【图像加密】基于GUI界面之混沌系统图像加密解密【Matlab 106期】
一、简介
Logistic混沌置乱,先不说有多复杂,其实很简单。
Logistic函数是源于一个人口统计的动力学系统,其系统方程形式如下:
X(k+1) = u * X(k) * [1 - X(k)],(k=0,1,…,n)
先不用管这个方程是怎么得出来的,觉得不舒服的话自己百度去。可以看出这个方程是非线性的,迭代的形式。要使用的话,我们需要知道两个东西:
① 初值:X(0)
② 参数:u
为什么这个方程可以称作混沌呢?它什么时候是一个混沌系统呢?这个也是有条件的:
① 0 < X(0) < 1
② 3.5699456… < u <=4
当满足上述两个条件时,Logistic函数工作于混沌状态。这两个条件是怎么来的请百度,我们这里只说算法和实现。什么是混沌状态:顾名思义就是一种无序的、不可预测的、混乱的、摸不到头、摸不到尾的状态。混沌状态时会出现什么现象,我们以下面的参数为例:
① X(0) = 0.1
② u = 4
当迭代n次后,我们就得到了X(1)、X(2)、…,X(n)这么n个值。那么这就是一个混沌序列,是一维的暂且称作序列A,也就是我们想要得到的序列,在MATLAB中,可以看出X(i)(i=1,2,…,n)的取值是在(0,1)之间的——这是一个很好地特性,就像图像灰度值是在(0,255)之间一样。那么我们把这个一维序列归一化到(0,255)之间得到序列B。
再来看加密过程。对于一幅MN大小的图像(暂且称为Picture),我们需要产生一个同样大小的矩阵来对其进行加密。如此说来,只需要迭代MN次得到序列A,再转成序列B,此时序列B是一维的,将其转化成M*N的二维矩阵(暂且称为Fuck)。因此,用Fuck与Picutre进行异或,便可得到一幅新的图像,称作Rod,如此便完成了一次图像加密,加密后的图像为Rod。
Rod=Picture⊕Fuck(⊕表示异或)
这样我们手中的秘钥是:u,X(0)
此种加密方式称作序列加密,可以看出这种加密方式改变了下像素的灰度(直方图变了),没有改变位置。解密同样道理:Picture = Rod⊕Fuck。
二、源代码
function varargout = encrypt(varargin)
% ENCRYPT MATLAB code for encrypt.fig
% ENCRYPT, by itself, creates a new ENCRYPT or raises the existing
% singleton*.
%
% H = ENCRYPT returns the handle to a new ENCRYPT or the handle to
% the existing singleton*.
%
% ENCRYPT('CALLBACK',hObject,eventData,handles,...) calls the local
% function named CALLBACK in ENCRYPT.M with the given input arguments.
%
% ENCRYPT('Property','Value',...) creates a new ENCRYPT or raises the
% existing singleton*. Starting from the left, property value pairs are
% applied to the GUI before encrypt_OpeningFcn gets called. An
% unrecognized property name or invalid value makes property application
% stop. All inputs are passed to encrypt_OpeningFcn via varargin.
%
% *See GUI Options on GUIDE's Tools menu. Choose "GUI allows only one
% instance to run (singleton)".
%
% See also: GUIDE, GUIDATA, GUIHANDLES
% Edit the above text to modify the response to help encrypt
% Last Modified by GUIDE v2.5 24-Dec-2019 21:56:19
% Begin initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
gui_Singleton = 1;
gui_State = struct('gui_Name', mfilename, ...
'gui_Singleton', gui_Singleton, ...
'gui_OpeningFcn', @encrypt_OpeningFcn, ...
'gui_OutputFcn', @encrypt_OutputFcn, ...
'gui_LayoutFcn', [] , ...
'gui_Callback', []);
if nargin && ischar(varargin{
1})
gui_State.gui_Callback = str2func(varargin{
1});
end
if nargout
[varargout{
1:nargout}] = gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{
:});
else
gui_mainfcn(gui_State, varargin{
:});
end
% End initialization code - DO NOT EDIT
% --- Executes just before encrypt is made visible.
function encrypt_OpeningFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles, varargin)
% This function has no output args, see OutputFcn.
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% varargin command line arguments to encrypt (see VARARGIN)
% Choose default command line output for encrypt
handles.output = hObject;
% Update handles structure
guidata(hObject, handles);
% UIWAIT makes encrypt wait for user response (see UIRESUME)
% uiwait(handles.figure1);
% --- Outputs from this function are returned to the command line.
function varargout = encrypt_OutputFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% varargout cell array for returning output args (see VARARGOUT);
% hObject handle to figure
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Get default command line output from handles structure
varargout{
1} = handles.output;
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton1.
function pushbutton1_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
[filename,filepath] = uigetfile({
'*.bmp;*.jpg;*.png;*.jpeg;*.tif','文件类型 (*.bmp,*.jpg,*.png,*.jpeg,*.tif)';'*.*', '所有文件(*.*)'},'Pick an image');
file = strcat(filepath,filename);
im = imread(file);
axes(handles.axes1);
imshow(im);
imwrite(im,'snap.bmp');
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton2.
function pushbutton2_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton2 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
obj = videoinput('winvideo',1,'YUY2_1280x720')%1280x720 160x120 176x144 320x240 352x288 640x480
% vidRes = get(obj, 'VideoResolution');
% nBands = get(obj, 'NumberOfBands');
% preview(obj);%getsnapshot(obj);
vidRes = get(obj, 'VideoResolution');
nBands = get(obj, 'NumberOfBands');
hImage = image( zeros(vidRes(2), vidRes(1), nBands),'parent',handles.axes1);
preview(obj, hImage);
frame = getsnapshot(obj);
frame = ycbcr2rgb(frame);
imwrite(frame,'snap.bmp','bmp');
pic = imread('snap.bmp');
axes(handles.axes1);
imshow(pic);
title(date,'color','r');
function edit1_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
% Hints: get(hObject,'String') returns contents of edit1 as text
% str2double(get(hObject,'String')) returns contents of edit1 as a double
% input = str2num(get(hObject,'String'));%这里get后面要注意
% if(isempty(input))
% set(hObject,'String','0')
% end
guidata(hObject,handles)
% --- Executes during object creation, after setting all properties.
function edit1_CreateFcn(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to edit1 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles empty - handles not created until after all CreateFcns called
% Hint: edit controls usually have a white background on Windows.
% See ISPC and COMPUTER.
if ispc && isequal(get(hObject,'BackgroundColor'), get(0,'defaultUicontrolBackgroundColor'))
set(hObject,'BackgroundColor','white');
end
% --- Executes on button press in pushbutton3.
function pushbutton3_Callback(hObject, eventdata, handles)
% hObject handle to pushbutton3 (see GCBO)
% eventdata reserved - to be defined in a future version of MATLAB
% handles structure with handles and user data (see GUIDATA)
a=imread('snap.bmp');
R=a(:,:,1); %取图像的R层像素
G=a(:,:,2); %取图像的G层像素
B=a(:,:,3); %取图像的B层像素
[M1,N1]=size(R);
[M2,N2]=size(G);
[M3,N3]=size(B);
h=0.01; %混沌序列初始化
x=zeros(1,40001);x(1)= str2num(get(handles.edit1,'String'));
y=zeros(1,40001);y(1)=0;
z=zeros(1,40001);z(1)=0;
w=zeros(1,40001);w(1)=0;
v=zeros(1,40001);v(1)=0;
for n=1:40000 %产生混沌序列初始化,欧拉法
x(n+1)=x(n)+h*(3.5*(y(n)-x(n)-(-1.2+0.3*(w(n)*w(n)))*x(n)));
y(n+1)=y(n)+h*(2.1*y(n)-z(n)-0.2*(y(n)-x(n))-0.2*(1.2+7*abs(v(n)))*y(n));
z(n+1)=z(n)+h*(2.1*y(n)-z(n));
w(n+1)=w(n)+h*(x(n));
v(n+1)=v(n)+h*(y(n));
end
for n=1:40000 %对3个序列进行改进
x(n)=x(n)*1000000-round(x(n)*1000000);
y(n)=y(n)*1000000-round(y(n)*1000000);
z(n)=z(n)*1000000-round(z(n)*1000000);
w(n)=w(n)*1000000-round(w(n)*1000000);
v(n)=v(n)*1000000-round(v(n)*1000000);
end
% %对R通道进行加密
for j=1:N1 %用位异或法对像素进行置乱
aa=(uint8((M1*N1*(x(N1+j)+0.5))*ones(M1,1)));
g1(:,j)=bitxor(R(:,j),aa);
h1(:,j)=bitxor(g1(:,j),aa); %对像素置乱进行解密
end
for i=1:M1 %行置乱
t(1:N1)=y(1:N1);
[t1,index1]=sort(t(1:N1));
t1=flipud(t1);
g2(i,:)=g1(i,index1);
h2(i,index1)=g2(i,:);
end
for j=1:N1 %列置乱
t(1:M1)=z(1:M1);
[t1,index1]=sort(t(1:M1));
index1=flipud(index1);
g3(:,j)=g2(index1,j);
h3(index1,j)=g3(:,j);
end
% %对G通道进行加密
for j=1:N2 %用位异或法对像素进行置乱
bb=(uint8((M2*N2*(x(N2+j)+0.5))*ones(M2,1)));
j1(:,j)=bitxor(G(:,j),bb);
k1(:,j)=bitxor(j1(:,j),bb); %对像素置乱进行解密
end
for i=1:M2 %行置乱
t(1:N2)=x(1:N2);
[t2,index2]=sort(t(1:N2));
t2=flipud(t2);
j2(i,:)=j1(i,index2);
k2(i,index2)=j2(i,:);
end
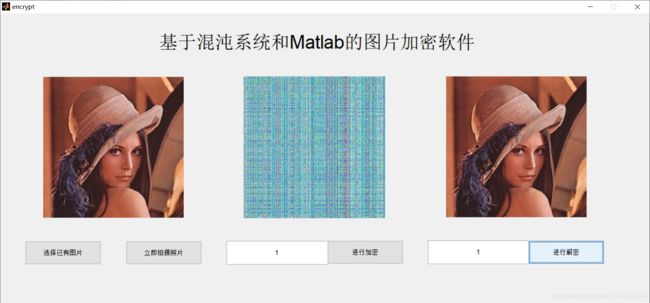
三、运行结果
四、备注
完整代码或者代写添加QQ912100926
往期回顾>>>>>>
【图像压缩】图像处理教程系列之图像压缩【Matlab 074期】
【图像分割】图像处理教程系列之图像分割(一)【Matlab 075期】
【图像分割】图像处理教程系列之图像分割(二)【Matlab 076期】
【模式识别】银行卡号之识别【Matlab 077期】
【模式识别】指纹识别【Matlab 078期】
【图像处理】基于GUI界面之DWT+DCT+PBFO改进图像水印隐藏提取【Matlab 079期】
【图像融合】CBF算法之图像融合【Matlab 080期】
【图像去噪】自适应形态学之图像去噪【Matlab 081期】
【图像增强】DEHAZENET和HWD之水下去散射图像增强【Matlab 082期】
【图像增强】PSO寻优ACE之图像增强【Matlab 083期】
【图像重建】ASTRA算法之图像重建【Matlab 084期】
【图像分割】四叉树之图像分割【Matlab 085期】
【图像分割】心脏中心线之提取【Matlab 086期】
【图像识别】SVM植物叶子之疾病检测和分类【Matlab 087期】
【图像识别】基于GUI界面之模板匹配手写数字识别系统【Matlab 088期】
【图像识别】基于GUI界面之不变矩的数字验证码识别【Matlab 089期】
【图像识别】条形码识别系统【Matlab 090期】
【图像识别】基于GUI界面RGB和BP神经网络之人民币识别系统【Matlab 091期】
【图像识别】CNN卷积神经网络之验证码识别【Matlab 092期】
【图像分类】极限学习分类器之对遥感图像分类【Matlab 093期】
【图像变换】DIBR-3D之图像变换【Matalb 094期】
【图像分割】模糊聚类算法之FCM图像分割【Matlab 095期】
【模式识别】银行监控系统之人脸识别【Matlab 096期】
【模式识别】基于GUI界面之疲劳检测系统【Matlab 097期】
【图像识别】国外车牌识别【Matlab 098期】
【图像分割】最大类间方差法(otsu)之图像分割【Matlab 099期】
【图像分割】直觉模糊C均值聚类之图像分割IFCM【Matlab 100期】
【图像分割】基于matlab形态学重建和过滤改进FCM算法(FRFCM)之图像分割【Matlab 101期】
【图像增强】局部对比度增强CLAHE算法之直方图增强【Matlab 102期】
【图像融合】Frequency Partition之图像融合【Matlab 103期】
【图像评价】SVM之图像无参考质量评价【Matlab 104期】
【图像边缘检测】最小二乘法用于椭圆边缘检测【Matlab 105期】