Java 中的Comparable接口
Comparable是排序接口。若一个类实现了Comparable接口,就意味着该类支持排序。实现了Comparable接口的类的对象的列表或数组可以通过Collections.sort或 Arrays.sort进行自动排序。
此外,实现此接口的对象可以用作有序映射中的键或有序集合中的集合,无需指定比较器。
此接口只有一个方法compare,比较此对象与指定对象的顺序,如果该对象小于、等于或大于指定对象,则分别返回负整数、零或正整数。用法如下:
首先第一步,在要排序的类上实现Comparable接口:
class student implements Comparable
int studentScore;
String studentName;
public student (String studentName , int studentScore){
this. studentScore = studentScore;
this. studentName = studentName;
}
/**
* 然后第二步,在要排序的类中实现Comparable接口中的compareTo方法
*/
@Override
public int compareTo(PersonComparable o) {
// 从小到大排序 :this‐o
// 从大到小排序 :o‐this
//o 表示和当前对象比较的另外一个对象
if(this. studentScore!= o. studentScore){
return o. studentScore - this. studentScore;
}else{
return this. studentName - o. studentName;
}
}
}
下面以list集合为例:下面的代码是写在另一个类的主方法中
List
list.add(new student ("同学A", 90));
list.add(new student ("同学B", 80));
list.add(new student ("同学C", 90));
list.add(new student ("同学D", 85));
list.add(new student ("同学X", 80));
list.add(new student ("同学M", 75));
list.add(new student ("同学E", 75));
//第三步 调用sort 排序
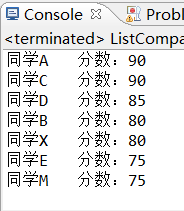
Collections.sort(list);
//for循环遍历输出
for (student student: list) {
System.out.println(student. studentName + "\t分数" +
student. studentScore);
}
结果如下: