深入理解spark优化器
目前的优化方法主要有:
一、spark优化方法介绍
一阶
- Gradient Descent 梯度下降
- Stochastic Gradient Descent 随机梯度下降
二阶
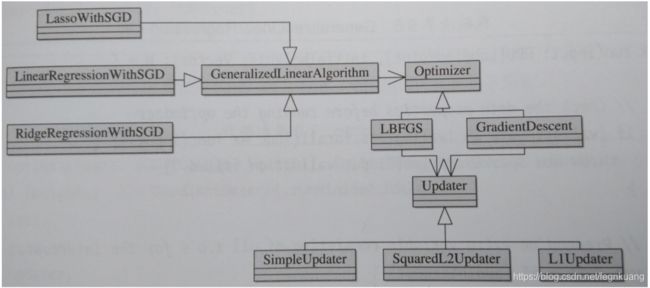
二、spark优化类图
三、源码分析
- spark mllib的optimization代码结构
optimization
Gradient -- 抽象类
LogisticGradient
LeastSquaresGradient
HingeGradient
GradientDescent
LBFGS
NNLS -- 非负最小二乘
Optimizer
Updater
- NNLS: 使用改进投影梯度法结合共轭梯度法来求解非负最小二乘
- GradientDescent.scala代码分析
梯度下降默认采用SGD方法。其中涉及到的矩阵向量运算spark调用了breeze库来执行。
package org.apache.spark.mllib.optimization
import scala.collection.mutable.ArrayBuffer
import breeze.linalg.{norm, DenseVector => BDV}
import org.apache.spark.annotation.DeveloperApi
import org.apache.spark.internal.Logging
import org.apache.spark.mllib.linalg.{Vector, Vectors}
import org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD
/**
* 利用梯度下降求解最优化问题的类
* @param gradient 梯度函数.
* @param updater 用于每次迭代后更新权重的更新器.
*/
class GradientDescent private[spark] (private var gradient: Gradient, private var updater: Updater)
extends Optimizer with Logging {
private var stepSize: Double = 1.0
private var numIterations: Int = 100
private var regParam: Double = 0.0
private var miniBatchFraction: Double = 1.0
private var convergenceTol: Double = 0.001
/**
* SGD初始化步长,默认1.0
* In subsequent steps, the step size will decrease with stepSize/sqrt(t)
*/
def setStepSize(step: Double): this.type = {
require(step > 0,
s"Initial step size must be positive but got ${step}")
this.stepSize = step
this
}
/**
* 设置SGD每次迭代的数据采样比.
* Default 1.0 (corresponding to deterministic/classical gradient descent)
*/
def setMiniBatchFraction(fraction: Double): this.type = {
require(fraction > 0 && fraction <= 1.0,
s"Fraction for mini-batch SGD must be in range (0, 1] but got ${fraction}")
this.miniBatchFraction = fraction
this
}
/**
* 设置SGD迭代次数,默认100.
*/
def setNumIterations(iters: Int): this.type = {
require(iters >= 0,
s"Number of iterations must be nonnegative but got ${iters}")
this.numIterations = iters
this
}
/**
* 设置正则参数,默认0.0.
*/
def setRegParam(regParam: Double): this.type = {
require(regParam >= 0,
s"Regularization parameter must be nonnegative but got ${regParam}")
this.regParam = regParam
this
}
/**
* 设置收敛误差. Default 0.001
* 用于判断迭代终止条件.
* 遵循以下逻辑:
*
* - If the norm of the new solution vector is greater than 1, the diff of solution vectors
* is compared to relative tolerance which means normalizing by the norm of
* the new solution vector.
* - If the norm of the new solution vector is less than or equal to 1, the diff of solution
* vectors is compared to absolute tolerance which is not normalizing.
*
* Must be between 0.0 and 1.0 inclusively.
*/
def setConvergenceTol(tolerance: Double): this.type = {
require(tolerance >= 0.0 && tolerance <= 1.0,
s"Convergence tolerance must be in range [0, 1] but got ${tolerance}")
this.convergenceTol = tolerance
this
}
/**
* Set the gradient function (of the loss function of one single data example)
* to be used for SGD.
*/
def setGradient(gradient: Gradient): this.type = {
this.gradient = gradient
this
}
/**
* Set the updater function to actually perform a gradient step in a given direction.
* 设置更新器函数,用于按照给定方向计算下降梯度,还可以在其中制定正则项
* The updater is responsible to perform the update from the regularization term as well,
* and therefore determines what kind or regularization is used, if any.
*/
def setUpdater(updater: Updater): this.type = {
this.updater = updater
this
}
/**
* :: DeveloperApi ::
* Runs gradient descent on the given training data.
* @param data training data
* @param initialWeights initial weights
* @return solution vector
*/
@DeveloperApi
def optimize(data: RDD[(Double, Vector)], initialWeights: Vector): Vector = {
val (weights, _) = GradientDescent.runMiniBatchSGD(
data,
gradient,
updater,
stepSize,
numIterations,
regParam,
miniBatchFraction,
initialWeights,
convergenceTol)
weights
}
}
/**
* :: DeveloperApi ::
* Top-level method to run gradient descent.
*/
@DeveloperApi
object GradientDescent extends Logging {
/**
* 使用小批量数据样本并行运行SGD
* 每次迭代中,对所有数据进行采样,求解近似梯度
* 每次迭代都要进行数据抽样,并计算数据抽样子集上的梯度平均值
*
* @param data 所有的输入数据. RDD格式, 每条数据格式为(label, [feature values]).
* @param gradient Gradient 对象,用于计算单样本的损失函数的梯度
* @param updater更新器函数按照给定方向计算下降梯度.
* @param stepSize 第一步的初始步长
* @param numIterations 迭代次数.
* @param regParam 正则项参数
* @param miniBatchFraction 每次迭代中数据抽样的比率,默认是1.0.
* @param convergenceTol 迭代结束条件,计算当前权重和上次权重的相对差值,计算时用到了L2范式,默认值是0.001.
* @return 返回一个二元组. 第一个元素是包含每个特征权重的列向量,第二个是包含每次迭代的随机损失的数组。
*/
def runMiniBatchSGD(
data: RDD[(Double, Vector)],
gradient: Gradient,
updater: Updater,
stepSize: Double,
numIterations: Int,
regParam: Double,
miniBatchFraction: Double,
initialWeights: Vector,
convergenceTol: Double): (Vector, Array[Double]) = {
// convergenceTol should be set with non minibatch settings
if (miniBatchFraction < 1.0 && convergenceTol > 0.0) {
logWarning("Testing against a convergenceTol when using miniBatchFraction " +
"< 1.0 can be unstable because of the stochasticity in sampling.")
}
if (numIterations * miniBatchFraction < 1.0) {
logWarning("Not all examples will be used if numIterations * miniBatchFraction < 1.0: " +
s"numIterations=$numIterations and miniBatchFraction=$miniBatchFraction")
}
val stochasticLossHistory = new ArrayBuffer[Double](numIterations)
// Record previous weight and current one to calculate solution vector difference
var previousWeights: Option[Vector] = None
var currentWeights: Option[Vector] = None
val numExamples = data.count()
// if no data, return initial weights to avoid NaNs
if (numExamples == 0) {
logWarning("GradientDescent.runMiniBatchSGD returning initial weights, no data found")
return (initialWeights, stochasticLossHistory.toArray)
}
if (numExamples * miniBatchFraction < 1) {
logWarning("The miniBatchFraction is too small")
}
// Initialize weights as a column vector
var weights = Vectors.dense(initialWeights.toArray)
val n = weights.size
/**
* 第一次迭代时,如果是L2范式,regVal 初始化为权重参数的平方之和
*/
var regVal = updater.compute(
weights, Vectors.zeros(weights.size), 0, 1, regParam)._2
var converged = false // indicates whether converged based on convergenceTol
var i = 1
while (!converged && i <= numIterations) {
val bcWeights = data.context.broadcast(weights)
// 数据抽样
// 计算,对该抽样集上的样本的子梯度进行求和,包含一次map-reduce操作。
这里求和采用了treeAggregate而不是aggregate,
主要是通过预reduce在性能上进行优化,
可以并行求和,防止直接reduce带来的OOM问题。
val (gradientSum, lossSum, miniBatchSize) = data.sample(false, miniBatchFraction, 42 + i)
.treeAggregate((BDV.zeros[Double](n), 0.0, 0L))(
seqOp = (c, v) => {
// c: (grad, loss, count), v: (label, features)
val l = gradient.compute(v._2, v._1, bcWeights.value, Vectors.fromBreeze(c._1))
(c._1, c._2 + l, c._3 + 1)
},
combOp = (c1, c2) => {
// c: (grad, loss, count)
(c1._1 += c2._1, c1._2 + c2._2, c1._3 + c2._3)
})
bcWeights.destroy()
if (miniBatchSize > 0) {
/**
* lossSum is computed using the weights from the previous iteration
* and regVal is the regularization value computed in the previous iteration as well.
*/
stochasticLossHistory += lossSum / miniBatchSize + regVal
val update = updater.compute(
weights, Vectors.fromBreeze(gradientSum / miniBatchSize.toDouble),
stepSize, i, regParam)
weights = update._1
regVal = update._2
previousWeights = currentWeights
currentWeights = Some(weights)
if (previousWeights != None && currentWeights != None) {
converged = isConverged(previousWeights.get,
currentWeights.get, convergenceTol)
}
} else {
logWarning(s"Iteration ($i/$numIterations). The size of sampled batch is zero")
}
i += 1
}
logInfo("GradientDescent.runMiniBatchSGD finished. Last 10 stochastic losses %s".format(
stochasticLossHistory.takeRight(10).mkString(", ")))
(weights, stochasticLossHistory.toArray)
}
/**
* Alias of `runMiniBatchSGD` with convergenceTol set to default value of 0.001.
*/
def runMiniBatchSGD(
data: RDD[(Double, Vector)],
gradient: Gradient,
updater: Updater,
stepSize: Double,
numIterations: Int,
regParam: Double,
miniBatchFraction: Double,
initialWeights: Vector): (Vector, Array[Double]) =
GradientDescent.runMiniBatchSGD(data, gradient, updater, stepSize, numIterations,
regParam, miniBatchFraction, initialWeights, 0.001)
private def isConverged(
previousWeights: Vector,
currentWeights: Vector,
convergenceTol: Double): Boolean = {
// To compare with convergence tolerance.
val previousBDV = previousWeights.asBreeze.toDenseVector
val currentBDV = currentWeights.asBreeze.toDenseVector
// This represents the difference of updated weights in the iteration.
val solutionVecDiff: Double = norm(previousBDV - currentBDV)
solutionVecDiff < convergenceTol * Math.max(norm(currentBDV), 1.0)
}
}