“AS3.0高级动画编程”学习:第三章等角投影(下)
在上一篇的最后,我们成功的用“等角投影”模拟出了立体空间的盒子模型,但是很快你就会发现这个示例的bug
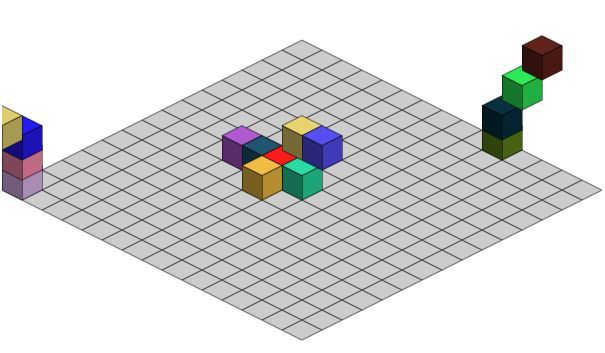
bug1:在已经有box的地方,再点击,将会重复创建box新实例。
bug2:后面添加的box,会挡住前面添加的box。
bug3:在边缘部分,如果用鼠标小心的点击,可以创建出很多超出world范围之外的盒子(即:看起来好象挂出去了)
我们按轻重缓急来处理吧:
bug2最严重,它直接影响了最终的3D视觉效果。产生它的原因是显示列表中,后添加的物体,其index值会比 前面添加物体的index值 要大,所以就挡住了前面的box。
仔细看一下IsoObject类
public function get depth():Number {
return (_position.x + _position.z) * .866 - _position.y * .707;
}
其实这里已经预留了“深度”属性,根据这个对所有的box进行depth属性排序即可。另外为了实现排序,我们应该把所有box类实例存放到一个数组里,这样才能利用Array的SortOn方法。(代码会在后面一起给出)
再来看bug1,重复创建的问题,这个解决起来比较容易:在创建box前,先检查对应的位置是否已经有box了,如果有,就不用处理了,这样就把问题转化为Point3D的坐标位置比较,所以我们得在Point3D中添加一个判断是否相等的方法
package {
public class Point3D {
public var x:Number;
public var y:Number;
public var z:Number;
public function Point3D(x:Number=0,y:Number=0,z:Number=0) {
this.x=x;
this.y=y;
this.z=z;
}
public function toString():String{
return "x=" + this.x + ",y=" + this.y + ",z=" + this.z;
}
//判断二个Point3D是否相等
public function equal(p:Point3D):Boolean{
return this.x==p.x&&this.y==p.y&&this.z==p.z;
}
}
}
注:as3不象c#那样有操作符重载,所以只能显式定义equal方法
最后来处理bug3,即box实例超出地图范围之外的问题(产生这个问题的根源就是as3.0的事件冒泡机制,在box实例上点击时,world会响应Click事件)
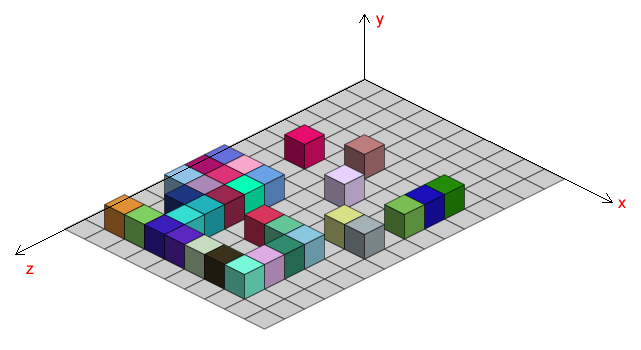
如上图,很明显:地图是有边界的,如果盒子超出地图的范围,其x,z坐标肯定也会大于某一个阈值,所以在创建box实例前对坐标检测就能处理了.
完整代码:
package{
import flash.display.Sprite;
import flash.display.StageAlign;
import flash.display.StageScaleMode;
import flash.events.Event;
import flash.events.MouseEvent;
import flash.geom.Point;
[SWF(backgroundColor=0xffffff,height="400",width='600')]
public class DepthTest extends Sprite
{
private var floor:Sprite;
private var world:Sprite;
private var objectList:Array;
private var rows:uint=15;//列数
private var cols:uint=10;//行数
private var cellSize:uint=20;//单元格大小
public function DepthTest()
{
stage.align = StageAlign.TOP_LEFT;
stage.scaleMode = StageScaleMode.NO_SCALE;
floor = new Sprite();
world = new Sprite();
addChild(floor);
addChild(world);
sizeInit();
objectList = new Array();
for(var i:int = 0; i < cols; i++)
{
for(var j:int = 0; j < rows; j++)
{
var tile:DrawnIsoTile = new DrawnIsoTile(cellSize, 0xcccccc);
tile.position = new Point3D(i * cellSize, 0, j * cellSize);
floor.addChild(tile);
}
}
stage.addEventListener(MouseEvent.CLICK, onWorldClick);
stage.addEventListener(Event.RESIZE,resizeHandler);
}
private function sizeInit():void{
floor.x = stage.stageWidth / 2 + 50;
floor.y = 100;
world.x = floor.x;
world.y = floor.y;
}
private function resizeHandler(e:Event):void{
sizeInit();
}
private function onWorldClick(event:MouseEvent):void
{
var pos:Point3D = IsoUtils.screenToIso(new Point(world.mouseX, world.mouseY));
pos.x = Math.round(pos.x / cellSize) * cellSize;
pos.y = Math.round(pos.y / cellSize) * cellSize;
pos.z = Math.round(pos.z / cellSize) * cellSize;
trace(pos.toString());
//检测box的位置是否挂出去了+重复创建检测
if (pos.x<0 || pos.x>(cols-1)*cellSize || pos.z<0 || pos.z>(rows-1)*cellSize || boxExist(pos)){
return;
}
var box:DrawnIsoBox = new DrawnIsoBox(cellSize, Math.random() *0xffffff, cellSize);
box.position = pos;
world.addChild(box);
objectList.push(box);
sortList();
}
//深度排序
private function sortList():void
{
objectList.sortOn("depth", Array.NUMERIC);
for(var i:int = 0; i < objectList.length; i++)
{
world.setChildIndex(objectList[i], i);
}
}
//检测指定的位置是否已经有box了
private function boxExist(p:Point3D):Boolean{
for(var i:int = 0; i < objectList.length; i++)
{
var b:* = objectList[i];
if (b is DrawnIsoBox ){
if (b.position.equal(p)){
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
}
}
设置行数,列数,画地板,添加子元素时的种种处理(深度排序,位置检查...)这一堆东东,以后会经常用到的,为了方便起见,干脆封装起来吧,另外:我们的as文件越来越多了,为了保持清晰的结构,把这些等角投影所用的基类新建一个iso的包来管理吧,结构如下图:
IsoWorld封装类:
package iso
{
import flash.display.Sprite;
import flash.geom.Rectangle;
public class IsoWorld extends Sprite
{
private var _floor:Sprite;
private var _objects:Array;
private var _world:Sprite;
private var _cols:uint=10;
private var _rows:uint=10;
private var _cellSize:uint=20;
public function IsoWorld(cols:uint=10,rows:uint=10,cellSize:uint=20)
{
this._cols = cols;
this._rows = rows;
this._cellSize = cellSize;
_floor = new Sprite();
addChild(_floor);
_world = new Sprite();
addChild(_world);
_objects = new Array();
}
public function set cellSize(v:uint):void{
this._cellSize = v;
}
public function get cellSize():uint{
return this._cellSize;
}
public function set rows(v:uint):void{
this._rows = v;
}
public function get rows():uint{
return this._rows;
}
public function set cols(v:uint):void{
this._cols = v;
}
public function get cols():uint{
return this._cols;
}
public function addChildToWorld(child:IsoObject):void
{
//检测box的位置是否挂出去了+重复创建检测
if (child.position.x<0 || child.position.x>(_cols-1)*_cellSize || child.position.z<0 || child.position.z>(_rows-1)*_cellSize || childPosExist(child.position)){
return;
}
_world.addChild(child);
_objects.push(child);
sort();
}
public function addChildToFloor(child:IsoObject):void
{
_floor.addChild(child);
}
public function sort():void
{
_objects.sortOn("depth", Array.NUMERIC);
for(var i:int = 0; i < _objects.length; i++)
{
_world.setChildIndex(_objects[i], i);
}
}
private function childPosExist(p:Point3D):Boolean{
for(var i:int = 0; i < _objects.length; i++)
{
var b:* = _objects[i];
if (b is IsoObject ){
if (b.position.equal(p)){
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
}
}
有了这个类,刚才的示例写起来就简练多了
package
{
import flash.display.*;
import flash.events.*;
import flash.geom.Point;
import iso.*;
[SWF(backgroundColor=0xffffff)]
public class WorldTest extends Sprite
{
private var world:IsoWorld;
public function WorldTest()
{
stage.align = StageAlign.TOP_LEFT;
stage.scaleMode = StageScaleMode.NO_SCALE;
world = new IsoWorld();
sizeInit();
addChild(world);
for(var i:int = 0; i < world.cols; i++)
{
for(var j:int = 0; j < world.rows; j++)
{
var tile:DrawnIsoTile = new DrawnIsoTile(world.cellSize, 0xcccccc);
tile.position = new Point3D(i * world.cellSize, 0, j * world.cellSize);
world.addChildToFloor(tile);
}
}
stage.addEventListener(MouseEvent.CLICK, onWorldClick);
stage.addEventListener(Event.RESIZE,resizeHandler);
}
private function sizeInit():void{
world.x = stage.stageWidth / 2;
world.y = stage.stageHeight/2;
}
private function resizeHandler(e:Event):void{
sizeInit();
}
private function onWorldClick(event:MouseEvent):void
{
var box:DrawnIsoBox = new DrawnIsoBox(world.cellSize, Math.random() * 0xffffff, world.cellSize);
var pos:Point3D = IsoUtils.screenToIso(new Point(world.mouseX, world.mouseY));
pos.x = Math.round(pos.x / world.cellSize) * world.cellSize;
pos.y = Math.round(pos.y / world.cellSize) * world.cellSize;
pos.z = Math.round(pos.z / world.cellSize) * world.cellSize;
box.position = pos;
world.addChildToWorld(box);
}
}
}
接下来考虑一下如何在地板上移动物体:
要移动当然要有速度,先在IsoObject上添加vx,vy,vz速度属性
protected var _vx:Number = 0;
protected var _vy:Number = 0;
protected var _vz:Number = 0;
public function set vx(value:Number):void
{
_vx = value;
}
public function get vx():Number
{
return _vx;
}
public function set vy(value:Number):void
{
_vy = value;
}
public function get vy():Number
{
return _vy;
}
public function set vz(value:Number):void
{
_vz = value;
}
public function get vz():Number
{
return _vz;
}
测试一下用键盘控制移动
package
{
import flash.display.*;
import flash.events.*;
import flash.ui.Keyboard;
import iso.*;
[SWF(backgroundColor=0xffffff,height=260,width=460)]
public class MotionTest extends Sprite
{
private var world:IsoWorld;
private var box:DrawnIsoBox;
private var speed:Number = 10;
public function MotionTest()
{
stage.align = StageAlign.TOP_LEFT;
stage.scaleMode = StageScaleMode.NO_SCALE;
world = new IsoWorld();
sizeInit();
addChild(world);
for(var i:int = 0; i < world.cols; i++)
{
for(var j:int = 0; j < world.rows; j++)
{
var tile:DrawnIsoTile = new DrawnIsoTile(world.cellSize, 0xcccccc);
tile.position = new Point3D(i * world.cellSize, 0, j * world.cellSize);
world.addChildToFloor(tile);
}
}
box = new DrawnIsoBox(world.cellSize, 0xff0000, world.cellSize);
//把box摆在world中央
box.x = world.cellSize*Math.round(world.cols/2);
box.z = world.cellSize*Math.round(world.rows/2);
world.addChildToWorld(box);
stage.addEventListener(KeyboardEvent.KEY_DOWN, onKeyDown);
stage.addEventListener(KeyboardEvent.KEY_UP, onKeyUp);
stage.addEventListener(Event.RESIZE,resizeHandler);
}
private function sizeInit():void{
world.x = stage.stageWidth / 2;
world.y = 50;
}
private function resizeHandler(e:Event):void{
sizeInit();
}
private function onKeyDown(event:KeyboardEvent):void
{
switch(event.keyCode)
{
case Keyboard.UP :
box.vx = -speed;
break;
case Keyboard.DOWN :
box.vx = speed;
break;
case Keyboard.LEFT :
box.vz = speed;
break;
case Keyboard.RIGHT :
box.vz = -speed;
break;
case Keyboard.END:
box.vy = -speed;
break;
case Keyboard.HOME:
box.vy = speed;
break;
default :
break;
}
addEventListener(Event.ENTER_FRAME, onEnterFrame);
}
private function onKeyUp(event:KeyboardEvent):void
{
box.vx = 0;
box.vz = 0;
box.vy = 0;
removeEventListener(Event.ENTER_FRAME, onEnterFrame);
}
private function onEnterFrame(event:Event):void
{
box.x += box.vx;
box.z += box.vz;
box.y += box.vy;
if (box.x<0){
box.x =0;
}
else if(box.x>world.cellSize*(world.cols-1)){
box.x = world.cellSize*(world.cols-1);
}
if (box.z<0){
box.z =0;
}
else if(box.z>world.cellSize*(world.rows-1)){
box.z = world.cellSize*(world.rows-1);
}
}
}
}
用上下左右及Home/End键可以控制box的移动,这里注意的是:虽然等角世界中的3D坐标系仍然是右手坐标系(参见3D基础),但整个坐标系做了旋转,y轴是垂直向上的,所以vy为负值时,物体将向上运动,反之向下,另外这个示例还展示了如何在等角空间中做边界检测。下面这个是该示例的升级版(加入了重力,反弹,摩擦力等因素)。
package
{
import iso.*;
import flash.display.*;
import flash.events.*;
import flash.filters.BlurFilter;
[SWF(backgroundColor=0xffffff,height=300,width=420)]
public class MotionTest2 extends Sprite
{
private var world:IsoWorld;
private var box:DrawnIsoBox;
private var shadow:DrawnIsoTile;
private var gravity:Number = 2;
private var friction:Number = 0.95;
private var bounce:Number = -0.9;
private var filter:BlurFilter;
public function MotionTest2()
{
stage.align = StageAlign.TOP_LEFT;
stage.scaleMode = StageScaleMode.NO_SCALE;
world = new IsoWorld();
sizeInit();
addChild(world);
for(var i:int = 0; i < world.cols; i++)
{
for(var j:int = 0; j < world.rows; j++)
{
var tile:DrawnIsoTile = new DrawnIsoTile(20, 0xcccccc);
tile.position = new Point3D(i * world.cellSize, 0, j * world.cellSize);
world.addChildToFloor(tile);
}
}
box = new DrawnIsoBox(world.cellSize, 0xff0000, world.cellSize);
//把box摆在world中央
box.x = world.cellSize*Math.round(world.cols/2);
box.z = world.cellSize*Math.round(world.rows/2);
world.addChildToWorld(box);
shadow = new DrawnIsoTile(world.cellSize, 0);
shadow.alpha = 0.5;
world.addChildToFloor(shadow);
filter = new BlurFilter();
addEventListener(Event.ENTER_FRAME, onEnterFrame);
stage.addEventListener(MouseEvent.CLICK, onClick);
stage.addEventListener(Event.RESIZE,resizeHandler);
}
private function sizeInit():void{
world.x = stage.stageWidth / 2;
world.y = 100;
}
private function resizeHandler(e:Event):void{
sizeInit();
}
private function onClick(event:MouseEvent):void
{
box.vx = Math.random() * 20 - 10;
box.vy = -5 -Math.random() * 25;
box.vz = Math.random() * 20 - 10;
}
private function onEnterFrame(event:Event):void
{
box.vy += gravity;//重力加速度
box.x += box.vx;
box.y += box.vy;
box.z += box.vz;
if(box.x > (world.cols-1)*world.cellSize)
{
box.x = (world.cols-1)*world.cellSize;
box.vx *= bounce;//反弹
}
else if(box.x < 0)
{
box.x = 0;
box.vx *= bounce;
}
if(box.z > (world.rows-1)*world.cellSize)
{
box.z = (world.rows-1)*world.cellSize;
box.vz *= bounce;
}
else if(box.z < 0)
{
box.z = 0;
box.vz *= bounce;
}
if(box.y > 0)
{
box.y = 0;
box.vy *= bounce;
}
//摩擦力
box.vx *= friction;
box.vy *= friction;
box.vz *= friction;
//影子坐标同步
shadow.x = box.x;
shadow.z = box.z;
//蚊子模糊
filter.blurX = filter.blurY = -box.y * .25;
shadow.filters = [filter];
}
}
}
用鼠标点击上面的Flash,box将随机向上弹起并落下,同时下面的阴影也会随之变化。
下一个问题:碰撞检测
把前面那个用键盘控制box移动的示例稍做修改,另外再增加一个静止不动的box
package
{
import iso.*;
import flash.display.*;
import flash.events.*;
import flash.ui.Keyboard;
[SWF(backgroundColor=0xffffff,height=260,width=460)]
public class CollisionTest1 extends Sprite
{
private var world:IsoWorld;
private var box:DrawnIsoBox;
private var speed:Number = 4;
public function CollisionTest()
{
stage.align = StageAlign.TOP_LEFT;
stage.scaleMode = StageScaleMode.NO_SCALE;
world = new IsoWorld();
sizeInit();
addChild(world);
for(var i:int = 0; i < world.cols; i++)
{
for(var j:int = 0; j < world.rows; j++)
{
var tile:DrawnIsoTile = new DrawnIsoTile(world.cellSize, 0xcccccc);
tile.position = new Point3D(i * world.cellSize, 0, j * world.cellSize);
world.addChildToFloor(tile);
}
}
box = new DrawnIsoBox(world.cellSize, 0xff0000, world.cellSize);
box.x = world.cellSize*Math.round(world.cols/2);
box.z = world.cellSize*Math.round(world.rows/2);
world.addChildToWorld(box);
//再放一个静止的box
var newBox:DrawnIsoBox = new DrawnIsoBox(world.cellSize, 0xcccccc, world.cellSize);
newBox.x = box.x + 2*world.cellSize;
newBox.z = box.z + 2*world.cellSize;
world.addChildToWorld(newBox);
stage.addEventListener(KeyboardEvent.KEY_DOWN, onKeyDown);
stage.addEventListener(KeyboardEvent.KEY_UP, onKeyUp);
stage.addEventListener(Event.RESIZE,resizeHandler);
}
private function sizeInit():void{
world.x = stage.stageWidth / 2;
world.y = 50;
}
private function resizeHandler(e:Event):void{
sizeInit();
}
private function onKeyDown(event:KeyboardEvent):void
{
switch(event.keyCode)
{
case Keyboard.UP :
box.vx = -speed;
break; 111
case Keyboard.DOWN :
box.vx = speed;
break;
case Keyboard.LEFT :
box.vz = speed;
break;
case Keyboard.RIGHT :
box.vz = -speed;
break;
default :
break;
}
addEventListener(Event.ENTER_FRAME, onEnterFrame);
}
private function onKeyUp(event:KeyboardEvent):void
{
box.vx = 0;
box.vz = 0;
removeEventListener(Event.ENTER_FRAME, onEnterFrame);
}
private function onEnterFrame(event:Event):void
{
box.x += box.vx;
box.y += box.vy;
box.z += box.vz;
world.sort();
}
}
}
用键盘控制红色的box,尽量去碰灰色不动的box,会发现红色box径直穿过灰色box,太假了。
仔细思考一下:如果红色box在移动的过程中,前方遇到了障碍物,而且这个障碍物是不可穿越的(可能有朋友会问:障碍物还有能穿越的么?确实有,比如在一些游戏中,允许角色穿墙而过),那么红色box就应该不能再前进。
让我们回过头来再看看IsoObject.as的定义,注意里面有二个属性:walkable,rect。这时候该它俩派上用场了,walkable表明该物体是否允许被穿越(默认为false),而rect用于返回该物体在等角空间中占用的矩形区域。
问题解决了:在IsoWorld中,每个物体去跟其它物体做个检测,检测二者的矩形区域是否有交集,如果有就表示碰上了,另外再看看其它物体是否允许穿越,如果不允许,则应该不能再向前运动了。
//判断obj是否能继续向前移动
public function canMove(obj:IsoObject):Boolean
{
var rect:Rectangle = obj.rect;
rect.offset(obj.vx, obj.vz);
for(var i:int = 0; i < _objects.length; i++)
{
var objB:IsoObject = _objects[i] as IsoObject;
if(obj != objB && !objB.walkable && rect.intersects(objB.rect))
{
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
将这个方法加入到IsoWorld.as中即可,然后刚才碰撞示例的Enter_Frame处理函数改为:
private function onEnterFrame(event:Event):void
{
if (world.canMove(box)){//移动先做下检测
box.x += box.vx;
box.y += box.vy;
box.z += box.vz;
world.sort();
}
}
现在再试试,碰撞检测的处理应该起作用了。
如果一个游戏里都是些单调的纯色盒子,很快就会看腻味了,所以下面我们会学习如何利用图片创建更好看的box,为了使用图片,我们需要一个新的基类:GraphicTile.as
package iso
{
import flash.display.DisplayObject;
public class GraphicTile extends IsoObject
{
public function GraphicTile(size:Number, classRef:Class, xoffset:Number, yoffset:Number):void
{
super(size);
var gfx:DisplayObject = new classRef() as DisplayObject;
gfx.x = -xoffset;
gfx.y = -yoffset;
addChild(gfx);
}
}
}
代码很短,但是“简约而不简单”,首先要注意是Class类型的参数,classRef:Class表明参数classRef必须是一个类的引用,即传一个类进去(初次接触可能感觉很怪,没关系,多看几遍就顺眼了),其次是偏移量参数,为什么要有偏移量?因为在之前的基类IsoObject中,sprite的注册点是正中心,所以无需偏移量校正,而使用图片时,图片默认的注册点是左上角,要想把图片正好校对到中心,就必须要用偏移量来调整。
另外一个问题:图片如何嵌入到as文件中?使用Embed标记--类似c#中的特性语法(attribute),废话了一堆,还是直接来看测试代码吧:
package
{
import flash.display.*;
import flash.events.*;
import flash.geom.Point;
import iso.*;
[SWF(backgroundColor=0xffffff,height=260,width=460)]
public class GraphicTest extends Sprite
{
private var world:IsoWorld;
[Embed(source="img/tile_01.png")]
private var Tile01:Class;
[Embed(source="img/tile_02.png")]
private var Tile02:Class;
public function GraphicTest()
{
stage.align = StageAlign.TOP_LEFT;
stage.scaleMode = StageScaleMode.NO_SCALE;
world = new IsoWorld();
sizeInit();
addChild(world);
for(var i:int = 0; i < world.cols; i++)
{
for(var j:int = 0; j < world.rows; j++)
{
var tile:GraphicTile = new GraphicTile(world.cellSize, Tile01, 20, 10);
tile.position = new Point3D(i * world.cellSize, 0, j * world.cellSize);
world.addChildToFloor(tile);
}
}
stage.addEventListener(MouseEvent.CLICK, onWorldClick);
stage.addEventListener(Event.RESIZE,resizeHandler);
}
private function sizeInit():void{
world.x = stage.stageWidth / 2;
world.y = 50;
}
private function resizeHandler(e:Event):void{
sizeInit();
}
private function onWorldClick(event:MouseEvent):void
{
var box:GraphicTile = new GraphicTile(world.cellSize, Tile02, 20, 30);
var pos:Point3D = IsoUtils.screenToIso(new Point(world.mouseX, world.mouseY));
pos.x = Math.round(pos.x / world.cellSize) * world.cellSize;
pos.y = Math.round(pos.y / world.cellSize) * world.cellSize;
pos.z = Math.round(pos.z / world.cellSize) * world.cellSize;
box.position = pos;
world.addChildToWorld(box);
}
}
}
拿鼠标在地图上点二下试试!
注:这里用到了二张图片,放在这里,方便大家下载回去测试


实际的游戏开发中,不可能所有地图都是用代码写死的,这样维护起来很麻烦,所以下面将学习到如何利用外部文件来存储地图信息,然后根据该配置文件来自动生成地图:
// this is a comment.
# 0 type:GraphicTile graphicClass:MapTest_Tile01 xoffset:20 yoffset:10 walkable:true
# 1 type:GraphicTile graphicClass:MapTest_Tile02 xoffset:20 yoffset:30 walkable:false
# 2 type:DrawnIsoBox color:0xff6666 walkable:false height:20
# 3 type:DrawnIsoTile color:0x6666ff walkable:false
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0
0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0
0 1 0 3 3 3 3 0 1 0
0 1 0 3 2 2 3 0 0 0
0 1 0 3 2 2 3 0 0 0
0 1 0 3 3 3 3 0 0 0
0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0
0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
这个是一个典型的地图描述信息,可以直接把它存储到txt记事本文件里,分析一下:
“// ”行表示注释,不用管,是给人看的,不是给代码看的
“#”行表示的是类型定义,即数据字典,这里1表示GraphicTile,2表示DrawnIsoBox,3表示DrawnIsoTile,后面为具体的实例生成参数(代码读取这些参数后,传到相应的构造函数中,以方便生成实例)
再下来的数字,就是地图的实际描述。
为了能正常解析地图配置信息,需要专门弄一个地图解析类(MapLoader):
package iso
{
import flash.events.Event;
import flash.events.EventDispatcher;
import flash.net.URLLoader;
import flash.net.URLRequest;
import flash.utils.getDefinitionByName;
public class MapLoader extends EventDispatcher
{
private var _grid:Array;
private var _loader:URLLoader;
private var _tileTypes:Object;
public function MapLoader()
{
_tileTypes = new Object();
}
public function loadMap(url:String):void
{
_loader = new URLLoader();
_loader.addEventListener(Event.COMPLETE, onLoad);
_loader.load(new URLRequest(url));
}
private function onLoad(event:Event):void
{
_grid = new Array();
var data:String = _loader.data;
//注:在不同的系统中的回车符的定义不同,有些系统用\r\n来表示回车,有些则只使用\n,所以这里要先过滤掉\r
if (data.indexOf("\r")!=-1){
var myPattern:RegExp = /\r/g;
data = data.replace(myPattern,"");
}
trace(data);
var lines:Array = data.split("\n");
for(var i:int = 0; i < lines.length; i++)
{
var line:String = lines[i];
if(isDefinition(line))//如果是类型定义,则解析类型定义
{
parseDefinition(line);
}
else if(!lineIsEmpty(line) && !isComment(line))
{
var cells:Array = line.split(" ");
_grid.push(cells);
}
}
//触发Event.COMPLETE事件
dispatchEvent(new Event(Event.COMPLETE));
}
//分析类型定义
private function parseDefinition(line:String):void
{
var tokens:Array = line.split(" ");
//trace(line);
//类似 下面中的某一行
//# 1 type:GraphicTile graphicClass:MapTest_Tile02 xoffset:20 yoffset:30 walkable:false
//# 2 type:DrawnIsoBox color:0xff6666 walkable:false height:20
//# 3 type:DrawnIsoTile color:0x6666ff walkable:false
tokens.shift();//删除掉第一个字符#
var symbol:String = tokens.shift() as String;//得到标志字符,即“1”
var definition:Object = new Object();
for(var i:int = 0; i < tokens.length; i++)
{
var key:String = tokens[i].split(":")[0];
var val:String = tokens[i].split(":")[1];
definition[key] = val;//将类似 type:GraphicTile graphicClass:MapTest_Tile02 xoffset:20 yoffset:30 walkable:false 以key-value的结构保存到object中
}
//trace("symbol:",symbol);
setTileType(symbol, definition);
}
//设置贴片类型
public function setTileType(symbol:String, definition:Object):void
{
_tileTypes[symbol] = definition;
}
//创建地图
public function makeWorld(size:Number):IsoWorld
{
var world:IsoWorld = new IsoWorld();
for(var i:int = 0; i < _grid.length; i++)
{
for(var j:int = 0; j < _grid[i].length; j++)
{
var cellType:String = _grid[i][j];
var cell:Object = _tileTypes[cellType];
var tile:IsoObject;
switch(cell.type)
{
case "DrawnIsoTile" :
tile = new DrawnIsoTile(size, parseInt(cell.color), parseInt(cell.height));
break;
case "DrawnIsoBox" :
tile = new DrawnIsoBox(size, parseInt(cell.color), parseInt(cell.height));
break;
case "GraphicTile" :
var graphicClass:Class = getDefinitionByName(cell.graphicClass) as Class;
tile = new GraphicTile(size, graphicClass, parseInt(cell.xoffset), parseInt(cell.yoffset));
break;
default :
tile = new IsoObject(size);
break;
}
tile.walkable = cell.walkable == true;//强制设置所有对象为可穿越(当然这是可选的,非必须)
tile.x = j * size;
tile.z = i * size;
world.addChild(tile);
}
}
return world;
}
//是否空行(只有该行有一个字符不为" "就算过了)
private function lineIsEmpty(line:String):Boolean
{
for(var i:int = 0; i < line.length; i++)
{
if(line.charAt(i) != " ") return false;
}
return true;
}
//判断该行是否为注释行
private function isComment(line:String):Boolean
{
return line.indexOf("//") == 0;
}
//判断该行是否为“类型定义”
private function isDefinition(line:String):Boolean
{
return line.indexOf("#") == 0;
}
}
}
关键的地方已经加了注释,应该不难懂,然后来测试一下:
package
{
import iso.*;
import flash.display.*;
import flash.events.Event;
[SWF(backgroundColor=0xffffff,height=260,width=460)]
public class MapTest extends Sprite
{
private var _world:IsoWorld;
private var _floor:IsoWorld;
private var mapLoader:MapLoader;
[Embed(source="img/tile_01.png")]
private var Tile01:Class;
[Embed(source="img/tile_02.png")]
private var Tile02:Class;
public function MapTest()
{
stage.align = StageAlign.TOP_LEFT;
stage.scaleMode = StageScaleMode.NO_SCALE;
mapLoader = new MapLoader();
mapLoader.addEventListener(Event.COMPLETE, onMapComplete);
mapLoader.loadMap("map/map.txt");//map.txt里就是刚才提到的地图配置信息
stage.addEventListener(Event.RESIZE,resizeHandler);
}
private function sizeInit():void{
if (_world!=null){
_world.x = stage.stageWidth / 2;
_world.y = 50;
}
}
private function resizeHandler(e:Event):void{
sizeInit();
}
private function onMapComplete(event:Event):void
{
_world = mapLoader.makeWorld(20);
addChild(_world);
sizeInit();
}
}
}
建议大家修改一下map.txt中的信息,然后重新运行看看效果。如果一切正常的话,只要地图信息修改了,as代码不用改一行就能自动生成新地图。最后再回过头来看一下地图信息中的graphicClass:MapTest_Tile01,我们在MapTest中对于的Tile01的定义是这样的:
[Embed(source="img/tile_01.png")]
private var Tile01:Class;
注意这里并没有MapTest_前缀,但是as3经过编译后,内部的名称会自动变成"类名_属性",所以在地图中一定要加上该前缀。