【C#本质论 五】方法和参数
前面四篇博客主要介绍了一些基本的操作内容,包含之前不了解的冷知识,以及一些新学到的C#较新版本的新知识,做个简单的小结:
- 新知识:元组、tryParse(out可内联)、字符串插值、空合并操作符、空条件操作符、可空修饰符、switch的模式匹配
- 冷知识:同类型单行声明赋值、字符串的不可变、字符串驻留技术、运算符优先级、预编译指令
对于个人来说还是小有帮助的,至少再看到一些奇怪的类似??的符号不会说不认识了。从本篇博客开始,了解下方法的调用和参数,依旧惯例,因为知道方法怎么调,所以还是使用新、老知识的方式。
新学概念
包括一些方法的多种参数形式,传递形式。
引用的方式传递值类型
三大引用类别的参数及返回引用:ref,out,in,返回引用:
1 ,使用ref方式,可以将一个值类型以传引用的方式传递,在IL代码里可以看到,传递的是一个地址(指向值)而非值的拷贝,所以通过这种方式可以改变值,使值类型可以像引用类型一样使用,需要注意的是引用类型传值之前必须赋值!,ref只是为现有变量分配别名,而非创建新变量并将实参的值拷贝给它。
public static void Main()
{
// ...
int first = 5;
int second = 6;
Swap(ref first, ref second);
System.Console.WriteLine(
$@"first = ""{ first }"", second = ""{ second }""");
// ...
}
private static void Swap(ref int x, ref int y)
{
int temp = x;
x = y;
y = temp;
}
} //交换first和second的值:first为6,second为5, 如果是值类型,其不会变
2, 使用out方式,C#7.0开始out类型不用事先声明,用法和ref类似,需要注意的是,out参数在方法里必须被赋值
public static int Main(string[] args)
{
if(args.Length == 0)
{
Console.WriteLine(
"ConvertToPhoneNumber.exe " );
Console.WriteLine(
"'_' indicates no standard phone button");
return 1;
}
foreach(string word in args)
{
foreach(char character in word)
{
#if !PRECSHARP7 //预编译指令,用来区分环境,只有7.0以上版本才允许使用内联而不用提前声明
if(TryGetPhoneButton(character, out char button))
#else
char button;
if(TryGetPhoneButton(character, out button))
#endif // PRECSHARP7
{
Console.Write(button);
}
else
{
Console.Write('_');
}
}
}
Console.WriteLine();
return 0;
}
3, 使用in方式,不仅可以让值类型以引用的方式传递,而且被调用的方法不能修改值类型。
private void Method(in int number) {
}
4,返回引用:7.0版本新增,可以返回对变量的引用,照常理说数组被方法改变后,里面的值就不会变化了,但是返回引用可以运行变量在没有接触到数组的前提下,直接修改数组里的元素,因为它持有这个元素的引用啊
public class Program
{
// Returning a reference
static public ref byte FindFirstRedEyePixel(byte[] image)
{
// Do fancy image detection perhaps with machine learning
for (int counter = 0; counter < image.Length; counter++)
{
if (image[counter] == (byte)ConsoleColor.Red)
{
return ref image[counter];
}
}
throw new InvalidOperationException("No pixels are red.");
}
public static void Main()
{
byte[] image = null;
// Load image
image = new byte[42];
for (int i = 0; i < image.Length; i++)
{
image[i] = (byte)ConsoleColor.Black;
}
image[(new Random()).Next(0, image.Length - 1)] = (byte)ConsoleColor.Red;
// Obtain a reference to the first red pixel
ref byte redPixel = ref FindFirstRedEyePixel(image);
// Update it to be Black
redPixel = (byte)ConsoleColor.Black;
System.Console.WriteLine((ConsoleColor)image[redPixel]); //byte数组里第一个元素颜色被更新为黑色
}
}
使用禁忌:只能返回对字段或数组元素的引用、其它返回引用的属性或方法、作为参数传递给返回引用的方法的引用(image).
参数数组、可空参数及具名参数
三种动态使用方法参数的方式:参数数组、可选参数及具名参数。
1,参数数组支持将数组作为参数传递,有个好处就是,可以充分使用这些参数:
public class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
string fullName;
// ...
// Call Combine() with four parameters
fullName = Combine(
Directory.GetCurrentDirectory(),
"bin", "config", "index.html");
Console.WriteLine(fullName);
// ...
// Call Combine() with only three parameters
fullName = Combine(
Directory.GetParent(Directory.GetCurrentDirectory()).FullName,
"Temp", "index.html");
Console.WriteLine(fullName);
// ...
// Call Combine() with an array
fullName = Combine(
new string[] {
$"C:{Path.DirectorySeparatorChar}", "Data",
"HomeDir", "index.html" });
Console.WriteLine(fullName);
// ...
}
static string Combine(params string[] paths)
{
string result = string.Empty;
foreach(string path in paths)
{
result = System.IO.Path.Combine(result, path); //将一系列参数拼接为一个完整路径
}
return result;
}
}
我感觉比较适合将某一类参数作为数组,聚类效应吧。注意,如果要使用参数数组,要放到参数列表最后一个。
2,可选参数,通常用法是给参数赋默认值,使用可选参数的时候如果不传值就用默认值。注意,如果要使用可空参数,要放到参数列表最后一个,默认值必须是常量或者能在编译时确定的值。
static int DirectoryCountLines(
string directory, string extension = "*.cs")
{
int lineCount = 0;
foreach(string file in
Directory.GetFiles(directory, extension))
{
lineCount += CountLines(file);
}
foreach(string subdirectory in
Directory.GetDirectories(directory))
{
lineCount += DirectoryCountLines(subdirectory);
}
return lineCount;
}
3,具名参数,调用者可利用具名参数显示指定值,但是有限制,如果参数名改变了,代码会报错
public class Program
{
public static void Main()
{
DisplayGreeting(
firstName: "Inigo", lastName: "Montoya");
}
public static void DisplayGreeting(
string firstName,
string middleName = default(string),
string lastName = default(string))
{
// ...
}
}
值得注意的是,可选参数、具名参数、方法重载这些方式可能会导致方法之间无法区分,这时候会优先选择最具体的方法,有个先后顺序:例如对于方法重载,int比long具体,long比double具体等等。还有就是如果两个方法都有相同参数,但一个使用可选参数,则优先使用另一个,因为编译器只使用调用者显式标识的参数。
C#冷知识
1,虽然完全限定的方法名称包括:命名空间.类型名称.方法名称,但是假定要调用的方法与发出调用的方法在同一个命名空间,就没必要指定命名空间,同理要调用的方法与发出调用的方法在同一个类型里 ,不仅没必要指定命名空间,而且没必要指定类型名称。
2,不能在方法中声明与参数同名的局部变量。
3,嵌套命名空间必须显示导入!,例如想使用StringBuilder,虽然添加了using System,但是还是需要有using System.Text,这解释了之前的疑惑。
using System; //不必须
using System.Text;
namespace ClassLibrary1
{
public class Class1
{
private StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
}
}
4,using指令允许省略命名空间,而using static 允许省略命名空间和类型名称,只需写静态成员名称。可以理解,因为静态方法不允许重复。
5,利用using指令为命名空间或类取一个别名,可以避免冲突(System.Timers和System.Threading下均有Timer类),例如这里的Timer类型就用CountDownTimerd代替。
namespace AddisonWesley.Michaelis.EssentialCSharp.Chapter05.Listing05_10
{
using System;
using System.Threading; //该命名空间下也包含Timer类
using CountDownTimer = System.Timers.Timer; //别名
public class HelloWorld
{
public static void Main()
{
CountDownTimer timer;
// ...
}
}
}
6,虽然C#允许提前返回,但为了增强代码可读性,应尽量确定单一的退出位置,而不是在方法的各个路径上散布return。
7,方法唯一性取决于方法名、参数类型和参数数量差异。
8,异常的捕获顺序应该由具体到不具体:
public static void Main()
{
try
{
Console.WriteLine("Begin executing");
Console.WriteLine("Throw exception");
throw new Exception("Arbitrary exception");
Console.WriteLine("End executing");
}
catch(FormatException exception)
{
Console.WriteLine(
"A FormatException was thrown");
}
catch(Exception exception)
{
Console.WriteLine(
$"Unexpected error: { exception.Message }");
throw;
}
catch
{
Console.WriteLine("Unexpected error!");
}
Console.WriteLine(
"Shutting down...");
}
需要注意的是,C#程序集中无论从System.Exception派生的类型都会表现的和从从System.Exception派生一样
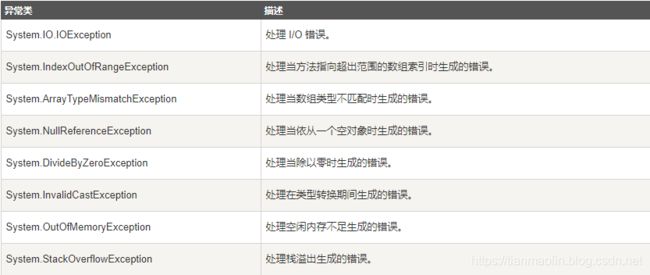
9,要在捕获并重新抛出异常时使用空的throw语句,以便保留调用栈信息。
C#新知识
1,虽然方法只能有一个返回值,但是可以利用元组,返回多个:
static (string First, string Last) GetName()
{
string firstName, lastName;
firstName = GetUserInput("Enter your first name: ");
lastName = GetUserInput("Enter your last name: ");
return (firstName, lastName);
}
2,表达式主题方法,如果方法只是返回简单语句这种方式,可以使用该方法:
private static string GetFullName(string firstName, string lastName) => $"{firstName}{lastName}";
3,最好将核心功能放到单一方法中供其他重载方法调用。