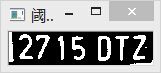
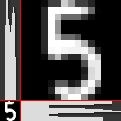车牌号识别
这篇文章接着之前的车牌识别,从输入的车图片中分割识别出车牌之后,将进行下一步:车牌号的识别,这里主要使用光学字符识别车牌字符。对每个检测到的车牌,将其每个字符分割出来,然后使用人工神经网络(artificial neural network,ANN)学习算法识别字符。
1.字符分割
将获得的车牌图像进行直方图均衡,然后采用阈值滤波器对图像进行处理,然后查找字符轮廓。
然后将字符逐一分割,
分割code:
#include float>(j) = vhist.at<float>(i);
j++;
}
for (int i = 0; i < hhist.cols; i++)
{
out.at<float>(j) = hhist.at<float>(i);
j++;
}
for (int x = 0; x for (int y = 0; y < lowdata.rows; y++)
{
out.at<float>(j) = (float)lowdata.at<unsigned char>(x, y);
j++;
}
}
return out;
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
Mat input = imread("E://opencvcodetext//ANPR//img_2.jpg");
cvtColor(input,input,CV_RGB2GRAY);
imshow("srcimg",input);
Mat img_threshold; //存放二值化后的车牌
threshold(input, img_threshold, 60, 255, CV_THRESH_BINARY_INV); //CV_THRESH_BINARY_INV参数可将白色点变为黑色,黑色点变为白色
imshow("阈值化车牌",img_threshold);
Mat img_contours ; //存放车牌号轮廓
img_threshold.copyTo(img_contours); //复制图像
//查找字符的轮廓
vector < vector 2.人工神经网络(ANN)
分类字符这一步将使用人工神经网络,即使用多层感知器(Multi-Layer Perceptron, MLP). MLP 由一个输入层、一个输出层和一个或多个隐藏层的 神经网络组成。每层有一个或多个神经元痛前一层和后一层相连。
如下图是一个3层的神经元感知器,有3个输入和2个输出,以及包含5个神经元的隐藏层。
每个神经元通过输入权重加上一个偏移项来计算输出值,并由所选择的激励函数进行转换。神经元结构为:
常见的激励函数有S型、高斯型、上图的hadrlim型。单层的单个神经元可以将输入向量分为两类,而一个有S个神经元的感知机,可以将输入向量分为2^S类
神经网络的详细理论可以参考:http://blog.csdn.net/zzwu/article/details/575050
3.特征提取及训练分类器
与SVM分类类似,使用ANN算法识别字符同样需要建立分类器、训练分类器,最后使用分类器识别字符。这里我们使用的特征不是像素值,而是分割字符水平和竖直的累积直方图与字符的低分辨率图像。
对每一个字符,通过使用countNonZero函数来按行或按列统计非零像素值个数,将其保存在mhist中,并对mhist进行归一化处理。
得到的特征图像如下图所示:(左下角为字符图像原始大小20*20,由上角为低分辨率采样后放大的图像100*100,右下角为水平直方图,左上角为垂直直方图)
提取特征完毕后,将特征与对应的标注写到xml文件中,code如下:
#include out.at<float>(j) = vhist.at<float>(i);
j++;
}
for (int i = 0; i < hhist.cols; i++)
{
out.at<float>(j) = hhist.at<float>(i);
j++;
}
for (int x = 0; x for (int y = 0; y < lowdata.rows; y++)
{
out.at<float>(j) = (float)lowdata.atchar>(x, y);
j++;
}
}
return out;
}
Mat Features(Mat in, int sizeData)
{
Mat vhist = ProjectedHistogram(in, VERTICAL);
Mat hhist = ProjectedHistogram(in, HORIZONTAL);
Mat lowData;
resize( in, lowData, Size (sizeData, sizeData));
int numCols = vhist.cols + hhist.cols + lowData.cols *lowData.cols;
Mat out = Mat ::zeros(1, numCols, CV_32F);
//将特征写到矩阵中
int j = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < vhist.cols; i++)
{
out.at <float> (j) = vhist.at<float>(i);
j++;
}
for (int i =0; i < hhist.cols; i++)
{
out.at<float>(j) = (float) hhist.at <float> (i);
j++;
}
for (int x = 0; x < lowData.cols; x++)
{
for (int y = 0; y < lowData.rows; y++)
{
out.at<float>(j) = (float) lowData.atchar>(x,y);
j++;
}
}
return out;
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
//char *path = "E://opencvcodetext//ANPR//characters";
Mat classes;
Mat trainingDataf5;
Mat trainingDataf10;
Mat trainingDataf15;
Mat trainingDataf20;
vector <int> trainingLabels;
for (int i = 0; i < numCharacters; i++)
{
int numFiles = numFilesChar[i];
for (int j = 0; j < numFiles; j++)
{
cout << "Character " << strCharacters[i] << " files" << j <<"\n";
stringstream ss (stringstream::in |stringstream::out);
ss << "E://opencvcodetext//ANPR//characters//" << strCharacters[i] <<"1.jpg";
Mat img = imread(ss.str(), 0);
//Mat img = imread("E://opencvcodetext//ANPR//characters//21.jpg",0);
imshow("char",img);
Mat f5 = Features(img, 5);
Mat f10 = Features(img, 10);
Mat f15 = Features(img, 15);
Mat f20 = Features(img, 20);
trainingDataf5.push_back(f5);
trainingDataf10.push_back(f10);
trainingDataf15.push_back(f15);
trainingDataf20.push_back(f20);
trainingLabels.push_back(i); //每一幅字符图片所对应的字符类别索引下标
}
}
//将矩阵转换成浮点矩阵
trainingDataf5.convertTo(trainingDataf5, CV_32FC1);
trainingDataf10.convertTo(trainingDataf10, CV_32FC1);
trainingDataf15.convertTo(trainingDataf15,CV_32FC1);
trainingDataf20.convertTo(trainingDataf20,CV_32FC1);
Mat (trainingLabels).convertTo(classes, CV_32FC1);
FileStorage fs("E://opencvcodetext//ANPR//characters//OCR.xml",FileStorage::WRITE);
fs << "trainingDataF5" << trainingDataf5;
fs << "trainingDataF10" << trainingDataf10;
fs <<"trainingDataF15" << trainingDataf15;
fs << "trainingDataF20" << trainingDataf20;
fs <<"classes" <20);
system("pause");
return 0;
} - 字符分类
(1) 得到ANN训练文件xml后,利用opencv中的CvANN_MLP类来使用ANN算法,识别字符。先通过create函数初始化该类,初始化时需要指定神经网络的层数、神经元数、激励函数、alpha和beta。
(2)训练完ANN分类器后,可以使用predict函数来对特征向量分类,该函数返回一行,大小为类的数量,该向量的每一个元素安阳了输入样本属于每个类的概率。字符的类别有向量中的最大值确定。
分类的code:
#include float>(j) = vhist.at<float>(i);
j++;
}
for (int i = 0; i < hhist.cols; i++)
{
out.at<float>(j) = hhist.at<float>(i);
j++;
}
for (int x = 0; x for (int y = 0; y < lowdata.rows; y++)
{
out.at<float>(j) = (float)lowdata.at<unsigned char>(x, y);
j++;
}
}
return out;
}
Mat Features(Mat in, int sizeData)
{
Mat vhist = ProjectedHistogram(in, VERTICAL);
Mat hhist = ProjectedHistogram(in, HORIZONTAL);
Mat lowData;
resize( in, lowData, Size (sizeData, sizeData));
int numCols = vhist.cols + hhist.cols + lowData.cols *lowData.cols;
Mat out = Mat ::zeros(1, numCols, CV_32F);
//将特征写到矩阵中
int j = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < vhist.cols; i++)
{
out.at <float> (j) = vhist.at<float>(i);
j++;
}
for (int i =0; i < hhist.cols; i++)
{
out.at<float>(j) = (float) hhist.at <float> (i);
j++;
}
for (int x = 0; x < lowData.cols; x++)
{
for (int y = 0; y < lowData.rows; y++)
{
out.at<float>(j) = (float) lowData.at<unsigned char>(x,y);
j++;
}
}
return out;
}
void train(Mat TrainData, Mat classes, int nlayers)
{
Mat layerSizes(1, 3, CV_32SC1);
layerSizes.at< int > (0) = TrainData.cols;
layerSizes.at <int> (1) = nlayers;
layerSizes.at < int > (2) = numCharacters;
ann.create(layerSizes, CvANN_MLP :: SIGMOID_SYM, 1, 1);
Mat trainClasses;
trainClasses.create(TrainData.rows, numCharacters, CV_32FC1);
for (int i =0; i < trainClasses.rows; i++)
{
for (int k = 0; k < trainClasses.cols; k++)
{
if( k == classes.at< int> (i))
trainClasses.at <float>(i,k)=1;
else
trainClasses.at<float>(i, k) = 0;
}
}
Mat weights( 1, TrainData.rows, CV_32FC1, Scalar::all(1));
ann.train( TrainData, trainClasses, weights);
//trained = true;
}
int Classify (Mat f)
{
int result = -1;
Mat output( 1, numCharacters, CV_32FC1);
ann.predict(f, output);
Point maxLoc;
double maxVal;
minMaxLoc(output, 0, &maxVal, 0, &maxLoc);
return maxLoc.x;
}
int main(int argc, char const *argv[])
{
//char *path = "E://opencvcodetext//ANPR//characters";
Mat classes;
Mat trainingData;
FileStorage fs;
fs.open("E:/opencvcodetext/ANPR/OCR.xml",FileStorage::READ);
fs [ "TrainingDataF10"] >> trainingData;
fs ["classes" ]>> classes;
train(trainingData, classes, 10); //训练神经网络
Mat input = imread("E:/opencvcodetext/ANPR/img_2.jpg",CV_LOAD_IMAGE_GRAYSCALE);
Mat img_threshold ;
threshold( input, img_threshold, 60, 255, CV_THRESH_BINARY_INV);
Mat img_contours;
img_threshold.copyTo(img_contours);
vector < vector 实验结果:这里的顺序改变了,应该要还原字符的位置。。而且识别也不是百分百的准确,出现了错误:将 7 识别为 T 了。
原图:![]()
最后,写一下调试程序的错误总结:
1. 二值黑白图像不等同于灰度图像
2. 图像的像素值是unsight char的
3. 在测试时,注意提取特征的一一对应,注意TrainingDataF10以及后面的 Features(auxRoi, 10) 的关系。
4. 另外,检测出的字符与原车牌的顺序有乱,应该进行调整(待续)