C++工程,protobuf工程应用(多路径下的编译),Makefile,CMakeList.txt,定义消息结构体proto文件,编辑prototxt文件,生成访问类,测试
文章目录
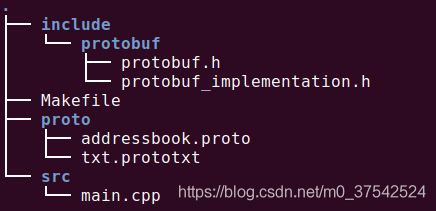
- 1,工程
-
- 1.1,定义消息结构体proto文件 --- addressbook.proto
- 1.2,文本格式prototxt 文件 --- txt.prototxt
- 1.3,protobuf操作接口
-
- 1.3.1,定义 --- protobuf.h
- 1.3.2,操作接口实现及测试代码 --- protobuf_implementation.h
- 1.4,Makefile
- 1.5,CMakeList.txt
- 2,编译测试
-
- 2.1,Makefile
-
- 2.1.1,生成访问类
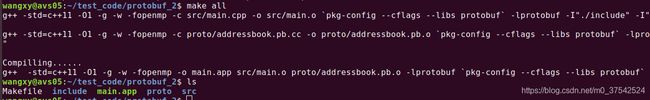
- 2.1.2,编译工程,生成可执行文件
- 2.1.3,测试
- 2.2,CMakeList.txt
-
- 2.2.1,生成Makefile
- 2.2.2,编译
- 2.2.3,测试
1,工程
| Makefile版本 | CMakeList.txt版本 |
 |
 |
1.1,定义消息结构体proto文件 — addressbook.proto
syntax = "proto2";
package tutorial;
message Person {
required string name = 1;
required int32 id = 2;
optional string email = 3;
enum PhoneType {
MOBILE = 0;
HOME = 1;
WORK = 2;
}
message PhoneNumber {
required string number = 1;
optional PhoneType type = 2 [default = HOME];
}
repeated PhoneNumber phones = 4;
}
message AddressBook {
repeated Person people = 1;
}
1.2,文本格式prototxt 文件 — txt.prototxt
people{
name: "123"
id: 1
email: "222"
phones{
number: "12334332"
type: HOME
}
}
1.3,protobuf操作接口
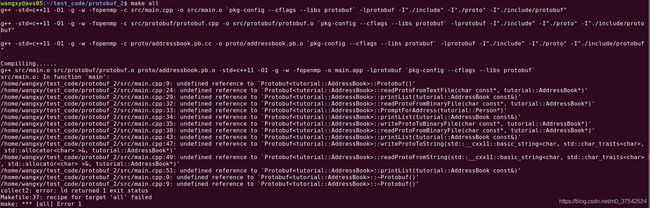
模板类的定义与实现有三种组织方式:
- 将定义与实现都放在同一个.h文件(头文件)中
- 将实现文件.cpp改成.h文件,并在定义文件中inculde该实现文件
- 在实现文件.cpp文件中实例化用到的所有模板
否则会报如下错误:undefined reference to `Protobuftutorial::AddressBook::Protobuf()
1.3.1,定义 — protobuf.h
#ifndef __PROTOBUF_H__
#define __PROTOBUF_H__
#include 1.3.2,操作接口实现及测试代码 — protobuf_implementation.h
#include "protobuf.h"
template <typename T> Protobuf<T>::Protobuf()
{
// Verify that the version of the library that we linked against is
// compatible with the version of the headers we compiled against.
GOOGLE_PROTOBUF_VERIFY_VERSION;
}
template <typename T> Protobuf<T>::~Protobuf() {
// Optional: Delete all global objects allocated by libprotobuf.
google::protobuf::ShutdownProtobufLibrary();
}
template <typename T> bool Protobuf<T>::readProtoFromTextFile(const char*
filename, T* proto) {
int fd = open(filename, O_RDONLY);
google::protobuf::io::FileInputStream* input = (
new google::protobuf::io::FileInputStream(fd));
bool success = google::protobuf::TextFormat::Parse(input, proto);
delete input;
close(fd);
return success;
}
template <typename T> bool Protobuf<T>::readProtoFromBinaryFile(const char*
filename, T* proto) {
std::ifstream model_file(filename);
return proto->ParseFromIstream(&model_file);
}
template <typename T> bool Protobuf<T>::writeProtoToBinaryFile(const char*
filename, T* proto) {
std::fstream model_file(filename,std::ios::out |std::ios::trunc |std::ios::binary);
return proto->SerializeToOstream(&model_file);
}
template <typename T> bool Protobuf<T>::readProtoFromString(std::string &buff,
T* proto) {
return proto->ParseFromString(buff);
}
template <typename T> bool Protobuf<T>::writeProtoToString(std::string &buff, T* proto) {
return proto->SerializeToString(&buff);
}
// Iterates though all people in the AddressBook and prints info about them.
template <typename T> void Protobuf<T>::printList(const T &address_book) {
for (int i = 0; i < address_book.people_size(); i++) {
const tutorial::Person &person = address_book.people(i);
std::cout << "Person ID: " << person.id() << std::endl;
std::cout << " Name: " << person.name() << std::endl;
if (person.has_email()) {
std::cout << " E-mail address: " << person.email() << std::endl;
}
for (int j = 0; j < person.phones_size(); j++) {
const tutorial::Person::PhoneNumber &phone_number = person.phones(j);
switch (phone_number.type()) {
case tutorial::Person::MOBILE:
std::cout << " Mobile phone #: ";
break;
case tutorial::Person::HOME:
std::cout << " Home phone #: ";
break;
case tutorial::Person::WORK:
std::cout << " Work phone #: ";
break;
}
std::cout << phone_number.number() << std::endl;
}
}
}
template <typename T> void Protobuf<T>::PromptForAddress(tutorial::Person *person) {
std::cout << "Enter person ID number: ";
int id;
std::cin >> id;
person->set_id(id);
std::cin.ignore(std::numeric_limits<std::streamsize>::max(),'\n');
// std::cin.ignore(256, '\n');//忽略最后的回车
std::cout << "Enter name: ";
getline(std::cin, *person->mutable_name());
std::cout << "Enter email address (blank for none): ";
std::string email;
getline(std::cin, email);
if (!email.empty()) {
person->set_email(email);
}
while (true) {
std::cout << "Enter a phone number (or leave blank to finish): ";
std::string number;
getline(std::cin, number);
if (number.empty()) {
break;
}
tutorial::Person::PhoneNumber *phone_number = person->add_phones();
phone_number->set_number(number);
std::cout << "Is this a mobile, home, or work phone? ";
std::string type;
getline(std::cin, type);
if (type == "mobile") {
phone_number->set_type(tutorial::Person::MOBILE);
} else if (type == "home") {
phone_number->set_type(tutorial::Person::HOME);
} else if (type == "work") {
phone_number->set_type(tutorial::Person::WORK);
} else {
std::cout << "Unknown phone type. Using default." << std::endl;
}
}
}
// Main function: Reads the entire address book from a file and prints all
// the information inside.
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
char *file_name = "proto/txt.prototxt";
char file_name_2[] = "binary.prototxt";
Protobuf<tutorial::AddressBook> pro;
tutorial::AddressBook address_book;
tutorial::AddressBook address_book_2;
tutorial::AddressBook address_book_3;
tutorial::AddressBook address_book_4;
if (argc != 2) {
std::cerr << "Usage: " << argv[0] << " ADDRESS_BOOK_FILE" << std::endl;
printf(" use dafaule address_book_file: %s\n", file_name);
}
else {
file_name = argv[1];
}
std::cout << "/************read txt file***********************/" << std::endl;
if(!pro.readProtoFromTextFile(file_name, &address_book))
{
std::cout<<"error opening train_val file"<<std::endl;
return -1;
}
pro.printList(address_book);
std::cout << "/***********add people and write binary file*****/" << std::endl;
pro.readProtoFromBinaryFile(file_name_2, &address_book_2);
pro.PromptForAddress(address_book_2.add_people());
pro.printList(address_book_2);
pro.writeProtoToBinaryFile(file_name_2, &address_book_2);
std::cout << "/************read binary file********************/" << std::endl;
if(!pro.readProtoFromBinaryFile(file_name_2, &address_book_3))
{
std::cout<<"error opening train_val file"<<std::endl;
return -1;
}
pro.printList(address_book_3);
std::cout << "/*************write-read string file*************/" << std::endl;
std::string buff;
pro.writeProtoToString(buff, &address_book_3);
pro.readProtoFromString(buff, &address_book_4);
pro.printList(address_book_4);
return 0;
}
1.4,Makefile
CXX=g++
LDFLAGS=-std=c++11 -O1 -g -w -fopenmp
CFLAGS = -lprotobuf
LIBS=`pkg-config --cflags --libs protobuf`
PROTO_FILE=addressbook
PROTO_SRC_DIR=./proto
PROTO_DST_DIR=./proto
TARGET=main.app
INC_PROTO = $(PROTO_DST_DIR)
INCLUDE_BASE = ./include
INC_PROTOBUF = $(INCLUDE_BASE)/protobuf
INCLUDE_DIR = -I"$(INCLUDE_BASE)" \
-I"$(INC_PROTO)" \
-I"$(INC_PROTOBUF)" \
SRC_PROTO = $(PROTO_SRC_DIR)/$(PROTO_FILE)
SRC_BASE = ./src
SRC_PROTOBUF = $(SRC_BASE)/protobuf
SRCS := $(wildcard $(SRC_BASE)/*.cpp) \
$(wildcard $(SRC_PROTOBUF)/*.cpp) \
OBJS := $(SRCS:%.cpp=%.o)
# 编译工程,生成可执行文件
all:$(OBJS) $(SRC_PROTO).pb.o
@echo "Compilling......"
$(CXX) $(LDFLAGS) -o $(TARGET) $^ $(CFLAGS) $(LIBS)
%.o:%.cpp
$(CXX) $(LDFLAGS) -c $< -o $@ $(LIBS) $(CFLAGS) $(INCLUDE_DIR)
@echo " "
$(SRC_PROTO).pb.o:$(SRC_PROTO).pb.cc
$(CXX) $(LDFLAGS) -c $< -o $@ $(LIBS) $(CFLAGS) $(INCLUDE_DIR)
@echo " "
# 生成访问类
cpp_out:
if [ ! -d $(PROTO_DST_DIR) ];then mkdir -p $(PROTO_DST_DIR); fi
protoc -I=$(PROTO_SRC_DIR) --cpp_out=$(PROTO_DST_DIR) $(PROTO_SRC_DIR)/$(PROTO_FILE).proto
.PHONY:clean
clean:
rm -rf $(TARGET) $(PROTO_DST_DIR)/*.pb.cc $(PROTO_DST_DIR)/*pb.h $(PROTO_DST_DIR)/*pb.o $(OBJS) *.prototxt
1.5,CMakeList.txt
#1.cmake verson,指定cmake版本
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.5)
#2.project name,指定项目的名称,一般和项目的文件夹名称对应
PROJECT(test_sqrt)
#3 Find required protobuf package
find_package(Protobuf REQUIRED)
if(PROTOBUF_FOUND)
message(STATUS "protobuf library found")
else()
message(FATAL_ERROR "protobuf library is needed but cant be found")
endif()
#4.生成pb.h、pb.cc必须要加的指令
include_directories(${PROTOBUF_INCLUDE_DIRS})
INCLUDE_DIRECTORIES(${CMAKE_CURRENT_BINARY_DIR})
PROTOBUF_GENERATE_CPP(PROTO_SRCS PROTO_HDRS ${CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR}/proto/addressbook.proto)
#5.head file path,头文件目录
INCLUDE_DIRECTORIES(${CMAKE_SOURCE_DIR}/include/protobuf)
#6.source directory,源文件目录
AUX_SOURCE_DIRECTORY(src DIR_SRCS)
#7.set environment variable,设置环境变量,编译用到的源文件全部都要放到这里,否则编译能够通过,
#但是执行的时候会出现各种问题,比如"symbol lookup error xxxxx , undefined symbol"
SET(TEST_MATH ${DIR_SRCS} ${PROTO_SRCS})
#8.add executable file,添加要编译的可执行文件
ADD_EXECUTABLE(${PROJECT_NAME} ${TEST_MATH})
#9.add link library,添加可执行文件所需要的库,比如我们用到了libm.so(命名规则:lib+name+.so),就添加该库的名称
TARGET_LINK_LIBRARIES(${PROJECT_NAME} ${PROTOBUF_LIBRARIES})
2,编译测试
2.1,Makefile
2.1.1,生成访问类
make cpp_out
2.1.2,编译工程,生成可执行文件
make all
2.1.3,测试
./protobuf
2.2,CMakeList.txt
2.2.1,生成Makefile
cmake ..
2.2.2,编译
make
2.2.3,测试
./test_sqrt ../proto/txt.prototxt