import导入模块
cli的目录结构如下
➜ cli tree
.
├── __pycache__
│ └── test.cpython-36.pyc
├── demo1
├── demo2
│ ├── __pycache__
│ │ └── test2.cpython-36.pyc
│ └── test2.py
└── test.py
若直接在test.py中import test2则会报以下错误
➜ cli python3
Python 3.6.0 (default, Jan 23 2017, 14:53:49)
[GCC 4.2.1 Compatible Apple LLVM 8.0.0 (clang-800.0.42.1)] on darwin
Type "help", "copyright", "credits" or "license" for more information.
>>> import test2
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "", line 1, in
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'test2'
通过以下方式查看import的搜索路径
>>> import sys
>>> sys.path
[
'',
'/usr/local/Cellar/python3/3.6.0/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.6/lib/python36.zip',
'/usr/local/Cellar/python3/3.6.0/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.6/lib/python3.6',
'/usr/local/Cellar/python3/3.6.0/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3
]
所以可以将test2.Py的路径加入上面的目录的方式来解决
>>> sys.path
[
'',
'/usr/local/Cellar/python3/3.6.0/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.6/lib/python36.zip',
'/usr/local/Cellar/python3/3.6.0/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.6/lib/python3.6',
'/usr/local/Cellar/python3/3.6.0/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3,
'./demo2/'
]
// 重新导入后没有再报错
>>> import test2
>>>
>>>
由于此时的test2.py文件内容为空
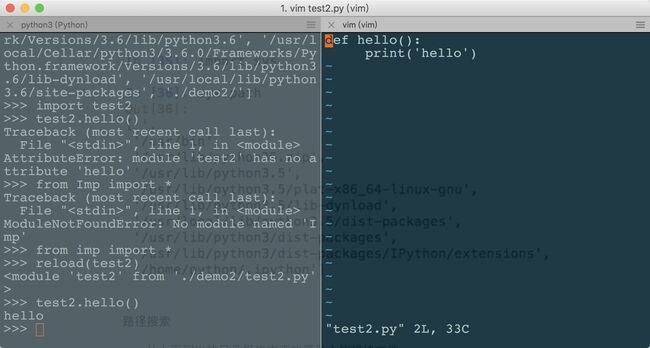
另开一个窗口编辑test2.py ,增加一个hello方法
回到左侧调用hello方法会报以下错误
>>> import test2
>>> test2.hello()
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "", line 1, in
AttributeError: module 'test2' has no attribute 'hello'
当然可以通过推出在重新导入的方式是可以的,另一种方式就是该篇的第二个话题:动态加载
动态加载模块
场景:开了2个窗口同时编辑同一个文件,但又不想退出重进
>>> from imp import *
>>> reload(test2)
此时在调用hello方法即可
>>> test2.hello()
hello