服务器数据同步:Rsync+Inotify实时同步
文章目录
- 一:Rsync 理论
-
- 1.1:什么是rsync?有什么作用
- 1.2:rsync源服务器的关系
- 二:Rsync 实验
-
- 2.1:rsync命令集锦
- 2.2:实验环境
- 2.3: 实验拓扑图
- 2.3: 实验过程
-
- 2.3.1: 配置源服务器
- 2.3.2: 客户机同步源服务的数据
- 三: Rsync配合inotify工具实现触发式传输同步
-
- 3.1: rsync实现同步的优劣
- 3.2: Inotify的介绍
- 3.3: 实时同步实验
-
- 3.3.1: 源服务器配置
- 3.3.2: 客户机服务器配置
一:Rsync 理论
1.1:什么是rsync?有什么作用
- rsync,全称为:Remote Sync(远程同步),是一款开源的快速增量备份工具,可以在不同主机之间镜像同步整个目录树
- 还支持本地复制,增量备份、保持连接和权限,或者与其他SSH,rsync主机同步
- 采用优化的同步算法,传输前执行压缩,因此非常适用于异地备份、镜像服务器等应用
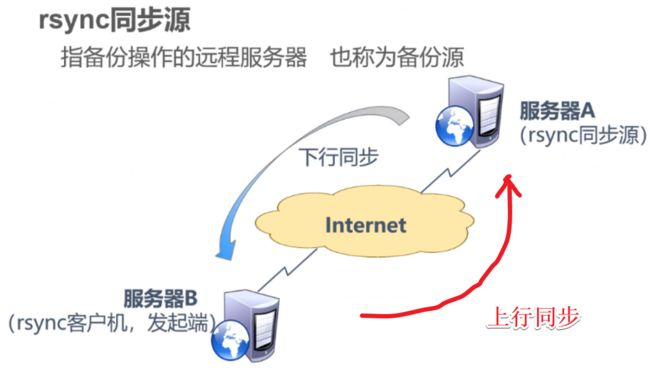
1.2:rsync源服务器的关系
二:Rsync 实验
2.1:rsync命令集锦
-
1、启动rsync服务:
rsync --daemon -
2、关闭rsync服务:
kill $(cat /var/run/rsyncd.pid) -
3、同步本地文件系统数据:rsync [选项] 原始位置 目标位置
例如: rsync /etc/fstab /opt '//同步本机的fstab文件到opt目录' rsync -rl /boot/grub /opt '//同步本机的grub目录到opt目录' '//如果想要在/opt目录下也创建一个boot目录,那么命令需要为:rsync -R rl /boot/grub /opt ' 常用选项: -a:归档模式,递归并保留对象属性,等同于 -rlptgoD -r 对子目录以递归模式处理,主要是针对目录来说的,如果单独传一个文件不需要加-r,但是传输的是目录必须加-r选项 -l 保留软链接 -p 保持文件权限 -v:显示同步过程的详细(verbose)信息 -z:在传输文件时进行压缩(compress) -H:保留硬连接文件 -A:保留ACL属性信息 --delete:删除"目标"中"源"没有的文件 --checksum:根据对象的校验和来决定是否跳过文件 --progress 在同步的过程中可以看到同步的过程状态,比如统计要同步的文件数量、同步的文件传输速度等等 路径的格式可以是本地路径,也可以是使用user@host:path或user@host::path的远程路径,如果主机和path路径之间使用单个冒号隔开,表示使用的是远程shell通信方式,而使用双冒号隔开的则表示的是连接rsync daemon -
4、源下行同步—客户机"拉" (恢复数据)(使用客户端将rsync服务器下的wwwroot共享模块下的内容同步到本地的/opt目录下(共享模块下的真实共享路径需要对other用户具有 ‘r’ 权限))
-
(1):命令格式
用户名@主机地址::共享模块名例如:
[root@client ~]# rsync -avz [email protected]::wwwroot /opt -
(2):命令格式:
rsync://用户名@主机地址/共享模块名例如:
[root@client ~]# rsync -avz rsync://[email protected]/wwwroot /opt
5、客户端上行同步—客户机"推" (备份数据)
-
命令格式
[root@client ~ ]# rsync -avz /var/www/html [email protected]::wwwroot“把站点目录上行往源去备份,备份到wwwroot模块”
6、rsync通过ssh的方式同步
-
命令与平常的scp命令类似
-
例如:将本地/opt/abc.txt上传到目标服务器/opt目录:
rsync -avz /opt/abc.txt [email protected]:/opt -
例如:将目标服务器/opt/qwe.txt文件下载到本地/opt目录下:
rsync -avz [email protected]:/opt/qwe.txt /opt
7、
/etcrsync.conf介绍-
vim /etc/rsyncd.conf motd file = /etc/rsyncd.motd #设置服务器信息提示文件,在该文件中编写提示信息 transfer logging = yes #开启rsync数据传输日志功能 log file = /var/log/rsyncd.log #设置日志文件名,可通过log format参数设置日志格式 pid file = /var/run/rsyncd.log #设置rsync进程号保存文件名称 lock file = /var/run/rsync.lock #设置锁文件名称 port = 873 #设置服务器监听的端口号,默认是873 address = 192.168.0.230 #设置本服务器所监听网卡接口的ip地址 uid = nobody #设置进行数据传输时所使用的帐户名或ID号,默认使用nobody gid = nobody #设置进行数据传输时所使用的组名或GID号,默认使用nobody #若为yes, rsync会首先进行chroot设置,将根映射在下面的path参数路径下,对客户端而言,系统的根就是path参数指定的路径。但这样做需要root权限,并且在同步符号连接资料时只会同步名称,不会同步内容。 use chroot = no read only = yes #是否允许客户端上传数据,yes表示不允许 max connections =10 #设置并发连接数,0表示无限制 [common] #自定义模块名,rsync通过模块定义同步的目录,可定义多个 comment = web content #定义注释说明字串 path = /common #同步目录的真是路径通过path指定 ignore errors #忽略一些IO错误 #exclude = test/ #exclude指定common目录下某个目录可以不同步数据 auth users = tom, jerry #设置允许连接服务器的账户,此账户可以是系统中不存在的用户 secrets file = /etc/rysncd.secrets #密码验证文件名,该文件权限要求为只读,建议为600,仅在设置auth users后有效 hosts allow = 192.168.0.0/255.255.255.0 #设置哪些主机可以同步数据,多ip和网段之间使用空格分隔 hosts deny=* #除了hosts allow定义的主机外,拒绝其他所有 list = false #客户端请求显示模块列表时,本模块名称是否显示,默认为true
-
2.2:实验环境
- VMware软件
| 主机名 | IP地址 | 安装服务 | 系统版本 |
|---|---|---|---|
| source | 192.168.100.140 | rsync,httpd | centos7.6 |
| client | 192.168.100.150 | rsync,inotify-tools |
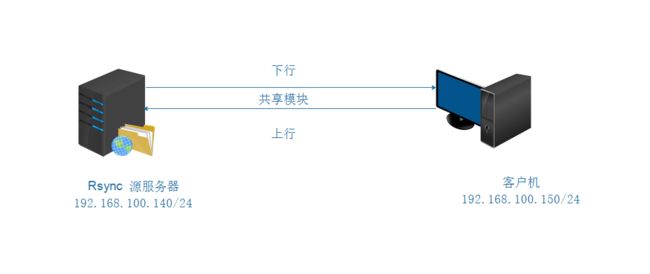
2.3: 实验拓扑图
2.3: 实验过程
2.3.1: 配置源服务器
-
1.安装rsync服务 [root@source ~]# rpm -qa | grep rsync rsync-3.1.2-4.el7.x86_64 2.修改配置文件 [root@source ~]# vim /etc/rsyncd.conf uid = nobody gid = nobody use chroot = yes '//禁锢在源目录' address=192.168.100.140 '//监听地址,源地址' port 873 '//监听端口号' log file= /var/log/rsyncd.log '//日志文件位置' pid file= /var/run/rsyncd.pid '//存放进程ID的文件位置' hosts allow 192.168.100.0/24 '//允许访问的客户机地址' ...... [wwwroot] '//共享模块名称' path = /var/www/html '//源目录的实际路径' comment = www.kgc.com read only = no '//是否只读' dont compress = *.gz *.tgz *.zip *.z *.Z *.rpm *.deb *.bz2 '//同步时不在压缩的文件类型' auth users = backuper '//授权账户' secrets file = /etc/rsyncd_users.db '//存放账户信息的数据文件' 3.创建用户密码文件 [root@source ~]# vim /etc/rsyncd_users.db '//创建存放账户信息的数据文件' backuper:123456 '//采用“用户名:密码”的记录格式,每行一个用户记录独立的账号数据,不依赖于系统账号' [root@source ~]# chmod 600 /etc/rsyncd_users.db '//给数据文件设置权限' 4.创建共享目录,这里选择apache的站点目录 [root@source ~]# yum install -y httpd 5.启动rsync服务并查看端口 [root@source ~]# rsync --daemon [root@source ~]# netstat -ntap | grep rsync tcp 0 0 192.168.100.140:873 0.0.0.0:* L 10413/rsync [root@source ~]# kill 10413 [root@source ~]# netstat -ntap | grep rsync [root@source ~]# rsync --daemon [root@source ~]# netstat -ntap | grep rsync tcp 0 0 192.168.100.140:873 0.0.0.0:* L 10437/rsync 6.共享目录下创建文件,共享给客户机 [root@source ~]# cd /var/www/html [root@source html]# vim index.html [root@source html]# cp index.html web.html [root@source html]# iptables -F [root@source html]# setenforce 0
2.3.2: 客户机同步源服务的数据
-
1.关闭防火墙 [root@client ~]# iptables -F [root@client ~]# setenforce 0 2.同步数据 '第一种方法把140的源下的wwwroot模块共享到客户机的/opt下' [root@client ~]# rsync -avz backuper@192.168.100.140::wwwroot /opt Password: [root@client ~]# ls /opt index.html web.html [root@client opt]# rm -ef *.html "第二种方法和上面语句功能一样,只是语句结构不同" [root@client opt]# rsync -avz rsync://backuper@192.168.100.140/wwwroot /opt Password: 3.创建免密同步且客户机同步的目录多余文件删除 [root@client opt]# vim /etc/server.pass [root@client opt]# chmod 600 /etc/server.pass [root@client opt]# rsync -avz --delete --password-file=/etc/server.pass backuper@192.168.100.140::wwwroot /opt/ [root@client opt]# ls index.html web.html
三: Rsync配合inotify工具实现触发式传输同步
3.1: rsync实现同步的优劣
- rsync的缺点
执行备份的时间固定,延迟明细,实时性差;
当同步源长期不变化时,密集的定期任务是不必要的
- rysnc的优点
一旦同步源出现变化,立即启用备份;
只要同步源不变化,则不执行备份
3.2: Inotify的介绍
- Inotify是一个Linux内核机制,它可以监控文件系统的操作,比如读取、写入、创建等。
- Inotify反应灵敏,用法非常简单,并且比cron任务的繁忙轮询高效
- 从版本 2.6.13 开始提供;
- 可以监控文件系统的变化情况,并作出通知响应;
- 辅助软件:inotify-tools
3.3: 实时同步实验
3.3.1: 源服务器配置
-
1.修改rsync配置文件,添加 [root@source html]# vi /etc/rsyncd.conf read only = no '//改为no,确保客户机有可读写共享模块的权限' 2.重启服务 [root@source html]# kill `cat /var/run/rsyncd.pid` '//关闭rsync服务' [root@source html]# netstat -ntap |grep rsync [root@source html]# rsync --daemon '//开启rsync服务' [root@source html]# netstat -ntap |grep rsync tcp 0 0 192.168.233.131:873 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 88302/rsync [root@source html]# chmod 777 /var/www/html "给共享目录777的权限"
3.3.2: 客户机服务器配置
-
1.修改内核文件 [root@client opt]# cat /proc/sys/fs/inotify/max_queued_events '//监控队列大小' 16384 [root@client opt]# cat /proc/sys/fs/inotify/max_user_instances '//最多监控实例数' 128 [root@client opt]# cat /proc/sys/fs/inotify/max_user_watches '//每个实例最多监控文件数' 8192 [root@client opt]# vi /etc/sysctl.conf [root@client opt]# sysctl -p "使内核文件,生效" fs.inotify.max_queued_events = 32768 fs.inotify.max_user_instances = 1024 fs.inotify.max_user_watches = 1048576 2.上传压缩包finalshell压缩包 [root@client opt]# mount.cifs //192.168.100.140/qq-Download /mnt "远程挂载的目录里有finalshell远程工具" [root@client opt]# cd /mnt 3.客户端安装inotify-tools辅助工具 [root@client mnt]# tar zxf inotify-tools-3.14.tar.gz -C /opt [root@client mnt]# cd /opt/inotify-tools-3.14/ [root@client inotify-tools-3.14]# yum install gcc gcc-c++ -y [root@client inotify-tools-3.14]# ./configure [root@client inotify-tools-3.14]# make && make install 4.重新打开一个终端,执行监控 [root@client ~]# inotifywait -mrq -e modify,create,move,delete /var/www/html '//运行持续监控监控' inotifywait:用于持续监控,实时输出结果 "一般用wait" inotifywatch:用于短期监控,任务完成后再出结果 5.客户机编辑脚本监控共享目录变化并启动,方便管理 [root@client ~]# vim /opt/inotify.sh "新开一个客户端创建" #!/bin/bash INOTIFY_CMD="inotifywait -mrq -e create,delete,move,modify,attrib,move,delete /var/www/html/" RSYNC_CMD="rsync -azH --delete --password-file=/etc/server.pass /var/www/html/ [email protected]::wwwroot/" $INOTIFY_CMD | while read DIRECTORY EVENT FILE do if [ $(pgrep rsync | wc -l) -le 0 ] ; then $RSYNC_CMD # echo "${FILE} was rsynced" >>/opt/inotify_rsync.log fi done [root@client ~]# chmod 755 /opt/inotify.sh [root@client ~]# chmod 777 /var/www/html [root@client ~]# chmod +x /opt/inotify.sh [root@client ~]# cd /opt [root@client opt]# ./inotify.sh '//执行脚本进行监控' 6.重新打开终端,测试rsync上传同步 [root@client html]# touch 456.txt [root@client html]# ls 123.txt 456.txt [root@source html]# ls 123.txt 456.txt [root@client html]# rm -rf 123.txt [root@client html]# ls 456.txt [root@source html]# ls 456.txt '//查看刚刚运行的脚本监控' rsync error: some files/attrs were not transferred (see previous errors) (code 23) at main.c(1052) [sender=3.0.9] '//发现会有这个报错,但是文件是正常传过去的,这里的这个报错我没有解决掉,如果有朋友解决了可以私信我或者评论告诉我,多谢!'