MATLAB——基于图像相减的纸牌识别系统
MATLAB------基于图像相减的纸牌识别系统
- 一、设计要求
- 二、编程思路
-
- 1、获取模板(含代码)
- 2、输入图像测试(含代码)
- 三、测试结果
- 四、性能分析
- 五、另外一道编程题(没错,就是手写数字识别)
-
- 1、图像相减方法
-
- Step1:采集手写数字图像数据
- Step2:运行MNIST_Pre.py程序对数据进行处理,变成二值化图像
- Step3:运行MNIST_Pro.py程序,将输入图片分别与各个模板图片进行减操作,计算剩余有灰度值的像素点数,选取最小值,进而对手写数字进行识别,输出结果
- Step4:测试
- Step5:性能分析
- 程序代码
- 2、基于TensorFlow的手写数字识别系统
-
- (1)步骤
- (2)测试
- (3)模型性能
- (4)程序代码
一、设计要求
这是数字图像处理课程作业的其中一道题目,设计要求如下。

所用的数据集是我舍友在网上下载的,个人觉得很高清,也懒得去拍照,就直接白嫖了,自己做测试的话,可以自行取材,注意拍摄的大小合适、位置恰当、光照均匀;如果出现光照不均,识别结果可能会偏离更多,需要提前消除光照不均的影响。
二、编程思路
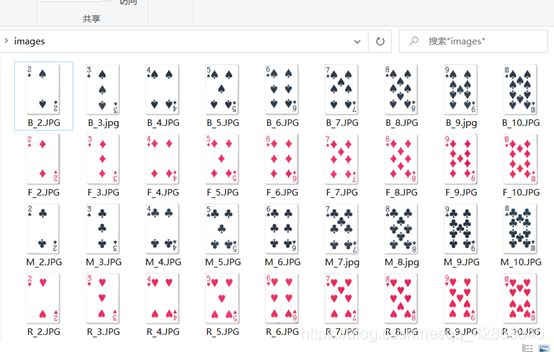
1、获取模板(含代码)
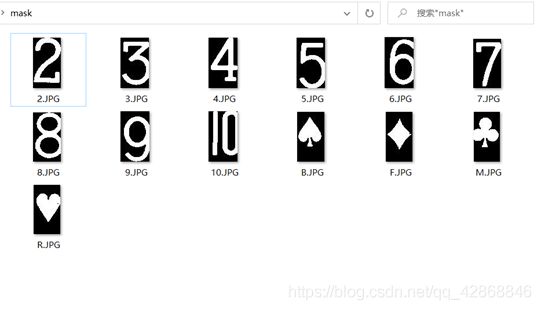
运行该程序之后,将获得差不多大小(大小会有几个像素的差别)的模板,存放在同根目录下的mask文件夹下,将所需要的数字和类型包含在待识别范围内,减小识别量。
%-------------GetImagesMask.m------------------------
clear;clc;
%用于获取模板
num = ['2' '3' '4' '5' '6' '7' '8' '9' '10'];
alpha = ['B' 'F' 'M' 'R'];
N = 1;
Al = 3;
for i=1:4
path=strcat('../images/',alpha(i),'_',num(N),'.JPG');
name = strcat(alpha(i),'_',num(N));
A = imread(path);
[x,y,z] = size(A);
Shape_Left_Top = A(x/6 : 7*x/24, y/25 : y/7, 1 : z);
% 图像二值化,反色
Shape_Left_Top_BW = ~im2bw(rgb2gray(Shape_Left_Top),0.5);
% 中值滤波去除椒盐噪声,[3,3]为窗口大小,不同噪声用不同的滤波器
mask_A = medfilt2(Shape_Left_Top_BW,[3,3]);
restore_path_A = strcat('../mask/',alpha(i),'.JPG');
imwrite(mask_A,restore_path_A); %将模板存放在mask文件夹中
end
for i = 1:9
if i==9
path=strcat('../images/',alpha(Al),'_',num(i),num(i+1),'.JPG');
name = strcat(alpha(Al),'_',num(i),num(i+1));
else
path=strcat('../images/',alpha(Al),'_',num(i),'.JPG');
name = strcat(alpha(Al),'_',num(i));
end
A = imread(path);
[x,y,z] = size(A);
Number_Left_Top = A(x/25 : x/6, y/30: y/7, 1 : z); %自己确定的大小,可更改
% 图像二值化,反色
Number_Left_Top_BW = ~im2bw(rgb2gray(Number_Left_Top),0.5);
% 中值滤波去除椒盐噪声,[3,3]为窗口大小
mask_N = medfilt2(Number_Left_Top_BW,[3,3]);
if i==9
restore_path_N = strcat('../mask/',num(i),num(i+1),'.JPG');
else
restore_path_N = strcat('../mask/',num(i),'.JPG');
end
imwrite(mask_N,restore_path_N);
end
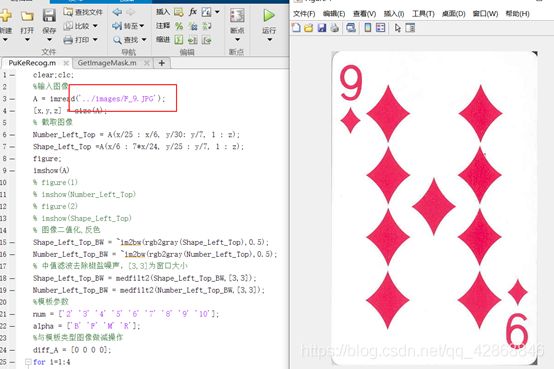
2、输入图像测试(含代码)
需要注意的是,将输入图像剪裁后的大小不一定与模板大小一致,所以要做预处理,选择模板与截取的输入图像中较小的一方的大小,然后截取另外一方为合适的大小。
%------------------PuKeRecog.m---------------------
clear;clc;
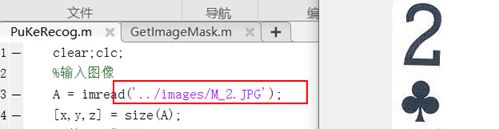
%输入图像
A = imread('../images/M_6.JPG');
[x,y,z] = size(A);
% 截取图像
Number_Left_Top = A(x/25 : x/6, y/30: y/7, 1 : z);
Shape_Left_Top =A(x/6 : 7*x/24, y/25 : y/7, 1 : z);
figure;
imshow(A)
% figure(1)
% imshow(Number_Left_Top)
% figure(2)
% imshow(Shape_Left_Top)
% 图像二值化,反色
Shape_Left_Top_BW = ~im2bw(rgb2gray(Shape_Left_Top),0.5);
Number_Left_Top_BW = ~im2bw(rgb2gray(Number_Left_Top),0.5);
% 中值滤波去除椒盐噪声,[3,3]为窗口大小
Shape_Left_Top_BW = medfilt2(Shape_Left_Top_BW,[3,3]);
Number_Left_Top_BW = medfilt2(Number_Left_Top_BW,[3,3]);
%模板参数
num = ['2' '3' '4' '5' '6' '7' '8' '9' '10'];
alpha = ['B' 'F' 'M' 'R'];
%分别与模板类型图像做减操作
diff_A = [0 0 0 0]; %用于存储与四个类型模板相减的差值
for i=1:4
path=strcat('../mask/',alpha(i),'.JPG');
mask_A = imread(path);
mask_A =~ mask_A;
mask_A =~ mask_A;
[h_m,w_m] = size(mask_A);
[h_a,w_a] = size(Shape_Left_Top_BW);
if h_m<h_a
H=h_m;
else
H=h_a;
end
if w_m<w_a
W=w_m;
else
W=w_a;
end
DD=zeros(H,W);
mask_A=double(mask_A);
for j=1:H
for k=1:W
DD(j,k) = Shape_Left_Top_BW(j,k) - mask_A(j,k);
end
end
diff_A(i) = sum(sum(abs(DD)));
end
[minVal_a minInd_a] = min(diff_A);
switch minInd_a
case 1
name=strcat('the kind is:',alpha(1));
disp(name)
case 2
name=strcat('the kind is:',alpha(2));
disp(name)
case 3
name=strcat('the kind is:',alpha(3));
disp(name)
case 4
name=strcat('the kind is:',alpha(4));
disp(name)
otherwise
disp('No found!')
end
%与模板数字图像做减操作
diff_N = [0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0]; %用于存储与九个数字模板相减的差值
for i=1:9
if i==9
path=strcat('../mask/',num(i),num(i+1),'.JPG');
else
path=strcat('../mask/',num(i),'.JPG');
end
mask_N = imread(path);
mask_N =~ mask_N;
mask_N =~ mask_N;
[h_m,w_m] = size(mask_N);
[h_a,w_a] = size(Number_Left_Top_BW);
if h_m<h_a
H=h_m;
else
H=h_a;
end
if w_m<w_a
W=w_m;
else
W=w_a;
end
DD=zeros(H,W);
mask_N=double(mask_N);
for j=1:H
for k=1:W
DD(j,k) = Number_Left_Top_BW(j,k) - mask_N(j,k);
end
end
diff_N(i) = sum(sum(abs(DD)));
end
[minVal_n minInd_n] = min(diff_N);
switch minInd_n
case 1
name=strcat('the number is:',num(1));
disp(name)
case 2
name=strcat('the number is: ',num(2));
disp(name)
case 3
name=strcat('the number is :',num(3));
disp(name)
case 4
name=strcat('the number is :',num(4));
disp(name)
case 5
name=strcat('the number is :',num(5));
disp(name)
case 6
name=strcat('the number is :',num(6));
disp(name)
case 7
name=strcat('the number is :',num(7));
disp(name)
case 8
name=strcat('the number is :',num(8));
disp(name)
case 9
name=strcat('the number is :',num(9),num(10));
disp(name)
otherwise
disp('No found!')
end
三、测试结果
测试1
输入为:
输出为:

测试2
输入为:

输出为:

测试3
输入为:
输出为:

测试4
输入为:
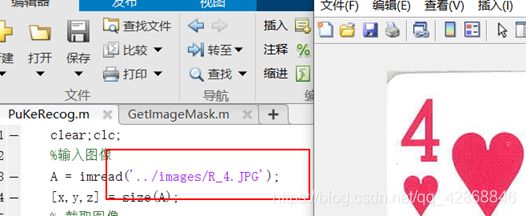
输出为:

四、性能分析
这种相减作差的识别方法优点是模板的形状一致,但对所拍摄图片的位置有很严格的要求,若是模板选择正确,拍摄纸牌的位置与模板一致,准确率是可以很高的,比手写数字识别还要高很多(手写数字的形状也不唯一,因此准确率很低。)但如果位置一旦出现偏差,那么识别错误的概率就会大大提高。
如下,类型识别错误,数字识别正确:
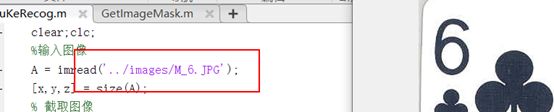

五、另外一道编程题(没错,就是手写数字识别)
1、图像相减方法
利用同样的图像相减方法,那识别正确率是相当的低呀!(虽然早就预料到了:),这次用的是Python,里面有些代码是借鉴网上大佬的,我很想找出处标明,但我发现我找不到了,害。
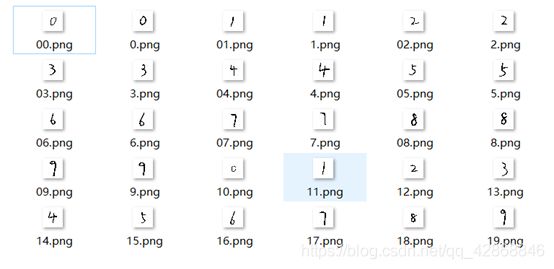
Step1:采集手写数字图像数据
Step2:运行MNIST_Pre.py程序对数据进行处理,变成二值化图像
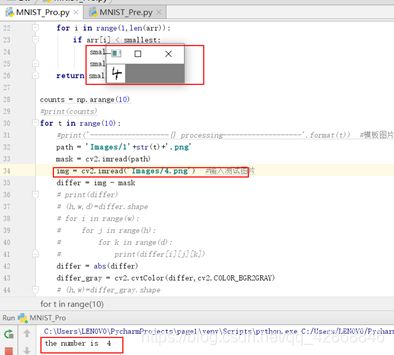
Step3:运行MNIST_Pro.py程序,将输入图片分别与各个模板图片进行减操作,计算剩余有灰度值的像素点数,选取最小值,进而对手写数字进行识别,输出结果
Step4:测试
Step5:性能分析
通过模板相减的办法进行识别,对模板要求很高,模板的位置、形状等不同,对同一图片的识别效果也会不同。加上手写数字的变化性很大,很难寻找到统一不变的特征。该模型识别率很低。
程序代码
#-------------------------------------MNIST_Pre.py----------------------------------------------
import cv2
global img
global point1,point2
def on_mouse(event,x,y,flags,param):
global img,point1,point2
img2 = img.copy()
if event == cv2.EVENT_LBUTTONDOWN:
point1 = (x,y)
cv2.circle(img2,point1,10,(0,255,0),5)
cv2.imshow('image',img2)
elif event == cv2.EVENT_MOUSEMOVE and (flags & cv2.EVENT_FLAG_LBUTTON): #按住左键拖拽
cv2.rectangle(img2,point1,(x,y),(255,0,0),5) #图像,矩形顶点,相对顶点,颜色,粗细
cv2.imshow('image',img2)
elif event == cv2.EVENT_LBUTTONUP: #左键释放
point2 = (x,y)
cv2.rectangle(img2,point1,point2,(0,0,255),5)
cv2.imshow('image',img2)
min_x = min(point1[0],point2[0])
min_y = min(point1[1],point2[1])
width = abs(point1[0]-point2[0])
height = abs(point1[1]-point2[1])
cut_img = img[min_y:min_y + height,min_x:min_x + width]
resize_img = cv2.resize(cut_img,(28,28)) #调整图像尺寸为28*28
ret,thresh_img = cv2.threshold(resize_img,127,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY) #二值化
cv2.imshow('result',thresh_img)
cv2.imwrite('Images/05.png',thresh_img) #存放位置
def main():
global img
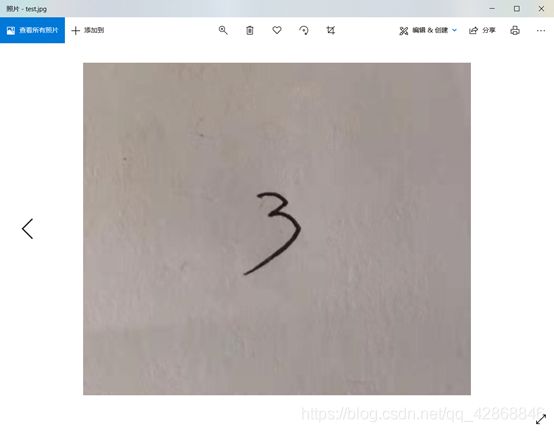
img = cv2.imread(r'C:\\Users\\LENOVO\\Desktop\\test.jpg')
img = cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
cv2.namedWindow('image')
cv2.setMouseCallback('image',on_mouse)
cv2.imshow('image',img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
#----------------------------------------MNIST_Pro.py---------------------------------------
import cv2
import numpy as np
# # 像素取反
# def get_img_reserve(img):
# #直接调用反选函数
# dst = cv2.bitwise_not(img)
# cv2.imshow("reserve",dst)
# cv2.imshow('src',img)
# return dst
#
# img = cv2.imread('Images/0.png')
# dst = get_img_reserve(img)
# kernel = np.ones((3,3),np.uint8)
# erosion = cv2.erode(dst,kernel,iterations = 1)
# cv2.imwrite('Images/pre_0.png',erosion)
# cv2.imshow('erode',erosion)
# cv2.waitKey()
def findSmallest(arr):
smallest = arr[0]
smallest_index = 0
for i in range(1,len(arr)):
if arr[i] < smallest:
smallest = arr[i]
smallest_index = i
return smallest_index
counts = np.arange(10)
#print(counts)
for t in range(10):
#print('-------------------{} processing-------------------'.format(t)) #模板图片
path = 'Images/1'+str(t)+'.png'
mask = cv2.imread(path)
img = cv2.imread('Images/6.png') #输入测试图片
differ = img - mask
# print(differ)
# (h,w,d)=differ.shape
# for i in range(w):
# for j in range(h):
# for k in range(d):
# print(differ[i][j][k])
differ = abs(differ)
differ_gray = cv2.cvtColor(differ,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
# (h,w)=differ_gray.shape
# for i in range(w):
# for j in range(h):
# print(differ[i][j])
ret,thresh = cv2.threshold(differ_gray,0,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
cv2.imwrite('Images/differ'+str(t)+'.png',thresh)
#cv2.imshow('differ',thresh)
(h, w) = thresh.shape
#print("width={}, height={}".format(w, h))
count = 0
for i in range(w):
for j in range(h):
if thresh[i][j] == 255:
count = count + 1
counts[t] = count
#print('count'+str(t)+'= ',count)
min = findSmallest(counts)
print('the number is ',min)
cv2.imshow('Writing Number',img)
cv2.waitKey()
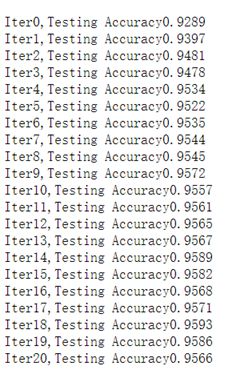
2、基于TensorFlow的手写数字识别系统
之前学习TensorFlow的时候,跟着大佬打过的代码,还是深度学习香,准确率也高,po这里,一起学习。
(1)步骤
Step1:载入TensorFlow里的mnist数据;
Step2:训练网络,利用梯度下降算法训练模型,利用AdamOptimizer优化器提高精确度;
Step3:载入自己的图像测试。
(2)测试
(3)模型性能
(4)程序代码
#我的TensorFlow版本是2,为了使用某些功能,将其表现为版本1,用的编辑器是jupyter
import tensorflow.compat.v1 as tf
tf.disable_v2_behavior()
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
#载入数据集
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets('MNIST_data',one_hot=True)
#每个数据集大小
batch_size = 30
#计算一共有多少个数据集
n_batch = mnist.train.num_examples // batch_size
#定义两个placeholder
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,784])
y = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[None,10])
#定义神经网络中间层
Weights_L1 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([784,30]))
biases_L1 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([30]))
Wx_plus_b_L1 = tf.matmul(x,Weights_L1) + biases_L1
L1 = tf.nn.tanh(Wx_plus_b_L1)
#创建一个简单的神经网络
W = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([30,10]))
b = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10]))
prediction = tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(L1,W)+b)
#二次代价函数
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=y,logits=prediction))
#使用梯度下降法
#train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.3).minimize(loss)
train_step = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(1e-3).minimize(loss)
#初始化变量
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
#结果存放在一个布尔型列表中
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y,1),tf.argmax(prediction,1)) #argmax返回一维张量中最大的值所在的位置
#求准确率
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction,tf.float32))
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
for epoch in range(21):
for batch in range(n_batch):
batch_xs,batch_ys = mnist.train.next_batch(batch_size)
sess.run(train_step,feed_dict={
x:batch_xs,y:batch_ys})
acc = sess.run(accuracy,feed_dict={
x:mnist.test.images,y:mnist.test.labels})
print('Iter' + str(epoch) + ",Testing Accuracy" + str(acc))
#图像预处理
import cv2
global img
global point1,point2
def on_mouse(event,x,y,flags,param):
global img,point1,point2
img2 = img.copy()
if event == cv2.EVENT_LBUTTONDOWN:
point1 = (x,y)
cv2.circle(img2,point1,10,(0,255,0),5)
cv2.imshow('image',img2)
elif event == cv2.EVENT_MOUSEMOVE and (flags & cv2.EVENT_FLAG_LBUTTON): #按住左键拖拽
cv2.rectangle(img2,point1,(x,y),(255,0,0),5) #图像,矩形顶点,相对顶点,颜色,粗细
cv2.imshow('image',img2)
elif event == cv2.EVENT_LBUTTONUP: #左键释放
point2 = (x,y)
cv2.rectangle(img2,point1,point2,(0,0,255),5)
cv2.imshow('image',img2)
min_x = min(point1[0],point2[0])
min_y = min(point1[1],point2[1])
width = abs(point1[0]-point2[0])
height = abs(point1[1]-point2[1])
cut_img = img[min_y:min_y + height,min_x:min_x + width]
resize_img = cv2.resize(cut_img,(28,28)) #调整图像尺寸为28*28
ret,thresh_img = cv2.threshold(resize_img,127,255,cv2.THRESH_BINARY) #二值化
cv2.imshow('result',thresh_img)
cv2.imwrite('images/test.png',thresh_img) #存放位置
def main():
global img
img = cv2.imread(r'C:\Users\LENOVO\Desktop\test.jpg')
img = cv2.cvtColor(img,cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
cv2.namedWindow('image')
cv2.setMouseCallback('image',on_mouse)
cv2.imshow('image',img)
cv2.waitKey(0)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
#利用训练好的模型进行测试
from PIL import Image
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
im = Image.open('images/test.png')
data = list(im.getdata())
result = [(255-x)*1.0/255.0 for x in data]
print(result)
# 为输入图像和目标输出类别创建节点
x = tf.placeholder("float", shape=[None, 784]) # 训练所需数据 占位符
# *************** 构建多层卷积网络 *************** #
def weight_variable(shape):
initial = tf.truncated_normal(shape, stddev=0.1) # 取随机值,符合均值为0,标准差stddev为0.1
return tf.Variable(initial)
def bias_variable(shape):
initial = tf.constant(0.1, shape=shape)
return tf.Variable(initial)
def conv2d(x, W):
return tf.nn.conv2d(x, W, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
def max_pool_2x2(x):
return tf.nn.max_pool(x, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1], strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME')
x_image = tf.reshape(x, [-1,28,28,1]) # -1表示任意数量的样本数,大小为28x28,深度为1的张量
W_conv1 = weight_variable([5, 5, 1, 32]) # 卷积在每个5x5的patch中算出32个特征。
b_conv1 = bias_variable([32])
h_conv1 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(x_image, W_conv1) + b_conv1)
h_pool1 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv1)
W_conv2 = weight_variable([5, 5, 32, 64])
b_conv2 = bias_variable([64])
h_conv2 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(h_pool1, W_conv2) + b_conv2)
h_pool2 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv2)
W_fc1 = weight_variable([7 * 7 * 64, 1024])
b_fc1 = bias_variable([1024])
h_pool2_flat = tf.reshape(h_pool2, [-1, 7*7*64])
h_fc1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(h_pool2_flat, W_fc1) + b_fc1)
# 在输出层之前加入dropout以减少过拟合
keep_prob = tf.placeholder("float")
h_fc1_drop = tf.nn.dropout(h_fc1, keep_prob)
# 全连接层
W_fc2 = weight_variable([1024, 10])
b_fc2 = bias_variable([10])
# 输出层
# tf.nn.softmax()将神经网络的输层变成一个概率分布
y_conv=tf.nn.softmax(tf.matmul(h_fc1_drop, W_fc2) + b_fc2)
saver = tf.train.Saver() # 定义saver
# *************** 开始识别 *************** #
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
saver.restore(sess, "save/model.ckpt")#这里使用了之前保存的模型参数
prediction = tf.argmax(y_conv,1)
predint = prediction.eval(feed_dict={
x: [result],keep_prob: 1.0}, session=sess)
print("recognize result: %d" %predint[0])
555数图作业让我没有头发
如需转载,请标明出处,xixixi。