文档相似度算法 Simhash
这篇文档简单介绍一下Simhash算法
一. Simhash 计算文档相似度的算法, 比如用在搜索引擎的爬虫系统中,收录重复的网页是毫无意义的,只会造成存储和计算资源的浪费。有时候我们需要处理类似的文档,比如新闻,很多不同新闻网的新闻内容十分相近,标题略有相似。如此问题,便可以应用Simhash 文档相似度算法,查看两篇文档相似程度,删去相似度高的web文档。
二. 传统比较两个文本相似性的方法,大多是将文本分词之后,转化为特征向量距离的度量,比如常见的欧氏距离、海明距离或者余弦角度等等。两两比较固然能很好地适应,但这种方法的一个最大的缺点就是,无法将其扩展到海量数据。
simhash是locality sensitive hash(局部敏感哈希)的一种,最早由Moses Charikar在《similarity estimation techniques from rounding algorithms》一文中提出。Google就是基于此算法实现网页文件查重的。我们假设有以下三段文本:
the cat sat on the mat
the cat sat on a mat
we all scream for ice cream
Simhash 算法实现:
1、选择simhash的位数,请综合考虑存储成本以及数据集的大小,比如说32位
2、将simhash的各位初始化为0
3、提取原始文本中的特征,一般采用各种分词的方式。比如对于"the cat sat on the mat",采用两两分词的方式得到如下结果:{"th", "he", "e ", " c", "ca", "at", "t ", " s", "sa", " o", "on", "n ", " t", " m", "ma"}
4、使用传统的32位hash函数计算各个word的hashcode,比如:"th".hash = -502157718
,"he".hash = -369049682,……
5、对各word的hashcode的每一位,如果该位为1,则simhash相应位的值加1;否则减1
6、对最后得到的32位的simhash,如果该位大于1,则设为1;否则设为0
海明距离的定义,为两个二进制串中不同位的数量。
按照Charikar在论文中阐述的,64位simhash,海明距离在3以内的文本都可以认为是近重复文本。当然,具体数值需要结合具体业务以及经验值来确定。
但是,使用上述方法产生的simhash用来比较两个文本之间的相似度,将其扩展到海量数据的近重复检测中去,时间复杂度和空间复杂度都太大。譬如说对于64位的待查询文本的simhash code来说,在海量的样本库(>1M)中查询与其海明距离在3以内的记录 有两种常规的思路。第一种是方案是查找待查询文本的64位simhash code的所有3位以内变化的组合,大约需要四万多次的查询
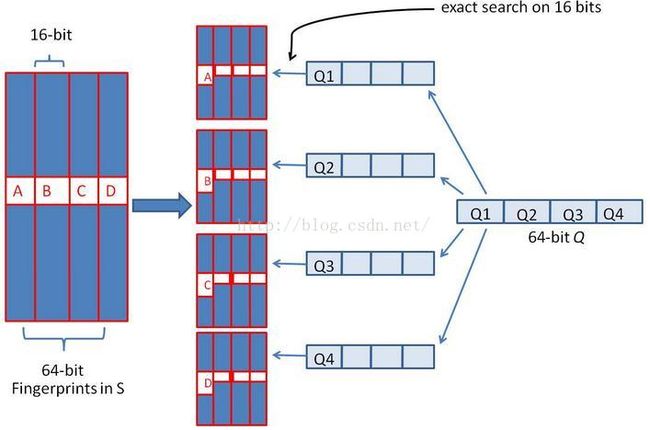
假设对64 位的 SimHash ,我们要找海明距离在 3 以内的所有签名。我们可以把 64 位的二进制签名均分成 4块,每块 16 位。根据鸽巢原理(也成抽屉原理,见组合数学),如果两个签名的海明距离在 3 以内,它们必有一块完全相同。
我们把上面分成的4 块中的每一个块分别作为前 16 位来进行查找。 建立倒排索引。
如果库中有2^34 个(大概 10 亿)签名,那么匹配上每个块的结果最多有 2^(34-16)=262144 个候选结果 (假设数据是均匀分布, 16 位的数据,产生的像限为 2^16 个,则平均每个像限分布的文档数则 2^34/2^16 = 2^(34-16)) ,四个块返回的总结果数为 4* 262144 (大概 100 万)。原本需要比较 10 亿次,经过索引,大概就只需要处理 100 万次了。由此可见,确实大大减少了计算量。
Java 代码实现:
package simhash;
/**
* Function: simHash 判断文本相似度,该示例程支持中文
* date: 2013-8-6 上午1:11:48
* @author june
* @version 0.1
*/
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.StringReader;
import java.math.BigInteger;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import org.wltea.analyzer.core.IKSegmenter;
import org.wltea.analyzer.core.Lexeme;
public class SimHash {
private String tokens;
private BigInteger intSimHash;
private String strSimHash;
private int hashbits = 64;
public SimHash(String tokens) throws IOException {
this.tokens = tokens;
this.intSimHash = this.simHash();
}
public SimHash(String tokens, int hashbits) throws IOException {
this.tokens = tokens;
this.hashbits = hashbits;
this.intSimHash = this.simHash();
}
HashMap wordMap = new HashMap();
public BigInteger simHash() throws IOException {
// 定义特征向量/数组
int[] v = new int[this.hashbits];
// 英文分词
// StringTokenizer stringTokens = new StringTokenizer(this.tokens);
// while (stringTokens.hasMoreTokens()) {
// String temp = stringTokens.nextToken();
// }
// 1、中文分词,分词器采用 IKAnalyzer3.2.8 ,仅供演示使用,新版 API 已变化。
StringReader reader = new StringReader(this.tokens);
// 当为true时,分词器进行最大词长切分
IKSegmenter ik = new IKSegmenter(reader, true);
Lexeme lexeme = null;
String word = null;
String temp = null;
while ((lexeme = ik.next()) != null) {
word = lexeme.getLexemeText();
// 注意停用词会被干掉
//System.out.println(word);
// 2、将每一个分词hash为一组固定长度的数列.比如 64bit 的一个整数.
BigInteger t = this.hash(word);
for (int i = 0; i < this.hashbits; i++) {
BigInteger bitmask = new BigInteger("1").shiftLeft(i);
// 3、建立一个长度为64的整数数组(假设要生成64位的数字指纹,也可以是其它数字),
// 对每一个分词hash后的数列进行判断,如果是1000...1,那么数组的第一位和末尾一位加1,
// 中间的62位减一,也就是说,逢1加1,逢0减1.一直到把所有的分词hash数列全部判断完毕.
if (t.and(bitmask).signum() != 0) {
// 这里是计算整个文档的所有特征的向量和
// 这里实际使用中需要 +- 权重,比如词频,而不是简单的 +1/-1,
v[i] += 1;
} else {
v[i] -= 1;
}
}
}
BigInteger fingerprint = new BigInteger("0");
StringBuffer simHashBuffer = new StringBuffer();
for (int i = 0; i < this.hashbits; i++) {
// 4、最后对数组进行判断,大于0的记为1,小于等于0的记为0,得到一个 64bit 的数字指纹/签名.
if (v[i] >= 0) {
fingerprint = fingerprint.add(new BigInteger("1").shiftLeft(i));
simHashBuffer.append("1");
} else {
simHashBuffer.append("0");
}
}
this.strSimHash = simHashBuffer.toString();
System.out.println(this.strSimHash + " length " + this.strSimHash.length());
return fingerprint;
}
private BigInteger hash(String source) {
if (source == null || source.length() == 0) {
return new BigInteger("0");
} else {
char[] sourceArray = source.toCharArray();
BigInteger x = BigInteger.valueOf(((long) sourceArray[0]) << 7);
BigInteger m = new BigInteger("1000003");
BigInteger mask = new BigInteger("2").pow(this.hashbits).subtract(new BigInteger("1"));
for (char item : sourceArray) {
BigInteger temp = BigInteger.valueOf((long) item);
x = x.multiply(m).xor(temp).and(mask);
}
x = x.xor(new BigInteger(String.valueOf(source.length())));
if (x.equals(new BigInteger("-1"))) {
x = new BigInteger("-2");
}
return x;
}
}
public int hammingDistance(SimHash other) {
BigInteger x = this.intSimHash.xor(other.intSimHash);
int tot = 0;
// 统计x中二进制位数为1的个数
// 我们想想,一个二进制数减去1,那么,从最后那个1(包括那个1)后面的数字全都反了,
// 对吧,然后,n&(n-1)就相当于把后面的数字清0,
// 我们看n能做多少次这样的操作就OK了。
while (x.signum() != 0) {
tot += 1;
x = x.and(x.subtract(new BigInteger("1")));
}
return tot;
}
public int getDistance(String str1, String str2) {
int distance;
if (str1.length() != str2.length()) {
distance = -1;
} else {
distance = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < str1.length(); i++) {
if (str1.charAt(i) != str2.charAt(i)) {
distance++;
}
}
}
return distance;
}
public List subByDistance(SimHash simHash, int distance) {
// 分成几组来检查
int numEach = this.hashbits / (distance + 1);
List characters = new ArrayList();
StringBuffer buffer = new StringBuffer();
int k = 0;
//for (int i = 0; i < this.intSimHash.bitLength(); i++) {
for (int i = 0; i < 64; i++) {
// 当且仅当设置了指定的位时,返回 true
boolean sr = simHash.intSimHash.testBit(i);
if (sr) {
buffer.append("1");
} else {
buffer.append("0");
}
if ((i + 1) % numEach == 0) {
// 将二进制转为BigInteger
BigInteger eachValue = new BigInteger(buffer.toString(), 2);
System.out.println("----" + eachValue);
buffer.delete(0, buffer.length());
characters.add(eachValue);
}
}
return characters;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
long startTime=System.currentTimeMillis();
List datalist = new LinkedList();
datalist = DbHelp.sourcedataseg(352835,352934);
for(CourtData d1: datalist){
String s1 = d1.content;
SimHash hash1 = new SimHash(s1, 64);
//List characters1 = new ArrayList();
//List characters2 = new ArrayList();
//characters1 = hash1.subByDistance(hash1, 3);
for(CourtData d2: datalist){
if(d1.id != d2.id ){
String s2 = d2.content;
SimHash hash2 = new SimHash(s2, 64);
//characters2 = hash2.subByDistance(hash2, 3);
//if((characters1.get(0)).equals(characters2.get(0)) || (characters1.get(1)).equals(characters2.get(1)) ||(characters1.get(2)).equals(characters2.get(2)) ||(characters1.get(3)).equals(characters2.get(3))){
int dishm = hash1.hammingDistance(hash2);
if(dishm <= 5){
System.out.println("d1.id:" + d1.id + " d2.id:" + d2.id + " dishm:" + dishm);
}
//}
}
}
}
long endTime=System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("运行时间:"+ (float)(endTime - startTime)/1000 + "s");
}
}
参考网址:
1. http://www.lanceyan.com/tag/simhash
2.http://blog.csdn.net/heiyeshuwu/article/details/44117473
3.http://www.cnblogs.com/chenying99/p/3830728.html