C#应用MemoryStream提高File读取速度
一、场景:
需要将有一定格式的File里的内容读取到已经定义的类中,譬如一个二进制文件里的内容读取到一个新的DataStructure里面。
1. File不是很大,一次将所有内容Load到内存中,不会占用太多Memory;
2. 二进制文件无法直接反序列化成一个Object,需要一个映射才能完成转换.
二、为什么不用FileStream:
首先,我们来看一下FileStream的代码以及原理:
FileStream fs = new FileStream(binaryFilePath, FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read);
Encoding enc = Encoding.ASCII;
using (BinaryReader br = new BinaryReader(fs,enc))
{
//
}
BinaryReader 提供了ReadInt16,ReadChar,ReadDouble,……但是每次Position.Seek都会去定位流的指针,所以会耗费一些时间。
但是如果我们一次性的将所有内容都独到内存(Memory)中,然后操作Memory是不是更快呢?
三、MemoryStream实现方法
FileStream fs = new FileStream(binaryFilePath, FileMode.Open, FileAccess.Read);
//Read all bytes into an array from the specified file.
int nBytes = (int)fs.Length;//计算流的长度
byte[] byteArray = new byte[nBytes];//初始化用于MemoryStream的Buffer
int nBytesRead = fs.Read(byteArray, 0, nBytes);//将File里的内容一次性的全部读到byteArray中去
using (MemoryStream br = new MemoryStream(byteArray))//初始化MemoryStream,并将Buffer指向FileStream的读取结果数组
{
/your code
}
四、性能分析
分别用以上两种方法Load File:1,2,3,4,5,6,将其Load的时间记录下来:
| File | File Size(Mb) | FileStream(ms) | MemoryStream(ms) | Performance Enhancement |
| 1 | 0.5 | 921 | 392 | 2.35 |
| 2 | 7.1 | 4454 | 1466 | 3.04 |
| 3 | 14 | 7848 | 3366 | 2.33 |
| 4 | 28 | 16025 | 6242 | 2.57 |
| 5 | 44 | 21196 | 9268 | 2.26 |
| 6 | 73 | 27533 | 14503 | 1.90 |
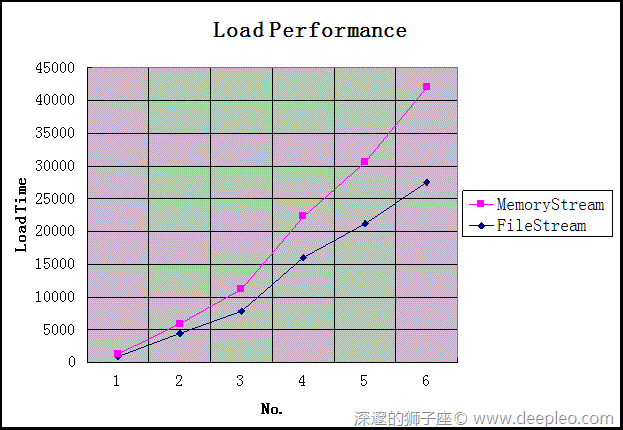
可以看出:应用了MemoryStream性能提高了2-3倍。
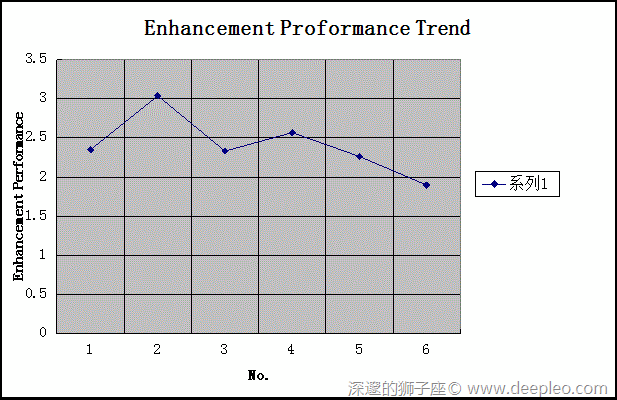
可以看出:随着File内容的增加,性能提高的就越来越缓慢,因为他占用了更多的内存空间,可以说是:“以空间换时间”。