模拟退火算法
一. 爬山算法 ( Hill Climbing )
作为对比,先介绍爬山算法。爬山算法是一种简单的贪心搜索算法,该算法每次从当前解的临近解空间中选择一个最优解作为当前解,直到达到一个局部最优解。
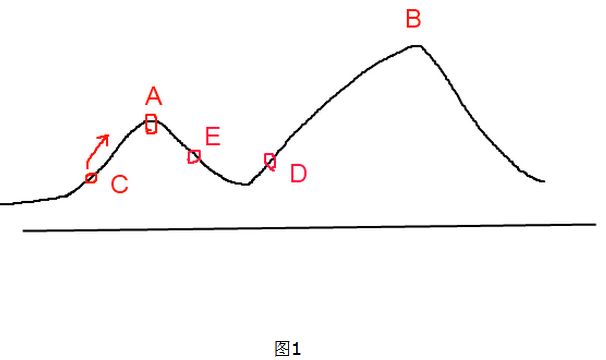
爬山算法实现很简单,其主要缺点是会陷入局部最优解,而不一定能搜索到全局最优解。如图1所示:假设C点为当前解,爬山算法搜索到A点这个局部最优解就会停止搜索,因为在A点无论向那个方向小幅度移动都不能得到更优的解。
二. 模拟退火(SA,Simulated Annealing)思想
爬山法是完完全全的贪心法,每次都鼠目寸光的选择一个当前最优解,因此只能搜索到局部的最优值。模拟退火其实也是一种贪心算法,但是它的搜索过程引入了随机因素。模拟退火算法以一定的概率来接受一个比当前解要差的解,因此有可能会跳出这个局部的最优解,达到全局的最优解。以图1为例,模拟退火算法在搜索到局部最优解A后,会以一定的概率接受到E的移动。也许经过几次这样的不是局部最优的移动后会到达D点,于是就跳出了局部最大值A。
模拟退火算法描述:
- 若J( Y(i+1) )>= J( Y(i) ) (即移动后得到更优解),则总是接受该移动
- 若J( Y(i+1) )< J( Y(i) ) (即移动后的解比当前解要差),则以一定的概率接受移动,而且这个概率随着时间推移逐渐降低(逐渐降低才能趋向稳定)
这里的“一定的概率”的计算参考了金属冶炼的退火过程,这也是模拟退火算法名称的由来。
根据热力学的原理,在温度为T时,出现能量差为Δt的降温的概率为P(Δt),表示为:
P(Δt) = e(- Δt/(kT) )
其中k是一个常数,e表示自然指数,且Δt<0。这条公式说白了就是:温度越高(T越大),出现一次能量差为Δt的降温的概率就越大;温度越低(T越小),则出现降温的概率就越小。又由于Δt总是小于0(否则就不叫退火了),因此Δt/kT < 0 ,所以P(Δt)的函数取值范围是(0,1) 。随着温度T的降低,P(Δt)会逐渐降低。
三. 模拟退火算法伪代码
/* * J(y):在状态y时的评价函数值 * Y(i):表示当前状态 * Y(i+1):表示新的状态 * r: 用于控制降温的快慢 * T: 系统的温度,系统初始应该要处于一个高温的状态 * T_min :温度的下限,若温度T达到T_min,则停止搜索 */ while( T > T_min ) { dE = J( Y(i+1) ) - J( Y(i) ) ; if ( dE >=0 ) //表达移动后得到更优解,则总是接受移动 Y(i+1) = Y(i) ; //接受从Y(i)到Y(i+1)的移动 else { if ( exp( dE/T ) > random( 0 , 1 ) ) Y(i+1) = Y(i) ; //接受从Y(i)到Y(i+1)的移动 } T = r * T ; //降温退火 ,0<r<1 。r越大,降温越慢;r越小,降温越快 /* * 若r过大,则搜索到全局最优解的可能会较高,但搜索的过程也就较长。若r过小,则搜索的过程会很快,但最终可能会达到一个局部最优值 */ i ++ ; }
四. 使用模拟退火算法解决旅行商问题
旅行商问题 ( TSP , Traveling Salesman Problem ) :有N个城市,要求从其中某个问题出发,唯一遍历所有城市,再回到出发的城市,求最短的路线。
旅行商问题属于所谓的NP完全问题,精确的解决TSP只能通过穷举所有的路径组合,其时间复杂度是O(N!) 。
使用模拟退火算法可以比较快的求出TSP的一条近似最优路径。(使用遗传算法也是可以的)模拟退火解决TSP的思路:
- 产生一条新的遍历路径P(i+1),计算路径P(i+1)的长度L( P(i+1) )
- 若L(P(i+1)) < L(P(i)),则接受P(i+1)为新的路径,否则以模拟退火的那个概率接受P(i+1) ,然后降温
- 重复步骤1,2直到满足退出条件
产生新的遍历路径的方法有很多,下面列举其中3种:
- 随机选择2个节点,交换路径中的这2个节点的顺序。
- 随机选择2个节点,将路径中这2个节点间的节点顺序逆转。
- 随机选择3个节点m,n,k,然后将节点m与n间的节点移位到节点k后面。
参考代码
#include <iostream> #include <sstream> #include <fstream> #include <string> #include <cstring> #include <iterator> #include <algorithm> #include <climits> #include <cmath> #include <cstdlib> using namespace std; const int nCities = 10; //城市数量 const double SPEED = 0.98; //退火速度 const int INITIAL_TEMP = 1000; //初始温度 const int L = 10 * nCities; //Markov 链的长度 struct unit //一个解 { double length; //代价,总长度 int path[nCities]; //路径 bool operator < (const struct unit &other) const { return length < other.length; } }; unit bestone = {INT_MAX, {0} }; //最优解 double length_table[nCities][nCities]; //distance class saTSP { public: int init_dis(); // create matrix to storage the Distance each city void SA_TSP(); void CalCulate_length(unit &p); //计算长度 void print(unit &p); //打印一个解 void getNewSolution(unit &p); // 从邻域中获去一个新解 bool Accept(unit &bestone, unit &temp, double t);//新解以Metropolis 准则接受 }; //stl 中 generate 的辅助函数对象 class GenbyOne { public: GenbyOne (int _seed = -1): seed(_seed){} int operator() (){return seed += 1;} private: int seed; }; void saTSP::SA_TSP() { srand((int)time(0)); int i = 0; double r = SPEED; double t = INITIAL_TEMP; const double t_min = 0.001; //温度下限,若温度达到t_min ,则停止搜索 //choose an initial solution ~ unit temp; generate(temp.path, temp.path + nCities, GenbyOne(0)); random_shuffle(temp.path, temp.path + nCities); CalCulate_length(temp); memcpy(&bestone, &temp, sizeof(temp)); // while the stop criterion is not yet satisfied do while ( t > t_min ) { for (i = 0; i < L; i++) { getNewSolution(temp); //cout << "dkkd:" << bestone.length << endl; if(Accept(bestone,temp, t)) { memcpy(&bestone, &temp, sizeof(unit)); } else { memcpy(&temp, &bestone, sizeof(unit)); } } t *= r; //退火 } return; } bool saTSP::Accept(unit &bestone, unit &temp, double t) { if (bestone.length > temp.length) //获得更短的路径 { return true; } else { if ((int)(exp((bestone.length - temp.length) / t) * 100) > (rand() % 101) ) { return true; } } return false; } void saTSP::getNewSolution(unit &p) { int i = rand() % nCities; int j = rand() % nCities; if (i > j) { int t = i; i = j; j = t; } else if (i == j) { return; } int choose = rand() % 3; if ( choose == 0) {//交换 int temp = p.path[i]; p.path[i] = p.path[j]; p.path[j] = temp; } else if (choose == 1) {//置逆 reverse(p.path + i, p.path + j); } else {//移位 if (j + 1 == nCities) //边界处不处理 { return; } rotate(p.path + i, p.path + j, p.path + j + 1); } CalCulate_length(p); } int saTSP::init_dis() // create matrix to storage the Distance each city { int i = 0, j = 0; string line; double word; ifstream infile("del2.txt"); if(!infile) { cout << "Cannot open the file" << endl; return 0; } while(getline(infile, line)) { j = 0; istringstream instream(line); while(instream >> word) { length_table[i][j] = word; ++j; } ++i; } } void saTSP::CalCulate_length(unit &p) { int j = 0; p.length = 0; for (j = 1; j < nCities; j++) { p.length += length_table[ p.path[j-1] ][ p.path[j] ]; } p.length += length_table[p.path[ nCities - 1] ][ p.path[0] ]; } void saTSP::print( unit &p) { int i; cout << "代价是:" << p.length << endl; cout << "路径是:"; for (i = 0; i < nCities; i++) { cout << p.path[i] << " "; } cout << endl; } int main(int argc, char* argv[]) { saTSP sa; sa.init_dis(); sa.SA_TSP(); sa.CalCulate_length(bestone); sa.print(bestone); return 0; }
del2.txt
0 5 1272 2567 1653 2097 1425 1177 3947 3 5 0 4 2511 1633 2077 1369 1157 3961 1518 1272 4 0 1 380 1490 821 856 3660 385 2567 2511 1 0 1 2335 1562 2165 3995 933 1653 1633 380 1 0 1 1041 1135 3870 456 2097 2077 1490 2335 1 0 1 920 2170 1920 1425 1369 821 1562 1041 1 0 1 4290 626 1177 1157 856 2165 1135 920 1 0 1 1290 3947 3961 3660 3995 3870 2170 4290 1 0 4 3 1518 385 993 456 1920 626 1290 4 0
运行结果

参考