ZYNQ基础----裸机USB的使用
前言
在ZYNQ上中有USB的控制器,最近在使用pluto sdr进行数据传输的时候,觉得串口太慢,但是也没有找到关于USB的在裸机下的资料。一般都是用操作系统来做的,这就很郁闷了啊,我一个FPGA小白,现在还不会linux啊。然后就上GitHub上找了找看看有没有人做过zynq裸机的usb的demo,嘿,你别说,还真有。
FPGA工程链接地址如下:
Zynq_winUSB FPGA repo
然后还这个作者还提供了一个测试软件,C#写的,看不太懂,但是可以知道是使用libusb这个跨平台的库写的。那么之后自己在进行上位机代码编写的时候,就使用这个libusb这个库就可以了。
上位机链接地址如下:
usb_loop
1. 搭建自己的USB硬件平台
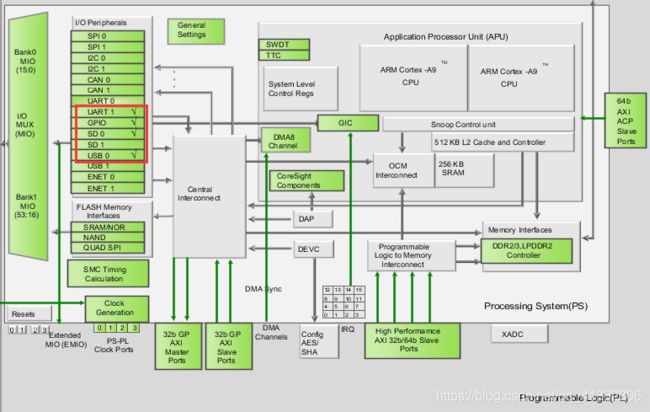
1.1 硬件平台
使能串口,方便打印调试信息,使能USB进行USB的裸机的实验,GPIO使能一个,是因为需要使用到USB的复位信号。
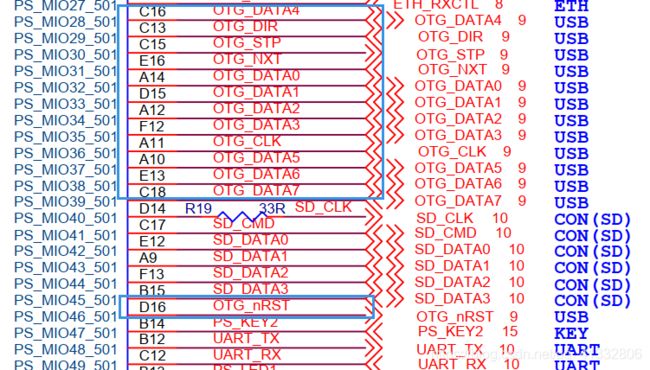

作为一个拿来主义的小白,硬件平台搭好之后,当然是直接把别人的代码拿来用了啊,简单又方便。

1.1.1 USB ID号
在代码中有几个比较重要的文件,首先是这个USB_CONFIG.h文件,这个文件里面提供用于配置USB设备ID的信息。通过更改这个文件里面的信息,就能够将usb接入到电脑上的时候,看到更改之后的信息。

1.1.2 生成设备描述信息
在一下两个文件当中,实现了设备信息的声明。
通过调用zynq系统的api函数,来完成设备描述文件的生成。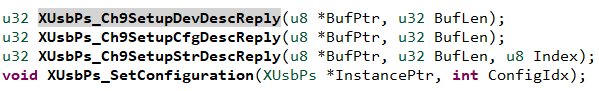
1.1.3 usb设备的初始化和中断的控制
其实设备的初始化和中断的控制,可以直接打开vitis里面的示例demo就可以了。

设备的初始化就根据这里面来就可以。在初始化的时候,需要对usb设备进行配置。代码中配置了两个断电,一个端点用于传输控制包,一个端点用于进行块传输。

1.1.4 收发数据的API
在代码中,原作者使用了Ringbuffer的结构来进行数据的接收发送,从这个API看来,发送和接收数据的API主要就是两个,在使用的时候,如果不去深究代码中具体干了什么事的话,使用这两个收发数据的API就可以了。

有了zynq的ps程序之后,就可以进行上位机的编写了,可以先使用上面那个作者提供的一个回环的例子,进行简单的上位机的测试,来验证一下zynq上运行的代码功能是否正确。
2. 上位机
上位机对于我这个不是做软件的人来说就有点麻烦了啊,不过通过查询一些资料写个简简单单的小程序应该还是可以的哈。
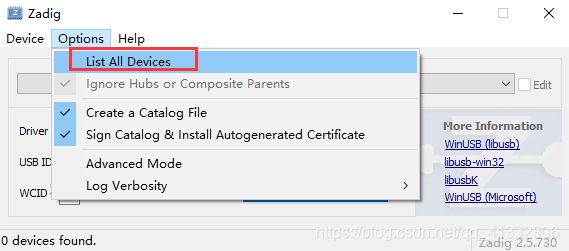
2.1 使用Zadig安装驱动
Zadig是一个开源的软件,用来给usb设备提供驱动的。使用这个软件,能够很方便地给我们地设备安装好libusb的驱动。
首先,让vitis里面的程序运行起来,然后将usb,连接到电脑上。

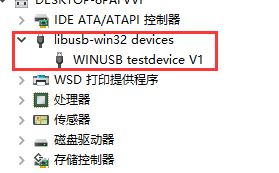
这个时候,在电脑上可能会识别出一个通用串行设备。这个设备的名称,就是前面在vitis当中设置的那个名字
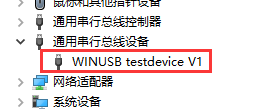

接下来使用Zaig来给这个设备添加一个libusb的驱动。Zadig的下载地址在这里:Zadig。
2.2 测试程序
libusb是一个开源的跨平台的库,在github上就能够找到。有关使用方法在它的主页上有链接可以参考。下面就是驱动文件夹中自带的一个测试例子,我稍微做了点更改
#include "stdafx.h"
#pragma comment (lib, "libusb.lib")
#include "lusb0_usb.h"
#include 现在就可以进行PC和ZYNQ之间的数据传输了。
PC上运行结果:

ZYNQ上的运行结果:
![]()
参考:
Zynq_winUSB FPGA repo