【Hadoop】Avro源码分析(一):Schema
- 抽象类Schema
- Type
- 类图
- 原生类型Schema的创建
- 保留字段
- RecordSchema类
- Name与Names
- Field类
- RecordShema的定义
- toString的实现
- 测试代码
有关Avro的schema介绍已经在前一篇中给出了。本篇主要分析org.apache.avro.schema.java源码,以此深入了解schema。
1. 抽象类Schema
schema是abstract class,并且继承自JsonProperties。
Type
Schema.Type给出schema的类型:
/** The type of a schema. */
public enum Type {
RECORD, ENUM, ARRAY, MAP, UNION, FIXED, STRING, BYTES,
INT, LONG, FLOAT, DOUBLE, BOOLEAN, NULL;
private String name;
private Type() { this.name = this.name().toLowerCase(); }
public String getName(turn name;e}
};类图
primitive type所对应schema类均继承 Schema,如图:

complex type所对应的schema类中RecordSchema、EnumSchema、FixedSchema都继承 NamedSchema(因为record、enum、fixed类型中均有name 字段);其余的schema类继承 Schema。
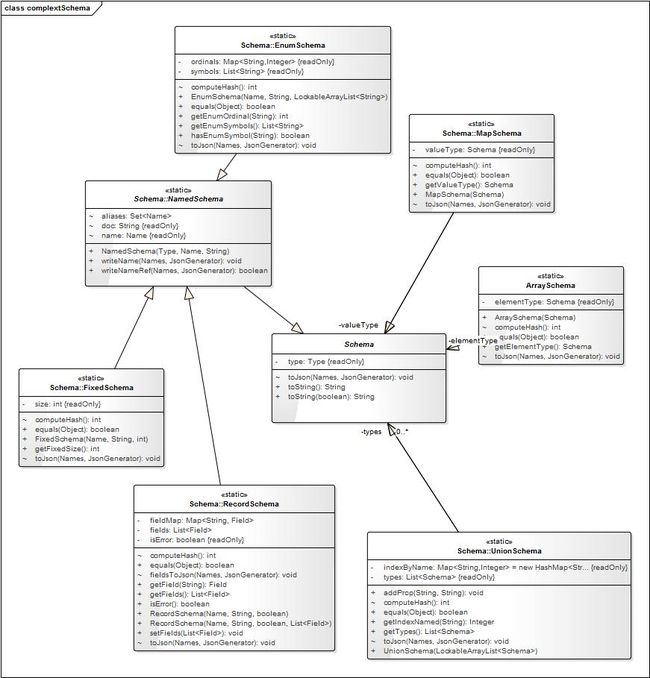
原生类型Schema的创建
原生类型所对应的Schema可以直接通过create()进行创建:
/** Create a schema for a primitive type. */
public static Schema create(Type type) {
switch (type) {
case STRING: return new StringSchema();
case BYTES: return new BytesSchema();
case INT: return new IntSchema();
case LONG: return new LongSchema();
case FLOAT: return new FloatSchema();
case DOUBLE: return new DoubleSchema();
case BOOLEAN: return new BooleanSchema();
case NULL: return new NullSchema();
default: throw new AvroRuntimeException("Can't create a: "+type);
}
}保留字段
在schema中可能会出现的字段:
private static final Set SCHEMA_RESERVED = new HashSet();
static {
Collections.addAll(SCHEMA_RESERVED,
"doc", "fields", "items", "name", "namespace",
"size", "symbols", "values", "type", "aliases");
} 更多有关schema.java的method请参看API文档。
2. RecordSchema类
因为record类型比较常见,本文重点研究RecordSchema;先从类Name开始。
Name与Names
Name存放name与namespace字段,定义如下:
static class Name {
private final String name; // name
private final String space; // namespace
private final String full; //space + ”.” + name
}class Names中存放Name到Schema的映射
static class Names extends LinkedHashMap<Name, Schema> {
private String space; // default namespace
}Field类
类Field对应于record中的field字段,其定义如下:
/** A field within a record. */
public static class Field extends JsonProperties {
/** How values of this field should be ordered when sorting records. */
public enum Order {
ASCENDING, DESCENDING, IGNORE;
private String name;
private Order() { this.name = this.name().toLowerCase(); }
};
private final String name; // name of the field.
private int position = -1;
private final Schema schema;
private final String doc;
private final JsonNode defaultValue;
private final Order order;
private Set aliases;
} class Field中包含
- name 这个filed的名称
- position 表示这个field在record的所有field中的位置
- schema 对应这个filed的类型Schema
- doc 对这个field的详细的说明
- JsonNode defaultValue为JsonTree中node
- Order order用来做排序
field有两个构造器
public Field(String name, Schema schema, String doc, Object defaultValue)
public Field(String name, Schema schema, String doc, Object defaultValue, Order order)field的toString()方法
@Override
public String toString() {
return name + " type:" + schema.type + " pos:" + position;
}RecordShema的定义
RecordShema中field字段是用List存放,Map存放field的name与field之间的映射。
private static class RecordSchema extends NamedSchema {
private List fields;
private Map fieldMap; //name -> field
private final boolean isError;
} toString()的实现
toString()方法包含对整个RecordSchema的解析。首先,我们来看外层基类Schema中定义
public String toString() { return toString(false); }
/**pretty if true, pretty-print JSON.
*/
public String toString(boolean pretty) {
try {
StringWriter writer = new StringWriter();
JsonGenerator gen = FACTORY.createJsonGenerator(writer);
if (pretty) gen.useDefaultPrettyPrinter();
toJson(new Names(), gen);
gen.flush();
return writer.toString();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new AvroRuntimeException(e);
}
}有两个toString()方法,实现了有换行的pretty-print打印,与没有换行的纯String打印;并且调用了toJson()的方法。
RecordShema中的toJson()的定义
void toJson(Names names, JsonGenerator gen) throws IOException {
if (writeNameRef(names, gen)) return;
String savedSpace = names.space; // save namespace
gen.writeStartObject();
gen.writeStringField("type", isError?"error":"record");
writeName(names, gen);
names.space = name.space; // set default namespace
if (getDoc() != null)
gen.writeStringField("doc", getDoc());
if (fields != null) {
gen.writeFieldName("fields");
fieldsToJson(names, gen);
}
writeProps(gen);
aliasesToJson(gen);
gen.writeEndObject();
names.space = savedSpace; // restore namespace
}将整个schema以JSON来做解析,存在JsonGenerator中。
3. 测试代码
List fields = new ArrayList();
fields.add(new Field("field_name1", Schema.create(Type.STRING), null, null));
fields.add(new Field("field_name2", Schema.create(Type.INT), null, null));
// create RecordSchema
Schema schema = Schema.createRecord("foobar", "just a test", "avro.test", false, fields);
// get full-name and doc
System.out.println(schema.getFullName());
System.out.println(schema.getDoc());
// get field
System.out.println(schema.getField("field_name1").toString());
// field name
System.out.println(schema.getField("field_name2").name());
// field position
System.out.println(schema.getField("field_name2").pos());
// field schema
System.out.println(schema.getField("field_name2").schema().toString());
// field order
System.out.println(schema.getField("field_name2").order().toString());
System.out.println(schema.toString());
//print the fields
StringWriter writer = new StringWriter();
JsonGenerator gen = Schema.FACTORY.createJsonGenerator(writer);
schema.fieldsToJson(new Names(), gen);
gen.flush();
System.out.println(writer.toString());