【Android】抽象布局 — include、merge 、ViewStub
在布局优化中,Androi的官方提到了这三种布局
一、布局重用
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width=”match_parent”
android:layout_height=”match_parent”
android:background="@color/app_bg"
android:gravity="center_horizontal">
<include layout="@layout/titlebar"/>
<TextView android:layout_width=”match_parent”
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/hello"
android:padding="10dp" />
LinearLayout> 1)
标签必须使用单独的layout属性。 2) 可以使用其他属性。
标签若指定了ID属性,而你的layout也定义了ID,则你的layout的ID会被覆盖。 3) 在include标签中所有的android:layout_*都是有效的,前提是必须要写layout_width和layout_height两个属性。
4) 布局中可以包含两个相同的include标签,引用时可以使用如下方法解决
比如这个布局文件:
<ScrollView xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:scrollbars="vertical" >
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:focusable="true"
android:focusableInTouchMode="true"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:padding="10dip" >
<include
android:id="@+id/discovered_servers"
layout="@layout/discovered_servers_element" />
<include
android:id="@+id/bookmarks"
layout="@layout/bookmarks_element" />
<include android:id="@+id/bookmarks_favourite"
layout="@layout/bookmarks_element" />
<include
android:id="@+id/new_conn"
layout="@layout/new_conn_element" />
LinearLayout>
ScrollView>这里我们include了两次res/layout/bookmarks_element.xml,这个子布局内容如下:
<merge xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" >
<TextView
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:paddingBottom="10dip"
android:paddingTop="10dip"
android:text="@string/bookmarks"
android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceLarge" />
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/bookmarks_list"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:padding="10dip" />
merge>如果向下面这样调用是错的,
LinearLayout fav_bookmarks = findViewById(R.id.bookmarks_list); // WRONG!!!!正确的方法是这样:
View bookmarks_container_2 = findViewById(R.id.bookmarks_favourite);
bookmarks_container_2.findViewById(R.id.bookmarks_list);二、减少视图层级
首先主需要一个配置文件activity_main.xml
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="merge标签使用" />
RelativeLayout>再来一个最简单的Activity,文件名MainActivity.java
package com.example.merge;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
}
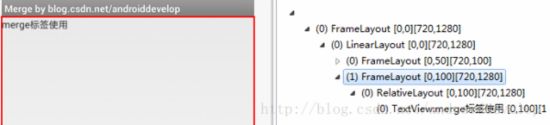
}按着上面的代码创建工程,运行后使用“DDMS -> Dump View Hierarchy for UI Automator”工具,截图如下:
最下面两层RelativeLayout与TextView就是 activity_main.xml 布局中的内容,上面的FrameLayout是Activity setContentView添加的顶层视图。下面使用merge标签可以查看下区别。
布局文件 activity_main.xml 修改内容如下:
<merge xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="merge标签使用" />
merge>使用“DDMS -> Dump View Hierarchy for UI Automator”工具,截图如下:
可以看到,FrameLayout下面直接就是TextView,与之前的相比少了一层 RelativeLayout 而实现的效果相同。
那么,什么情况考虑使用
一种是向上面的例子一样,子视图不需要指定任何针对父视图的布局属性,例子中TextView仅仅需要直接添加到父视图上用于显示就行。
另外一种是假如需要在LinearLayout里面嵌入一个布局(或者视图),而恰恰这个布局(或者视图)的根节点也是LinearLayout,这样就多了一层没有用的嵌套,无疑这样只会拖慢程序速度。而这个时候如果我们使用merge根标签就可以避免那样的问题,官方文档 Android Layout Tricks #3: Optimize by merging 中的例子演示的就是这种情况。
只能作为XML布局的根标签使用。 - 当 Inflate 以
开头的布局文件时,必须指定一个父ViewGroup,并且必须设定attachToRoot为 true。
三、需要时使用
限于篇幅,这里只大概总结一下ViewStub的使用方法,详细介绍和使用写到后面的文章中。
<ViewStub
android:id="@+id/stub_import"
android:inflatedId="@+id/panel_import"
android:layout="@layout/progress_overlay"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="bottom" /> 当你想加载布局时,可以使用下面其中一种方法:
((ViewStub) findViewById(R.id.stub_import)).setVisibility(View.VISIBLE); or
View importPanel = ((ViewStub) findViewById(R.id.stub_import)).inflate(); 当调用inflate()函数的时候,ViewStub被引用的资源替代,并且返回引用的view。 这样程序可以直接得到引用的view而不用再次调用函数findViewById()来查找了。
注:ViewStub 目前有个缺陷就是还不支持
更多
【参考资料】:
1、Android抽象布局 — include、merge 、ViewStub
2、Tech Stuff: Android
3、Android 性能优化 四 布局优化merge标签的使用
4、Android之merge布局
5、 Android实战技巧:ViewStub的应用