安卓学习日志 — Day03
文章目录
-
- 概述
- 目标
- 实现步骤
-
- 问题分析
- 列表项布局
- 数据来源
- 自定义适配器
- 显示到页面当中
- 其他页面
- 总结
- 参考
概述
继续构建Miwok语言应用,理解适配器的使用,并自定义适配器。
目标
上次利用视图回收机制在页面中实现了数据的展示,但Miwok是一个用于学习语言的app ,因此需要提供两种语言的参照,如同一个单词需要展示 Miwok 和 English 两种语言的。
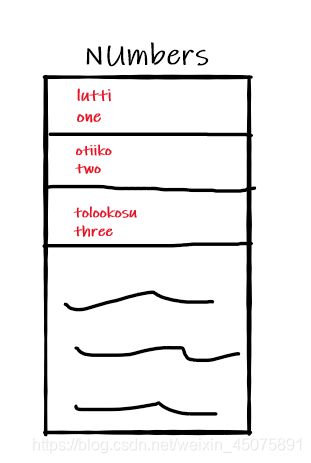
比如在学习 Numbers 的页面中每行需显示该数字的 Miwok 和 English 版本,最终需要实现的样子应该类似这样:
实现步骤
问题分析
上次在实现一个页面中显示 1~n 的数字时使用到了 ArrayAdapter ,以及 ArrayList 并让每个数字都作为一个列表项显示在Android 为我们提供的布局 文件android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1 当中。 ArrayAdapter 帮助我们管理 ArrayList 中的 String 对象,
点开该布局文件,会发现其实就只是一个 TextView ,其内容如下:
<TextView xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@android:id/text1"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:textAppearance="?android:attr/textAppearanceListItemSmall"
android:gravity="center_vertical"
android:paddingStart="?android:attr/listPreferredItemPaddingStart"
android:paddingEnd="?android:attr/listPreferredItemPaddingEnd"
android:minHeight="?android:attr/listPreferredItemHeightSmall" />
之前在创建 数据适配器 ArrayAdapter 实例的语句为:
ArrayAdapter<String> adapter = new ArrayAdapter<String>(this, android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1, words);
ArrayAdapter 指定了泛型 String 表示这个适配器管理的数据为String类型,同时我们传入了一个 包含 String对象 的 列表数据 words。
页面中显示的每个数字列表项,其实就是通过这个android.R.layout.simple_list_item_1 布局而创建的实例,因此 ArrayAdapter 默认管理的视图和对象为 单个 TextView 和 String。
而最终想要实现的效果为 每个列表项中 包含 Miwok 和 English 两个语言版本,为达到这一效果,就需要自定义列表项的布局文件,并自定义适配器 ,再让这个适配器管理自定义的列表项布局视图。
列表项布局
那么首先来定义列表项的布局文件,最终效果中的列表项分为两部分:Miwok 和 English ,那么可以考虑使用垂直布局的 LinearLayout 并嵌套 2个 TextView 来分别显示两种语言的单词版本。
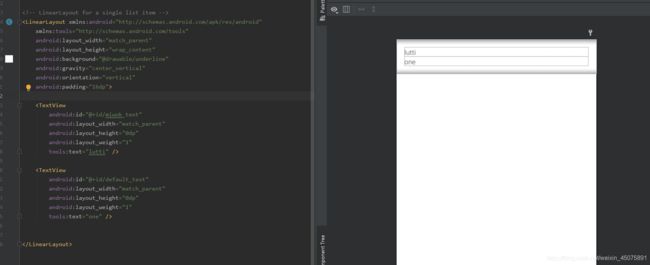
创建列表项的布局文件(list_item.xml)如下:
使用 ViewGroup LinearLayout 作为列表项布局的基本视图,android:orientation="vertical" 使布局中的 两个 TextView 垂直排列,同时设置 TextView 的 layout_height 为 0dp、layout_weight 为 1 让其高度均值分布。
数据来源
我们需要在每个列表项显示 2个 语言的字符串,因此可以考虑使用对象来封装每个列表项中需要显示的数据,可以更好的控制数据。
定义一个 Word 类型,并包含两个语言版本 的字符串 的属性 、一个 初始化 该类的构造函数 和 两个属性的 Getter 方法。
Word.java :
public class Word {
/**
* Default(English) translation for the word
*/
private String defaultTranslation;
/**
* Miwok translation for the word
*/
private String miwokTranslation;
/**
* Create a new Word object.
*
* @param defaultTranslation is the word in a language that the user is already familiar with
* (such as English)
* @param miwokTranslation is the word in the Miwok language
*/
public Word(String defaultTranslation, String miwokTranslation) {
this.defaultTranslation = defaultTranslation;
this.miwokTranslation = miwokTranslation;
}
}
之后就可以 将一个包含 Word 对象的数组列表交给 适配器来管理。
自定义适配器
Android 提供的 ArrayAdapter 只能管理 单个 TextView 和 String 对象,而我们自己的列表项需要显示两条数据(一个Word对象),或许可以对现有的 ArrayAdapter 进行扩展,让它管理 自定义的 Word 对象 和 自定义的列表项布局 ,这就需要自定义适配器(继承基适配器)。
自定义的适配器需要继承 ArrayAdapter 接收一个泛型 Word 表示管理一个包含 Word 的数据列表。
自定义适配器 WordAdapter.java 如下:
public class WordAdapter extends ArrayAdapter<Word> {
/**
* This is our own custom constructor (it doesn't mirror a superclass constructor).
* The context is used to inflate the layout file, and the list is the data we want
* to populate into the lists.
*
* @param context The current context. Used to inflate the layout file.
* @param words A List of Word objects to display in a list
*/
public WordAdapter(Activity context, ArrayList<Word> words) {
// Here, we initialize the ArrayAdapter's internal storage for the context and the list.
// the second argument is used when the ArrayAdapter is populating a single TextView.
// Because this is a custom adapter for two TextViews and an ImageView, the adapter is not
// going to use this second argument, so it can be any value. Here, we used 0.
super(context, 0, words);
}
}
自定义适配器 WordAdapter 继承自 ArrayAdapter ,并指定泛型 Word 表示管理一组 Word 对象。
还有一个接收两个参数(上下文、数据来源)的构造函数,在构造函数中只有一行语句,该语句将上下文 context 和数量来源 words,传递给了 父类 ArrayAdapter 的构造函数,并指定了 列表布局资源的 id 为 0,这个 0 是一个不存在的布局资源 ID 相当于 没有指定要使用的视图资源。
因为 WordAdapter 继承自 ArrayAdapter ,即 WordAdapter 默认也将默认管理单个 Textview 和 String 对象, 所以 在调用父类 ArrayAdapter 的构造函数时传入 布局资源ID为 0。
另外 还是需要让自定义的这个适配器 WordAdapter 将 Word 对象和 列表项布局资源 联系起来,实现 适配器的基础功能 视图回收。
经查阅资料,发现 ArrayAdapter 有一个 getView() 方法,用于分配要显示的 视图,那么重写这个方法让其 将 一个 Word 对象 和 自定义的布局资源 作为要 显示的 列表项视图 交给 Numbers页面根视图 ListView 并显示即可:
在 WordAdapter 中重写 getView 方法:
/**
* Provides a view for an AdapterView (ListView, GridView, etc.)
*
* @param position The position in the list of data that should be displayed in the
* list item view.
* @param convertView The recycled view to populate.
* @param parent The parent ViewGroup that is used for inflation.
* @return The View for the position in the AdapterView.
*/
@Override
public View getView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {
// Check if the existing view is being reused, otherwise inflate the view
View itemView = convertView;
if (itemView == null) {
itemView = LayoutInflater.from(getContext()).inflate(
R.layout.list_item, parent, false);
}
// Get the {@link Word} object located at this position in the list
Word currentWord = getItem(position);
// Find the TextView in the list_item.xml layout with the ID miwok_text
TextView miwokTextView = (TextView) itemView.findViewById(R.id.miwok_text);
// Get the miwok text from the current Word object and
// set this text on the miwok TextView
miwokTextView.setText(currentWord.getMiwokTranslation());
// Find the TextView in the list_item.xml layout with the ID default_text
TextView defaultTextView = (TextView) itemView.findViewById(R.id.default_text);
// Get the version number from the current Word object and
// set this text on the default(english) TextView
defaultTextView.setText(currentWord.getDefaultTranslation());
// Return the whole list item layout (containing 2 TextViews)
// so that it can be shown in the ListView
return itemView;
}
重写的 getView 方法接收 3个参数 position(将在屏幕中显示的对象在数组列表中所处的索引位置)、convertView(被回收的列表项视图对象)、parent (被回收视图的父视图,即根视图 ListView)。
重写的 getView 方法基本做了三件事情:
- 13 ~ 17 行,得到被回收的视图
itemView,如果该视图为 空对象则根据列表项的布局资源list_item创建一个(被回收的视图存在空的情况是因为 在Numbers 的页面刚加载时,并没有多余 的视图用于 回收,这是被回收的视图对象itemView就是一个空对象null)。 - 20 ~ 32 行,调用继承自
ArrayAdapter的getItem方法 得到 下一个 将要被显示的Word对象,然后通过预先在 列表项布局资源中对于的视图 ID 将 这个对象的属性 分别设置为被回收的视图itemView需要显示的内容。 - 36 行,将这个 被赋予新内容的 列表项视图
itemView返回出去,即可将 新的Word对象显示在 页面根视图ListView当中,重复利用了视图资源 而不造成资源浪费。
显示到页面当中
列表项布局、数据来源、自定义的适配器都有了,下面只需让其将数据显示到页面即可,
在 Numbers 页面的 onCreate 方法中更改 代码如下:
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_numbers);
// Create a array list of words
ArrayList<Word> words = new ArrayList<Word>();
words.add(new Word("one", "lutti"));
words.add(new Word("two", "otiiko"));
words.add(new Word("three", "tolookosu"));
words.add(new Word("four", "oyyisa"));
words.add(new Word("five", "massokka"));
words.add(new Word("six", "temmokka"));
words.add(new Word("seven", "kenekaku"));
words.add(new Word("eight", "kawinta"));
words.add(new Word("nine", "wo'e"));
words.add(new Word("ten", "na'aacha"));
// Create an {@link ArrayAdapter}, whose data source is a list of Strings. The
// adapter knows how to create layouts for each item in the list, using the
// simple_list_item_1.xml layout resource defined in the Android framework.
// This list item layout contains a single {@link TextView}, which the adapter will set to
// display a single word.
WordAdapter adapter = new WordAdapter(this, words);
// Find the {@link ListView} object in the view hierarchy of the {@link Activity}.
// There should be a {@link ListView} with the view ID called list, which is declared in the
// activity_numbers.xml layout file.
ListView listLayout = (ListView) findViewById(R.id.list);
// Make the {@link ListView} use the {@link ArrayAdapter} we created above, so that the
// {@link ListView} will display list items for each word in the list of words.
// Do this by calling the setAdapter method on the {@link ListView} object and pass in
// 1 argument, which is the {@link ArrayAdapter} with the variable name itemsAdapter.
listLayout.setAdapter(adapter);
}
和 ArrayAdapter 的使用基本相同:
- 7 ~ 17 行,准备数据来源
words(一个包含Word对象的数字列表) - 25 行,创建自定义适配器
WordAdapter对象 adapter,传入参数 context 上下文、words 数据来源(这里没有指定布局资源是因为在WordAdapter的getView` 方法中 已经实现了 自定义布局资源和 Word 对象的适配) - 30 行,获取用于显示列表项的根视图
ListView对象。 - 36 行,为根视图
ListView对象设置 适配器 为自定义的WordAdapter对象adpter。
至此 使用自定义适配器在 Numbers 页面中 每个列表项 显示 两条数据 的目标完成。
其他页面
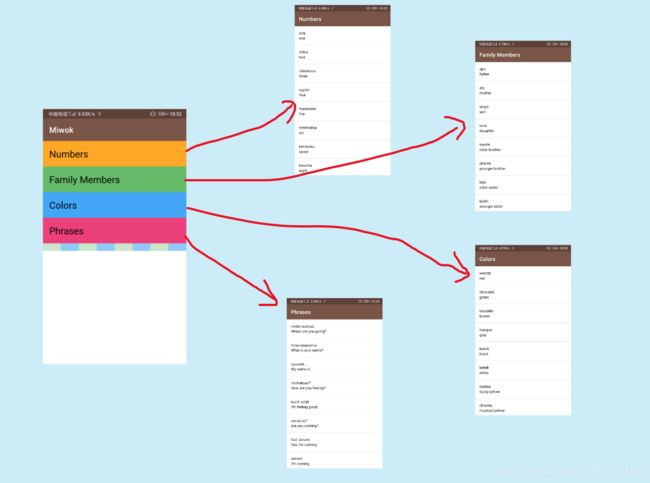
另外 3个 页面 Family Members、Color 和 Phrases 的需求也 和 Numbers 页面一样(在页面的每个列表项中显示单词 的 Miwok 和 English 两个语言版本)。
这几个也需要用到 同样的 页面布局(根视图 ListView)、列表项布局(list_item.xml)和 自定义的适配器 WordAdapter。
可以考虑让每个页面都 使用同一个页面布局(根视图 ListView)文件,所以在 Numbers 页面的 xml 布局文件上 鼠标右击 --> Refactor(重构) --> Rename(重命名)为 word_list,然后在 word_list.xml 布局文件中 将 根视图 ListView 的 tools:context 属性和值删除(这个属性指定了 布局文件作用与哪个页面 Activity),最终 word_list.xml 内容如下:
<ListView xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:id="@+id/list"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" />
然后 在 所有 页面的 onCreate 方法中,重复之前的步骤(准备数据来源 --> 创建适配器 --> 获取根视图 --> 为根视图绑定适配器)。
注意: 每个页面在加载时要使用 刚刚准备好的这个 word_list.xml 布局资源。
比如 Colors 页面的 onCreate 方法如下(第四行 指定了 页面的布局资源):
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.word_list);
// Create a array list of words
ArrayList<Word> words = new ArrayList<Word>();
words.add(new Word("red", "weṭeṭṭi"));
words.add(new Word("green", "chokokki"));
words.add(new Word("brown", "ṭakaakki"));
words.add(new Word("gray", "ṭopoppi"));
words.add(new Word("black", "kululli"));
words.add(new Word("white", "kelelli"));
words.add(new Word("dusty yellow", "ṭopiisə"));
words.add(new Word("mustard yellow", "chiwiiṭə"));
// Create an {@link ArrayAdapter}, whose data source is a list of Strings. The
// adapter knows how to create layouts for each item in the list, using the
// simple_list_item_1.xml layout resource defined in the Android framework.
// This list item layout contains a single {@link TextView}, which the adapter will set to
// display a single word.
WordAdapter adapter = new WordAdapter(this, words);
// Find the {@link ListView} object in the view hierarchy of the {@link Activity}.
// There should be a {@link ListView} with the view ID called list, which is declared in the
// activity_numbers.xml layout file.
ListView listLayout = (ListView) findViewById(R.id.list);
// Make the {@link ListView} use the {@link ArrayAdapter} we created above, so that the
// {@link ListView} will display list items for each word in the list of words.
// Do this by calling the setAdapter method on the {@link ListView} object and pass in
// 1 argument, which is the {@link ArrayAdapter} with the variable name itemsAdapter.
listLayout.setAdapter(adapter);
}
另外几个页面的 onCreate 方法 也是一样的,唯一的的区别是 数据来源 中每个数据 的 值不一样(这是肯定的,每个页面显示的是该页面的词汇)。
最终每个页面的 实现效果如下:
总结
通过 继承 实现了 自定义适配器,根据需求实现了 功能的扩展。
通过自定义适配器还可以实现 更多复杂的功能,如在每个列表项中为单词 添加图片 或 音频 等资源。
参考
How does ArrayAdapter getView() method works?
Using an ArrayAdapter with ListView
What Are Adapters in Android
Performance Tips for Android’s ListView