链接脚本使用----- 将二进制文件作为一个段
在分析Linux内核编译流程的时候,看到arch/arm/boot/compressed/piggy.gzip.S将压缩后的Linux内核(arch/arm/boot/compressed/piggy.gzip)包含进来:
1: .section .piggydata,#alloc
2: .globl input_data
3: t_data:
4: .incbin "arch/arm/boot/compressed/piggy.gzip"
5: .globl input_data_end
6: t_data_end:
我们是不是也可以利用这种方法将一副图片作为可执行程序的一个段,然后再程序中访问这个段来达到显示图片的目的?下面是我的做法:
仿照piggy.gzip.S实现demo.S:
1: .section .peng
2: .incbin "./logo.jpg"
main.c
1: #include <stdio.h>
2:
3: extern unsigned int __peng_start;
4: extern unsigned int __peng_end;
5:
6: char *p = (char *)(&__peng_start);
7: //我们要获取__peng_start的存放地址,作为字符串首地址,或者数组名来使用。
8: int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
9: {
10: int i;
11: unsigned int len = 0;
12:
13: len = (unsigned int)(&__peng_end) - (unsigned int)(&__peng_start);
14:
15: printf("len = %x\n", len);
16:
17: printf("%p\n", &__peng_start);
18: printf("%p\n", &__peng_end);
19:
20: for(i=0; i<len; i++)
21: {
22: if (i % 16 == 0)
23: {
24: printf("\n");
25: }
26: printf("%3x ", *p++&0xff);
27: }
28:
29:
30: return 0;
31: }
Makefile
1: CC=gcc -Wall
2:
3: main:main.o demo.o
4: $(CC) $^ -Tload.lds -o $@
5:
6: main.o:main.c
7:
8: demo.o:demo.S
9:
10:
11: clean:
12: $(RM) *.o main
load.lds
1: OUTPUT_FORMAT("elf32-i386", "elf32-i386",
2: "elf32-i386")
3: OUTPUT_ARCH(i386)
4: ENTRY(_start)
5: SEARCH_DIR("/usr/i486-linux-gnu/lib32"); SEARCH_DIR("/usr/local/lib32"); SEARCH_DIR("/lib32"); SEARCH_DIR("/usr/lib32"); SEARCH_DIR("/usr/i486-linux-gnu/lib"); SEARCH_DIR("/usr/local/lib"); SEARCH_DIR("/lib"); SEARCH_DIR("/usr/lib");
6: SECTIONS
7: {
8: /* Read-only sections, merged into text segment: */
9: PROVIDE (__executable_start = SEGMENT_START("text-segment", 0x08048000)); . = SEGMENT_START("text-segment", 0x08048000) + SIZEOF_HEADERS;
10: .interp : { *(.interp) }
11: .note.gnu.build-id : { *(.note.gnu.build-id) }
12: .hash : { *(.hash) }
13: .gnu.hash : { *(.gnu.hash) }
14: .dynsym : { *(.dynsym) }
15: .dynstr : { *(.dynstr) }
16: .gnu.version : { *(.gnu.version) }
17: .gnu.version_d : { *(.gnu.version_d) }
18: .gnu.version_r : { *(.gnu.version_r) }
19: .peng :
20: {
21: . = ALIGN(4);
22: __peng_start = .;
23: *(.peng);
24: __peng_end = .;
25: . = ALIGN(4);
26: }
27: .rel.dyn :
28: {
29: *(.rel.init)
30: *(.rel.text .rel.text.* .rel.gnu.linkonce.t.*)
31: *(.rel.fini)
32: *(.rel.rodata .rel.rodata.* .rel.gnu.linkonce.r.*)
33: *(.rel.data.rel.ro* .rel.gnu.linkonce.d.rel.ro.*)
34: *(.rel.data .rel.data.* .rel.gnu.linkonce.d.*)
35: *(.rel.tdata .rel.tdata.* .rel.gnu.linkonce.td.*)
36: *(.rel.tbss .rel.tbss.* .rel.gnu.linkonce.tb.*)
37: *(.rel.ctors)
38: *(.rel.dtors)
39: *(.rel.got)
40: *(.rel.bss .rel.bss.* .rel.gnu.linkonce.b.*)
41: *(.rel.ifunc)
42: }
43: .rel.plt :
44: {
45: *(.rel.plt)
46: PROVIDE_HIDDEN (__rel_iplt_start = .);
47: *(.rel.iplt)
48: PROVIDE_HIDDEN (__rel_iplt_end = .);
49: }
50: .init :
51: {
52: KEEP (*(.init))
53: } =0x90909090
54: .plt : { *(.plt) *(.iplt) }
55: .text :
56: {
57: *(.text.unlikely .text.*_unlikely)
58: *(.text .stub .text.* .gnu.linkonce.t.*)
59: /* .gnu.warning sections are handled specially by elf32.em. */
60: *(.gnu.warning)
61: } =0x90909090
62: .fini :
63: {
64: KEEP (*(.fini))
65: } =0x90909090
66: PROVIDE (__etext = .);
67: PROVIDE (_etext = .);
68: PROVIDE (etext = .);
69: .rodata : { *(.rodata .rodata.* .gnu.linkonce.r.*) }
70: .rodata1 : { *(.rodata1) }
71: .eh_frame_hdr : { *(.eh_frame_hdr) }
72: .eh_frame : ONLY_IF_RO { KEEP (*(.eh_frame)) }
73: .gcc_except_table : ONLY_IF_RO { *(.gcc_except_table .gcc_except_table.*) }
74: /* Adjust the address for the data segment. We want to adjust up to
75: the same address within the page on the next page up. */
76: . = ALIGN (CONSTANT (MAXPAGESIZE)) - ((CONSTANT (MAXPAGESIZE) - .) & (CONSTANT (MAXPAGESIZE) - 1)); . = DATA_SEGMENT_ALIGN (CONSTANT (MAXPAGESIZE), CONSTANT (COMMONPAGESIZE));
77: /* Exception handling */
78: .eh_frame : ONLY_IF_RW { KEEP (*(.eh_frame)) }
79: .gcc_except_table : ONLY_IF_RW { *(.gcc_except_table .gcc_except_table.*) }
80: /* Thread Local Storage sections */
81: .tdata : { *(.tdata .tdata.* .gnu.linkonce.td.*) }
82: .tbss : { *(.tbss .tbss.* .gnu.linkonce.tb.*) *(.tcommon) }
83: .preinit_array :
84: {
85: PROVIDE_HIDDEN (__preinit_array_start = .);
86: KEEP (*(.preinit_array))
87: PROVIDE_HIDDEN (__preinit_array_end = .);
88: }
89: .init_array :
90: {
91: PROVIDE_HIDDEN (__init_array_start = .);
92: KEEP (*(SORT(.init_array.*)))
93: KEEP (*(.init_array))
94: PROVIDE_HIDDEN (__init_array_end = .);
95: }
96: .fini_array :
97: {
98: PROVIDE_HIDDEN (__fini_array_start = .);
99: KEEP (*(.fini_array))
100: KEEP (*(SORT(.fini_array.*)))
101: PROVIDE_HIDDEN (__fini_array_end = .);
102: }
103: .ctors :
104: {
105: /* gcc uses crtbegin.o to find the start of
106: the constructors, so we make sure it is
107: first. Because this is a wildcard, it
108: doesn't matter if the user does not
109: actually link against crtbegin.o; the
110: linker won't look for a file to match a
111: wildcard. The wildcard also means that it
112: doesn't matter which directory crtbegin.o
113: is in. */
114: KEEP (*crtbegin.o(.ctors))
115: KEEP (*crtbegin?.o(.ctors))
116: /* We don't want to include the .ctor section from
117: the crtend.o file until after the sorted ctors.
118: The .ctor section from the crtend file contains the
119: end of ctors marker and it must be last */
120: KEEP (*(EXCLUDE_FILE (*crtend.o *crtend?.o ) .ctors))
121: KEEP (*(SORT(.ctors.*)))
122: KEEP (*(.ctors))
123: }
124: .dtors :
125: {
126: KEEP (*crtbegin.o(.dtors))
127: KEEP (*crtbegin?.o(.dtors))
128: KEEP (*(EXCLUDE_FILE (*crtend.o *crtend?.o ) .dtors))
129: KEEP (*(SORT(.dtors.*)))
130: KEEP (*(.dtors))
131: }
132: .jcr : { KEEP (*(.jcr)) }
133: .data.rel.ro : { *(.data.rel.ro.local* .gnu.linkonce.d.rel.ro.local.*) *(.data.rel.ro* .gnu.linkonce.d.rel.ro.*) }
134: .dynamic : { *(.dynamic) }
135: .got : { *(.got) *(.igot) }
136: . = DATA_SEGMENT_RELRO_END (12, .);
137: .got.plt : { *(.got.plt) *(.igot.plt) }
138: .data :
139: {
140: *(.data .data.* .gnu.linkonce.d.*)
141: SORT(CONSTRUCTORS)
142: }
143: .data1 : { *(.data1) }
144: _edata = .; PROVIDE (edata = .);
145: __bss_start = .;
146: .bss :
147: {
148: *(.dynbss)
149: *(.bss .bss.* .gnu.linkonce.b.*)
150: *(COMMON)
151: /* Align here to ensure that the .bss section occupies space up to
152: _end. Align after .bss to ensure correct alignment even if the
153: .bss section disappears because there are no input sections.
154: FIXME: Why do we need it? When there is no .bss section, we don't
155: pad the .data section. */
156: . = ALIGN(. != 0 ? 32 / 8 : 1);
157: }
158: . = ALIGN(32 / 8);
159: . = ALIGN(32 / 8);
160: _end = .; PROVIDE (end = .);
161: . = DATA_SEGMENT_END (.);
162: /* Stabs debugging sections. */
163: .stab 0 : { *(.stab) }
164: .stabstr 0 : { *(.stabstr) }
165: .stab.excl 0 : { *(.stab.excl) }
166: .stab.exclstr 0 : { *(.stab.exclstr) }
167: .stab.index 0 : { *(.stab.index) }
168: .stab.indexstr 0 : { *(.stab.indexstr) }
169: .comment 0 : { *(.comment) }
170: /* DWARF debug sections.
171: Symbols in the DWARF debugging sections are relative to the beginning
172: of the section so we begin them at 0. */
173: /* DWARF 1 */
174: .debug 0 : { *(.debug) }
175: .line 0 : { *(.line) }
176: /* GNU DWARF 1 extensions */
177: .debug_srcinfo 0 : { *(.debug_srcinfo) }
178: .debug_sfnames 0 : { *(.debug_sfnames) }
179: /* DWARF 1.1 and DWARF 2 */
180: .debug_aranges 0 : { *(.debug_aranges) }
181: .debug_pubnames 0 : { *(.debug_pubnames) }
182: /* DWARF 2 */
183: .debug_info 0 : { *(.debug_info .gnu.linkonce.wi.*) }
184: .debug_abbrev 0 : { *(.debug_abbrev) }
185: .debug_line 0 : { *(.debug_line) }
186: .debug_frame 0 : { *(.debug_frame) }
187: .debug_str 0 : { *(.debug_str) }
188: .debug_loc 0 : { *(.debug_loc) }
189: .debug_macinfo 0 : { *(.debug_macinfo) }
190: /* SGI/MIPS DWARF 2 extensions */
191: .debug_weaknames 0 : { *(.debug_weaknames) }
192: .debug_funcnames 0 : { *(.debug_funcnames) }
193: .debug_typenames 0 : { *(.debug_typenames) }
194: .debug_varnames 0 : { *(.debug_varnames) }
195: /* DWARF 3 */
196: .debug_pubtypes 0 : { *(.debug_pubtypes) }
197: .debug_ranges 0 : { *(.debug_ranges) }
198: .gnu.attributes 0 : { KEEP (*(.gnu.attributes)) }
199: /DISCARD/ : { *(.note.GNU-stack) *(.gnu_debuglink) *(.gnu.lto_*) }
200: }
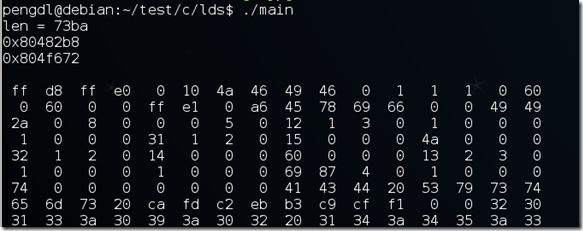
下面是运行main的结果:
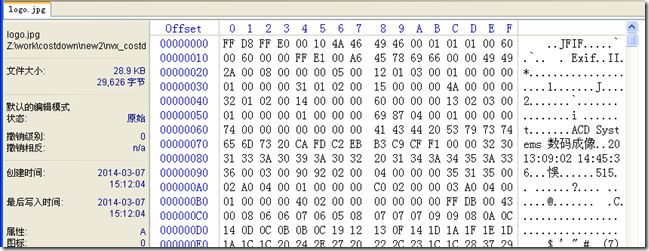
用winhex打开logo.jpg可以看到如下:
可以看到二者是一致的。(29626 = 0x73BA)