OpenGL 正交投影、透视除法、透视投影
正交投影(Orthographic projection)、透视除法(perspective division)、
透视投影(Perspective Projection)
在3D世界中正交投影矩阵 被 透视投影矩阵所代替。
归一化设备坐标
OpenGL的坐标空间是[-1, 1],x,y轴超过该区域的都将被切掉 看不见。
手机像素是 1280 X 720,归一化后 坐标空间从[1280X720],映射到[-1,1]
问题:导致物体变形,因为 x,y轴坐标长度都是1 - (-1)= 2,但x,y轴像素数量不同。y轴像素多,单位坐标就会变长。
办法:是短的轴映射为1,长的轴根据与短轴的比例 映射。[0, 1280] ,[0, 720]----》[-1280/720 , 1280/720],[-1, 1]。这个空间被称作
虚拟坐标空间。
在虚拟坐标空间上操作顶点,为了OpenGL最终正确渲染,渲染前还需 将虚拟坐标 映射为 归一设备坐标。
而这个映射叫做
正交投影(orthographic projection)
二维世界
正交投影(归 一化设备坐标,不变形)
该方法位于Matrix中
@Override
public void onSurfaceChanged(GL10 gl, int width, int height) {
gl.glViewport(0, 0, width, height);
final float aspectRatio = width > height ?
(float) width / (float) height :
(float) height / (float) width;
if (width > height) {
Matrix.orthoM(projectionMatrix, 0, -aspectRatio, aspectRatio, -1f, 1f, -1f, 1f);
} else {
Matrix.orthoM(projectionMatrix, 0, -1f, 1f, -aspectRatio, aspectRatio, -1f, 1f);
}
}
投影后的特点是 物体的远近,不影响投影的大小。
三维世界
透视除法
归一化设备之前,OpenGL执行的额外操作 透视除法
w分量除以x,y,z分量(w默认值是1),产生三维幻想 透视效应
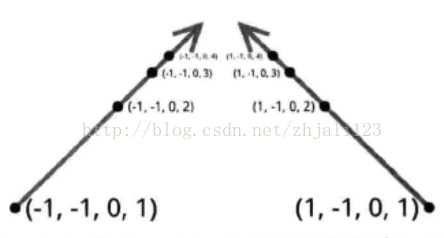
上图点坐标都是(-1, -1, 0),但是设置w后,(x,y,z,w)实际是(x/w, y/w, z/w),w越大越趋向于 归一化设备坐标的中心(0, 0, 0)。
其中z的数都为0,单凭w值就营造出三维效果。
透视投影矩阵(Perspective Projection)
不应指定投影除法中点的w值,而要通过矩阵生成。
视椎体(Frustum)
由透视投影矩阵和投影除法创造(如下图)
远端(far side):
近端(near side):
Focal Point:following the lines that extend from the large end to the small end of the frustum and then following them past the small end util they meet together.
Focal Length: represent by the value of z, The distance between the focal point and the small end of the frustum.
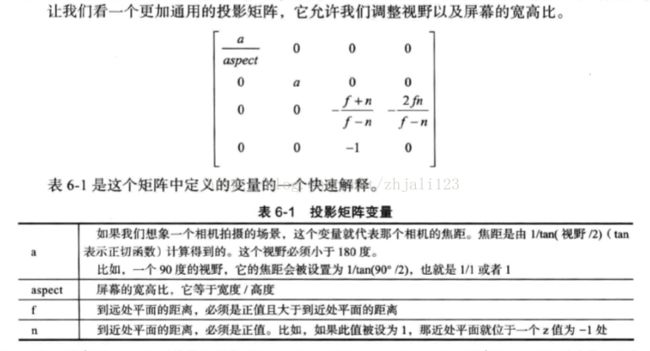
通用投影矩阵:调整视野,屏幕宽高比
以下公式 通过物体与焦点的距离(z)来映射w,z越大,w越大,物体越小
透视投影Android Matrix有两个方法,
frustumM()
有缺陷,影响某些类型的投影
perspectiveM(),
从Android的ICS(Ice Cream Sandwich)引入
所以最好自己写perspectiveM: r1
public static void perspectiveM (float[] m, float yFovInDegrees, float aspect,
float n, float f) {
final float angleInRadians = (float) (yFovInDegrees * Math.PI / 180.0);
final float a = (float) (1.0 / Math.tan(angleInRadians / 2.0));
m[0] = a / aspect;
m[1] = 0f;
m[2] = 0f;
m[3] = 0f;
m[4] = 0f;
m[5] = a;
m[6] = 0f;
m[7] = 0f;
m[8] = 0f;
m[9] = 0f;
m[10] = -((f+n) / (f-n));
m[11] = -1f;
m[12] = 0f;
m[13] = 0f;
m[14] = -((2f * f * n) / (f - n));
m[15] = 0f;
}
较宽的视野会引起形变
正交投影与透视投影区别
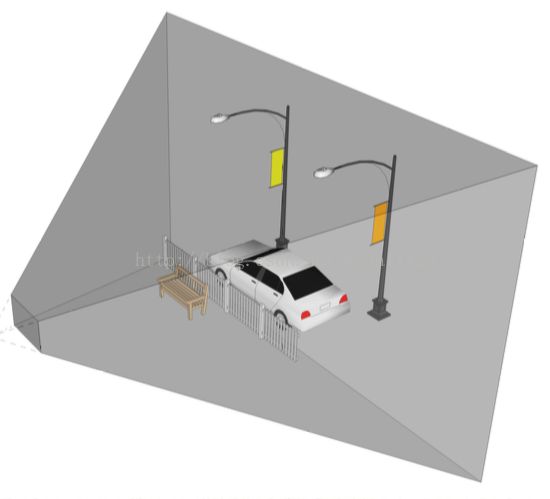
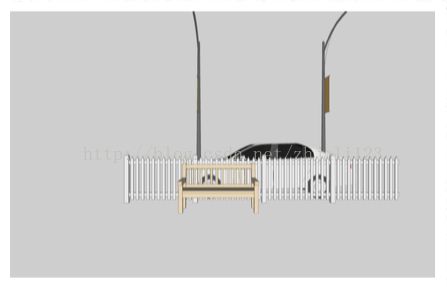
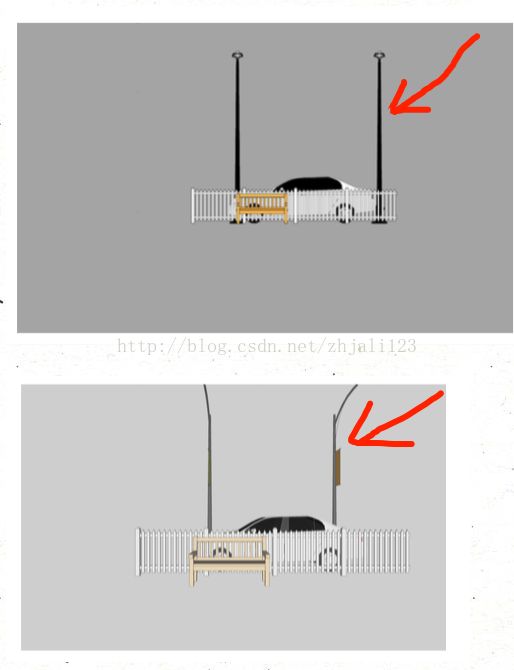
正交投影中平行的光 照射到与其平行的物体就变成点或者线了,看不到平行物体的侧面(就是图中的小旗子)
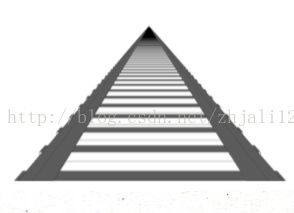
透视投影中平行的光实际上发散出去的(就像人眼看平行的铁轨,明明是平行的,但是透视效果确实两个平行铁轨越远越相较于某一点),实际的光是不平行的 当然就可以看到物体的侧面。
模型矩阵
用于移动物体,将模型矩阵合并到投影矩阵中
private final float[] modelMatrix = new float[16];
onSurfaceChanged() {
setIdentityM(modelMatrix, 0);
translateM(modelMatrix, 0, 0f, 0f, -2f);
}
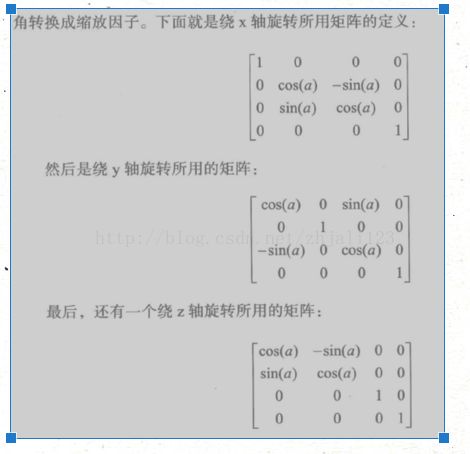
旋转矩阵
tow transformation steps and three different coordinate spaces;
Clip Space
4component of coordinates x,y,z,w
Any coordinate show rang in [-w, w], or it wil be cliped and can't be visible.
And is Clip space
Projection matrix
W越大离屏幕越远
Depth buffer:
the component Z as Depth buffer