(四)skearn-特征选择
1、删除方差低的特征
from sklearn.feature_selection import VarianceThreshold
X = [[0, 0, 1], [0, 1, 0], [1, 0, 0], [0, 1, 1], [0, 1, 0], [0, 1, 1]]按照公式 Var[X]=p(1−p) V a r [ X ] = p ( 1 − p ) 给出,下面是删除大于0.8的那列属性,
因为5/6>0.8,5是0的个数,6是总的个数。
sel = VarianceThreshold(threshold=(.8 * (1 - .8)))
sel.fit_transform(X)array([[0, 1],
[1, 0],
[0, 0],
[1, 1],
[1, 0],
[1, 1]])
分析:删除了第一列数据
2、单变量特征选择
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.feature_selection import SelectKBest
from sklearn.feature_selection import chi2
iris = load_iris()
X, y = iris.data, iris.target
X.shape(150, 4)
X_new = SelectKBest(chi2, k=2).fit_transform(X, y)
X_new.shape(150, 2)
注意:SelectKBest(chi2, k=2)的第一个参数
对于回归:f_regression,mutual_info_regression
对于分类:chi2,f_classif,mutual_info_classif
X_new[:5]array([[1.4, 0.2],
[1.4, 0.2],
[1.3, 0.2],
[1.5, 0.2],
[1.4, 0.2]])
X[:5]array([[5.1, 3.5, 1.4, 0.2],
[4.9, 3. , 1.4, 0.2],
[4.7, 3.2, 1.3, 0.2],
[4.6, 3.1, 1.5, 0.2],
[5. , 3.6, 1.4, 0.2]])
分析:保留了最后2列数据
3、递归特征消除
(1)RFECV在交叉验证循环中执行RFE以找到最佳数量的特征
示例显示如何检索Friedman#1数据集中的先验未知的5个信息功能
from sklearn.datasets import make_friedman1
from sklearn.feature_selection import RFECV
from sklearn.svm import SVR
X, y = make_friedman1(n_samples=50, n_features=10, random_state=0)X.shape,y.shape((50, 10), (50,))
X[:2],y[:2](array([[0.5488135 , 0.71518937, 0.60276338, 0.54488318, 0.4236548 ,
0.64589411, 0.43758721, 0.891773 , 0.96366276, 0.38344152],
[0.79172504, 0.52889492, 0.56804456, 0.92559664, 0.07103606,
0.0871293 , 0.0202184 , 0.83261985, 0.77815675, 0.87001215]]),
array([17.2134918 , 19.37965436]))
estimator = SVR(kernel="linear")
# step=1每次删除的特征数目为1, cv=5是交叉验证
selector = RFECV(estimator, step=1, cv=5)
selector = selector.fit(X, y)#10个中选择的特征
selector.support_ array([ True, True, True, True, True, False, False, False, False,
False])
#特征排序
selector.ranking_array([1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 6, 4, 3, 2, 5])
(2)显示数字分类任务中像素的重要性
from sklearn.svm import SVC
from sklearn.datasets import load_digits
from sklearn.feature_selection import RFE
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Load the digits dataset
digits = load_digits()
X = digits.images.reshape((len(digits.images), -1))
y = digits.target
# Create the RFE object and rank each pixel
svc = SVC(kernel="linear", C=1)
# n_features_to_select=1,选择一个特征(默认是一半)
rfe = RFE(estimator=svc, n_features_to_select=1, step=1)
rfe.fit(X, y)
#特征排序
ranking = rfe.ranking_.reshape(digits.images[0].shape)rankingarray([[64, 50, 31, 23, 10, 17, 34, 51],
[57, 37, 30, 43, 14, 32, 44, 52],
[54, 41, 19, 15, 28, 8, 39, 53],
[55, 45, 9, 18, 20, 38, 1, 59],
[63, 42, 25, 35, 29, 16, 2, 62],
[61, 40, 5, 11, 13, 6, 4, 58],
[56, 47, 26, 36, 24, 3, 22, 48],
[60, 49, 7, 27, 33, 21, 12, 46]])
# Plot pixel ranking
#把每个特征的重要性通过颜色表示
plt.matshow(ranking, cmap=plt.cm.Blues)
plt.colorbar()
plt.title("Ranking of pixels with RFE")
plt.show()(3)通过交叉验证消除递归特征:递归特征消除示例,可自动调整通过交叉验证选择的特征数量
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.svm import SVC
from sklearn.model_selection import StratifiedKFold
from sklearn.feature_selection import RFECV
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
# Build a classification task using 3 informative features
X, y = make_classification(n_samples=1000, n_features=25, n_informative=3,
n_redundant=2, n_repeated=0, n_classes=8,
n_clusters_per_class=1, random_state=0)
# Create the RFE object and compute a cross-validated score.
svc = SVC(kernel="linear")
# The "accuracy" scoring is proportional to the number of correct
# classifications
rfecv = RFECV(estimator=svc, step=1, cv=StratifiedKFold(2),
scoring='accuracy')
rfecv.fit(X, y)
#最优的参数个数
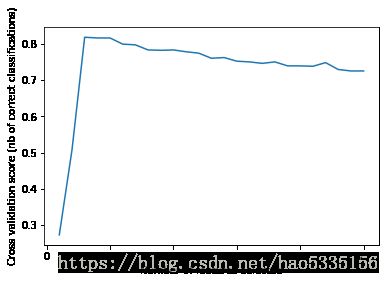
print("Optimal number of features : %d" % rfecv.n_features_)
# Plot number of features VS. cross-validation scores
plt.figure()
plt.xlabel("Number of features selected")
plt.ylabel("Cross validation score (nb of correct classifications)")
plt.plot(range(1, len(rfecv.grid_scores_) + 1), rfecv.grid_scores_)
plt.show()Optimal number of features : 3
4.使用特定模型进行特征选择
(1)基于L1的特征选择from sklearn.svm import LinearSVC
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.feature_selection import SelectFromModel
iris = load_iris()
X, y = iris.data, iris.target
X.shape(150, 4)
lsvc = LinearSVC(C=0.01, penalty="l1", dual=False).fit(X, y)
model = SelectFromModel(lsvc, prefit=True)
X_new = model.transform(X)
X_new.shape(150, 3)
(2)基于树的特征选择
from sklearn.ensemble import ExtraTreesClassifier
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.feature_selection import SelectFromModel
iris = load_iris()
X, y = iris.data, iris.target
X.shape(150, 4)
clf = ExtraTreesClassifier()
clf = clf.fit(X, y)
clf.feature_importances_ array([0.03418912, 0.05932486, 0.3624408 , 0.54404521])
model = SelectFromModel(clf, prefit=True)
X_new = model.transform(X)
X_new.shape (150, 2)