十分钟掌握pyecharts十类顶级图,都很实用!
本文是为了帮助大家快速掌握十大顶级绘图方法,重点解释数据是如何呈现在不同类型图中。
使用pip install pyecharts 安装,安装后的版本为 v1.6
pyecharts几行代码就能绘制出有特色的的图形,绘图API链式调用,使用方便。
1 仪表盘
from pyecharts import charts
# 仪表盘
gauge = charts.Gauge()
gauge.add('Python小例子', [('Python机器学习', 30), ('Python基础', 70.),
('Python正则', 90)])
gauge.render(path="./data/仪表盘.html")
print('ok')
仪表盘中共展示三项,每项的比例为30%,70%,90%,如下图默认名称显示第一项:Python机器学习,完成比例为30%
2 漏斗图
from pyecharts import options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import Funnel, Page
from random import randint
def funnel_base() -> Funnel:
c = (
Funnel()
.add("豪车", [list(z) for z in zip(['宝马', '法拉利', '奔驰', '奥迪', '大众', '丰田', '特斯拉'],
[randint(1, 20) for _ in range(7)])])
.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="豪车漏斗图"))
)
return c
funnel_base().render('./img/car_funnel.html')
print('ok')
以7种车型及某个属性值绘制的漏斗图,属性值大越靠近漏斗的大端。
3 日历图
import datetime
import random
from pyecharts import options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import Calendar
def calendar_interval_1() -> Calendar:
begin = datetime.date(2019, 1, 1)
end = datetime.date(2019, 12, 27)
data = [
[str(begin + datetime.timedelta(days=i)), random.randint(1000, 25000)]
for i in range(0, (end - begin).days + 1, 2) # 隔天统计
]
calendar = (
Calendar(init_opts=opts.InitOpts(width="1200px")).add(
"", data, calendar_opts=opts.CalendarOpts(range_="2019"))
.set_global_opts(
title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="Calendar-2019年步数统计"),
visualmap_opts=opts.VisualMapOpts(
max_=25000,
min_=1000,
orient="horizontal",
is_piecewise=True,
pos_top="230px",
pos_left="100px",
),
)
)
return calendar
calendar_interval_1().render('./img/calendar.html')
print('ok')
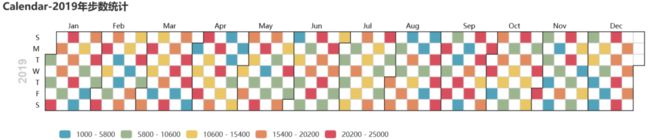
绘制2019年1月1日到12月27日的步行数,官方给出的图形宽度900px不够,只能显示到9月份,本例使用opts.InitOpts(width="1200px")做出微调,并且visualmap显示所有步数,每隔一天显示一次:
4 图(graph)
import json
import os
from pyecharts import options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import Graph, Page
def graph_base() -> Graph:
nodes = [
{"name": "cus1", "symbolSize": 10},
{"name": "cus2", "symbolSize": 30},
{"name": "cus3", "symbolSize": 20}
]
links = []
for i in nodes:
if i.get('name') == 'cus1':
continue
for j in nodes:
if j.get('name') == 'cus1':
continue
links.append({"source": i.get("name"), "target": j.get("name")})
c = (
Graph()
.add("", nodes, links, repulsion=8000)
.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="customer-influence"))
)
return c
构建图,其中客户点1与其他两个客户都没有关系(link),也就是不存在有效边:
5 水球图
from pyecharts import options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import Liquid, Page
from pyecharts.globals import SymbolType
def liquid() -> Liquid:
c = (
Liquid()
.add("lq", [0.67, 0.30, 0.15])
.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="Liquid"))
)
return c
liquid().render('./img/liquid.html')
水球图的取值[0.67, 0.30, 0.15]表示下图中的三个波浪线,一般代表三个百分比:
6 饼图
from pyecharts import options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import Pie
from random import randint
def pie_base() -> Pie:
c = (
Pie()
.add("", [list(z) for z in zip(['宝马', '法拉利', '奔驰', '奥迪', '大众', '丰田', '特斯拉'],
[randint(1, 20) for _ in range(7)])])
.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="Pie-基本示例"))
.set_series_opts(label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(formatter="{b}: {c}"))
)
return c
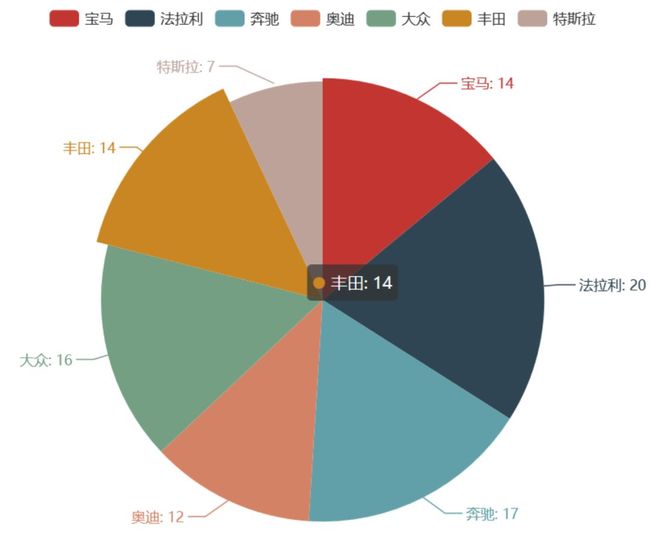
pie_base().render('./img/pie_pyecharts.html')7 极坐标
import random
from pyecharts import options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import Page, Polar
def polar_scatter0() -> Polar:
data = [(alpha, random.randint(1, 100)) for alpha in range(101)] # r = random.randint(1, 100)
print(data)
c = (
Polar()
.add("", data, type_="bar", label_opts=opts.LabelOpts(is_show=False))
.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="Polar"))
)
return c
polar_scatter0().render('./img/polar.html')
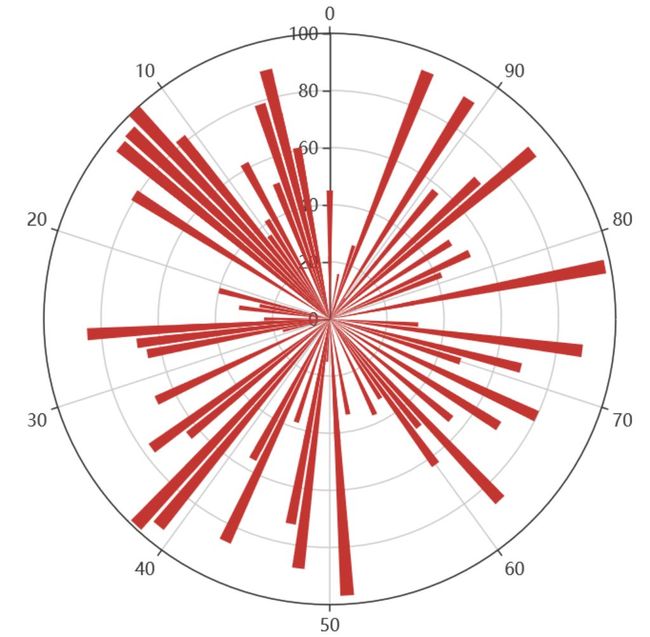
极坐标表示为(夹角,半径),如(6,94)表示"夹角"为6,半径94的点:
8 词云图
from pyecharts import options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import Page, WordCloud
from pyecharts.globals import SymbolType
words = [
("Python", 100),
("C++", 80),
("Java", 95),
("R", 50),
("JavaScript", 79),
("C", 65)
]
def wordcloud() -> WordCloud:
c = (
WordCloud()
# word_size_range: 单词字体大小范围
.add("", words, word_size_range=[20, 100], shape='cardioid')
.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="WordCloud"))
)
return c
wordcloud().render('./img/wordcloud.html')
("C",65)表示在本次统计中C语言出现65次
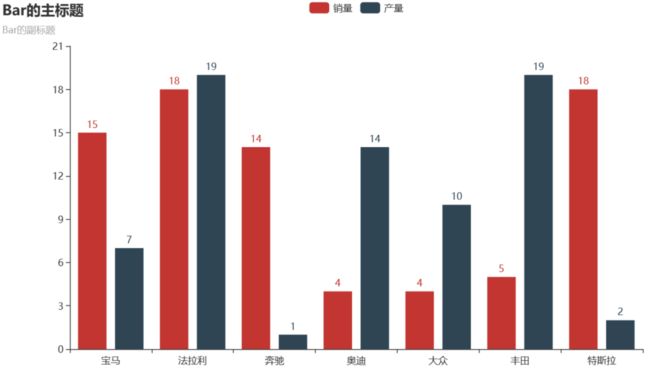
9 系列柱状图
from pyecharts import options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import Bar
from random import randint
def bar_series() -> Bar:
c = (
Bar()
.add_xaxis(['宝马', '法拉利', '奔驰', '奥迪', '大众', '丰田', '特斯拉'])
.add_yaxis("销量", [randint(1, 20) for _ in range(7)])
.add_yaxis("产量", [randint(1, 20) for _ in range(7)])
.set_global_opts(title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="Bar的主标题", subtitle="Bar的副标题"))
)
return c
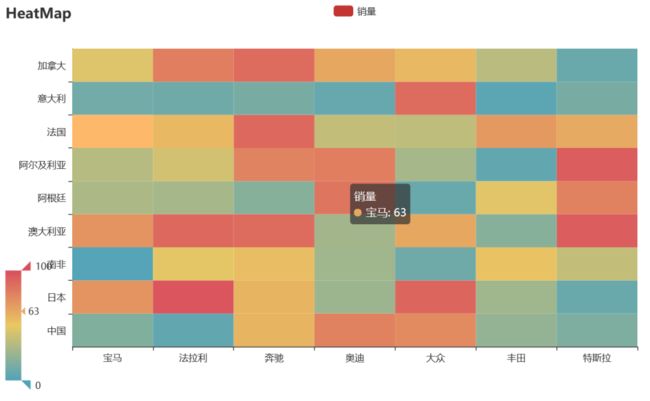
bar_series().render('./img/bar_series.html')10 热力图
import random
from pyecharts import options as opts
from pyecharts.charts import HeatMap
def heatmap_car() -> HeatMap:
x = ['宝马', '法拉利', '奔驰', '奥迪', '大众', '丰田', '特斯拉']
y = ['中国','日本','南非','澳大利亚','阿根廷','阿尔及利亚','法国','意大利','加拿大']
value = [[i, j, random.randint(0, 100)]
for i in range(len(x)) for j in range(len(y))]
c = (
HeatMap()
.add_xaxis(x)
.add_yaxis("销量", y, value)
.set_global_opts(
title_opts=opts.TitleOpts(title="HeatMap"),
visualmap_opts=opts.VisualMapOpts(),
)
)
return c
heatmap_car().render('./img/heatmap_pyecharts.html')
阅读更多:
拉格朗日乘数法的原理,我用10幅图把它讲清楚