数据库国际化(i18n)
Database Internationalization(I18N)/Localization(L10N) design patterns
文章内容来源于以下引用,因为以下链接需要才可以访问,所以特意搬过来,方便查看
https://medium.com/walkin/database-internationalization-i18n-localization-l10n-design-patterns-94ff372375c6
In this Digital Age, we always want to expand our business to different parts of the world to bring more sales thus more profits. Expanding the business to different parts of the world is not easy if your application is not localized. This is because, Different parts of the world have different languages, different metric systems, different formats of representing the data, different currencies etc. In this article, I am going to present different database design patterns for content localization.
First, let me give you a brief introduction to
Internationalization/Localization if you are not aware of them.
Internationalization(I18N) is the process of designing a software
application so that it can potentially be adapted to various languages and
regions without engineering changes
Localization(L10N) is the process of adapting internationalized software
for a specific region or language by adding locale-specific components and
translating the text.
Localization doesn’t mean content translations essentially. But supporting local
- date and time formats
- number format
- time zones
- calendars
- currency presentation
- tax/VAT
- temperature and other measures
- postal codes, telephone numbers
- address formatting
- country/state/region/province codes
Now let’s dig into the patterns.
- Separate columns for each field:-
This is the easiest approach among all others. In this approach, we will add
a new column to the table for every field which needs to support
localization.
In all the patterns that I am going to show I will try to localize the products table.
See the below image of products table.

If you observe there are columns following column_name_languageCode.
Since products need to support the name, price, description for various languages,
So it has a column of every type for every language.
Pros:-
- easy to implement. No complex querying.
Cons:-
- Not scalable.
- The number of columns in the table grows rapidly based on the number of languages your application supports.
- If you miss a single column for any language your application might throw errors.
- Hard to manage data formats(time for various regions), metric systems etc.
- Separate rows for each language:-
In this approach instead of making a new column for every language, We will manage data in the rows based on a column like language_code.

Sample data looks like
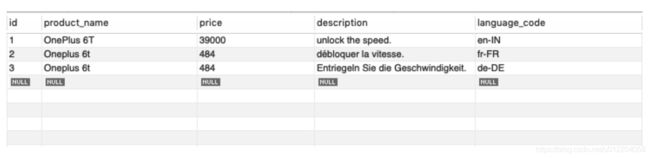
Pros:-
- simple and efficient.
- Querying becomes simple based for a specific language_code. ?
Cons:-
- Not centralized. Various tables can support various languages. So You don’t know how many languages your application supports clearly.
- In your analytics system, calculation metrics for the same product becomes tough since we are managing multiple entries of the same one(But region based metrics become simpler ?).
Note:- To centralize make a languages table and use the foreign key relationships by adding all languages etc. From now, all approaches I will follow it.
- Separate translation table:-
Under this approach, we will maintain a single translation table for all the tables in the Database which requires Internationalization. Here I am showing an example of a product and product_type.
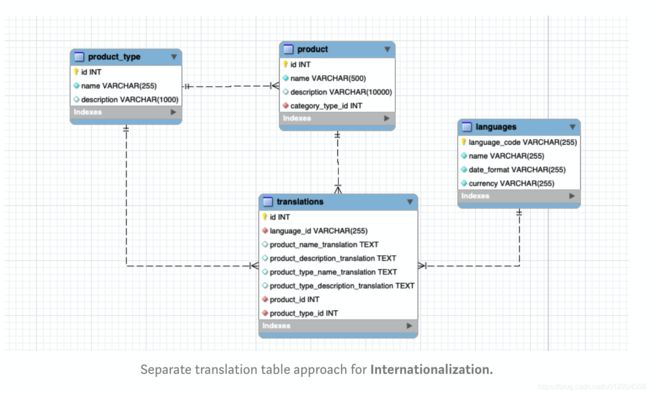
Pros:-
- More centralized localization.
- Now we can manage all properties such as date format(yyyy/mm/dd, dd/mm/yyyy etc.), currency(Dollar, INR, Euro etc.) etc based on the language we are supporting.
Cons:-
- Requires joining the tables to get the translations.
- All language related translations under the same table for all tables in the DB.
- Needs proper indexing to get efficiency.
Note:-
1.You can choose the above approach with the combination of Separate columns for each field approach.
Doing so all translation will be under a single row but as we support a new language, requires altering table for adding a new translation column.
- Separate translation table approach:-
In this approach Instead of putting all translation under the same table, we will write a separate translation table for each table which requires localization.
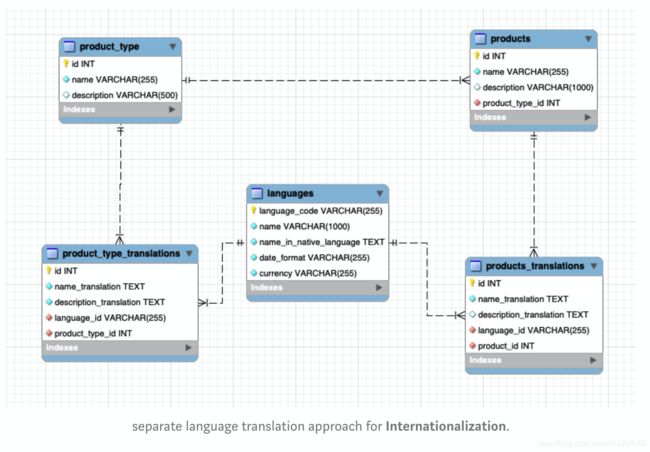
Pros:-
- No need for joining table for non translated data.
- Since separate tables are there for translations querying becomes easy.
- No discrepancies in data.
- Besides content translations, Effective localization is possible by storing other localization data under languages table.
These are some of the patterns I could think off. If you know any other approach please let me know in the comments section. Will be happy read them.
Hope this article is useful to you. Thanks for reading ?.