c++全排列 next_permutation()函数
c++全排列
转载博客:https://www.cnblogs.com/cstdio1/p/11311500.html
对于next_permutation函数,其函数原型为:
#include < algorithm>
bool next_permutation(iterator start,iterator end)
当当前序列不存在下一个排列时,函数返回false,否则返回true
同时,相对应的,上一个排列即为prev_permutation(int *begin, int end)
看如下代码:
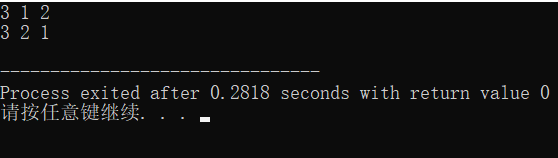
#include 
注意:当我们把while(next_permutation(num,num+3))中的3改为2时,输出就变为了下图所示:
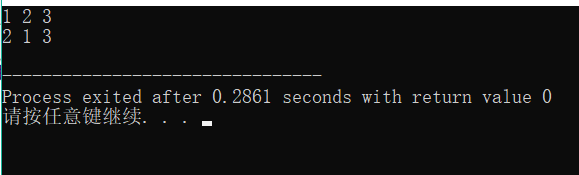
说明此时只针对1,2进行了全排列,有两个,后面的3没有变化,同时改变了数组前两个的值。
由此可以看出,next_permutation(num,num+n)函数是对数组num中的前n个元素进行全排列,同时并改变num数组的值。
另外,需要强调的是,next_permutation()在使用前需要对欲排列数组按升序排序,否则只能找出该序列之后的全排列数。
维基百科上全排列的实现:
循环法:
#include 递归法:
#include next_permutation 可以自定义比较函数 例如:POJ 1256
题目中要求的字典序是:A’<‘a’<‘B’<‘b’<…<‘Z’<‘z’,所以在用函数之前必须得按照题目要求的进行排序
#include