STL堆算法性能分析与优化方法(GCC4.4.2 stl_heap.h源代码分析与改进方案)
堆是常用的数据结构,经常用于实现优先队列中,huffman编码中的就用到了优先队列。
本质上就是用数组实现的完全二叉树保证父节点的关键码都大于或者等于其子节点的关键码(最大堆,反过来是最小堆),下图是一个最大堆示意。
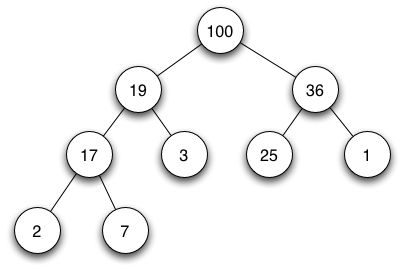
那么在STL中有相应的堆算法,如判断一个序列是否为堆__is_heap,将一个序列建立为堆make_heap,向堆中插入元素push_heap,删除元素pop_heap,对堆排序等等sort_heap。个人认为STL的make_heap和pop_heap的实现并不是最好的,性能上也稍受影响。
就以建堆操作为例子吧,有两种方法:
- 就是用shift up的方法,所谓shift up就是前面的序列已经是堆了,再加入一个元素放到末尾,然后由底端向上通过和父节点比较交换到达合适的位置。这种方法也适合与push_heap也就是插入元素操作。用这种方法建堆复杂度是o(nlong(n))
- 更好的方案是采用shift down方法,这是假定我们已经知道要建堆区间的情况下。具体可以参考数据结构课本这方法的代价是o(n)的。
关于元素删除:
元素删除其实就是把堆顶端的元素删除,将堆末尾的元素赋值到堆顶端然后再利用shift down操作向下调整到合适的位置。
STL的算法实现中包括对一个区间建立堆结构和元素的删除都没有用shift down操作,统统用的是shift up(__push_heap),
比如说元素的删除,它会把堆顶元素删除,然后尝试着把从位置1到最后一个元素的位置都向上移动一位并且通过调整保持堆结构,最后
再次调用shift_up将尾元素向上移动到合适的位置。在网上查了下http://www.cppblog.com/guogangj/archive/2009/10/29/99729.html
其实就是下图这种算法,删除元素也是O(log(n))的代价,但是我觉得还是用shift down更直观,同时能够减少一定的比较移动的次数,虽然时间复杂度不变。
下图如果用shift down的话就是把8直接放到原来1的位置向下不断调整直到到达合适的位置。
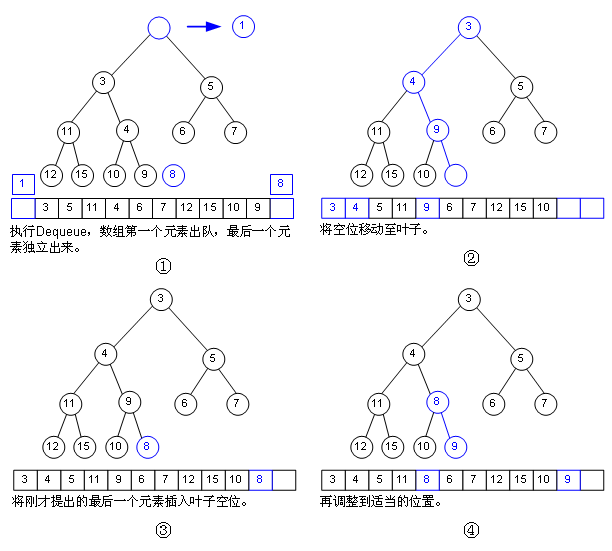
shift up(__push_heap)的源代码如下:
//shift_up! 将位于first+holeIndex的值为value的元素shift up操作,最远直到
//first+topIndex位置
 代码
代码
2 void
3 __push_heap(_RandomAccessIterator __first,
4 _Distance __holeIndex, _Distance __topIndex, _Tp __value)
5 {
6 _Distance __parent = (__holeIndex - 1 ) / 2 ;
7 while (__holeIndex > __topIndex && * (__first + __parent) < __value)
8 {
9 * (__first + __holeIndex) = * (__first + __parent);
10 __holeIndex = __parent;
11 __parent = (__holeIndex - 1 ) / 2 ;
12 }
13 * (__first + __holeIndex) = __value;
14 }
15
//删除操作会调用 __adjust_heap而__asjust_heap并没有直接执行shift down的操作,而是将堆普遍前移一位,最后再执行shift up操作(__push_heap)
 代码
代码
而初始给定区间构造堆得过程也是如此,其实可以用shift down操作的地方的那个元素删除,后面的元素前提,保持堆形态,然后再调用
shift up.
 代码
代码
* @brief Construct a heap over a range.
* @param first Start of heap.
* @param last End of heap.
* @ingroup heap
*
* This operation makes the elements in [first,last) into a heap.
*/
template < typename _RandomAccessIterator >
void
make_heap(_RandomAccessIterator __first, _RandomAccessIterator __last)
{
typedef typename iterator_traits < _RandomAccessIterator > ::value_type
_ValueType;
typedef typename iterator_traits < _RandomAccessIterator > ::difference_type
_DistanceType;
// concept requirements
__glibcxx_function_requires(_Mutable_RandomAccessIteratorConcept <
_RandomAccessIterator > )
__glibcxx_function_requires(_LessThanComparableConcept < _ValueType > )
__glibcxx_requires_valid_range(__first, __last);
if (__last - __first < 2 )
return ;
const _DistanceType __len = __last - __first;
_DistanceType __parent = (__len - 2 ) / 2 ;
while ( true )
{
std::__adjust_heap(__first, __parent, __len,
_ValueType( * (__first + __parent)));
if (__parent == 0 )
return ;
__parent -- ;
}
}
我尝试着改变算法采用shift down,其实改变的工作量很小,并且做了实验验证了新
算法的正确性,和与原实现的效率对比。我仅仅测试了对于最大堆给定区间建堆,删除元素的情况。
如果需要最小堆那么你还要改写对应的带有防函数模板参数变量的函数。
实验的结果是采用shift_down之后删除操作和以前几乎完全一样,但是建堆会快一些。
allen:~/study/c++/stl$ ./makeheap_perf
[==========] Running 3 tests from 3 test cases.
[----------] Global test environment set-up.
[----------] 1 test from my_make_heap
[ RUN ] my_make_heap.perf
15.97 s
[ OK ] my_make_heap.perf (16024 ms)
[----------] 1 test from my_make_heap (16024 ms total)
[----------] 1 test from stl_make_heap
[ RUN ] stl_make_heap.perf
21.40 s
[ OK ] stl_make_heap.perf (21516 ms)
[----------] 1 test from stl_make_heap (21516 ms total)
[----------] 1 test from make_heap
[ RUN ] make_heap.func
[ OK ] make_heap.func (54 ms)
[----------] 1 test from make_heap (54 ms total)
[----------] Global test environment tear-down
[==========] 3 tests from 3 test cases ran. (37595 ms total)
[ PASSED ] 3 tests.
综上所述,由于GCC实现的STL 堆算法没有用shift down 操作,虽然负责度不变,我个人还是认为用将尾元素替换被删除的头元素然后执行shift down操作的算法可读性更强,并且能够减少一定的比较次数,实验也证明确实如此。如果你特别在意性能的话,例如堆是性能瓶颈,需要大量的元素多次建堆,可以自己改写相应算法,如果不是大量操作的话其实性能差异可以忽略不记了:)。
改写的话其实也只需要改写一点点啦,不需要造轮子的地方就不造,最后再赞一下google test,太好用了:)
实验程序如下:
 代码
代码
2 * ==============================================================================
3 *
4 * \file makeheap_perf.cc
5 *
6 * \author [email protected]
7 *
8 * \date 2009-11-28 12:14:41.518985
9 *
10 * Description: 测试建立最大堆(注意这里仅仅测试最大堆,最小堆类似)
11 *
12 * 1.stl算法效率(gcc 4.4.2)
13 * 2.我修改后的算法效率及正确性(加入shift down函数)
14 * 我对原算法做了最小的修改,注意如果用最小堆,你还需要改
15 * 相应的带有防函数typname __Compare 模板参数的函数。
16 * g++ -O3 -o makeheap_perf makeheap_perf.cc -lgtest -I$BOOST_ROOT
17 *
18 * ==============================================================================
19 */
20
21 #include < iostream >
22 #include < algorithm >
23 #include < vector >
24 #include < gtest / gtest.h > // using google test
25 #include < boost / progress.hpp > // using boost timer
26 #include < ctime > // std::time
27 // using boost random
28 #include < boost / random / linear_congruential.hpp >
29 #include < boost / random / uniform_int.hpp >
30 #include < boost / random / uniform_real.hpp >
31 #include < boost / random / variate_generator.hpp >
32 #ifdef BOOST_NO_STDC_NAMESPACE
33 namespace std {
34 using ::time;
35 }
36 #endif
37 typedef boost::minstd_rand base_generator_type;
38 using namespace std;
39
40 // two global vector, we will use them as heap holder
41 vector < double > vec;
42 vector < double > vec1;
43 vector < double > vec2;
44 const int VecSize = 1024 * 1024 ;
45 const int LoopTimes = 400 ;
46
47 // 以0-1的随机浮点数填充
48 void init_vec() {
49 vec.resize(VecSize);
50 vec1.resize(VecSize);
51 vec2.resize(VecSize);
52
53
54 base_generator_type generator( 42u );
55 boost::uniform_real <> uni_dist( 0 , 1 );
56 boost::variate_generator < base_generator_type & , boost::uniform_real <> > uni(generator, uni_dist);
57
58 for ( int i = 0 ; i < VecSize; i ++ ) {
59 vec[i] = uni();
60 }
61
62 }
63 // ----------------------------------改写后的shift down 和建堆操作
64 // shift down 操作,将__first + __holeIndex位置的元素
65 // (其值为__value如果原来不是就相当于先赋值为__value)
66 // 向下shift down,最远到达__first + len - 1位置
67 template < typename _RandomAccessIterator, typename _Distance, typename _Tp >
68 void shift_down(_RandomAccessIterator __first, _Distance __holeIndex,
69 _Distance __len, _Tp __value)
70 {
71 _Distance __secondChild = 2 * __holeIndex + 2 ; // 右子节点index
72
73 while (__secondChild < __len) {
74 // 执行后secondChild代表两个子节点中较大的节点
75 if ( * (__first + __secondChild) < * (__first + (__secondChild - 1 )) )
76 __secondChild -- ;
77
78 // 如果比子节点小
79 if ( __value < * (__first + __secondChild)) {
80 * (__first + __holeIndex) = * (__first + __secondChild);
81 __holeIndex = __secondChild; // 继续shift down
82 __secondChild = 2 * __holeIndex + 2 ;
83 }
84 else
85 break ;
86 }
87
88 // 最后一层可能存在只有左子节点情况
89 if (__secondChild == __len) {
90 __secondChild -- ;
91 if ( __value < * (__first + __secondChild)) {
92 * (__first + __holeIndex) = * (__first + __secondChild);
93 __holeIndex = __secondChild;
94 }
95 }
96
97 // 将__value赋值到最后确定的位置
98 * (__first + __holeIndex) = __value;
99 }
100
101
102 template < typename _RandomAccessIterator >
103 void my_make_heap(_RandomAccessIterator __first, _RandomAccessIterator __last)
104 {
105 typedef typename iterator_traits < _RandomAccessIterator > ::value_type
106 _ValueType;
107 typedef typename iterator_traits < _RandomAccessIterator > ::difference_type
108 _DistanceType;
109
110 if (__last - __first < 2 )
111 return ;
112
113 const _DistanceType __len = __last - __first;
114 _DistanceType __parent = (__len - 2 ) / 2 ;
115 while ( true )
116 {
117 shift_down(__first, __parent, __len,
118 _ValueType( * (__first + __parent)));
119 if (__parent == 0 )
120 return ;
121 __parent -- ;
122 }
123 }
124
125 // -------------改写后的删除操作
126 template < typename _RandomAccessIterator, typename _Tp >
127 inline void
128 __my_pop_heap(_RandomAccessIterator __first, _RandomAccessIterator __last,
129 _RandomAccessIterator __result, _Tp __value)
130 {
131 typedef typename iterator_traits < _RandomAccessIterator > ::difference_type
132 _Distance;
133 * __result = * __first;
134 shift_down(__first, _Distance( 0 ), _Distance(__last - __first),
135 __value);
136 }
137
138 template < typename _RandomAccessIterator >
139 inline void
140 my_pop_heap(_RandomAccessIterator __first, _RandomAccessIterator __last)
141 {
142 typedef typename iterator_traits < _RandomAccessIterator > ::value_type
143 _ValueType;
144
145 __my_pop_heap(__first, __last - 1 , __last - 1 ,
146 _ValueType( * (__last - 1 )));
147 }
148
149
150 // stl 自带的make_heap,以及pop_heap函数的性能测试,对vec1操作
151 void stl_make_heap() {
152 boost::progress_timer timer;
153 for ( int i = 0 ; i < LoopTimes; i ++ ) {
154 copy(vec.begin(), vec.end(), vec1.begin());
155 // 建堆
156 make_heap(vec1.begin(), vec1.end());
157 /// /逐次删除所有的堆中元素
158 // for (int j = 0; j < VecSize; j++) {
159 // pop_heap(vec1.begin(), vec1.end() - j);
160 // }
161
162 }
163 }
164
165 // 修改后的my_make_heap,以及pop_heap函数测试,对vec2操作
166 void my_make_heap() {
167 boost::progress_timer timer;
168 for ( int i = 0 ; i < LoopTimes; i ++ ) {
169 copy(vec.begin(), vec.end(), vec2.begin());
170 // 建堆
171 my_make_heap(vec2.begin(), vec2.end());
172 /// /逐次删除所有的堆中元素
173 // for (int j = 0; j < VecSize; j++) {
174 // pop_heap(vec2.begin(), vec2.end() - j);
175 // }
176
177 }
178 }
179
180 // 测试my_make_heap是否正确的建堆,及删除堆元素是否正确
181 void test_equal_vec() {
182 copy(vec.begin(), vec.end(), vec2.begin());
183 my_make_heap(vec2.begin(), vec2.end());
184 EXPECT_EQ( 1 , std::__is_heap(vec2.begin(), vec2.end()));
185 // 测试删除堆元素操作是否正确
186 // int j;
187 // for (j = 0; j < VecSize/2 + 5; j++) {
188 // pop_heap(vec2.begin(), vec2.end() - j);
189 // }
190
191 // EXPECT_EQ(1, std::__is_heap(vec2.begin(), vec2.end()-j));
192 }
193
194 TEST(stl_make_heap, perf)
195 {
196 stl_make_heap();
197 }
198
199 TEST(my_make_heap, perf)
200 {
201 my_make_heap();
202 }
203
204 TEST(make_heap, func)
205 {
206 test_equal_vec();
207 }
208
209
210
211 int main( int argc, char * argv[])
212 {
213 init_vec();
214
215 testing::InitGoogleTest( & argc, argv);
216 return RUN_ALL_TESTS();
217 }