MVP架构实现Android手机记步功能
做了有几个APP了,总结下目前的架构重构, 正好有个android手机记步功能,那就写篇文章记录个人在开发一个App项目过程中的一个基本流程, 以及所采用的架构, 技术的运用。
1、架构选择
MVP架构是目前开发AndroidApp最火的架构, 可能MVVM更加吸引人, 但是MVP更加成熟且易于上手. 相比与Activity/Fragment包揽一切的传统开发架构又更加灵活, 便于产品的更新迭代。

mvp-architecture
- Model
- 对外提供业务数据API.
- 内部实现本地数据, 网络数据的存取等.
- 只有Presenter可以访问, 与View隔离
- Presenter
- 持有View对象, 对View进行操作
- 持有Model层提供的数据接口对象, 可通过依赖注入解耦此部分.
- 从数据接口对象中获取数据并处理, 更新View.
- View
- UI层, 包含所有UI相关组件.
- 持有对应的Presenter的对象, 可通过依赖注入解耦此部分.
- 由Presenter来负责更新UI.
2、开源库选择
快速开发一个项目, 且抱着不重复造轮子的思想, 选择一些开源库辅助开发是很必要的. 当然, 同类的开源库可能很多, 选择上可能更多是个人喜好和使用习惯的问题, 在此不做比较(可以哪天单立个开源库选择的话题讨论下).
以下根据个人经验和当前项目的情况初步选择的一些库(个人喜欢的很多其他库会在后续项目中采用哦~):
· ButterKnife将Android视图和回调方法绑定到字段和方法上。
采用最新版本8.2.1, 需要如下配置:
1、在
中,添加:
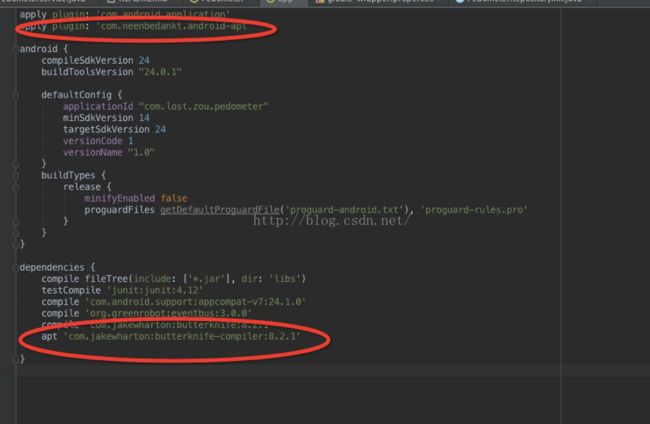
apply plugin: 'com.neenbedankt.android-apt'
dependencies {
...
compile 'com.jakewharton:butterknife:8.2.1'
apt 'com.jakewharton:butterknife-compiler:8.2.1'
}
如:
2、在
中添加:
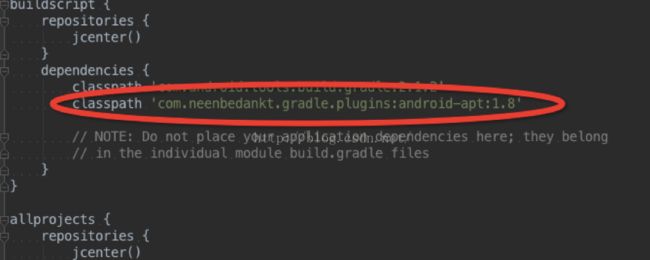
classpath 'com.neenbedankt.gradle.plugins:android-apt:1.8'
如:
· EventBus安卓优化的事件总线,简化了活动、片段、线程、服务等的通信。
添加依赖库如上:
1、EventBus是一个Android端优化的publish/subscribe消息总线,简化了应用程序内各组件间、组件与后台线程间的通信。比如请求网络,等网络返回时通过Handler或Broadcast通知UI,两个Fragment之间需要通过Listener通信,这些需求都可以通过EventBus实现。
2、这个会经常用到,那就全局注册吧,见BaseApplication
protected final static EventBusGLOBAL_EVENT_BUS = EventBus.getDefault();
3、Android手机记步器实现
任何手机记步的本质原理都是加速度传感器(重力传感器)实现的,在周期的运动过程中,传感器输出的数据可以转化成正余弦函数,波峰和波峰之间就可以算成步数。
当然,Android4.4及以上提供了一种低功耗的直接步数输出方法,但是有些低配的手机就不支持咯,所以还是得回到本质的用加速度计数据来滤波、转化得到步数。码字太累,加速度计步的原理我就不说了,反正我懂,你们网上一搜一大把。
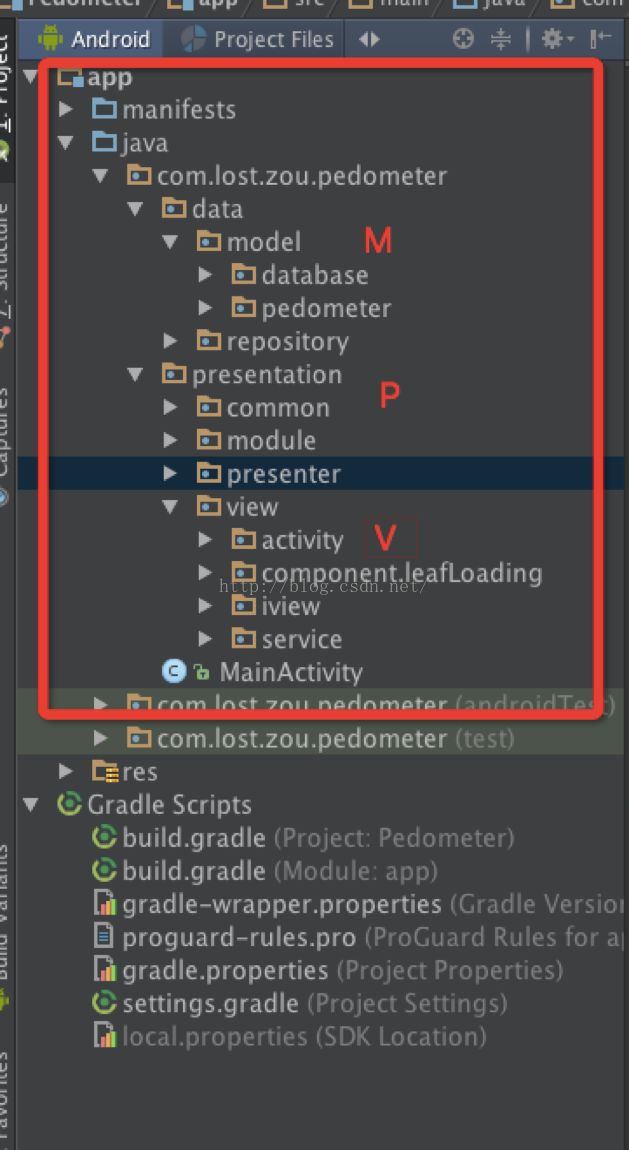
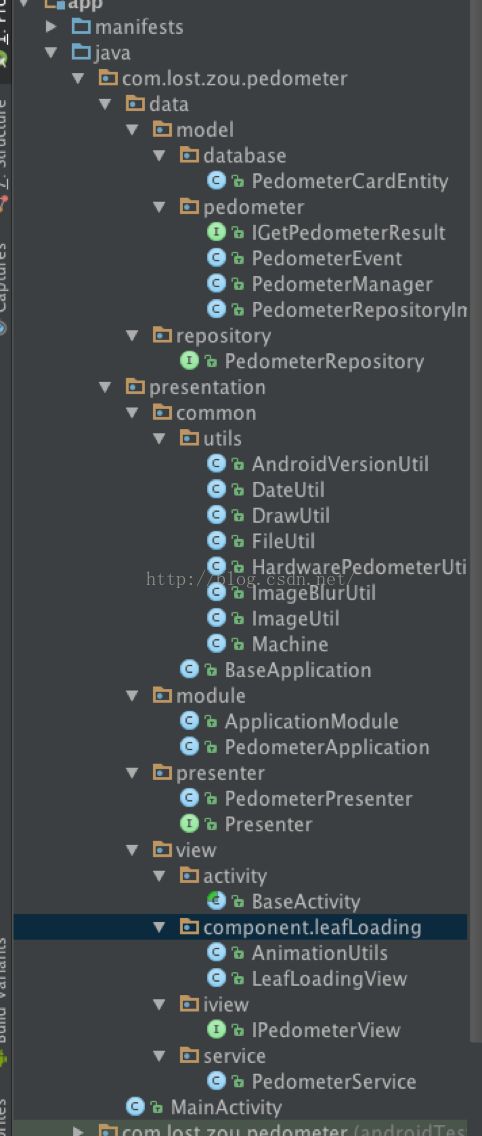
4、搭建框架
框架如图,分为M、V、P三层,我习惯将View放在表现成下面。来张展开的图,看起来结构更加清楚明了。
4、1数据层:分数据库和数据逻辑处理等。其中的核心为记步数据的获取,原始加速度传感器数据的处理,实现类PedometerRepositoryIml。
详细的不多说,自己看代码去吧。
当步数发生改变时,发送EventBus消息更新View:
PedometerEvent event = new PedometerEvent();
event.mIsUpdate = true;
BaseApplication.postEvent(event);
并实现PedometerRepository接口。
@Override
public void getPedometerStep(IGetPedometerResult result) {
result.onSuccessGet(mTodayStepEntity);
}
对应的在表现层,调用接口PedometerRepository。
4、2记步器表现层PedometerPresenter
通用Presenter
/**
* Interface representing a Presenter in a model view presenter (MVP) pattern.
*/
public interface Presenter {
/**
* Method that control the lifecycle of the view. It should be called in the view's
* (Activity or Fragment) onResume() method.
*/
void resume();
/**
* Method that control the lifecycle of the view. It should be called in the view's
* (Activity or Fragment) onPause() method.
*/
void pause();
/**
* Method that control the lifecycle of the view. It should be called in the view's
* (Activity or Fragment) onDestroy() method.
*/
void destroy();
}
实现生命周期。
PedometerPresenter实现View与数据的交互。用于更新View的显示。
/**
* 监听数据
*/
@Subscribe
public void onEventMainThread(PedometerEvent event) {
if (event.mIsUpdate) {
getPedometerStep();
}
}
/**
* 获取计步器的数据
*/
public void getPedometerStep() {
mPedometerRepository.getPedometerStep(new IGetPedometerResult() {
@Override
public void onSuccessGet(PedometerCardEntity cardEntity) {
if (mView != null) {
mView.onReaderPedometer(cardEntity);
}
}
});
}
4、3View层
定义记步器View接口,
public interface IPedometerView {
void onReaderPedometer(PedometerCardEntity cardEntity);
}
在我们的view 层去实现它。
@Override
public void onReaderPedometer(PedometerCardEntity cardEntity) {
if (cardEntity != null) {
tvSteps.setText(cardEntity.getStepCount() + "步");
tvTargetSteps.setText("目标步数:" + cardEntity.getTargetStepCount() + "步");
mProgress = (int) (100 * cardEntity.getStepCount() / (cardEntity.getTargetStepCount() * 1.0f));
RotateAnimation rotateAnimation = AnimationUtils.initRotateAnimation(false, 1500, true,
Animation.INFINITE);
fanPic.startAnimation(rotateAnimation);
leafLoading.setProgress(mProgress);
}
}
更新View的显示。
4、4记步器
记步通过*计步器管理类:1、记步服务管理,PedometerManager进行管理。核心是记步计步器服务:PedometerService
/**
* @author zoubo
* 计步器服务,启动条件:
* 1、有TYPE_STEP_COUNTER; 2、版本为4.4(19)以上
*/
public class PedometerService extends Service {
private Context mContext;
private SensorManager mSensorManager; // 传感器服务
private PedometerRepositoryIml mPedometerRepositoryIml; // 传感器监听对象
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent intent) {
return null;
}
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
mContext = BaseApplication.getAppContext();
Log.i("zou", " onCreate" );
mPedometerRepositoryIml = ApplicationModule.getInstance().getPedometerRepository();
mPedometerRepositoryIml.initData();
ApplicationModule.getInstance().getPedometerManager().init();
mSensorManager = (SensorManager) mContext.getSystemService(Context.SENSOR_SERVICE);
if (HardwarePedometerUtil.supportsHardwareStepCounter(mContext)) {
mSensorManager.registerListener(mPedometerRepositoryIml, mSensorManager.getDefaultSensor(Sensor.TYPE_STEP_COUNTER),
SensorManager.SENSOR_DELAY_UI);
} else if (HardwarePedometerUtil.supportsHardwareAccelerometer(mContext)) {
mSensorManager.registerListener(mPedometerRepositoryIml, mSensorManager.getDefaultSensor(Sensor.TYPE_ACCELEROMETER), SensorManager.SENSOR_DELAY_UI);
}
}
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
Log.i("zou", " onStartCommand" );
return START_STICKY;
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
Log.i("zou", " onDestroy" );
if (mPedometerRepositoryIml != null) {
mPedometerRepositoryIml.onDestroy();
mSensorManager.unregisterListener(mPedometerRepositoryIml);
mPedometerRepositoryIml = null;
}
mSensorManager = null;
mContext = null;
}
}
最终效果如图:
GitHub地址:https://github.com/ZBJDSBJ/Pedometer