《数据流通关键技术》之一:同态加密.md
同态加密
同态加法:输入密文1 + 输入密文2 = 加密结果 (这个结果解密后 = 明文1 + 明文2)
百度百科定义: 加法同态,如果存在有效算法⊕,E(x+y)=E(x)⊕E(y)或者 x+y=D(E(x)⊕E(y))成立,并且不泄漏 x 和 y
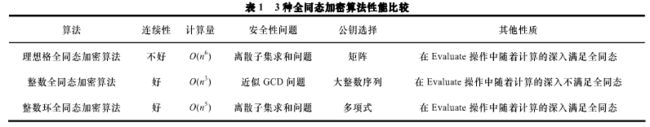
同态算法实现有几种
参考资料
paillier同态加密算法的java实现
import java.math.*;
import java.util.*;
/**
* Paillier Cryptosystem
*
* References:
* [1] Pascal Paillier,
* "Public-Key Cryptosystems Based on Composite Degree Residuosity Classes,"
* EUROCRYPT'99. URL:
* http:
* //www.gemplus.com/smart/rd/publications/pdf/Pai99pai.pdf
*
* [2] Paillier cryptosystem from Wikipedia. URL:
* http://en.
* wikipedia.org/wiki/Paillier_cryptosystem
*
* @author Kun Liu ([email protected])
* @version 1.0
*/
public class Paillier {
/**
* p and q are two large primes. lambda = lcm(p-1, q-1) =
* (p-1)*(q-1)/gcd(p-1, q-1).
*/
private BigInteger p, q, lambda;
/**
* n = p*q, where p and q are two large primes.
*/
public BigInteger n;
/**
* nsquare = n*n
*/
public BigInteger nsquare;
/**
* a random integer in Z*_{n^2} where gcd (L(g^lambda mod n^2), n) = 1.
*/
private BigInteger g;
/**
* number of bits of modulus
*/
private int bitLength;
/**
* Constructs an instance of the Paillier cryptosystem.
*
* @param bitLengthVal
* number of bits of modulus
* @param certainty
* The probability that the new BigInteger represents a prime
* number will exceed (1 - 2^(-certainty)). The execution time of
* this constructor is proportional to the value of this
* parameter.
*/
public Paillier(int bitLengthVal, int certainty) {
KeyGeneration(bitLengthVal, certainty);
}
/**
* Constructs an instance of the Paillier cryptosystem with 512 bits of
* modulus and at least 1-2^(-64) certainty of primes generation.
*/
public Paillier() {
KeyGeneration(512, 64);
}
/**
* Sets up the public key and private key.
*
* @param bitLengthVal
* number of bits of modulus.
* @param certainty
* The probability that the new BigInteger represents a prime
* number will exceed (1 - 2^(-certainty)). The execution time of
* this constructor is proportional to the value of this
* parameter.
*/
public void KeyGeneration(int bitLengthVal, int certainty) {
bitLength = bitLengthVal;
/*
* Constructs two randomly generated positive BigIntegers that are
* probably prime, with the specified bitLength and certainty.
*/
p = new BigInteger(bitLength / 2, certainty, new Random());
q = new BigInteger(bitLength / 2, certainty, new Random());
n = p.multiply(q);
nsquare = n.multiply(n);
g = new BigInteger("2");
lambda = p.subtract(BigInteger.ONE).multiply(q.subtract(BigInteger.ONE))
.divide(p.subtract(BigInteger.ONE).gcd(q.subtract(BigInteger.ONE)));
/* check whether g is good. */
if (g.modPow(lambda, nsquare).subtract(BigInteger.ONE).divide(n).gcd(n).intValue() != 1) {
System.out.println("g is not good. Choose g again.");
System.exit(1);
}
}
/**
* Encrypts plaintext m. ciphertext c = g^m * r^n mod n^2. This function
* explicitly requires random input r to help with encryption.
*
* @param m
* plaintext as a BigInteger
* @param r
* random plaintext to help with encryption
* @return ciphertext as a BigInteger
*/
public BigInteger Encryption(BigInteger m, BigInteger r) {
return g.modPow(m, nsquare).multiply(r.modPow(n, nsquare)).mod(nsquare);
}
/**
* Encrypts plaintext m. ciphertext c = g^m * r^n mod n^2. This function
* automatically generates random input r (to help with encryption).
*
* @param m
* plaintext as a BigInteger
* @return ciphertext as a BigInteger
*/
public BigInteger Encryption(BigInteger m) {
BigInteger r = new BigInteger(bitLength, new Random());
return g.modPow(m, nsquare).multiply(r.modPow(n, nsquare)).mod(nsquare);
}
/**
* Decrypts ciphertext c. plaintext m = L(c^lambda mod n^2) * u mod n, where
* u = (L(g^lambda mod n^2))^(-1) mod n.
*
* @param c
* ciphertext as a BigInteger
* @return plaintext as a BigInteger
*/
public BigInteger Decryption(BigInteger c) {
BigInteger u = g.modPow(lambda, nsquare).subtract(BigInteger.ONE).divide(n).modInverse(n);
return c.modPow(lambda, nsquare).subtract(BigInteger.ONE).divide(n).multiply(u).mod(n);
}
/**
* sum of (cipher) em1 and em2
*
* @param em1
* @param em2
* @return
*/
public BigInteger cipher_add(BigInteger em1, BigInteger em2) {
return em1.multiply(em2).mod(nsquare);
}
/**
* main function
*
* @param str
* intput string
*/
public static void main(String[] str) {
/* instantiating an object of Paillier cryptosystem */
Paillier paillier = new Paillier();
/* instantiating two plaintext msgs */
BigInteger m1 = new BigInteger("20");
BigInteger m2 = new BigInteger("60");
/* encryption */
BigInteger em1 = paillier.Encryption(m1);
BigInteger em2 = paillier.Encryption(m2);
/* printout encrypted text */
System.out.println(em1);
System.out.println(em2);
/* printout decrypted text */
System.out.println(paillier.Decryption(em1).toString());
System.out.println(paillier.Decryption(em2).toString());
/*
* test homomorphic properties -> D(E(m1)*E(m2) mod n^2) = (m1 + m2) mod
* n
*/
// m1+m2,求明文数值的和
BigInteger sum_m1m2 = m1.add(m2).mod(paillier.n);
System.out.println("original sum: " + sum_m1m2.toString());
// em1+em2,求密文数值的乘
BigInteger product_em1em2 = em1.multiply(em2).mod(paillier.nsquare);
System.out.println("encrypted sum: " + product_em1em2.toString());
System.out.println("decrypted sum: " + paillier.Decryption(product_em1em2).toString());
/* test homomorphic properties -> D(E(m1)^m2 mod n^2) = (m1*m2) mod n */
// m1*m2,求明文数值的乘
BigInteger prod_m1m2 = m1.multiply(m2).mod(paillier.n);
System.out.println("original product: " + prod_m1m2.toString());
// em1的m2次方,再mod paillier.nsquare
BigInteger expo_em1m2 = em1.modPow(m2, paillier.nsquare);
System.out.println("encrypted product: " + expo_em1m2.toString());
System.out.println("decrypted product: " + paillier.Decryption(expo_em1m2).toString());
//sum test
System.out.println("--------------------------------");
Paillier p = new Paillier();
BigInteger t1 = new BigInteger("21");System.out.println(t1.toString());
BigInteger t2 = new BigInteger("50");System.out.println(t2.toString());
BigInteger t3 = new BigInteger("50");System.out.println(t3.toString());
BigInteger et1 = p.Encryption(t1);System.out.println(et1.toString());
BigInteger et2 = p.Encryption(t2);System.out.println(et2.toString());
BigInteger et3 = p.Encryption(t3);System.out.println(et3.toString());
BigInteger sum = new BigInteger("1");
sum = p.cipher_add(sum, et1);
sum = p.cipher_add(sum, et2);
sum = p.cipher_add(sum, et3);
System.out.println("sum: "+sum.toString());
System.out.println("decrypted sum: "+p.Decryption(sum).toString());
System.out.println("--------------------------------");
System.out.println("zzz: " + paillier.Decryption(t2).toString());
}
}
出来结果:
13188115001329041466094923295714064720892766934190823328679547088592860109527221219286072067239183521034906906273679208494852070235173690540150955781810002490692011557667175018515922139290076570661347202294875399729242496962326955810530687359315960423533954538402671452225983994053502872234293434939199384585
13678667320106764366579622352503036580734540429939429977729753453452877577348542871669013300334509345801149900132361778981285676501213176144924569613279244026948213397983022933062190378401107445099993967338183278972327280087534369568354351328264465285086446400486697298102393201183864886288004672158387780159
20
60
original sum: 80
encrypted sum: 3105278900979558245245469197257040960844571226076955376599511046924091310931579897139519846194157801156335602480253988771736129391736684508623369434692079721587671361259413560346951653378607056187182286829172233377858370762084705362097281267081671253447103852739525249001875018765282604068896271908688639379
decrypted sum: 80
original product: 1200
encrypted product: 24650637220545287825397538167107062568448781971515844634172722947336535353419025365650643368093069345795944293051106541548128315639180700247729014856462711516507602039033894973125106994421989018266338026423883615957774059400280379353013342512139539463902734476926740351999980392172857193389573135161712639593
decrypted product: 1200
--------------------------------
21
50
50
1174025372438549804243688228990352504001398197278444803576135787761114631254464750690957323521519373469190738958458084711571829080807228712311378072606509745153964301533618942023461051720684084337954033373821837854889261120534218882320993025259114203529470607220856873427857223172071868243571394898445025796
77064035435600201313943547599319458883318067244120844257066665038184179240895049413267195716517252429406841311211735239929735964569547162482009298674739119710284353238165038708768255032271781443458425951649126388918352441893104733887271134502562838637067035658088484478844256290045228094768627031056269725512
42396921128414689923557451921252255656539157245164480357537432637278995994897549633266674233945850754671718858931024203437878819579533212401198837982037563698907853783851524034688712195169674625441764855841280398346340935141249612529333614012402926826511677525728956840460953532037471445382947630284884159452
sum: 2093899257042663779598860019746941416026084028211567932319374709933618886869747104464528688770039557807441917097431900366188859254809777881831312829617679574931260175370831420777241951082338498795827132476546262053236830192816046669279708899616433752915102538142230479889754562460952327621848613365543817254
decrypted sum: 121
--------------------------------
zzz: 5506240486837368822118836774995999547777877118836017948862722905891002617718756265936166589812973005313622109262515813585057665520149274075582674291833237
注意:这里的公钥和私钥和RSA不同,RSA是私钥解密(公钥加密(明文))=明文 ,但是同态加密中这点不成立,见如上试验结果
真正的公式是 私钥解密(公钥加密(被加数) + 公钥加密(加数))= 和(被加数+加数),但是对单个加数解密无效
内部实现是一种升级操作(比如加的,升级为乘;乘的,升级为乘方)
这里有篇预测,同态是重要的算法,用在人工智能中
这将是改变个人数据交易的算法,甚至是改变世界的算法
所有算法都是硬编码在区块链智能合约的,不存在算法作假的可能;
所有个人数据都是用个人公钥加密,存放在个人地址的,只有个人私钥才能解开(而且数据带有公安机关的签名)
-
需求方要买数据,找交易所,定好数据格式,数据格式和需求方同态加密公钥写入智能合约,不可篡改
-
用户用需求方同态公钥,对自己明文数据同态加密,注意,需求方虽然有同态私钥,但是无法解得正确的输入数据,同态私钥仅能解开计算结果(将结果发给公证机关,公证机关对密文公证签名后)
-
智能合约运行,逐项进行同态加密相加,得出累计结果
-
需求方用同态加密私钥进行解密,得出结果(就是芝麻信用分)
问题:
-
不能运行太复杂的模型(而且模型是公开的,容易被人盗用,一般可以放多个版本迷惑)
-
读取权重并逆向工程的问题(现在权重也是加密的,同态可以相乘)
-
数据造假问题 要有权威机构对密文进行认证,或者利用区块链的特性,比如锚定圈圈链,社交信息直接从圈圈链取
如上,太复杂,参考微信指纹支付
-
支付宝、微信的后台系统不会保存用户支付指纹(用户隐私信息明文只存在于TEE中,像指纹那样,其实数据量也不大);TEE根证书方案按微信方案来
-
政府机关数据上链,利用区块链,特定隐私条目,hash后,进行签名(比如公安局签名,证明这个人的身份证号码信息正确);多个可信签名,可以相互验证,比如公安,车管所,税务
-
商业数据,App自己走银行四要素验证,交钱
-
用户隐私数据灌装,验证指纹和密码,根据可信证书链灌装(灌装身份证信息,传输过程密文,TEE中是明文)
算法灌装
- 指纹支付时,先调用iOS / Android系统api,校验用户指纹是否正确,如果正确,通过支付接口,上送本地缓存的token。
Paillier算法明细
Paillier公钥加密算法。
Paillier公钥加密算法具有语义安全性,即给定明文m1,m2不存在多项式时间算法来区分E(m1)和E(m2)。
性质:
* Homomorphic
* Self-blinding
算法描述:
密钥生成:
选择两大素数p和q,计算N=pq以及lambda=lcm(p-1,q-1)。随机选择g属于Z*,使得gcd(L(g^lambda mod N^2), N) = 1,其中L(x)=(x-1)/N。这里为用户公钥,lambda为用户私钥。
加密过程:
对于明文m,选择随机数r,密文c=E(m mod N, r mod N) = g^m * r^N mod N^2。
此处,E(·)声明为使用公钥pk=的加密操作。
解密过程:
给定密文,其对应的明文D(c) = L(c^lambda mod N^2)/ L(g^lambda mod N^2) mod N。
其中,D(·)声明为使用私钥sk=lambda的解密操作。