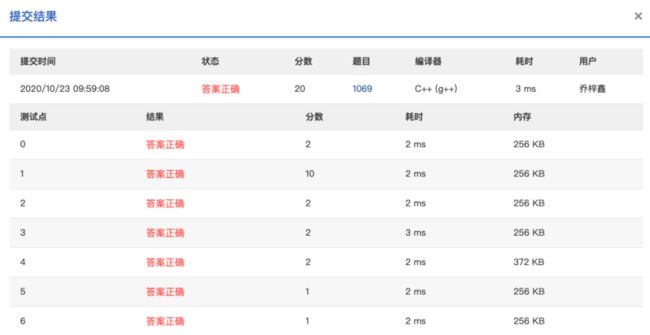
- CentOS7 python安装Ta-lib 0.6.x【talib不能直接安装,必须先安装ta_lib之c++库才可以】
weixin_43343144
服务器运维
正常流程:CentOS7python安装Ta-lib【talib不能直接安装,必须先安装ta_lib之c++库才可以】_centos7安装ta-lib-CSDN博客不同的版本参考如下!参考官方文档:ta-lib·PyPI务必下载匹配版本的【ta-lib-0.6.4-src.tar.gz】才可以正常安装$wgethttps://github.com/ta-lib/ta-lib/releases/do
- 机器学习——分类、回归、聚类、LASSO回归、Ridge回归(自用)
代码的建筑师
模型学习模型训练机器学习机器学习分类回归正则化项LASSORidge朴素
纠正自己的误区:机器学习是一个大范围,并不是一个小的方向,比如:线性回归预测、卷积神经网络和强化学都是机器学习算法在不同场景的应用。机器学习最为关键的是要有数据,也就是数据集名词解释:数据集中的一行叫一条样本或者实例,列名称为特征或者属性。样本的数量称为数据量,特征的数量称为特征维度机器学习常用库:Numpy和sklearn朴素的意思是特征的各条件都是相互独立的机器学习(模型、策略、算法)损失函数
- 第二十二章: 静态多态与动态多态的衔接_《C++ Templates》notes
郭涤生
c/c++c++开发语言笔记
静态多态与动态多态的衔接核心知识点代码示例与测试用例测试用例输出多选题设计题关键技术总结核心知识点静态多态vs动态多态静态多态:编译期多态,通过模板实现,代码生成效率高,但灵活性差。动态多态:运行期多态,通过虚函数实现,灵活性高,但存在虚表开销。类型擦除(TypeErasure)核心思想:将不同类型的对象统一为通用接口,隐藏具体类型信息。实现方式:通常结合基类指针和模板注册机制。桥接模式(Brid
- jetson nano 实现串口的字节输出
诶我就不告诉你
单片机嵌入式硬件
实现jetosnnano的字节输出,但是存在一定的问题主要为在制作数据包的过程中,我遇到了当输出字节为0x0a的情况下串口会连续输出0x0d0x0a这时候需要在串口部分进行一定的配置防止自动换行的输出/*防止自动换行*/opt.c_oflag&=~OPOST;//禁用输出处理标志,防止自动转换换行符感谢博主JetsonNano入坑之路----(10)C/C++语言读写UART或USB串口数据_je
- C++在线OJ负载均衡项目
平凡的小y
c++开发语言
1.演示项目项目源码链接:2.项目所用技术和开发环境所用技术C++STL标准库Boost准标准库(字符串切割)cpp-httplib第三方开源网络库ctemplate第三方开源前端网页渲染库jsoncpp第三方开源序列化、反序列化库负载均衡设计MySQLCconnectAce前端在线编辑器html/css/js/jquery/ajax开发环境Ubuntu云服务器vscodeMysqlWorkben
- C++:函数指针进阶(三):Lambda函数详解:概念详解
FishAnd_Yu
#C++精华c++C++Lamdba
1:Lambda函数语法C++语法的基本格式为:[capture](parameters)->return_type{/*...*/}(1)[capture]:[]内为外部变量的传递方式,值、引用等,如下[]//表示的是在lambda定义之前的域,对外部参数的调用;[=]//表示外部参数直接传值[&]//表示外部参数传引用,可修改值。当默认捕获符是&时,后继的简单捕获符必须不以&开始。而当默认捕获
- 异步编程中的并发编程优化
AI天才研究院
架构师必知必会系列自然语言处理人工智能语言模型编程实践开发语言架构设计
文章目录1.简介2.基本概念术语说明什么是异步编程?为什么要异步编程?浅谈异步编程模型基于事件驱动的模型基于消息队列的模型基于协程的模型为什么要进行并发优化?3.基本算法原理和具体操作步骤1.串行执行2.并行执行3.任务分片4.超时重试5.异步回调6.消息队列7.缓存8.异步框架9.模型选择4.具体代码实例和解释说明模块划分1.串行执行2.并行执行3.任务分片4.超时重试5.异步回调6.消息队列7
- ArrayList 和 LinkedList区别
重生之我在成电转码
java多线程系统
一、底层实现特性ArrayListLinkedList数据结构动态数组(Object[]数组)双向链表(每个节点有前驱和后继)内存布局连续内存,空间利用率高非连续内存,空间占用大元素访问方式下标随机访问(基于索引)只能顺序遍历,找元素慢⏱二、时间复杂度对比(核心!)操作ArrayListLinkedList随机访问O(1)O(n)头部插入O(n)(全体后移)O(1)中间插入O(n)O(n)尾部插入
- 于STM32F103C8T6的智能灯泡控制系统C++源码实现
程序员Thomas
STM32单片机智能灯泡stm32c++嵌入式硬件
以下是一个基于STM32F103C8T6的智能灯泡控制系统C++源码实现,整合了PWM调光、WiFi控制和环境感知功能。该代码已在STM32CubeIDE中验证,支持直接烧录运行:#include"main.h"#include#include"wifi.h"//LED设备抽象类(3设计)classLEDDevice{protected:TIM_HandleTypeDef*pwmTimer;uin
- 基于STM32的平衡车外设控制应用案例,提供C++源码
程序员Thomas
STM32单片机平衡车stm32c++单片机
基于STM32的平衡车外设控制应用案例**下面是一个使用STM32控制平衡车的简单应用案例,包含姿态传感器读取、电机控制和串口通信功能。主要功能使用MPU6050传感器读取姿态数据使用PID控制器调整平衡车姿态通过串口输出调试信息电机速度控制C++源代码#include"stm32f10x.h"#include//定义常量#definePWM_MIN1000#definePWM_MAX2000#d
- 深入理解C++中的std::string::substr成员函数:子串操作的艺术
星途码客
c++c++开发语言
引言在C++编程中,字符串处理是一项常见且重要的任务。std::string类作为C++标准库中的一部分,提供了丰富的成员函数来支持字符串的各种操作,其中substr成员函数在获取字符串子串方面扮演着关键角色。本文将深入探讨std::string::substr函数的工作原理、使用方法、异常处理以及性能考量,帮助读者全面掌握这一强大的字符串处理工具。题目:探索C++std::string::sub
- npm error gyp info
计算机辅助工程
npm前端node.js
在使用npm安装Node.js包时,可能会遇到各种错误,其中gyp错误是比较常见的一种。gyp是Node.js的一个工具,用于编译C++代码。这些错误通常发生在需要编译原生模块的npm包时。下面是一些常见的原因和解决方法:常见原因及解决方法Python未安装或版本不兼容:Node.js使用Python来运行gyp。确保你的系统上安装了Python,并且版本与node-gyp兼容。通常推荐使用Pyt
- 算法训练(leetcode)第四十六天 | 110. 字符串接龙、105. 有向图的完全可达性、106. 岛屿的周长
Star Patrick
刷题日记算法leetcode职场和发展
刷题记录*110.字符串接龙105.有向图的完全可达性邻接矩阵邻接表106.岛屿的周长深搜简化代码*110.字符串接龙题目地址使用广搜。本题相当于求最短路径,因此使用广搜。如何应用广搜是一个难点,因为题目给的是字符串而非图的表示(邻接矩阵、邻接表),因此需要自行构建连接关系。题目要求每一步只能修改一个字符,因此从起始字符串开始,对字符串中的每一个字符进行修改,修改后在输入的字符串列表中查找是否存在
- Java架构师成长之路
hweiyu00
分享spring微服务springcloudjava
概述本教程主要从6个方面,全面讲解Java技术栈的知识。1.性能调优深入理解MySQL底层原理、索引逻辑,数据结构与算法。使用Explain进行优化分析MVCC原理剖析日志机制解析2.框架源码掌握Spring底层原理带你手写一个Spring解析IOC、AOP源码、以及事务原理3.并发编程剖析Java底层锁机制CAS、JUC工具使用、AQS源码分析以及并发的集合类的讲解4.分布式开发剖析分布式中使用
- 笔记:代码随想录算法训练营day60:并查集理论基础、寻找存在的路径
jingjingjing1111
笔记
本文为学习并查集理论基础|代码随想录、代码随想录过程中的思考find是找的顶头上司,而不是当前上司,最后怎么也得找到一个顶头上司的上司是自己,要不然这个结构也不成立使用issame替换会使被操作者为当前节点,而非根节点。join(u,v)的功能为将v的根节点挂到u的根节点下模拟过程可以看出,join中的find中的路径压缩要在长度大于2(路径大于1)的时候才会体现出来107.寻找存在的路径卡码网题
- 【Matlab光伏功率预测】基于RF随机森林算法的多变量光伏功率预测(附MATLAB代码)
天天科研工作室
光伏功率预测算法matlab随机森林机器学习
【Matlab光伏功率预测】基于RF随机森林算法的多变量光伏功率预测(附MATLAB代码)文章目录【Matlab光伏功率预测】基于RF随机森林算法的多变量光伏功率预测(附MATLAB代码)文章介绍基本步骤代码分享运行结果参考资料文章介绍随机森林可以应用于光伏功率预测,这是一项重要的任务,旨在估计光伏发电系统的输出功率。光伏功率预测在可再生能源管理、电网调度和能源计划等领域具有广泛的应用。随机森林回
- C++缺省参数函数重载
ConFig.
c++算法数据结构
缺省参数大家知道什么是备胎吗?C++中函数的参数也可以配备胎。3.1缺省参数概念缺省参数是声明或定义函数时为函数的参数指定一个默认值。在调用该函数时,如果没有指定实参则采用该默认值,否则使用指定的实参。voidTestFunc(inta=0){cout_a=(int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*capacity);ps->_top=0;ps->_capacity=capacity;}i
- Golang算法(二)数据结构
小烧卖
算法GO语言
数据结构栈队列双向链表二叉搜索树红黑树栈typeStackstruct{head*Node}typeNodestruct{datainterface{}next*Node}funcNewStack()*Stack{s:=&Stack{head:&Node{data:nil,next:&Node{},},}returns}func(s*Stack)Push(datainterface{}){n:=&
- 数据结构之顺序表和栈
Dust-Chasing
数据结构算法c语言
一、顺序表1.1顺序表的概念及结构顺序表是用一段物理地址连续的存储单元依次存储数据元素的线性结构,一般情况下采用数组存储。在数组上完成数据的增删查改。1.2静态顺序表静态顺序表,即使用定长的数组来存储元素,用下面一张图就可以清楚看懂1.3动态顺序表动态顺序表:使用动态开辟的数组存储。与静态顺序表不同,动态顺序表使用的数组大小可以动态变化,从而实现更灵活的储存数据。二、动态顺序表的实现静态顺序表只适
- 数据结构之链表(单链表)
Dust-Chasing
数据结构链表c语言
目录一、链表的概念二、链表的分类三、单链表的实现1.创建新的节点2.打印链表3.链表的头插和尾插尾插:要注意第一次插入时链表为空的情况。头插:4.单链表的头删和尾删尾删:注意链表中只有一个元素的情况。且要保存尾节点的前一个节点。头删:5.单链表的查找一、链表的概念链表是一种物理存储结构上非连续、非顺序的存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的指针链接次序实现的。链表实际上就像一列火车一样,每一个
- 某人想将手中的一张面值100元的人民币换成10元、5元、2元和1元面值的票子。要求换正好40张,且每种票子至少一张。问:有几种换法?(C语言)
热心市民小汪
代码练习C语言c语言学习java
一、首先分析题目有两点1、总和是100元。2、一共分为四十张且每种至少有一张。二、思路分析。10元的为s张,5元的为w张,2元的为e张,1元的为y张。n为有几种换算法首先,每个至少有一张a>=1,b>=1,c>=1,d>=1。#includeintmain(){inttotal;for(ints=1;s<=10;s++){for(intw=1;w<=20;w++){for(inte=1;e<=40
- 186.HarmonyOS NEXT系列教程之列表切换案例数据管理详解
harmonyos-next
温馨提示:本篇博客的详细代码已发布到git:https://gitcode.com/nutpi/HarmonyosNext可以下载运行哦!HarmonyOSNEXT系列教程之列表切换案例数据管理详解效果演示1.数据模型设计1.1ListInfo类@ObservedexportclassListInfo{//列表项数据结构icon:ResourceStr='';//图标资源name:Resource
- 震惊! “深度学习”都在学习什么
扉间798
深度学习学习人工智能
常见的机器学习分类算法俗话说三个臭皮匠胜过诸葛亮这里面集成学习就是将单一的算法弱弱结合算法融合用投票给特征值加权重AdaBoost集成学习算法通过迭代训练一系列弱分类器,给予分类错误样本更高权重,使得后续弱分类器更关注这些样本,然后将这些弱分类器线性组合成强分类器,提高整体分类性能。(一)投票机制投票是一种直观且常用的算法融合策略。在多分类问题中,假设有多个分类器对同一数据进行分类判断。每个分类器
- 【论文阅读】Availability Attacks Create Shortcuts
开心星人
论文阅读论文阅读
还得重复读这一篇论文,有些地方理解不够透彻可用性攻击通过在训练数据中添加难以察觉的扰动,使数据无法被机器学习算法利用,从而防止数据被未经授权地使用。例如,一家私人公司未经用户同意就收集了超过30亿张人脸图像,用于构建商业人脸识别模型。为解决这些担忧,许多数据投毒攻击被提出,以防止数据被未经授权的深度模型学习。它们通过在训练数据中添加难以察觉的扰动,使模型无法从数据中学习太多信息,从而导致模型在未见
- 在SPSS中进行单因素方差分析(One-Way ANOVA)是一种常见的统计分析方法,用于比较三个或更多独立组之间的均值差异。
zhangfeng1133
均值算法算法
在SPSS中进行单因素方差分析(One-WayANOVA)是一种常见的统计分析方法,用于比较三个或更多独立组之间的均值差异。以下是进行单因素方差分析的详细步骤:---###1.**数据准备**-**因变量**:需要分析的连续变量(如成绩、收入等)。-**自变量**:分类变量(如组别、性别等),通常是一个名义变量。数据结构示例:|组别(自变量)|成绩(因变量)||----------------|-
- 最新智能优化算法: 贪婪个体优化算法(Greedy Man Optimization Algorithm,GMOA)求解23个经典函数测试集,MATLAB代码
IT猿手
MATLAB智能优化算法算法matlab开发语言人工智能智能优化算法
一、贪婪个体优化算法贪婪个体优化算法(GreedyManOptimizationAlgorithm,GMOA)是HamedNozari与HosseinAbdi于2024年提出的一种新型受生物启发的元启发式算法,它模拟了抵抗变化的竞争个体的行为。GMOA引入了两个独特的机制:MMO抵抗机制,防止过早替换解;周期性寄生虫清除机制,促进多样性并避免停滞。该算法旨在解决传统优化算法中的过早收敛和缺乏多样性
- 2025最新智能优化算法:改进型雪雁算法(Improved Snow Geese Algorithm, ISGA)求解23个经典函数测试集
荣华富贵8
程序员的知识储备1程序员的知识储备2程序员的知识储备3经验分享
摘要随着智能优化算法的不断发展,解决高维、复杂的优化问题已成为研究的重要课题。雪雁算法(SnowGeeseAlgorithm,SGA)作为一种新兴的自然启发式优化算法,以其高效的全局搜索能力受到了广泛关注。然而,雪雁算法在处理多峰、多约束和高维复杂问题时,仍面临收敛速度较慢和易陷入局部最优解的问题。为此,本文提出了一种改进型雪雁算法(ISGA),通过引入自适应权重调整机制和混合局部搜索策略,增强了
- 代码随想录算法训练营Day10 | Leetcode 150逆波兰表达式求值、239滑动窗口最大值、 347前 K 个高频元素
Dominic_Holmes
leetcodepython算法数据结构
代码随想录算法训练营Day10|Leetcode150逆波兰表达式求值、239滑动窗口最大值、347前K个高频元素一、反转字符串相关题目:Leetcode150文档讲解:Leetcode150视频讲解:Leetcode1501.Leetcode150.逆波兰表达式求值给你一个字符串数组tokens,表示一个根据逆波兰表示法表示的算术表达式。请你计算该表达式。返回一个表示表达式值的整数。注意:有效的
- 如何进行PHP性能优化?
破碎的天堂鸟
PHP学习php性能优化开发语言
PHP性能优化是一个复杂且多方面的过程,涉及从代码层面到服务器配置的多个方面。以下是一些关键的优化技巧和最佳实践:选择合适的数据结构(如数组、对象等)可以显著提高程序的运行效率。缓存是提升PHP性能的有效手段之一。可以通过页面缓存、数据缓存、内存缓存等方式来减少重复计算。例如,使用APC、Memcached或Redis进行内存缓存,或者利用文件系统进行数据缓存。使用索引、优化SQL查询语句以及使用
- 卷积神经网络 - 理解卷积核的尺寸 k×k×Cin
谦亨有终
AI学习笔记cnn人工智能神经网络深度学习机器学习
卷积神经网络中,每个卷积核的尺寸为k×k×Cin,这一设计的核心原因在于多通道输入的数据结构和跨通道特征整合的需求。以下是详细解释:1.输入数据的结构输入形状:假设输入数据为三维张量,形状为H×W×Cin,其中:H:高度(Height)W:宽度(Width)Cin:通道数(Channelsin)多通道的物理意义:对于RGB图像,Cin=3(红、绿、蓝三通道)。对于中间层的特征图,Cin可能为64、
- 分享100个最新免费的高匿HTTP代理IP
mcj8089
代理IP代理服务器匿名代理免费代理IP最新代理IP
推荐两个代理IP网站:
1. 全网代理IP:http://proxy.goubanjia.com/
2. 敲代码免费IP:http://ip.qiaodm.com/
120.198.243.130:80,中国/广东省
58.251.78.71:8088,中国/广东省
183.207.228.22:83,中国/
- mysql高级特性之数据分区
annan211
java数据结构mongodb分区mysql
mysql高级特性
1 以存储引擎的角度分析,分区表和物理表没有区别。是按照一定的规则将数据分别存储的逻辑设计。器底层是由多个物理字表组成。
2 分区的原理
分区表由多个相关的底层表实现,这些底层表也是由句柄对象表示,所以我们可以直接访问各个分区。存储引擎管理分区的各个底层
表和管理普通表一样(所有底层表都必须使用相同的存储引擎),分区表的索引只是
- JS采用正则表达式简单获取URL地址栏参数
chiangfai
js地址栏参数获取
GetUrlParam:function GetUrlParam(param){
var reg = new RegExp("(^|&)"+ param +"=([^&]*)(&|$)");
var r = window.location.search.substr(1).match(reg);
if(r!=null
- 怎样将数据表拷贝到powerdesigner (本地数据库表)
Array_06
powerDesigner
==================================================
1、打开PowerDesigner12,在菜单中按照如下方式进行操作
file->Reverse Engineer->DataBase
点击后,弹出 New Physical Data Model 的对话框
2、在General选项卡中
Model name:模板名字,自
- logbackのhelloworld
飞翔的马甲
日志logback
一、概述
1.日志是啥?
当我是个逗比的时候我是这么理解的:log.debug()代替了system.out.print();
当我项目工作时,以为是一堆得.log文件。
这两天项目发布新版本,比较轻松,决定好好地研究下日志以及logback。
传送门1:日志的作用与方法:
http://www.infoq.com/cn/articles/why-and-how-log
上面的作
- 新浪微博爬虫模拟登陆
随意而生
新浪微博
转载自:http://hi.baidu.com/erliang20088/item/251db4b040b8ce58ba0e1235
近来由于毕设需要,重新修改了新浪微博爬虫废了不少劲,希望下边的总结能够帮助后来的同学们。
现行版的模拟登陆与以前相比,最大的改动在于cookie获取时候的模拟url的请求
- synchronized
香水浓
javathread
Java语言的关键字,可用来给对象和方法或者代码块加锁,当它锁定一个方法或者一个代码块的时候,同一时刻最多只有一个线程执行这段代码。当两个并发线程访问同一个对象object中的这个加锁同步代码块时,一个时间内只能有一个线程得到执行。另一个线程必须等待当前线程执行完这个代码块以后才能执行该代码块。然而,当一个线程访问object的一个加锁代码块时,另一个线程仍然
- maven 简单实用教程
AdyZhang
maven
1. Maven介绍 1.1. 简介 java编写的用于构建系统的自动化工具。目前版本是2.0.9,注意maven2和maven1有很大区别,阅读第三方文档时需要区分版本。 1.2. Maven资源 见官方网站;The 5 minute test,官方简易入门文档;Getting Started Tutorial,官方入门文档;Build Coo
- Android 通过 intent传值获得null
aijuans
android
我在通过intent 获得传递兑现过的时候报错,空指针,我是getMap方法进行传值,代码如下 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
public
void
getMap(View view){
Intent i =
- apache 做代理 报如下错误:The proxy server received an invalid response from an upstream
baalwolf
response
网站配置是apache+tomcat,tomcat没有报错,apache报错是:
The proxy server received an invalid response from an upstream server. The proxy server could not handle the request GET /. Reason: Error reading fr
- Tomcat6 内存和线程配置
BigBird2012
tomcat6
1、修改启动时内存参数、并指定JVM时区 (在windows server 2008 下时间少了8个小时)
在Tomcat上运行j2ee项目代码时,经常会出现内存溢出的情况,解决办法是在系统参数中增加系统参数:
window下, 在catalina.bat最前面
set JAVA_OPTS=-XX:PermSize=64M -XX:MaxPermSize=128m -Xms5
- Karam与TDD
bijian1013
KaramTDD
一.TDD
测试驱动开发(Test-Driven Development,TDD)是一种敏捷(AGILE)开发方法论,它把开发流程倒转了过来,在进行代码实现之前,首先保证编写测试用例,从而用测试来驱动开发(而不是把测试作为一项验证工具来使用)。
TDD的原则很简单:
a.只有当某个
- [Zookeeper学习笔记之七]Zookeeper源代码分析之Zookeeper.States
bit1129
zookeeper
public enum States {
CONNECTING, //Zookeeper服务器不可用,客户端处于尝试链接状态
ASSOCIATING, //???
CONNECTED, //链接建立,可以与Zookeeper服务器正常通信
CONNECTEDREADONLY, //处于只读状态的链接状态,只读模式可以在
- 【Scala十四】Scala核心八:闭包
bit1129
scala
Free variable A free variable of an expression is a variable that’s used inside the expression but not defined inside the expression. For instance, in the function literal expression (x: Int) => (x
- android发送json并解析返回json
ronin47
android
package com.http.test;
import org.apache.http.HttpResponse;
import org.apache.http.HttpStatus;
import org.apache.http.client.HttpClient;
import org.apache.http.client.methods.HttpGet;
import
- 一份IT实习生的总结
brotherlamp
PHPphp资料php教程php培训php视频
今天突然发现在不知不觉中自己已经实习了 3 个月了,现在可能不算是真正意义上的实习吧,因为现在自己才大三,在这边撸代码的同时还要考虑到学校的功课跟期末考试。让我震惊的是,我完全想不到在这 3 个月里我到底学到了什么,这是一件多么悲催的事情啊。同时我对我应该 get 到什么新技能也很迷茫。所以今晚还是总结下把,让自己在接下来的实习生活有更加明确的方向。最后感谢工作室给我们几个人这个机会让我们提前出来
- 据说是2012年10月人人网校招的一道笔试题-给出一个重物重量为X,另外提供的小砝码重量分别为1,3,9。。。3^N。 将重物放到天平左侧,问在两边如何添加砝码
bylijinnan
java
public class ScalesBalance {
/**
* 题目:
* 给出一个重物重量为X,另外提供的小砝码重量分别为1,3,9。。。3^N。 (假设N无限大,但一种重量的砝码只有一个)
* 将重物放到天平左侧,问在两边如何添加砝码使两边平衡
*
* 分析:
* 三进制
* 我们约定括号表示里面的数是三进制,例如 47=(1202
- dom4j最常用最简单的方法
chiangfai
dom4j
要使用dom4j读写XML文档,需要先下载dom4j包,dom4j官方网站在 http://www.dom4j.org/目前最新dom4j包下载地址:http://nchc.dl.sourceforge.net/sourceforge/dom4j/dom4j-1.6.1.zip
解开后有两个包,仅操作XML文档的话把dom4j-1.6.1.jar加入工程就可以了,如果需要使用XPath的话还需要
- 简单HBase笔记
chenchao051
hbase
一、Client-side write buffer 客户端缓存请求 描述:可以缓存客户端的请求,以此来减少RPC的次数,但是缓存只是被存在一个ArrayList中,所以多线程访问时不安全的。 可以使用getWriteBuffer()方法来取得客户端缓存中的数据。 默认关闭。 二、Scan的Caching 描述: next( )方法请求一行就要使用一次RPC,即使
- mysqldump导出时出现when doing LOCK TABLES
daizj
mysqlmysqdump导数据
执行 mysqldump -uxxx -pxxx -hxxx -Pxxxx database tablename > tablename.sql
导出表时,会报
mysqldump: Got error: 1044: Access denied for user 'xxx'@'xxx' to database 'xxx' when doing LOCK TABLES
解决
- CSS渲染原理
dcj3sjt126com
Web
从事Web前端开发的人都与CSS打交道很多,有的人也许不知道css是怎么去工作的,写出来的css浏览器是怎么样去解析的呢?当这个成为我们提高css水平的一个瓶颈时,是否应该多了解一下呢?
一、浏览器的发展与CSS
- 《阿甘正传》台词
dcj3sjt126com
Part Ⅰ:
《阿甘正传》Forrest Gump经典中英文对白
Forrest: Hello! My names Forrest. Forrest Gump. You wanna Chocolate? I could eat about a million and a half othese. My momma always said life was like a box ochocol
- Java处理JSON
dyy_gusi
json
Json在数据传输中很好用,原因是JSON 比 XML 更小、更快,更易解析。
在Java程序中,如何使用处理JSON,现在有很多工具可以处理,比较流行常用的是google的gson和alibaba的fastjson,具体使用如下:
1、读取json然后处理
class ReadJSON
{
public static void main(String[] args)
- win7下nginx和php的配置
geeksun
nginx
1. 安装包准备
nginx : 从nginx.org下载nginx-1.8.0.zip
php: 从php.net下载php-5.6.10-Win32-VC11-x64.zip, php是免安装文件。
RunHiddenConsole: 用于隐藏命令行窗口
2. 配置
# java用8080端口做应用服务器,nginx反向代理到这个端口即可
p
- 基于2.8版本redis配置文件中文解释
hongtoushizi
redis
转载自: http://wangwei007.blog.51cto.com/68019/1548167
在Redis中直接启动redis-server服务时, 采用的是默认的配置文件。采用redis-server xxx.conf 这样的方式可以按照指定的配置文件来运行Redis服务。下面是Redis2.8.9的配置文
- 第五章 常用Lua开发库3-模板渲染
jinnianshilongnian
nginxlua
动态web网页开发是Web开发中一个常见的场景,比如像京东商品详情页,其页面逻辑是非常复杂的,需要使用模板技术来实现。而Lua中也有许多模板引擎,如目前我在使用的lua-resty-template,可以渲染很复杂的页面,借助LuaJIT其性能也是可以接受的。
如果学习过JavaEE中的servlet和JSP的话,应该知道JSP模板最终会被翻译成Servlet来执行;而lua-r
- JZSearch大数据搜索引擎
颠覆者
JavaScript
系统简介:
大数据的特点有四个层面:第一,数据体量巨大。从TB级别,跃升到PB级别;第二,数据类型繁多。网络日志、视频、图片、地理位置信息等等。第三,价值密度低。以视频为例,连续不间断监控过程中,可能有用的数据仅仅有一两秒。第四,处理速度快。最后这一点也是和传统的数据挖掘技术有着本质的不同。业界将其归纳为4个“V”——Volume,Variety,Value,Velocity。大数据搜索引
- 10招让你成为杰出的Java程序员
pda158
java编程框架
如果你是一个热衷于技术的
Java 程序员, 那么下面的 10 个要点可以让你在众多 Java 开发人员中脱颖而出。
1. 拥有扎实的基础和深刻理解 OO 原则 对于 Java 程序员,深刻理解 Object Oriented Programming(面向对象编程)这一概念是必须的。没有 OOPS 的坚实基础,就领会不了像 Java 这些面向对象编程语言
- tomcat之oracle连接池配置
小网客
oracle
tomcat版本7.0
配置oracle连接池方式:
修改tomcat的server.xml配置文件:
<GlobalNamingResources>
<Resource name="utermdatasource" auth="Container"
type="javax.sql.DataSou
- Oracle 分页算法汇总
vipbooks
oraclesql算法.net
这是我找到的一些关于Oracle分页的算法,大家那里还有没有其他好的算法没?我们大家一起分享一下!
-- Oracle 分页算法一
select * from (
select page.*,rownum rn from (select * from help) page
-- 20 = (currentPag