F35.(亲测-方法记录)Ubuntu-darknet-YOLOV3算法的使用(训练、测试、性能指标)(亲测成功-2019.07.09-批量测试将继续更新)
注:训练环境为Linux、写作环境为win10。
1.程序的运行环境:
1)系统:Ubuntu16.04
2)显卡:TITAN XP
3)CUDA:9.1
4)CUDNN:7.5
5)运行内存32G
6)pycharm
7)anaconda
2.资源的下载:
本文基于darknet框架Linux系统训练YOLOV3数据集,下载darknet文件:链接:https://download.csdn.net/download/qq_41900772/11340101 下载文件结构见下图所示:
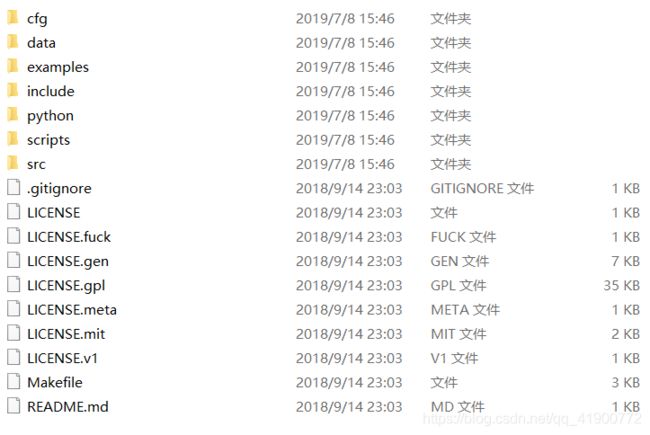
该文档中训练时主要用到:cfg、data,以及后文中所建立的数据集。
该文档中个文件夹所存放的文件的作用:
1)cfg:cfg文件夹中主要存放了网络训练所需要的网络配置文件
2)data:主要存放了,网络测试所需测试图片、网络训练所需训练类别名文件(如:voc.names、coco.names)
3)example:主要存放了可能会用到的一些函数评价接口。
4)python:存放了网络对应的python接口。
5)Makefile文件为训练所需的最重要的配置文件。
3.VOC格式的数据集的制作
在主目录下建立文件夹VOC,在该文件夹下建立数据集。
数据集目录:
1.VOCdevkit #根目录
1.1VOC2019 #不同年份的数据集,名称年份可以改
1.1.1Annotations #存放xml文件,与JPEGImages中的图片一一对应,解释图片的内容等等
1.1.2ImageSets #该目录下存放的都是txt文件,txt文件中每一行包含一个图片的名称,末尾会加上±1表示正负样本
1.1.2.1Action(训练过程中用不到)
1.1.2.2Layout(训练过程中用不到)
1.1.1.3Main
1.1.1.4Segmentation(训练过程中用不到)
1.1.3JPEGImages #存放源图片
1.1.4SegmentationClass #存放的是图片,语义分割相关(训练过程中用不到)
1.1.5SegmentationObject #存放的是图片,实例分割相关(训练过程中用不到)
制作数据集:
1)根据上目录建立数据集
2)加纳所有图片名称进行重排序
3)将训练图片放入JPEGImages文件夹中
4)采用Imagelabel工具对训练图片进行标注,生成xml文件
5)将上一步所生成的xml文件放入(注意:图片与xml文件要一一对应)
6)在Main文件夹下生成train.txt、test.txt两个文件,两个文件中为训练图片的名字
7)将xml文件转换成txt格式文件
Main文件夹下的文件
根据xml文件生成与xml文件相对应的数据单序列,分为训练集与测试集,数据名要存放在Main文件夹下的.txt文件中以作备用
将.xml文件转换到.txt文件
从.xml文件到VOC2019文件夹中“label”文件夹中的.txt文件(标注图像的坐标及中心点信息),同时,在VOCdevkit同级文件夹下生成train.txt、test.txt两个文件,两个文件的内容为训练图片的路径(该步骤提取训练所需要的信息)
至此,数据集制作完成。
制作数据集总结,
按照VOC数据集的结构搭建好框架后,将训练图片、对应xml文件以及以上两个程序,放到相应位置,修改好程序中相应信息,进行执行程序并检查相应的文件生成情况,检查无误,数据集制作完成。接下来进行训练过程中相关配置文件的配置工作。
4.接下来进行文件的配置
文件配置过程需要进行配置的文件:
Makefikle文件配置(最重要)
voc.data(数据集文件配置)文件配置、
voc.names(训练过程中的类别名儿,在voc.data文件中调用)文件配置、
yolov3.cfg文件配置
4.1Makefile文件配置
Linux中Makefile文件配置工作非常重要。在Linux中使用Mousepad编译器或者pycharm编译器打开,不要使用默认的gcc编译器打开。打开后界面如下图所示::
 YOLOV3中,在Makefile文件配置时根据自己设备情况进行配置,配置前四行即可,GPU、CUDA、CUDNN、OPENCV(2/3版本置1),其他不需要修改。Makefile文件配置完成后再主目录下右键打开终端,输入命令:make,回车完成编译。
YOLOV3中,在Makefile文件配置时根据自己设备情况进行配置,配置前四行即可,GPU、CUDA、CUDNN、OPENCV(2/3版本置1),其他不需要修改。Makefile文件配置完成后再主目录下右键打开终端,输入命令:make,回车完成编译。
4.2 训练数据配置
打开cfg文件夹下的voc.data文件,打开文件后界面如下:

在该文件中内容主要包括:
classese:类别数量
train:路径为voc数据集文件夹下的2019_train.txt文件的路径
test:路径为voc数据集文件夹下的2019_test.txt文件的路径
names:为data文件夹下的voc.names
backup:为主目录下backup文件夹(主要用来存放训练生成的.weights文件(模型)和.backup文件(用于训练过程中断后继续训练时所用文件))
eval:为voc评价标准
4.3训练类别配置
修改训练数据的类别名的文件
4.4 网络模型配置
打开相应的YOLOV3模型文件,如图示:
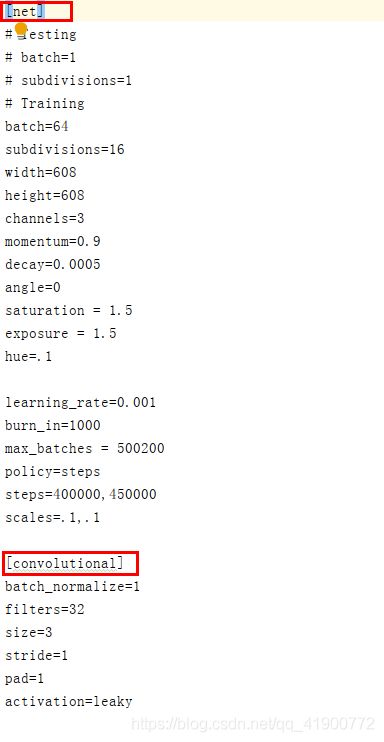
该文件中主要包括了三部分:网络(net)层、convolutional(卷积)层、yolo层。在文件配置时需要配置net和yolo层的信息,
1)net配置:
训练过程中将testing下两行注释掉(如果测试时将training下两行注释掉)batch、subdivisions的值根据自己的需要进行修改
(注意:当GPU显存比较小时将subdivisions调大batch/subdivisions的值为训练时一次传入训练的图片)
其他的之不需要配置
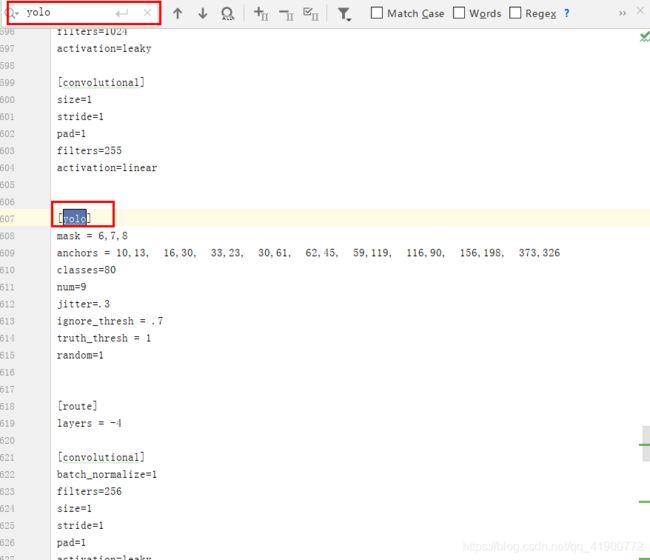
2)yolo配置
打开文件后按Ctrl+F键进行搜索yolo,会搜出3个yolo,所以yolo部分需要修改3次(每次修改都有相同)yolo上边的filter改为“3*(5+类别数)”yolo下边classes改为自己的类别数,random为多尺度训练,如果GPU显存很小将其置为0。3个yolo出均需修改。
3)使用k-means可以适当修改anchors值以满足自己训练的需要
至此,文件配置完成。接下来开始训练。
5.训练
5.1模型的保存
训练时默认:迭代次数小于1000时毎迭代100次保存一次模型,迭代次数大于等于1000时毎一万次保存一次模型,保存的模型结果保存在主目录下的backup文件夹下,同时,会保存.backup模型(该模型为:当训练中断时,若想要继续接着上次训练可以使用这个模型),若想修改毎多少次保存一次模型的次数,可以在DarkNet主目录下examples/detector.c文件中进行修改
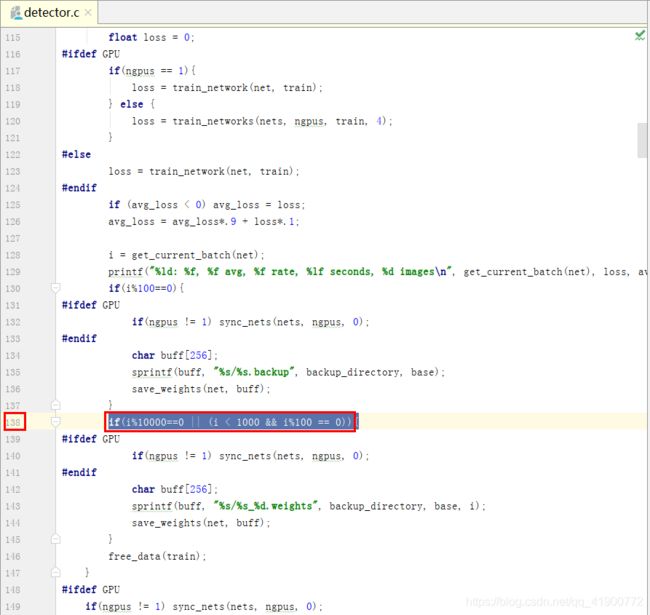
修改完成后,在DarkNet主目录下鼠标右键打开终端输入命令:make,回车进行重新编译
5.2训练
5.2.1.使用预训练模型训练数据(效果较不使用预训练模型要好)
预训练是在ImageNet上按分类的方式进行预训练160轮,使用SGD优化方法,初始学习率0.1,每次下降4倍,到0.0005时终止。除了训练224x224尺寸的图像外,还是用448x448尺寸的图片。
预训练模型下载链接: https://download.csdn.net/download/qq_41900772/11340093
初次训练模型需要使用darknet53.conv.74作为预训练模型,之后在次训练新数据可以使用已经训练完的模型作为预训练模型,
在DarkNet主目录下打开终端输入训练命令进行训练。
1)不保存训练日志的训练命令:
./darknet detector train cfg/voc.data cfg/yolov3-voc.cfg scripts/darknet53.conv.74
解析:
1)在DarkNet主目录下编译完成,则DarkNet框架训练环境搭建完成。可以使用命令:“./darknet”
2)detector为训练文件(底层c程序)
3)train表示该命令为训练命令(当测试时输入测试命令将train改为test)
4)cfg/voc.data:表示配置的数据集的参数文件(注意路径)
5)cfgyolov3-voc.cfg:表示配置的网络参数文件(注意路径)
6)scripts/darknet53.conv.74:表示训练所需要的预训练模型(注意路径)
2)保存训练日志的训练命令:
./darknet detector train cfg/voc.data cfg/yolov3-voc.cfg scripts/darknet53.conv.74 | tee train_yolov3-voc.log
解析:
1)在DarkNet主目录下编译完成,则DarkNet框架训练环境搭建完成。可以使用命令:“./darknet”
2)detector为训练文件(底层c程序)
3)train表示该命令为训练命令(当测试时输入测试命令将train改为test)
4)cfg/voc.data:表示配置的数据集的参数文件(注意路径)
5)cfgyolov3-voc.cfg:表示配置的网络参数文件(注意路径)
6)scripts/darknet53.conv.74:表示训练所需要的预训练模型(注意路径)
7)| tee train_yolov3-voc.log:表示训练时保存日志文件(保存在DarkNet主目录下)
3)使用GPU、不保存训练日志的训练命令:
./darknet detector train cfg/voc.data cfg/yolov3-voc.cfg scripts/darknet53.conv.74 -gpus 0,1,... | tee train_yolov3-voc.log
解析:
1)在DarkNet主目录下编译完成,则DarkNet框架训练环境搭建完成。可以使用命令:“./darknet”
2)detector为训练文件(底层c程序)
3)train表示该命令为训练命令(当测试时输入测试命令将train改为test)
4)cfg/voc.data:表示配置的数据集的参数文件(注意路径)
5)cfgyolov3-voc.cfg:表示配置的网络参数文件(注意路径)
6)scripts/darknet53.conv.74:表示训练所需要的预训练模型(注意路径)
7)-gpus 0,1:使用多GPU进行训练模型时添加改程序,可指定特定GPU进行训练网络,即:当设备拥有n个GPU时,可以同时使用GPU进行加速训练n个网络。
使用GPU、保存训练日志的训练命令:
./darknet detector train cfg/voc.data cfg/yolov3-voc.cfg scripts/darknet53.conv.74 -gpus 0,1.....
解析:
1)在DarkNet主目录下编译完成,则DarkNet框架训练环境搭建完成。可以使用命令:“./darknet”
2)detector为训练文件(底层c程序)
3)train表示该命令为训练命令(当测试时输入测试命令将train改为test)
4)cfg/voc.data:表示配置的数据集的参数文件(注意路径)
5)cfgyolov3-voc.cfg:表示配置的网络参数文件(注意路径)
6)scripts/darknet53.conv.74:表示训练所需要的预训练模型(注意路径)
7)-gpus 0,1:使用多GPU进行训练模型时添加改程序,,可指定特定GPU进行训练网络,即:当设备拥有n个GPU时,可以同时使用GPU进行加速训练n个网络。
当多GPU训练时模型保存:https://github.com/pjreddie/darknet/issues/664#issuecomment-405448653
5.2.2训练日志参数的介绍
1)Region 82(94/106):表示cfg文件中yolo-layer的索引值,三个值,82/94/106
2)Avg IOU:表示在训练过程中预测的bounding box与标注的bounding box的交并比(两个框的相交/两个框的并),该值期望越大越好,目标值为1
3)Class:表示标注物体的分类准确率,该值期望越大越好,目标期望值为1
4)obj:表示预测有目标的概率,该值期望越大越好,目标值为1
5)No obj:表示预测没有目标的概率,该值期望越小越好,目标期望值为0
6).5R:表示以IOU=0.5为阈值时被召回(recall)。recall=检出的正样本/实际的正样本
7).75R:表示以IOU=0.75为阈值时被召回(recall)
8)count:表示正样本的数量
![]()
在该图片中:
1)20277:表示当前训练的迭代次数
2)0.038915:表示训练总的Loss损失
3)0.42692 avg: 表示平均Loss,该值期望越低越好,一般该值低于0.060730 avg就可以终止训练了。
4)0.000100 rate: 代表当前的学习率,是在.cfg文件中定义的。(因为本人已经训练,训练过程中未截图,所以该图借鉴了他人的图,本人训练时学习率为0.001)
5)0.302128 seconds: 表示当前批次训练花费的总时间(batch/subdivisions)
6)162216 images:表示到目前所参与训练的总的图片数量
5.2.3 当avg低于0.06时即可停止训练了
Linux系统下在训练时的当前终端按下Ctrl+c进行停止训练
5.2.3训练停止后想接着上次训练接着训练
接着上次训练接着训练,在DarkNet主目录下鼠标右键打开终端,输入以下命令:
./darknet detector train cfg/voc.data cfg/yolov3-voc.cfg backup/yolov3-voc.backup
回车,即可接着上次的训练继续训练
解释:
该条命令同前边介绍的训练命令只是将预训练权重改为上次训练时保存在DarkNet主目录下的backup文件夹下的yolov3-voc.backup文件
5.3 训练日志可视化
输入保存训练日志训练命令训练后,在DarkNet主目录下会生成train_yolov3-voc.log(.log)的训练日志文件。使用visualization_train_yolov3-voc_log.py(存放在与训练日志文件同级目录下) Python脚本程序度训练日志文件进行可视化,运行程序后会得到loss变化曲线和Avg IOU曲线
1)visualization_train_yolov3-voc_log.py程序如下所示:
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import os
# ==================可能需要修改的地方=====================================#
g_log_path = "train_yolov3-voc.log" # 此处修改为你的训练日志文件名
# ==========================================================================#
def extract_log(log_file, new_log_file, key_word):
'''
:param log_file:日志文件
:param new_log_file:挑选出可用信息的日志文件
:param key_word:根据关键词提取日志信息
:return:
'''
with open(log_file, "r") as f:
with open(new_log_file, "w") as train_log:
for line in f:
# 去除多gpu的同步log
if "Syncing" in line:
continue
# 去除nan log
if "nan" in line:
continue
if key_word in line:
train_log.write(line)
f.close()
train_log.close()
def drawAvgLoss(loss_log_path):
'''
:param loss_log_path: 提取到的loss日志信息文件
:return: 画loss曲线图
'''
line_cnt = 0
for count, line in enumerate(open(loss_log_path, "rU")):
line_cnt += 1
result = pd.read_csv(loss_log_path, skiprows=[iter_num for iter_num in range(line_cnt) if ((iter_num < 500))],
error_bad_lines=False,
names=["loss", "avg", "rate", "seconds", "images"])
result["avg"] = result["avg"].str.split(" ").str.get(1)
result["avg"] = pd.to_numeric(result["avg"])
fig = plt.figure(1, figsize=(6, 4))
ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 1, 1)
ax.plot(result["avg"].values, label="Avg Loss", color="#ff7043")
ax.legend(loc="best")
ax.set_title("Avg Loss Curve")
ax.set_xlabel("Batches")
ax.set_ylabel("Avg Loss")
def drawIOU(iou_log_path):
'''
:param iou_log_path: 提取到的iou日志信息文件
:return: 画iou曲线图
'''
line_cnt = 0
for count, line in enumerate(open(iou_log_path, "rU")):
line_cnt += 1
result = pd.read_csv(iou_log_path, skiprows=[x for x in range(line_cnt) if (x % 39 != 0 | (x < 5000))],
error_bad_lines=False,
names=["Region Avg IOU", "Class", "Obj", "No Obj", "Avg Recall", "count"])
result["Region Avg IOU"] = result["Region Avg IOU"].str.split(": ").str.get(1)
result["Region Avg IOU"] = pd.to_numeric(result["Region Avg IOU"])
result_iou = result["Region Avg IOU"].values
# 平滑iou曲线
for i in range(len(result_iou) - 1):
iou = result_iou[i]
iou_next = result_iou[i + 1]
if abs(iou - iou_next) > 0.2:
result_iou[i] = (iou + iou_next) / 2
fig = plt.figure(2, figsize=(6, 4))
ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 1, 1)
ax.plot(result_iou, label="Region Avg IOU", color="#ff7043")
ax.legend(loc="best")
ax.set_title("Avg IOU Curve")
ax.set_xlabel("Batches")
ax.set_ylabel("Avg IOU")
if __name__ == "__main__":
loss_log_path = "train_log_loss.txt"
iou_log_path = "train_log_iou.txt"
if os.path.exists(g_log_path) is False:
exit(-1)
if os.path.exists(loss_log_path) is False:
extract_log(g_log_path, loss_log_path, "images")
if os.path.exists(iou_log_path) is False:
extract_log(g_log_path, iou_log_path, "IOU")
drawAvgLoss(loss_log_path)
drawIOU(iou_log_path)
plt.show()
2)运行程序后得到loss变化曲线和Avg IOU曲线图
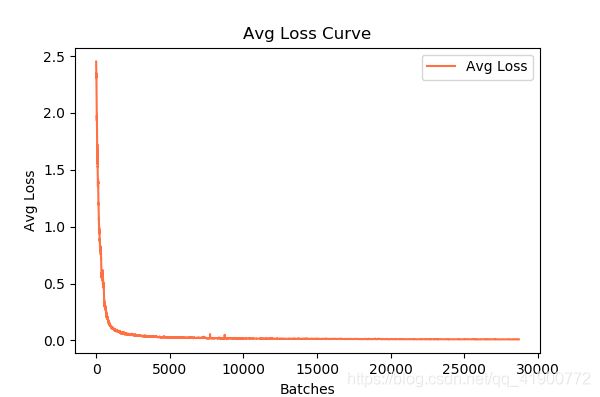
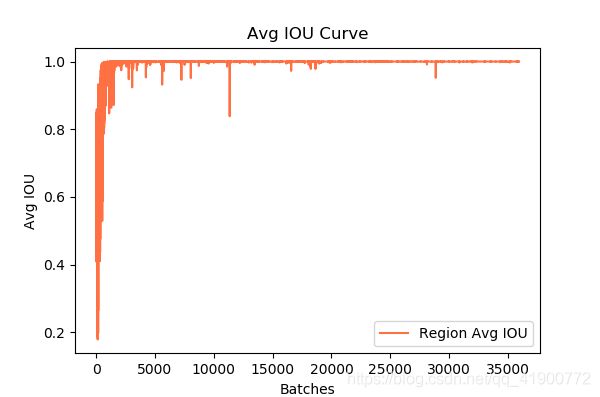
(注:该图为本人训练日志所生成的图)
5.4 训练完后,对模型进行微调微调继续训练新数据样本
初次训练模型时需要下载预训练模型:darknet53.conv.74训练完后,在DarkNet主目录下的backup文件夹下会生成训练模型,当下次训练新数据时,使用上次已经训练过的模型作为预训练模型继续训练,需要对训练的模型进行微调。
1)使用-clear对模型进行微调
通过模型训练出的backup或者final.weights文件代替预训练模型darknet53.conv.74,并在训练命令的末尾加上-clear命令,这样模型的训练会从初始状态开始,
./darknet cfg/yolo.data cfg/yolo.cfg backup/model_pre.backup -clear
这样重新训练的模型就是在原模型微调的基础上训练的结果,这样模型的收敛速度较快,迭代次数将从0开始计算.
2)不使用-clear对模型进行微调
不用-clear命令,训练则不会从初始状态开始,读取原模型的backup或者weights的时候也会读取其中的迭代次数及learning rage.比如原模型的迭代次数微40000次,最终的学习率为0.00001,那么新模型训练的时候也会从40000次开始迭代,并从0.00001的学习率开始,那么此时就需要修改cfg文件的max_batches以及learning rate .
比如我的模型1的cfg是这样的,初始learning rate为0.001:
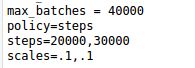
那么新模型如果想迭代30000次,并有初始0.001的学习率你需要修改max_batches和steps:

本文训练过程借鉴了:
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_34806812/article/details/81459982
https://blog.csdn.net/hunterhe/article/details/89923092
6.网络的评价体系(个人建议采用6.3)
6.1 召回率的计算(个人建议采用6.3)
6.1.1 不修改源程序
因为找到example文件夹下的detector文件找到以下函数处:发现设置的路径为/data/coco_val.list,所以如果下直接使用命令行程序而不做修改源程序的话需要在data文件夹下建立相应的文件,并把需要计算召回率(recall)的图片路径放入该文件中。

在linux系统的命令行窗口中输入命令:
./darknet detector recall cfg/voc.data cfg/bolo.voc.cfg backup/yolov3voc.weights
解释命令:./darknet + detector(训练+测试程序)+recall(召回率计算命令)+ cfg/voc.data (数据集配置文件) + cfg/bolo.voc.cfg(网络配置文件) + backup/yolov3voc.weights(模型文件)
注意:需要在data文件夹下建立文件名为“coco_val_5k”的测试图片文件路径的文件(可以将voc文件夹下的测试图片路径文件中的路径信息复制到”coco_val_5k“中)
6.1.2 修改源程序
在example文件夹中找到detector.c文件打开并找到下图中的函数。


修改detector.c文件中validate_detector_recall函数:
将它原有的:
list plist = get_paths(“data/coco_val_5k.list”);
修改为 :
list plist = get_paths("*/darknet/voc/2019_test”);
即可
在linux命令行中输入命令:
./darknet detector recall cfg/voc.data cfg/bolo.voc.cfg backup/yolov3voc.weights
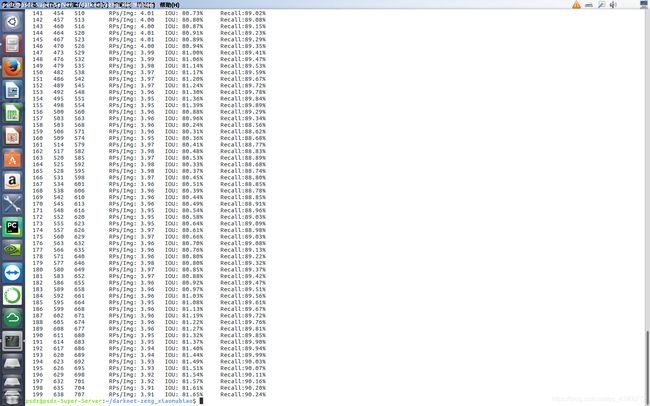
上图中输出结果即为计算的召回率,输出结果的格式为:
Number Correct Total Rps/Img IOU Recall
其中:
1)Number表示处理到第几张图片。
2)Correct表示正确的识别除了多少bbox。这个值算出来的步骤是这样的,丢进网络一张图片,网络会预测出很多bbox,每个bbox都有其置信概率,概率大于threshold的bbox与实际的bbox,也就是labels中txt的内容计算IOU,找出IOU最大的bbox,如果这个最大值大于预设的IOU的threshold,那么correct加一。
3)IOU: 这个是预测出的bbox和实际标注的bbox的交集 除以 他们的并集。显然,这个数值越大,说明预测的结果越好。
4)Recall召回率, 意思是检测出物体的个数 除以 标注的所有物体个数。通过代码我们也能看出来就是Correct除以Total的值。
平均召回率计算:"num(recall)/n"即对算求的每张图片的召回率进行相加求取平均
本节参考:https://www.jianshu.com/p/7ae10c8f7d77/
6.2 使用voc_eval.py进行计算mAP(个人建议采用6.3)
本节参考:https://blog.csdn.net/sihaiyinan/article/details/87903923 (内容不错)
yolov3计算mAP有两种方法,第一种是使用faster rcnn中的voc_eval.py进行计算,另一种是通过修改yolov3中的代码进行计算。相比较而言第一种方法简单一些。
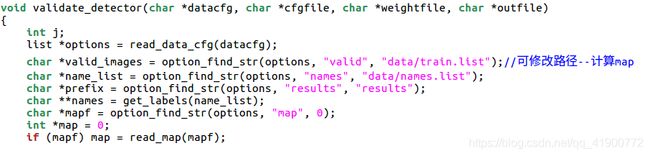
如上图所示,在detector.c中找到validate_detector函数,发现路径为/data/train.list,所以使用之前需要在data文件夹中建立相应文件并把需要计算map的图片路径内容放在该文件下。
在yolov3文件夹darknet主目录下打开终端命令行窗口并且输入命令:
./darknet detector valid data/voc1.data data/yolov3-voc.cfg backup/yolov3-voc.backup
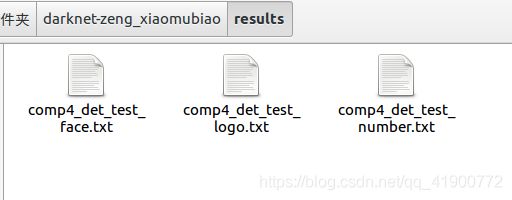
在results文件夹子会生成名为”comp4_det_test_“的每一类的文件信息,如下图示
打开每一类的文件,文件内容如下图示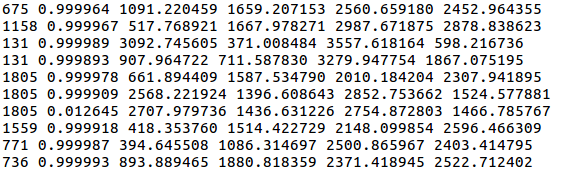
第一列是图像名字(不带后缀),第二列是置信度,剩下依次是xmin、ymin、xmax、ymax
生成每一类的文件后,使用voc_eval.py文件计算map即可。
计算map需要到文件:
1)各类检测到的目标框txt文件
2)Annotations文件
3)验证图像名字列表
4)compute_mAP.py + voc_eval.py
compute_mAP.py代码及解析
#-*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import os
import numpy as np
from voc_eval import voc_eval # 注意将voc_eval.py和compute_mAP.py放在同一级目录下
detpath = 'Path to dets txt' # 各类txt文件路径
detfiles = os.listdir(detpath)
classes = ('__background__', # always index 0 数据集类别
'class1', 'class2', 'class3', 'class4', 'class5', 'class6')
aps = [] # 保存各类ap
recs = [] # 保存recall
precs = [] # 保存精度
annopath = 'Path to Annotations' + '{:s}.xml' # annotations的路径,{:s}.xml方便后面根据图像名字读取对应的xml文件
imagesetfile = 'Path to VOC2007/ImageSets/Main/test.txt' # 读取图像名字列表文件
cachedir = 'Path to annotations_cache/'
for i, cls in enumerate(classes):
if cls == '__background__':
continue
for f in detfiles: # 读取cls类对应的txt文件
if f.find(cls) != -1:
filename = detpath + f
rec, prec, ap = voc_eval( # 调用voc_eval.py计算cls类的recall precision ap
filename, annopath, imagesetfile, cls, cachedir, ovthresh=0,
use_07_metric=False)
aps += [ap]
print('AP for {} = {:.4f}'.format(cls, ap))
print('recall for {} = {:.4f}'.format(cls, rec[-1]))
print('precision for {} = {:.4f}'.format(cls, prec[-1]))
print('Mean AP = {:.4f}'.format(np.mean(aps)))
print('~~~~~~~~')
print('Results:')
for ap in aps:
print('{:.3f}'.format(ap))
print('{:.3f}'.format(np.mean(aps)))
print('~~~~~~~~')
voc_eval.py源代码及解析
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# --------------------------------------------------------
# Fast/er R-CNN
# Licensed under The MIT License [see LICENSE for details]
# Written by Bharath Hariharan
# --------------------------------------------------------
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
import os
import cPickle
import numpy as np
def parse_rec(filename):
""" Parse a PASCAL VOC xml file """
tree = ET.parse(filename)
objects = []
for obj in tree.findall('object'):
obj_struct = {}
obj_struct['name'] = obj.find('name').text
obj_struct['pose'] = obj.find('pose').text
obj_struct['truncated'] = int(obj.find('truncated').text)
obj_struct['difficult'] = int(obj.find('difficult').text)
bbox = obj.find('bndbox')
obj_struct['bbox'] = [int(bbox.find('xmin').text),
int(bbox.find('ymin').text),
int(bbox.find('xmax').text),
int(bbox.find('ymax').text)]
objects.append(obj_struct)
return objects
def voc_ap(rec, prec, use_07_metric=False): # voc2007的计算方式和voc2012的计算方式不同,目前一般采用第二种
""" ap = voc_ap(rec, prec, [use_07_metric])
Compute VOC AP given precision and recall.
If use_07_metric is true, uses the
VOC 07 11 point method (default:False).
"""
if use_07_metric:
# 11 point metric
ap = 0.
for t in np.arange(0., 1.1, 0.1):
if np.sum(rec >= t) == 0:
p = 0
else:
p = np.max(prec[rec >= t])
ap = ap + p / 11.
else:
# correct AP calculation
# first append sentinel values at the end
mrec = np.concatenate(([0.], rec, [1.]))
mpre = np.concatenate(([0.], prec, [0.]))
# compute the precision envelope
for i in range(mpre.size - 1, 0, -1):
mpre[i - 1] = np.maximum(mpre[i - 1], mpre[i])
# to calculate area under PR curve, look for points
# where X axis (recall) changes value
i = np.where(mrec[1:] != mrec[:-1])[0]
# and sum (\Delta recall) * prec
ap = np.sum((mrec[i + 1] - mrec[i]) * mpre[i + 1])
return ap
## 程序入口
def voc_eval(detpath, # 保存检测到的目标框的文件路径,每一类的目标框单独保存在一个文件
annopath, # Annotations的路径
imagesetfile, # 测试图片名字列表
classname, # 类别名称
cachedir, # 缓存文件夹
ovthresh=0.5, # IoU阈值
use_07_metric=False): # mAP计算方法
"""rec, prec, ap = voc_eval(detpath,
annopath,
imagesetfile,
classname,
[ovthresh],
[use_07_metric])
Top level function that does the PASCAL VOC evaluation.
detpath: Path to detections
detpath.format(classname) should produce the detection results file.
annopath: Path to annotations
annopath.format(imagename) should be the xml annotations file.
imagesetfile: Text file containing the list of images, one image per line.
classname: Category name (duh)
cachedir: Directory for caching the annotations
[ovthresh]: Overlap threshold (default = 0.5)
[use_07_metric]: Whether to use VOC07's 11 point AP computation
(default False)
"""
# assumes detections are in detpath.format(classname)
# assumes annotations are in annopath.format(imagename)
# assumes imagesetfile is a text file with each line an image name
# cachedir caches the annotations in a pickle file
# first load gt 获取真实目标框
# 当程序第一次运行时,会读取Annotations下的xml文件获取每张图片中真实的目标框
# 然后把获取的结果保存在annotations_cache文件夹中
# 以后再次运行时直接从缓存文件夹中读取真实目标
if not os.path.isdir(cachedir):
os.mkdir(cachedir)
cachefile = os.path.join(cachedir, 'annots.pkl')
# read list of images
with open(imagesetfile, 'r') as f:
lines = f.readlines()
imagenames = [x.strip() for x in lines]
if not os.path.isfile(cachefile):
# load annots
recs = {}
for i, imagename in enumerate(imagenames):
recs[imagename] = parse_rec(annopath.format(imagename))
if i % 100 == 0:
print 'Reading annotation for {:d}/{:d}'.format(
i + 1, len(imagenames))
# save
print 'Saving cached annotations to {:s}'.format(cachefile)
with open(cachefile, 'w') as f:
cPickle.dump(recs, f)
else:
# load
with open(cachefile, 'r') as f:
recs = cPickle.load(f)
# extract gt objects for this class 提取该类的真实目标
class_recs = {}
npos = 0 #保存该类一共有多少真实目标
for imagename in imagenames:
R = [obj for obj in recs[imagename] if obj['name'] == classname] # 保存名字为imagename的图片中,类别为classname的目标框的信息
bbox = np.array([x['bbox'] for x in R]) #目标框的坐标
difficult = np.array([x['difficult'] for x in R]).astype(np.bool) #是否是难以识别的目标
det = [False] * len(R) #每一个目标框对应一个det[i],用来判断该目标框是否已经处理过
npos = npos + sum(~difficult) #计算总的目标个数
class_recs[imagename] = {'bbox': bbox, # 把每一张图像中的目标框信息放到class_recs中
'difficult': difficult,
'det': det}
# read dets
detfile = detpath.format(classname) # 打开classname类别检测到的目标框文件
with open(detfile, 'r') as f:
lines = f.readlines()
splitlines = [x.strip().split(' ') for x in lines]
image_ids = [x[0] for x in splitlines] # 图像名字
confidence = np.array([float(x[1]) for x in splitlines]) # 置信度
BB = np.array([[float(z) for z in x[2:]] for x in splitlines]) # 目标框坐标
# sort by confidence 按照置信度排序
sorted_ind = np.argsort(-confidence)
sorted_scores = np.sort(-confidence)
BB = BB[sorted_ind, :]
image_ids = [image_ids[x] for x in sorted_ind]
# go down dets and mark TPs and FPs
nd = len(image_ids) # 统计检测到的目标框个数
tp = np.zeros(nd) # 创建tp列表,列表长度为目标框个数
fp = np.zeros(nd) # 创建fp列表,列表长度为目标框个数
for d in range(nd):
R = class_recs[image_ids[d]] # 得到图像名字为image_ids[d]真实的目标框信息
bb = BB[d, :].astype(float) # 得到图像名字为image_ids[d]检测的目标框坐标
ovmax = -np.inf
BBGT = R['bbox'].astype(float) # 得到图像名字为image_ids[d]真实的目标框坐标
if BBGT.size > 0:
# compute overlaps 计算IoU
# intersection
ixmin = np.maximum(BBGT[:, 0], bb[0])
iymin = np.maximum(BBGT[:, 1], bb[1])
ixmax = np.minimum(BBGT[:, 2], bb[2])
iymax = np.minimum(BBGT[:, 3], bb[3])
iw = np.maximum(ixmax - ixmin + 1., 0.)
ih = np.maximum(iymax - iymin + 1., 0.)
inters = iw * ih
# union
uni = ((bb[2] - bb[0] + 1.) * (bb[3] - bb[1] + 1.) +
(BBGT[:, 2] - BBGT[:, 0] + 1.) *
(BBGT[:, 3] - BBGT[:, 1] + 1.) - inters)
overlaps = inters / uni
ovmax = np.max(overlaps) # 检测到的目标框可能预若干个真实目标框都有交集,选择其中交集最大的
jmax = np.argmax(overlaps)
if ovmax > ovthresh: # IoU是否大于阈值
if not R['difficult'][jmax]: # 真实目标框是否难以识别
if not R['det'][jmax]: # 该真实目标框是否已经统计过
tp[d] = 1. # 将tp对应第d个位置变成1
R['det'][jmax] = 1 # 将该真实目标框做标记
else:
fp[d] = 1. # 否则将fp对应的位置变为1
else:
fp[d] = 1. # 否则将fp对应的位置变为1
# compute precision recall
fp = np.cumsum(fp) # 按列累加,最大值即为tp数量
tp = np.cumsum(tp) # 按列累加,最大值即为fp数量
rec = tp / float(npos) # 计算recall
# avoid divide by zero in case the first detection matches a difficult
# ground truth
prec = tp / np.maximum(tp + fp, np.finfo(np.float64).eps) # 计算精度
ap = voc_ap(rec, prec, use_07_metric) # 计算ap
return rec, prec, ap
根据具体情况修改具体程序的内容,执行compute_mAP.py(注意需要将两文件放到统级文件夹中)及科技算数出结果
6.3综合计算性能指标
修改yolov3的darknet文件夹example文件夹中的detector程序(计算ap值、recall值、avg iou值、precision值、fp、tp以及绘制P-R曲线指标所需的precision和recall值等值)-------------------6.3节的指标计算非常重要--------------------
在detector文件中添加计算map的函数并进行设置。
在linux系统终端命令行中输入命令计算map。
操作的具体步骤为:
1.找到detector.c文件的最后一段代码:
if(0==strcmp(argv[2], "test")) test_detector(datacfg, cfg, weights, filename, thresh, hier_thresh, outfile, fullscreen);
else if(0==strcmp(argv[2], "train")) train_detector(datacfg, cfg, weights, gpus, ngpus, clear);
else if(0==strcmp(argv[2], "valid")) validate_detector(datacfg, cfg, weights, outfile);
else if(0==strcmp(argv[2], "valid2")) validate_detector_flip(datacfg, cfg, weights, outfile);
else if(0==strcmp(argv[2], "recall")) validate_detector_recall(datacfg, cfg, weights);
在其后面加上一条代码语句:
else if(0==strcmp(argv[2], "map")) validate_detector_map(datacfg, cfg, weights, thresh);
2.在detector.c程序中的任意位置添加以下代码:
typedef struct {
box b;
float p;
int class_id;
int image_index;
int truth_flag;
int unique_truth_index;
} box_prob;
int detections_comparator(const void *pa, const void *pb)
{
box_prob a = *(box_prob *)pa;
box_prob b = *(box_prob *)pb;
float diff = a.p - b.p;
if (diff < 0) return 1;
else if (diff > 0) return -1;
return 0;
}
void validate_detector_map(char *datacfg, char *cfgfile, char *weightfile, float thresh_calc_avg_iou)
{
list *options = read_data_cfg(datacfg); //get .data file
char *valid_images = option_find_str(options, "valid", "data/train.txt"); //point to the path of valid images
char *difficult_valid_images = option_find_str(options, "difficult", NULL); //get the path to the 'difficult', if it doesn't exist,replace it with NULL
char *name_list = option_find_str(options, "names", "data/names.list"); // find name of each category
char **names = get_labels(name_list);
//char *mapf = option_find_str(options, "map", 0); // get the 'map', what is the map
//int *map = 0;
//if (mapf) map = read_map(mapf);
FILE* reinforcement_fd = NULL;
network *net = load_network(cfgfile, weightfile, 0);
set_batch_network(net, 1);
//fuse_conv_batchnorm(net);
//calculate_binary_weights(net);
srand(time(0));
list *plist = get_paths(valid_images);
char **paths = (char **)list_to_array(plist);
char **paths_dif = NULL;
if (difficult_valid_images) {
list *plist_dif = get_paths(difficult_valid_images);
paths_dif = (char **)list_to_array(plist_dif);
}
layer l = net->layers[net->n - 1];
int classes = l.classes;
int m = plist->size;
int i = 0;
int t;
const float thresh = .005;
const float nms = .45;
const float iou_thresh = 0.5;
int nthreads = 4;
image *val = calloc(nthreads, sizeof(image));
image *val_resized = calloc(nthreads, sizeof(image));
image *buf = calloc(nthreads, sizeof(image));
image *buf_resized = calloc(nthreads, sizeof(image));
pthread_t *thr = calloc(nthreads, sizeof(pthread_t));
load_args args = {0};
args.w = net->w;
args.h = net->h;
//args.type = IMAGE_DATA;
args.type = LETTERBOX_DATA;
//const float thresh_calc_avg_iou = 0.24;
float avg_iou = 0;
int tp_for_thresh = 0;
int fp_for_thresh = 0;
box_prob *detections = calloc(1, sizeof(box_prob));
int detections_count = 0;
int unique_truth_count = 0;
int *truth_classes_count = calloc(classes, sizeof(int));
for (t = 0; t < nthreads; ++t) {
args.path = paths[i + t];
args.im = &buf[t];
args.resized = &buf_resized[t];
thr[t] = load_data_in_thread(args);
}
time_t start = time(0);
for (i = nthreads; i < m + nthreads; i += nthreads) {
fprintf(stderr, "%d\n", i);
for (t = 0; t < nthreads && i + t - nthreads < m; ++t) {
pthread_join(thr[t], 0);
val[t] = buf[t];
val_resized[t] = buf_resized[t];
}
for (t = 0; t < nthreads && i + t < m; ++t) {
args.path = paths[i + t];
args.im = &buf[t];
args.resized = &buf_resized[t];
thr[t] = load_data_in_thread(args);
}
for (t = 0; t < nthreads && i + t - nthreads < m; ++t) {
const int image_index = i + t - nthreads;
char *path = paths[image_index];
char *id = basecfg(path);
float *X = val_resized[t].data;
network_predict(net, X);
int nboxes = 0;
float hier_thresh = 0;
detection *dets;
if (args.type == LETTERBOX_DATA) {
//int letterbox = 1;
dets = get_network_boxes(net, val[t].w, val[t].h, thresh, hier_thresh, 0, 1, &nboxes);
}
else {
//int letterbox = 0;
dets = get_network_boxes(net, 1, 1, thresh, hier_thresh, 0, 0, &nboxes);
}
//detection *dets = get_network_boxes(&net, val[t].w, val[t].h, thresh, hier_thresh, 0, 1, &nboxes, letterbox); // for letterbox=1
if (nms) do_nms_sort(dets, nboxes, l.classes, nms);
char labelpath[4096];
find_replace(path, "images", "labels", labelpath);
find_replace(labelpath, "JPEGImages", "labels", labelpath);
find_replace(labelpath, ".jpg", ".txt", labelpath);
find_replace(labelpath, ".JPEG", ".txt", labelpath);
int num_labels = 0;
box_label *truth = read_boxes(labelpath, &num_labels);
int i, j;
for (j = 0; j < num_labels; ++j) {
truth_classes_count[truth[j].id]++;
}
// difficult
box_label *truth_dif = NULL;
int num_labels_dif = 0;
if (paths_dif)
{
char *path_dif = paths_dif[image_index];
char labelpath_dif[4096];
//replace_image_to_label(path_dif, labelpath_dif);
find_replace(path_dif, "images", "labels", labelpath_dif);
find_replace(labelpath_dif, "JPEGImages", "labels", labelpath_dif);
find_replace(labelpath_dif, ".jpg", ".txt", labelpath_dif);
find_replace(labelpath_dif, ".JPEG", ".txt", labelpath_dif);
truth_dif = read_boxes(labelpath_dif, &num_labels_dif);
}
const int checkpoint_detections_count = detections_count;
for (i = 0; i < nboxes; ++i) {
int class_id;
for (class_id = 0; class_id < classes; ++class_id) {
float prob = dets[i].prob[class_id];
if (prob > 0) {
detections_count++;
detections = realloc(detections, detections_count * sizeof(box_prob));
detections[detections_count - 1].b = dets[i].bbox;
detections[detections_count - 1].p = prob;
detections[detections_count - 1].image_index = image_index;
detections[detections_count - 1].class_id = class_id;
detections[detections_count - 1].truth_flag = 0;
detections[detections_count - 1].unique_truth_index = -1;
int truth_index = -1;
float max_iou = 0;
for (j = 0; j < num_labels; ++j)
{
box t = { truth[j].x, truth[j].y, truth[j].w, truth[j].h };
//printf(" IoU = %f, prob = %f, class_id = %d, truth[j].id = %d \n",
//box_iou(dets[i].bbox, t), prob, class_id, truth[j].id);
float current_iou = box_iou(dets[i].bbox, t);
if (current_iou > iou_thresh && class_id == truth[j].id) {
if (current_iou > max_iou) {
max_iou = current_iou;
truth_index = unique_truth_count + j;
}
}
}
// best IoU
if (truth_index > -1) {
detections[detections_count - 1].truth_flag = 1;
detections[detections_count - 1].unique_truth_index = truth_index;
}
else {
// if object is difficult then remove detection
for (j = 0; j < num_labels_dif; ++j) {
box t = { truth_dif[j].x, truth_dif[j].y, truth_dif[j].w, truth_dif[j].h };
float current_iou = box_iou(dets[i].bbox, t);
if (current_iou > iou_thresh && class_id == truth_dif[j].id) {
--detections_count;
break;
}
}
}
// calc avg IoU, true-positives, false-positives for required Threshold
if (prob > thresh_calc_avg_iou) {
int z, found = 0;
for (z = checkpoint_detections_count; z < detections_count-1; ++z)
if (detections[z].unique_truth_index == truth_index) {
found = 1; break;
}
if(truth_index > -1 && found == 0) {
avg_iou += max_iou;
++tp_for_thresh;
}
else
fp_for_thresh++;
}
}
}
}
unique_truth_count += num_labels;
//static int previous_errors = 0;
//int total_errors = fp_for_thresh + (unique_truth_count - tp_for_thresh);
//int errors_in_this_image = total_errors - previous_errors;
//previous_errors = total_errors;
//if(reinforcement_fd == NULL) reinforcement_fd = fopen("reinforcement.txt", "wb");
//char buff[1000];
//sprintf(buff, "%s\n", path);
//if(errors_in_this_image > 0) fwrite(buff, sizeof(char), strlen(buff), reinforcement_fd);
free_detections(dets, nboxes);
free(id);
free_image(val[t]);
free_image(val_resized[t]);
}
}
if((tp_for_thresh + fp_for_thresh) > 0)
avg_iou = avg_iou / (tp_for_thresh + fp_for_thresh);
// SORT(detections)
qsort(detections, detections_count, sizeof(box_prob), detections_comparator);
typedef struct {
double precision;
double recall;
int tp, fp, fn;
} pr_t;
// for PR-curve
pr_t **pr = calloc(classes, sizeof(pr_t*));
for (i = 0; i < classes; ++i) {
pr[i] = calloc(detections_count, sizeof(pr_t));
}
printf("detections_count = %d, unique_truth_count = %d \n", detections_count, unique_truth_count);
int *truth_flags = calloc(unique_truth_count, sizeof(int));
int rank;
for (rank = 0; rank < detections_count; ++rank) {
if(rank % 100 == 0)
printf(" rank = %d of ranks = %d \r", rank, detections_count);
if (rank > 0) {
int class_id;
for (class_id = 0; class_id < classes; ++class_id) {
pr[class_id][rank].tp = pr[class_id][rank - 1].tp;
pr[class_id][rank].fp = pr[class_id][rank - 1].fp;
}
}
box_prob d = detections[rank];
// if (detected && isn't detected before)
if (d.truth_flag == 1) {
if (truth_flags[d.unique_truth_index] == 0)
{
truth_flags[d.unique_truth_index] = 1;
pr[d.class_id][rank].tp++; // true-positive
}
}
else {
pr[d.class_id][rank].fp++; // false-positive
}
for (i = 0; i < classes; ++i)
{
const int tp = pr[i][rank].tp;
const int fp = pr[i][rank].fp;
const int fn = truth_classes_count[i] - tp; // false-negative = objects - true-positive
pr[i][rank].fn = fn;
if ((tp + fp) > 0) pr[i][rank].precision = (double)tp / (double)(tp + fp);
else pr[i][rank].precision = 0;
if ((tp + fn) > 0) pr[i][rank].recall = (double)tp / (double)(tp + fn);
else pr[i][rank].recall = 0;
}
}
free(truth_flags);
double mean_average_precision = 0;
for (i = 0; i < classes; ++i) {
double avg_precision = 0;
int point;
for (point = 0; point < 11; ++point) {
double cur_recall = point * 0.1;
double cur_precision = 0;
for (rank = 0; rank < detections_count; ++rank)
{
if (pr[i][rank].recall >= cur_recall) { // > or >=
if (pr[i][rank].precision > cur_precision) {
cur_precision = pr[i][rank].precision;
}
}
}
printf("class_id = %d, point = %d, cur_recall = %.4f, cur_precision = %.4f \n", i, point, cur_recall, cur_precision);
avg_precision += cur_precision;
}
avg_precision = avg_precision / 11; // ??
printf("class_id = %d, name = %s, \t ap = %2.2f %% \n", i, names[i], avg_precision*100);
mean_average_precision += avg_precision;
}
printf("---------------------caculate end!!------------------------\n");
const float cur_precision = (float)tp_for_thresh / ((float)tp_for_thresh + (float)fp_for_thresh);
const float cur_recall = (float)tp_for_thresh / ((float)tp_for_thresh + (float)(unique_truth_count - tp_for_thresh));
const float f1_score = 2.F * cur_precision * cur_recall / (cur_precision + cur_recall);
printf(" for thresh = %1.2f, precision = %1.2f, recall = %1.2f, F1-score = %1.2f \n",
thresh_calc_avg_iou, cur_precision, cur_recall, f1_score);
printf(" for thresh = %0.2f, TP = %d, FP = %d, FN = %d, average IoU = %2.2f %% \n",
thresh_calc_avg_iou, tp_for_thresh, fp_for_thresh, unique_truth_count - tp_for_thresh, avg_iou * 100);
mean_average_precision = mean_average_precision / classes;
printf("\n mean average precision (mAP) = %f, or %2.2f %% \n", mean_average_precision, mean_average_precision*100);
for (i = 0; i < classes; ++i) {
free(pr[i]);
}
free(pr);
free(detections);
free(truth_classes_count);
fprintf(stderr, "Total Detection Time: %f Seconds\n", (double)(time(0) - start));
if (reinforcement_fd != NULL) fclose(reinforcement_fd);
}
3.detector.c中代码设置完成后在linux终端命令行中输入以下命令:
./darknet detector map data/voc.data cfg/yolov3-voc.cfg yolov3-voc.weights
即可计算map值
4.在Linux终端输入上一节的命令,执行结果如下图所示: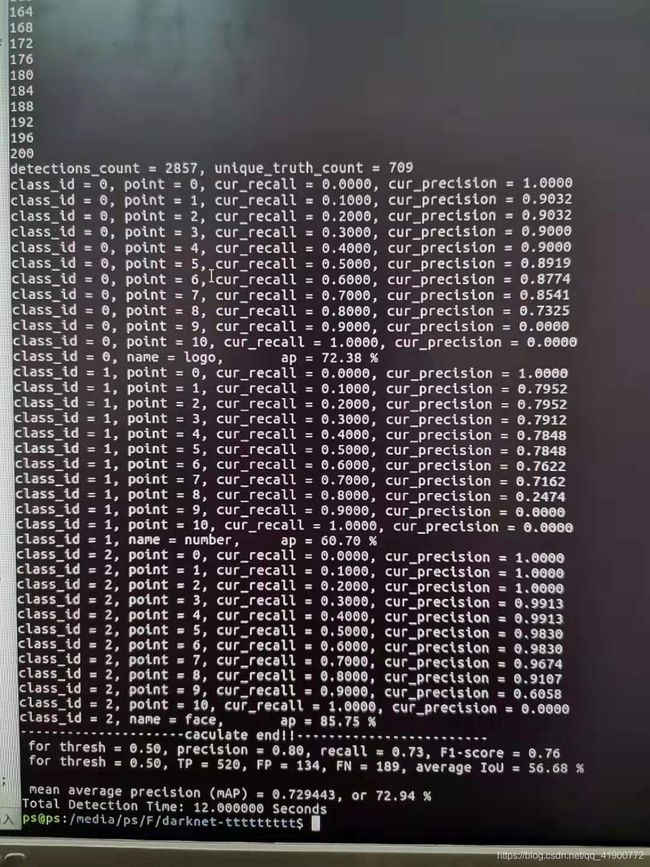
其中:
每个AP中输出的“cur_recall与cur_precision”为P-R指标曲线绘制所需要的数据;
“caculate end!!”下方的指标即为算法所求的指标:ap值、recall值、avg iou值、precision值等。
7.detector.c文件中评价函数的使用
7.1 对于单张图片测试(test)
- 测试单张图片:./darknet detector test
文件中batch和subdivisions两项必须为1。 - 测试时还可以用-thresh和-hier选项指定对应参数。
7.2 (valid)
-
./darknet detector valid
-
文件中batch和subdivisions两项必须为1。 -
结果生成在
的results指定的目录下以 开头的若干文件中,若 没有指定results,那么默认为 /results。
7.3(recall)
-
validate_detector_recall函数定义和调用改为:
函数中:void validate_detector_recall(char *datacfg, char *cfgfile, char *weightfile) 主函数中调用:validate_detector_recall(datacfg, cfg, weights); -
validate_detector_recall内的plist和paths的如下初始化代码:
list *plist = get_paths("data/voc.2007.test"); char **paths = (char **)list_to_array(plist); 修改为: list *options = read_data_cfg(datacfg); char *valid_images = option_find_str(options, "valid", "data/train.list"); list *plist = get_paths(valid_images); char **paths = (char **)list_to_array(plist); -
上述修改完之后务必记住要在darknet下重新make一下就可以进行recall命令:
./darknet detector recall cfg/voc.data cfg/yolo-voc.cfg backup/yolo-voc_final.weights
7.4批量测试图片
1. 用下面代码替换detector.c文件(example文件夹下)的void test_detector函数(注意有3处输出批量测试图片的路径要改成自己批量保存图片的路径)
void test_detector(char *datacfg, char *cfgfile, char *weightfile, char *filename, float thresh, float hier_thresh, char *outfile, int fullscreen)
{
list *options = read_data_cfg(datacfg);
char *name_list = option_find_str(options, "names", "data/names.list");
char **names = get_labels(name_list);
image **alphabet = load_alphabet();
network *net = load_network(cfgfile, weightfile, 0);
set_batch_network(net, 1);
srand(2222222);
double time;
char buff[256];
char *input = buff;
float nms=.45;
int i=0;
while(1){
if(filename){
strncpy(input, filename, 256);
image im = load_image_color(input,0,0);
image sized = letterbox_image(im, net->w, net->h);
//image sized = resize_image(im, net->w, net->h);
//image sized2 = resize_max(im, net->w);
//image sized = crop_image(sized2, -((net->w - sized2.w)/2), -((net->h - sized2.h)/2), net->w, net->h);
//resize_network(net, sized.w, sized.h);
layer l = net->layers[net->n-1];
float *X = sized.data;
time=what_time_is_it_now();
network_predict(net, X);
printf("%s: Predicted in %f seconds.\n", input, what_time_is_it_now()-time);
int nboxes = 0;
detection *dets = get_network_boxes(net, im.w, im.h, thresh, hier_thresh, 0, 1, &nboxes);
//printf("%d\n", nboxes);
//if (nms) do_nms_obj(boxes, probs, l.w*l.h*l.n, l.classes, nms);
if (nms) do_nms_sort(dets, nboxes, l.classes, nms);
draw_detections(im, dets, nboxes, thresh, names, alphabet, l.classes);
free_detections(dets, nboxes);
if(outfile)
{
save_image(im, outfile);
}
else{
save_image(im, "predictions");
#ifdef OPENCV
cvNamedWindow("predictions", CV_WINDOW_NORMAL);
if(fullscreen){
cvSetWindowProperty("predictions", CV_WND_PROP_FULLSCREEN, CV_WINDOW_FULLSCREEN);
}
show_image(im, "predictions");
cvWaitKey(0);
cvDestroyAllWindows();
#endif
}
free_image(im);
free_image(sized);
if (filename) break;
}
else {
printf("Enter Image Path: ");
fflush(stdout);
input = fgets(input, 256, stdin);
if(!input) return;
strtok(input, "\n");
list *plist = get_paths(input);
char **paths = (char **)list_to_array(plist);
printf("Start Testing!\n");
int m = plist->size;
if(access("/home/FENGsl/darknet/data/out",0)==-1)//"/home/FENGsl/darknet/data"修改成自己的路径*************************************************
{
if (mkdir("/home/FENGsl/darknet/data/out",0777))//"/home/FENGsl/darknet/data"修改成自己的路径*************************************************
{
printf("creat file bag failed!!!");
}
}
for(i = 0; i < m; ++i){
char *path = paths[i];
image im = load_image_color(path,0,0);
image sized = letterbox_image(im, net->w, net->h);
//image sized = resize_image(im, net->w, net->h);
//image sized2 = resize_max(im, net->w);
//image sized = crop_image(sized2, -((net->w - sized2.w)/2), -((net->h - sized2.h)/2), net->w, net->h);
//resize_network(net, sized.w, sized.h);
layer l = net->layers[net->n-1];
float *X = sized.data;
time=what_time_is_it_now();
network_predict(net, X);
printf("Try Very Hard:");
printf("%s: Predicted in %f seconds.\n", path, what_time_is_it_now()-time);
int nboxes = 0;
detection *dets = get_network_boxes(net, im.w, im.h, thresh, hier_thresh, 0, 1, &nboxes);
//printf("%d\n", nboxes);
//if (nms) do_nms_obj(boxes, probs, l.w*l.h*l.n, l.classes, nms);
if (nms) do_nms_sort(dets, nboxes, l.classes, nms);
draw_detections(im, dets, nboxes, thresh, names, alphabet, l.classes);
free_detections(dets, nboxes);
if(outfile){
save_image(im, outfile);
}
else{
char b[2048];
sprintf(b,"/home/FENGsl/darknet/data/out/%s",GetFilename(path));//"/home/FENGsl/darknet/data"修改成自己的路径*******************************
save_image(im, b);
printf("save %s successfully!\n",GetFilename(path));
#ifdef OPENCV
cvNamedWindow("predictions", CV_WINDOW_NORMAL);
if(fullscreen){
cvSetWindowProperty("predictions", CV_WND_PROP_FULLSCREEN, CV_WINDOW_FULLSCREEN);
}
show_image(im, "predictions");
cvWaitKey(0);
cvDestroyAllWindows();
#endif
}
free_image(im);
free_image(sized);
if (filename) break;
}
}
}
}
2. 在前面添加*GetFilename(char *p)函数(注意后面的注释)
#include "darknet.h"
#include
#include
#include
#include
static int coco_ids[] = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,27,28,31,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,46,47,48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,67,70,72,73,74,75,76,77,78,79,80,81,82,84,85,86,87,88,89,90};
char *GetFilename(char *p)
{
static char name[20]={""};
char *q = strrchr(p,'/') + 1;
strncpy(name,q,6);//注意后面的6,如果你的测试集的图片的名字字符(不包括后缀)是其他长度,请改为你需要的长度(官方的默认的长度是6)
return name;
}
-
在darknet下重新make,执行命令即可
-
执行批量测试命令如下:
./darknet detector test cfg/voc.data cfg/yolov3-voc.cfg backup/yolov3-voc_final.weights layer filters size input output ....... 106 detection Loading weights from yolov3.weights...Done! Enter Image Path: -
Enter Image Path:后面输入你的txt文件路径(你准备好的所有测试图片的路径全部存放在一个txt文件里),你可以复制voc.data文件里的valid后面的路径,就可以了,如下:
classes= 3
train =/home/FENGsl/darknet/data/train.txt
valid = /home/FENGsl/darknet/data/2007_test.txt
names = data/voc.names
backup = backup
- 然后你所有的图片都保存在了data/out文件夹下
7.5 根据坐标裁剪原图并保存(本小节参考了:输出yolo的测试结果,根据坐标裁剪原图并保存)
7.5.1 单张图片
主要对src/image.c文件中的draw_detections函数做了修改。
//添加了 char *filename ,为了得到当前的图片名。
void draw_detections(image im, int num, float thresh, box *boxes, float **probs, float **masks, char **names, image **alphabet, int classes, char *filename)
{
printf("num %d\n", num);
float rawmax[num];
int i,j;
int params[3];
char savePath[100] = "";
//为了得到top19的框,将每个框按照最大概率值进行了排序,取了top19. b,c矩阵都是为了得到top9对应的原框的下标,好得到坐标点。
for(i =0; i rawmax[i]){
rawmax[i] = probs[i][j]; }
}
}
for( i =0;i 0)
printf("rawmax[ %d]:%f\n",i,rawmax[i]);
}
float b[num];
int c[num];
for(i =0; i im.w-1) right = im.w-1;
if(top < 0) top = 0;
if(bot > im.h-1) bot = im.h-1;
printf("c[%d]=%d %d %d %d %d\n", i,c[i],left,right,top,bot);
//接下来的操作需要导入opencv,在文件头应该加入
#ifdef OPENCV
#include "opencv2/highgui/highgui_c.h"
#include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc_c.h"
#endif
CvRect box = cvRect(left, top, right-left, bot-top);
IplImage* src = cvLoadImage(filename, -1);
CvSize size = cvSize(right-left, bot-top);
IplImage* roi = cvCreateImage(size, src->depth,src->nChannels);
cvSetImageROI(src, box);
cvCopy(src,roi,NULL);
char name1[4] = "dog";
char name2[5] = ".jpg";
char newname[100];
sprintf(newname,"%s_%d%s",name1,i,name2 ); //保存的图片名dog_i.jpg
cvSaveImage(newname,roi,0);
cvReleaseImage(&src);
cvReleaseImage(&roi);
}
因为这里讲行数参数加入了 char * filename,所以应该在对应的头文件中修改函数定义。
include/darknet.h ,修改函数定义为:
void draw_detections(image im, int num, float thresh, box *boxes, float **probs, float **masks, char **names, image **alphabet, int classes, char* filename);
examples/detector.c 的函数调用改为:
draw_detections(im, l.w*l.h*l.n, thresh, boxes, probs, masks, names, alphabet, l.classes, filename);
还有一些别的地方,因为加入了这个参数需要改动,根据make的提示,修改即可。
7.5.2批量图片
如果需要检测批量图片,只需要修改examples/detector.c 中的test_detector()函数
//加入filelist.读取test.txt,test.txt中每行保存一个图片路径
char **filelist = get_labels("../test.txt");
将:
while(1){
if(filename){……
……
}
修改为:
int index = 0;
while(filelist[index] != NULL){
filename = filelist[index];
printf("filename: %s\n", filename);
if(filename){ ……
……
index++;
}
去掉:
if(outfile){
save_image(im, outfile);
}
else{
save_image(im, "predictions");
#ifdef OPENCV
cvNamedWindow("predictions", CV_WINDOW_NORMAL);
if(fullscreen){
cvSetWindowProperty("predictions", CV_WND_PROP_FULLSCREEN, CV_WINDOW_FULLSCREEN);
}
show_image(im, "predictions");
cvWaitKey(0);
cvDestroyAllWindows();
#endif
}
if (filename) break;
修改后的test_detector()完整的为:
void test_detector(char *datacfg, char *cfgfile, char *weightfile, char *filename, float thresh, float hier_thresh, char *outfile, int fullscreen)
{
list *options = read_data_cfg(datacfg);
char *name_list = option_find_str(options, "names", "data/names.list");
char **names = get_labels(name_list);
image **alphabet = load_alphabet();
network *net = load_network(cfgfile, weightfile, 0);
set_batch_network(net, 1);
srand(2222222);
double time;
char buff[256];
char *input = buff;
int j;
float nms=.3;
char **filelist = get_labels("/home/wc/YOLO/darknet/data/test.txt");
int index = 0;
while(filelist[index] != NULL){
filename = filelist[index];
printf("filename: %s\n", filename);
// while(1){
if(filename){
strncpy(input, filename, 256);
} else {
printf("Enter Image Path: ");
fflush(stdout);
input = fgets(input, 256, stdin);
if(!input) return;
strtok(input, "\n");
}
image im = load_image_color(input,0,0);
image sized = letterbox_image(im, net->w, net->h);
//image sized = resize_image(im, net->w, net->h);
//image sized2 = resize_max(im, net->w);
//image sized = crop_image(sized2, -((net->w - sized2.w)/2), -((net->h - sized2.h)/2), net->w, net->h);
//resize_network(net, sized.w, sized.h);
layer l = net->layers[net->n-1];
box *boxes = calloc(l.w*l.h*l.n, sizeof(box));
float **probs = calloc(l.w*l.h*l.n, sizeof(float *));
for(j = 0; j < l.w*l.h*l.n; ++j) probs[j] = calloc(l.classes + 1, sizeof(float *));
float **masks = 0;
if (l.coords > 4){
masks = calloc(l.w*l.h*l.n, sizeof(float*));
for(j = 0; j < l.w*l.h*l.n; ++j) masks[j] = calloc(l.coords-4, sizeof(float *));
}
float *X = sized.data;
time=what_time_is_it_now();
network_predict(net, X);
printf("%s: Predicted in %f seconds.\n", input, what_time_is_it_now()-time);
//printf(boxes);
get_region_boxes(l, im.w, im.h, net->w, net->h, thresh, probs, boxes, masks, 0, 0, hier_thresh, 1);
if (nms) do_nms_sort(boxes, probs, l.w*l.h*l.n, l.classes, nms);
//else if (nms) do_nms_sort(boxes, probs, l.w*l.h*l.n, l.classes, nms);
//printf("start draw_detection");
draw_detections(im, l.w*l.h*l.n, thresh, boxes, probs, masks, names, alphabet, l.classes, filename);
/*
if(outfile){
save_image(im, outfile);
}
else{
save_image(im, "predictions");
#ifdef OPENCV
cvNamedWindow("predictions", CV_WINDOW_NORMAL);
if(fullscreen){
cvSetWindowProperty("predictions", CV_WND_PROP_FULLSCREEN, CV_WINDOW_FULLSCREEN);
}
show_image(im, "predictions");
cvWaitKey(0);
cvDestroyAllWindows();
#endif
}
*/
free_image(im);
free_image(sized);
free(boxes);
free_ptrs((void **)probs, l.w*l.h*l.n);
// if (filename) break;
index++;
}
}
*********************待更新