
// 发送文本邮件使用的方法
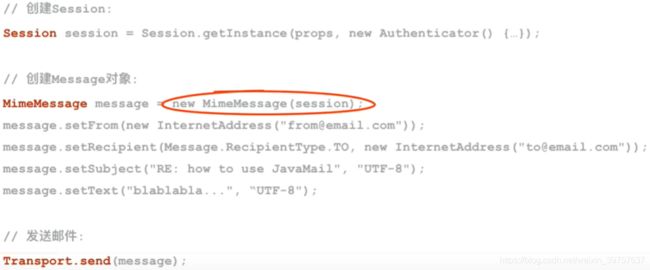
static Message createTextMessage(Session session, String from, String to, String subject, String body)
throws MessagingException {
MimeMessage message = new MimeMessage(session);
message.setFrom(new InternetAddress(from));
message.setRecipient(Message.RecipientType.TO, new InternetAddress(to));
message.setSubject(subject, "UTF-8");
message.setText(body, "UTF-8"); // 发送文本邮件
return message;
}
// 发送HTML格式文本邮件使用的方法
static Message createHtmlMessage(Session session, String from, String to, String subject, String body)
throws MessagingException {
MimeMessage message = new MimeMessage(session);
message.setFrom(new InternetAddress(from));
message.setRecipient(Message.RecipientType.TO, new InternetAddress(to));
message.setSubject(subject, "UTF-8");
message.setText(body, "UTF-8", "html");
return message;
}
// 发送带附件邮件使用的方法
static Message createMessageWithAttachment(Session session, String from, String to, String subject, String body,
String fileName, InputStream input) throws MessagingException, IOException {
MimeMessage message = new MimeMessage(session);
message.setFrom(new InternetAddress(from));
message.setRecipient(Message.RecipientType.TO, new InternetAddress(to));
message.setSubject(subject, "UTF-8");
Multipart multipart = new MimeMultipart(); // 带附件
// 添加text:
BodyPart textpart = new MimeBodyPart();
textpart.setContent(body, "text/html;charset=utf-8");
multipart.addBodyPart(textpart);
// 添加image:
BodyPart imagepart = new MimeBodyPart();
imagepart.setFileName(fileName);
imagepart.setDataHandler(new DataHandler(new ByteArrayDataSource(input, "application/octet-stream")));
multipart.addBodyPart(imagepart);
message.setContent(multipart);
return message;
}
// 将附件内嵌在文本中使用的方法
static Message createMessageWithInlineImage(Session session, String from, String to, String subject, String body,
String fileName, InputStream input) throws MessagingException, IOException {
MimeMessage message = new MimeMessage(session);
message.setFrom(new InternetAddress(from));
message.setRecipient(Message.RecipientType.TO, new InternetAddress(to));
message.setSubject(subject, "UTF-8");
Multipart multipart = new MimeMultipart();
// 添加text:
BodyPart textpart = new MimeBodyPart();
textpart.setContent(body, "text/html;charset=utf-8");
multipart.addBodyPart(textpart);
// 添加image:
BodyPart imagepart = new MimeBodyPart();
imagepart.setFileName(fileName);
imagepart.setDataHandler(new DataHandler(new ByteArrayDataSource(input, "image/jpeg")));
// 与HTML的 关联:
imagepart.setHeader("Content-ID", "
关联:
imagepart.setHeader("Content-ID", "" );
multipart.addBodyPart(imagepart);
message.setContent(multipart);
return message;
}
}
接收邮件
// 可以打印出邮件信息
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Properties;
import javax.mail.Address;
import javax.mail.Authenticator;
import javax.mail.BodyPart;
import javax.mail.Flags;
import javax.mail.Folder;
import javax.mail.Message;
import javax.mail.MessagingException;
import javax.mail.Multipart;
import javax.mail.Part;
import javax.mail.PasswordAuthentication;
import javax.mail.Session;
import javax.mail.Store;
import javax.mail.URLName;
import javax.mail.internet.InternetAddress;
import javax.mail.internet.MimeMessage;
import javax.mail.internet.MimeMessage.RecipientType;
import javax.mail.internet.MimeUtility;
import com.sun.mail.pop3.POP3SSLStore;
public class Pop3 {
final String popHost;
final String username;
final String password;
final boolean debug;
public Pop3(String popHost, String username, String password) {
this.popHost = popHost;
this.username = username;
this.password = password;
this.debug = true;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Pop3 pop = new Pop3("pop.qq.com", "[email protected]", "yr143364");
Folder folder = null;
Store store = null;
try {
store = pop.createSSLStore();
folder = store.getFolder("INBOX");
folder.open(Folder.READ_WRITE);
System.out.println("Total messages: " + folder.getMessageCount());
System.out.println("New messages: " + folder.getNewMessageCount());
System.out.println("Unread messages: " + folder.getUnreadMessageCount());
System.out.println("Deleted messages: " + folder.getDeletedMessageCount());
Message[] messages = folder.getMessages();
for (Message message : messages) {
printMessage((MimeMessage) message);
}
} finally {
if (folder != null) {
try {
folder.close(true);
} catch (MessagingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (store != null) {
try {
store.close();
} catch (MessagingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public Store createSSLStore() throws MessagingException {
Properties props = new Properties();
props.setProperty("mail.store.protocol", "pop3");
props.setProperty("mail.pop3.port", "995"); // 主机端口号
props.setProperty("mail.pop3.host", this.popHost);// POP3主机名
// 启动SSL:
props.put("mail.smtp.socketFactory.class", "javax.net.ssl.SSLSocketFactory");
props.put("mail.smtp.socketFactory.port", "995");
URLName url = new URLName("pop3", this.popHost, 995, "", this.username, this.password);
Session session = Session.getInstance(props, null);
session.setDebug(this.debug); // 显示调试信息
Store store = new POP3SSLStore(session, url);
store.connect();
return store;
}
Session createTLSStore() {
Properties props = new Properties();
props.put("mail.smtp.host", this.popHost); // POP3主机名
props.put("mail.smtp.port", "587"); // 主机端口号
props.put("mail.smtp.auth", "true"); // 是否需要用户认证
props.put("mail.smtp.starttls.enable", "true"); // 启用TLS加密
Session session = Session.getInstance(props, new Authenticator() {
protected PasswordAuthentication getPasswordAuthentication() {
return new PasswordAuthentication(Pop3.this.username, Pop3.this.password);
}
});
session.setDebug(this.debug); // 显示调试信息
return session;
}
Session createInsecureStore() {
Properties props = new Properties();
props.put("mail.smtp.host", this.popHost); // POP3主机名
props.put("mail.smtp.port", "25"); // 主机端口号
props.put("mail.smtp.auth", "true"); // 是否需要用户认证
Session session = Session.getInstance(props, new Authenticator() {
protected PasswordAuthentication getPasswordAuthentication() {
return new PasswordAuthentication(Pop3.this.username, Pop3.this.password);
}
});
session.setDebug(this.debug); // 显示调试信息
return session;
}
static void printMessage(MimeMessage msg) throws IOException, MessagingException {
System.out.println("--------------------");
System.out.println("Subject: " + MimeUtility.decodeText(msg.getSubject()));
System.out.println("From: " + getFrom(msg));
System.out.println("To: " + getTo(msg));
System.out.println("Sent: " + msg.getSentDate().toString());
System.out.println("Seen: " + msg.getFlags().contains(Flags.Flag.SEEN));
System.out.println("Priority: " + getPriority(msg));
System.out.println("Size: " + msg.getSize() / 1024 + "kb");
System.out.println("Body: " + getBody(msg));
System.out.println("--------------------");
System.out.println();
}
static String getFrom(MimeMessage msg) throws IOException, MessagingException {
Address[] froms = msg.getFrom();
return addressToString(froms[0]);
}
static String getTo(MimeMessage msg) throws MessagingException, IOException {
// 使用 msg.getAllRecipients() 获取所有收件人
Address[] tos = msg.getRecipients(RecipientType.TO);
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (Address to : tos) {
list.add(addressToString(to));
}
return String.join(", ", list);
}
static String addressToString(Address addr) throws IOException {
InternetAddress address = (InternetAddress) addr;
String personal = address.getPersonal();
return personal == null ? address.getAddress()
: (MimeUtility.decodeText(personal) + " <" + address.getAddress() + ">");
}
static String getPriority(MimeMessage msg) throws MessagingException {
String priority = "Normal";
String[] headers = msg.getHeader("X-Priority");
if (headers != null) {
String header = headers[0];
if ("1".equals(header) || "high".equalsIgnoreCase(header)) {
priority = "High";
} else if ("5".equals(header) || "low".equalsIgnoreCase(header)) {
priority = "Low";
}
}
return priority;
}
static String getBody(Part part) throws MessagingException, IOException {
if (part.isMimeType("text/*")) {
return part.getContent().toString();
}
if (part.isMimeType("multipart/*")) {
Multipart multipart = (Multipart) part.getContent();
for (int i = 0; i < multipart.getCount(); i++) {
BodyPart bodyPart = multipart.getBodyPart(i);
String body = getBody(bodyPart);
if (!body.isEmpty()) {
return body;
}
}
}
return "";
}
}
HTTP请求响应协议
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.HttpURLConnection;
import java.net.URL;
import java.net.URLEncoder;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
class Response {
final int code;
final byte[] data;
public Response(int code, byte[] data) {
this.code = code;
this.data = data;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(1024);
sb.append(code).append("\n");
String s = new String(data, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
if (s.length() > 1024) {
sb.append(s.substring(0, 1024)).append("\n...");
} else {
sb.append(s);
}
return sb.toString();
}
}
public class HttpClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Response resp = get("https://www.douban.com");
System.out.println(resp);// get请求
Map<String, String> postMap = new HashMap<>();// 模拟post表单
postMap.put("form_email", "test");
postMap.put("form_password", "password");
Response postResp = post("https://www.douban.com/accounts/login", "application/x-www-form-urlencoded",
toFormData(postMap));// post请求
System.out.println(postResp);
}
static Response get(String theUrl) {
System.err.println("GET: " + theUrl);
HttpURLConnection conn = null;
try {
URL url = new URL(theUrl);
conn = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
ByteArrayOutputStream responseBuffer = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
try (InputStream input = conn.getInputStream()) {
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
for (;;) {
int n = input.read(buffer);
if (n == (-1)) {
break;
}
responseBuffer.write(buffer, 0, n);
}
}
return new Response(conn.getResponseCode(), responseBuffer.toByteArray());
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
if (conn != null) {
conn.disconnect();
}
}
}
static Response post(String theUrl, String contentType, String contentData) {
System.err.println("POST: " + theUrl);
HttpURLConnection conn = null;
try {
URL url = new URL(theUrl);
conn = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
conn.setRequestMethod("POST");
conn.setDoOutput(true); // 表示需要发送数据
byte[] postData = contentData.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
conn.setRequestProperty("Content-Type", contentType);
conn.setRequestProperty("Content-Length", String.valueOf(postData.length));
try (OutputStream output = conn.getOutputStream()) {
output.write(postData);
}
ByteArrayOutputStream responseBuffer = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
try (InputStream input = conn.getInputStream()) {
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
for (;;) {
int n = input.read(buffer);
if (n == (-1)) {
break;
}
responseBuffer.write(buffer, 0, n);
}
}
return new Response(conn.getResponseCode(), responseBuffer.toByteArray());
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
if (conn != null) {
conn.disconnect();
}
}
}
static String toFormData(Map<String, String> map) throws IOException {
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>(map.size());
for (String key : map.keySet()) {
list.add(key + "=" + URLEncoder.encode(map.get(key), "UTF-8"));
}
return String.join("&", list);
}
}
RMI远程调用
- 定义一个interface
import java.rmi.Remote;
import java.rmi.RemoteException;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
public interface Clock extends Remote {
// 必须继承自Remote
LocalDateTime currentTime() throws RemoteException; // 必须抛出
}
- 实现类
import java.rmi.RemoteException;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
public class ClockImpl implements Clock {
// 继承接口
@Override
public LocalDateTime currentTime() throws RemoteException {
return LocalDateTime.now();
}
}
- server
import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry;
import java.rmi.registry.Registry;
import java.rmi.server.UnicastRemoteObject;
public class ClockServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Clock impl = new ClockImpl();
// 得到一个stub对象
Clock stub = (Clock) UnicastRemoteObject.exportObject(impl, 1099);// 1099端口
LocateRegistry.createRegistry(1099);
Registry registry = LocateRegistry.getRegistry();
registry.bind("Clock", stub); // 绑定stub对象而非实例,远程调用需要使用这个名称
System.out.println("Clock server ready.");
}
}
- client
import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry;
import java.rmi.registry.Registry;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
public class ClockClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Registry registry = LocateRegistry.getRegistry(null); // null = "localhost",建立远程连接
Clock clock = (Clock) registry.lookup("Clock"); // 获得远程对象的引用
LocalDateTime dt = clock.currentTime(); // 调用RMI方法
System.out.println("RMI result: " + dt);
}
}
- 服务器端通过自动生成的stub类接收远程调用请求
XML&JSON
XML
.dtd表示数据结构可以被DTD或XSD验证
isbn元素必须包含属性lang
| 字符 | 表示 |
|---|---|
| < | < |
| > | > |
| & | & |
| " | " |
| ’ | ' |
解析XML
- 两种标准的解析XML的API:
- DOM:一次性读取XML,在内存中表示为树形结构
- SAX:以流的形式读取,使用事件回调
注:W3C DOM 标准被分为 3 个不同的部分:
- 核心 DOM - 针对任何结构化文档的标准模型
- XML DOM - 针对 XML 文档的标准模型
- HTML DOM - 针对 HTML 文档的标准模型
- 核心API
DocumentBuilderFactory dbf = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();// 操作工场
DocumentBuilder db = dbf.newDocumentBuilder();// 操作类
Document doc = db.parse('./hello.xml');// 传入文档
Element elt = doc.getDocumentElement();
import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilder;
import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilderFactory;
import org.w3c.dom.Document;
import org.w3c.dom.Node;
public class DOMSample {
static final String XML_URL = "http://rss.sina.com.cn/tech/internet/home28.xml";
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
DocumentBuilderFactory dbf = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
DocumentBuilder db = dbf.newDocumentBuilder();
Document doc = db.parse(XML_URL);
printNode(doc, 0);
}
static void printNode(Node n, int indent) {
for (int i = 0; i < indent; i++) {
System.out.print(' ');
}
switch (n.getNodeType()) {
case Node.DOCUMENT_NODE: // 文档节点也视为Node
System.out.println("Document: " + n.getNodeName());
break;
case Node.ELEMENT_NODE:
System.out.println("Element: " + n.getNodeName());
break;
case Node.TEXT_NODE:
System.out.println("Text: " + n.getNodeName() + " = " + n.getNodeValue());
break;
case Node.ATTRIBUTE_NODE:
System.out.println("Attr: " + n.getNodeName() + " = " + n.getNodeValue());
break;
case Node.CDATA_SECTION_NODE:
System.out.println("CDATA: " + n.getNodeName() + " = " + n.getNodeValue());
break;
case Node.COMMENT_NODE:
System.out.println("Comment: " + n.getNodeName() + " = " + n.getNodeValue());
break;
default:
System.out.println("NodeType: " + n.getNodeType() + ", NodeName: " + n.getNodeName());
}
for (Node child = n.getFirstChild(); child != null; child = child.getNextSibling()) {
printNode(child, indent + 1);
}
}
}
JSON
- json是一种类似JavaScript对象的数据表示格式(JavaScript Object Notation)
- 去除了JavaScript的执行语句,仅保留数据
- 特点:只允许使用utf-8编码,必须使用双引号,特殊字符使用
\转义 - 适合表示层次结构,结构简单速度快
- 浏览器直接支持json的读写,因此非常适合REST API做数据通讯
REST API是前后端分离的一套标准
// json数据,key-value形式
{
"data": [{
"name": "RoyKun"
},
{
"age": 22
},
{
"hobby": [{
"first": "study"
}, {
"second": "play"
}, {
"third": "sport"
}]
},
{
"language": ["C", "java", "Python"]
},
"just a test"
]
}
解析JSON
- JSR 353 API
- 第三方库(Jackson、Gson等)
- 使用Jackson:
// 使用Jackson
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.net.HttpURLConnection;
import java.net.URL;
import java.net.URLEncoder;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.DeserializationFeature;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.datatype.jsr310.JavaTimeModule;
public class JsonToBean {
// 豆瓣API搜索
static final String JSON_URL = "https://api.douban.com/v2/book/search?q=";
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ObjectMapper mapper = new ObjectMapper().registerModule(new JavaTimeModule());// 日期时间格式
mapper.configure(DeserializationFeature.FAIL_ON_UNKNOWN_PROPERTIES, false);// 忽略在javabean中找不到的属性
String json = search("java");// 返回下载的json字符串
SearchResult result = mapper.readValue(json, SearchResult.class);// 可以直接把一个json字符串反序列化为指定的javabean对象,这里指定为SearchResult了
// SearchResult的定义会事先参考下载的json数据
// 再将javabean对象转化为json输出
System.out.println(mapper.writerWithDefaultPrettyPrinter().writeValueAsString(result));
// 这样倒腾一下可以理解成规范数据
}
static String search(String q) {
HttpURLConnection conn = null;
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder(4096);
try {
URL url = new URL(JSON_URL + URLEncoder.encode(q, "UTF-8"));
conn = (HttpURLConnection) url.openConnection();
if (200 == conn.getResponseCode()) {
try (BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(conn.getInputStream(), "UTF-8"))) {
char[] buffer = new char[1024];
for (;;) {
int n = reader.read(buffer);
if (n == (-1)) {
break;
}
sb.append(buffer, 0, n);
}
}
return sb.toString();
}
throw new RuntimeException("Bad response code: " + conn.getResponseCode());
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
if (conn != null) {
conn.disconnect();
}
}
}
}
// javabean
import java.util.List;
public class SearchResult {
// 数据成员
public long count;
public long total;
public List<Book> books;
}
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.util.List;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.annotation.JsonDeserialize;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.annotation.JsonSerialize;
public class Book {
public String id;
public String title;
public String subtitle;
public List<String> author;
// 使用Annotion定制序列化和反序列化
@JsonSerialize(using = CustomLocalDateSerializer.class)
@JsonDeserialize(using = CustomLocalDateDeserializer.class)
public LocalDate pubdate;// 会用到上面的序列化和反序列化,都是自定义的对数据成员的小操作
public String url;
public String price;
}
在解释一下什么是JavaBean:
JavaBean 是一种JAVA语言写成的可重用组件。为写成JavaBean,类必须是具体的和公共的,并且具有无参数的构造器。JavaBean 通过提供符合一致性设计模式的公共方法暴露成员属性,即set和get方法。众所周知,属性名称符合这种模式,其他Java 类可以通过反射机制发现和操作这些JavaBean 的属性
// 自定义注解,格式化数据
import java.io.IOException;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonGenerator;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.JsonSerializer;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.SerializerProvider;
public class CustomLocalDateSerializer extends JsonSerializer<LocalDate> {
// 数据序列化
@Override
public void serialize(LocalDate value, JsonGenerator gen, SerializerProvider serializers) throws IOException {
gen.writeString(value.toString()); // 使用自定义的方法封装对象
}
}
import java.io.IOException;
import java.time.DateTimeException;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
import java.util.Locale;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonParser;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonProcessingException;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.DeserializationContext;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.JsonDeserializer;
public class CustomLocalDateDeserializer extends JsonDeserializer<LocalDate> {
// 反序列化数据
static DateTimeFormatter FORMATTER = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-M-d", Locale.US);
@Override
public LocalDate deserialize(JsonParser p, DeserializationContext ctxt)
throws IOException, JsonProcessingException {
String s = p.getValueAsString();
if (s != null) {
try {
return LocalDate.parse(s, FORMATTER); // 使用自定义的格式解析对象
} catch (DateTimeException e) {
// ignore
}
}
return null;
}
}
- Jackson提供了读写json的API,实现了json和javabean的相互转换,可使用Annotion定制序列化和反序列化