干货 | YOLOV5 训练自动驾驶数据集,并转成tensorrt【左侧有码】
- 准备数据集
- 环境配置
- 配置文件修改
- 训练
- 推理
- 转Tensorrt
- 遇到的Bugs
一、数据集准备
1,BDD数据集
让我们来看看BDD100K数据集的概览。
BDD100K是最大的开放式驾驶视频数据集之一,其中包含10万个视频和10个任务,目的是方便评估自动驾驶图像识别算法的的进展。每个高分辨率视频一共40秒。该数据集包括超过1000个小时的驾驶数据,总共超过1亿帧。这些视频带有GPU / IMU数据以获取轨迹信息。该数据集具有地理,环境和天气多样性,从而能让模型能够识别多种场景,具备更多的泛化能力。这些丰富的户外场景和复杂的车辆运动使感知任务更具挑战性。该数据集上的任务包括图像标记,车道检测,可驾驶区域分割,道路对象检测,语义分割,实例分割,多对象检测跟踪,多对象分割跟踪,领域自适应和模仿学习。我们可以在BDD100K数据网站上下载数据。
Bdd100k的标签是由Scalabel生成的JSON格式。
- labels [ ]:
- id: int32
- category: string (classification)
- manualShape: boolean (whether the shape of the label is created or modified manually)
- manualAttributes: boolean (whether the attribute of the label is created or modified manually)
- score: float (the confidence or some other ways of measuring the quality of the label.)
- attributes:
- occluded: boolean
- truncated: boolean
- trafficLightColor: "red|green|yellow|none"
- areaType: "direct | alternative" (for driving area)
- laneDirection: "parallel|vertical" (for lanes)
- laneStyle: "solid | dashed" (for lanes)
- laneTypes: (for lanes)
- box2d:
- x1: float
- y1: float
- x2: float
- y2: float道路对象类别包括以下几类:
[
"bike",
"bus",
"car",
"motor",
"person",
"rider",
"traffic light",
"traffic sign",
"train",
"truck"
]我们实际关注的只有- labels [ ]栏目下的内容。
2,YOLO数据格式
每个图片文件.jpg,都有同一命名的标签文件.txt。
标签文件中每个对象独占一行,格式为
其中:
- 例如:
= / = / - 注意:
如下图所示:
YOLO V5的标签文件和图像文件应位于同一目录下。
3,BDD数据转YOLO格式
Berkerley 提供了Bdd100k数据集的标签查看及标签格式转化工具。由于没有直接从bdd100k转换成YOLO的工具,因此我们首先得使用将bdd100k的标签转换为coco格式,然后再将coco格式转换为yolo格式。
- bdd to coco
我的目的是识别包括不同颜色交通灯在内的所有交通对象,因此我们需要对原版的bdd2coco.py进行一些修改,以获取交通灯颜色并产生新的类别。
这是修改完的核心代码:
for label in i['labels']:
annotation = dict()
category=label['category']
if (category == "traffic light"):
color = label['attributes']['trafficLightColor']
category = "tl_" + color
if category in id_dict.keys():
empty_image = False
annotation["iscrowd"] = 0
annotation["image_id"] = image['id']
x1 = label['box2d']['x1']
y1 = label['box2d']['y1']
x2 = label['box2d']['x2']
y2 = label['box2d']['y2']
annotation['bbox'] = [x1, y1, x2-x1, y2-y1]
annotation['area'] = float((x2 - x1) * (y2 - y1))
annotation['category_id'] = id_dict[category]
annotation['ignore'] = 0
annotation['id'] = label['id']
annotation['segmentation'] = [[x1, y1, x1, y2, x2, y2, x2, y1]]
annotations.append(annotation)在完成bdd100k格式到yolo格式的转换后,会获得bdd100k_labels_images_det_coco_train.json和bdd100k_labels_images_det_coco_val.json两个文件。
- Coco to yolo
在完成先前的转换之后,我们需要将训练集和验证集的coco格式标签转换为yolo格式。注意需要分别指定训练集和验证集图片位置,对应的coco标签文件位置,及生成yolo标签的目标位置。
config_train ={
"datasets": "COCO",
"img_path": "bdd100k_images/bdd100k/images/100k/train",
"label": "labels/bdd100k_labels_images_det_coco_train.json",
"img_type": ".jpg",
"manipast_path": "./",
"output_path": "labels/trains/",
"cls_list": "bdd100k.names",
}
config_valid ={
"datasets": "COCO",
"img_path": "bdd100k_images/bdd100k/images/100k/val",
"label": "labels/bdd100k_labels_images_det_coco_val.json",
"img_type": ".jpg",
"manipast_path": "./",
"output_path": "labels/valids/",
"cls_list": "bdd100k.names",
}除此之外,我们还得将所有的类别写入bdd100k.names文件。
person
rider
car
bus
truck
bike
motor
tl_green
tl_red
tl_yellow
tl_none
traffic sign
train
tl_green运行Bdd_preprocessing中的完整代码可以完成Bdd100k格式标签到YOLO标签格式的转换。
Bdd2coco以及coco2yolo的详细说明可以参看bdd100k代码库和convert2Yolo代码库。
二、环境配置
1,官方代码
https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/tree/v3.0
由于后面转tensorrt版本支持yolov5到3.0版本,所以以3.0版本进行实验。
环境配置可通过下面命令进行一键配置。
# pip install -r requirements.txt
# base ----------------------------------------
Cython
matplotlib>=3.2.2
numpy>=1.18.5
opencv-python>=4.1.2
pillow
PyYAML>=5.3
scipy>=1.4.1
tensorboard>=2.2
torch>=1.6.0
torchvision>=0.7.0
tqdm>=4.41.0
# coco ----------------------------------------
# pycocotools>=2.0
# export --------------------------------------
# packaging # for coremltools
# coremltools==4.0b4
# onnx>=1.7.0
# scikit-learn==0.19.2 # for coreml quantization
# extras --------------------------------------
# thop # FLOPS computation
# seaborn # plotting三、配置文件修改
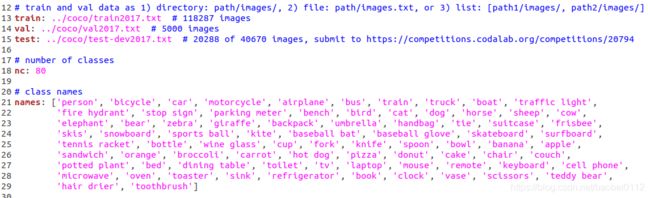
1,修改./data/coco.yaml--》存为bdd.yaml
修改内容:
(1)train/val/test 路径
其中的txt内容均为各集合图像实际绝对路径。
(2)nc:number class 类别数量,BDD数据类别为10
(3)names:前面bdd数据集介绍时候已经列出
2,./model/yolov5.yaml :
修改:nc为BDD数据类别数:10
3,./train.py
修改:
(1)--weights,这里s/m/l/x四个型号可以选择
(2)--cfg,这里s/m/l/x四个型号可以选择
(3)--data,选择根据coco.yaml修改后的bdd.yaml
(4)--batch-size 和 --img-size 可以再这里修改也可以默认不动,再训练命令行里设定
四、训练
默认训练命令,无需初始化模型
$ python train.py --data coco.yaml --cfg yolov5s.yaml --weights '' --batch-size 64
yolov5m 40
yolov5l 24
yolov5x 16训练过程中停止后 二次训练:
有预训练模型
python train.py --img 640 --batch 32 --epochs 300 --data './data/bdd.yaml' --cfg ./models/custom_yolov5x.yaml --weights "./weights/yolov5x.pt" --name yolov5x_bdd_prew --cache
从头训练
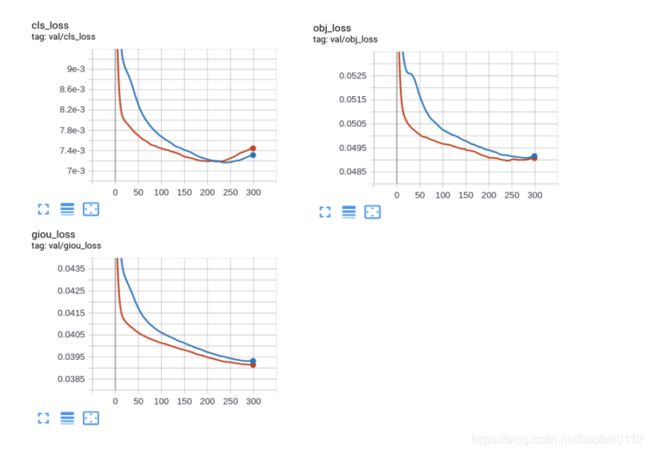
python train.py --img 640 --batch 32 --epochs 300 --data './data/bdd.yaml' --cfg ./models/custom_yolov5x.yaml --weights "" --name yolov5x_bdd --cache train_loss:
val_loss:
五、推断
可选参数:
- — weights: 训练权重的路径
- — source:推理目标的路径,可以是图片,视频,网络摄像头等
- — source:推理结果的输出路径
- — img-size:推理图片的大小
- — conf-thres: 对象置信阈值,默认0.4
- — iou-thres: NMS的IOU阈值,可以根据实际对象的重叠度调节,默认0.5
- — device: 选择使用CUDA或者CPU
- — view-img: 显示所有推理结果
- — save-txt:将每一帧的推理结果及边界框的位置,存入*.txt文件
- — classes:类别过滤,意思是只推理目标类别
- — agnostic-nms: 使用agnostic-nms NMS
python detect.py --source 0 # webcam
file.jpg # image
file.mp4 # video
path/ # directory
path/*.jpg # glob
rtsp://170.93.143.139/rtplive/470011e600ef003a004ee33696235daa # rtsp stream
rtmp://192.168.1.105/live/test # rtmp stream
http://112.50.243.8/PLTV/88888888/224/3221225900/1.m3u8 # http stream
六、转Tensorrt
1,工程配置
https://github.com/wang-xinyu/tensorrtx/tree/master/yolov5,
该项目提供了一大批常见模型的转Tensorrt方法。
环境要求:
GTX1080 / Ubuntu16.04 / cuda10.0 / cudnn7.6.5 / tensorrt7.0.0 / nvinfer7.0.0 / opencv3.3
高版本tensorrt7的变化如下:
2,生成转tensorrt的中间文件 yolov5.wts
拷贝 ./tensorrt/yolov5/gen_wts.py文件到./yolov5 工程下,修改其中加载模型路径,执行该python文件,得到yolov5.wts,并将其拷贝回 ./tensorrt/yolov5/下。
1. generate yolov5s.wts from pytorch with yolov5s.pt
git clone https://github.com/wang-xinyu/tensorrtx.git
git clone https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5.git
// download its weights 'yolov5s.pt'
// copy tensorrtx/yolov5/gen_wts.py into ultralytics/yolov5
// ensure the file name is yolov5s.pt and yolov5s.wts in gen_wts.py
// go to ultralytics/yolov5
python gen_wts.py
// a file 'yolov5s.wts' will be generated.
3,编译yolov5并生成tensorrt模型yolov5.engine
编译之前需要修改:
(1)选模型
(2)CMakeLists.txt
如果tensorrt是通过tar包解压安装的,还需要在CMakeList.txt中对tensorrt路径进行指定,不然会报错找不到nvinfer
(3)另外,如果系统是Ubuntu18.04的话还会存在opencv的问题,找不到libpng12.so和libjasper.so.
这个问题可通过https://blog.csdn.net/baobei0112/article/details/108991915 该博客内容找到答案。
(4)./tensorrt/yolov5/下新建个samples文件夹,把需要测试的图片放进去。
做好准备工作,下面就可以进行YOLOV5的engine编译工作。
build tensorrtx/yolov5 and run
// put yolov5s.wts into tensorrtx/yolov5
// go to tensorrtx/yolov5
// ensure the macro NET in yolov5.cpp is s
mkdir build
cd build
cmake ..
make
sudo ./yolov5 -s // serialize model to plan file i.e. 'yolov5s.engine'
sudo ./yolov5 -d ../samples // deserialize plan file and run inference, the images in samples will be processed.
4, Tensorrt各yolo模型对比