Mybatis事务的理解(Transaction以及DbUtil)
事务等级划分
首先要了解Mybatis对事务的操作,第一步是先了解数据库的事务隔离级别有哪些:
| 事务隔离级别 | 脏读 | 不可重复读 | 幻读 | 解释 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 读未提交(read-uncommitted) | 是 | 是 | 是 | 可以读到未提交的事物 |
| 不可重复读(read-committed) | 否 | 是 | 是 | 只能读提交的事物 |
| 可重复读(repeatable-read) | 否 | 否 | 是 | 事务提交前后都能读【MySql默认】 |
| 串行化(serializable) | 否 | 否 | 否 | serializable时会锁表,是最安全的,也是日常开发基本不会用 |
Mybatis无疑也是实现了数据库的这几种隔离级别,并且Mybatis支持无事务管理操作。下面看Mybatis枚举写出的事务等级:
**TransactionIsolationLevel **(事务等级枚举):
public enum TransactionIsolationLevel {
NONE(Connection.TRANSACTION_NONE),
//无事务
READ_COMMITTED(Connection.TRANSACTION_READ_COMMITTED),
//不可重复读
READ_UNCOMMITTED(Connection.TRANSACTION_READ_UNCOMMITTED),
//读未提交
REPEATABLE_READ(Connection.TRANSACTION_REPEATABLE_READ),
//可重复读
SERIALIZABLE(Connection.TRANSACTION_SERIALIZABLE);
//串行化
private final int level;
private TransactionIsolationLevel(int level) {
this.level = level;
}
public int getLevel() {
return level;
}
}
Transaction** (事务接口)*
/*
抽取了事务的四个公共特性:获取连接,提交,回滚以及关闭连接
*/
public interface Transaction {
Connection getConnection() throws SQLException;
void commit() throws SQLException;
void rollback() throws SQLException;
void close() throws SQLException;
}
Transaction实现类:
一般我们在配置Mybatis(不整合spring)时,一般是在mybatisConfig.xml文件手动指定一种事务管理类型的,如下
<configuration>
<properties resource="db/mysqlconn.properties">properties>
<settings>
<setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/>
<setting name="aggressiveLazyLoading" value="false"/>
<setting name="jdbcTypeForNull" value="NULL"/>
<setting name="logImpl" value="LOG4J"/>
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
settings>
<typeAliases>
<package name="pojo" />
typeAliases>
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC" />
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<property name="driver" value="${driver}" />
<property name="url" value="${url}" />
<property name="username" value="${username}" />
<property name="password" value="${password}" />
dataSource>
environment>
environments>
<mappers>
<package name="mapper" />
mappers>
configuration>
JDBC事务管理的源码(JdbcTranction):
public JdbcTransaction(DataSource ds, TransactionIsolationLevel desiredLevel, boolean desiredAutoCommit) {
dataSource = ds;
level = desiredLevel;
autoCommmit = desiredAutoCommit;
}
public JdbcTransaction(Connection connection) {
this.connection = connection;
}
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
if (connection == null) {
//调用openConnection
openConnection();
}
return connection;
}
//基于connecttion对象的提交
public void commit() throws SQLException {
if (connection != null && !connection.getAutoCommit()) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Committing JDBC Connection [" + connection + "]");
}
connection.commit();
}
}
public void rollback() throws SQLException {
if (connection != null && !connection.getAutoCommit()) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Rolling back JDBC Connection [" + connection + "]");
}
connection.rollback();
}
}
protected void openConnection() throws SQLException {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Opening JDBC Connection");
}
connection = dataSource.getConnection();
if (level != null) {
connection.setTransactionIsolation(level.getLevel());
}
setDesiredAutoCommit(autoCommmit);
}
}
可以看出JDBC的事物都是通过Connection这个对象来实现的。
ManagedTransaction(Manager事物管理):
public class ManagedTransaction implements Transaction {
private static final Log log = LogFactory.getLog(ManagedTransaction.class);
private DataSource dataSource;
private TransactionIsolationLevel level;
private Connection connection;
private boolean closeConnection;
public ManagedTransaction(Connection connection, boolean closeConnection) {
this.connection = connection;
this.closeConnection = closeConnection;
}
public ManagedTransaction(DataSource ds, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean closeConnection) {
this.dataSource = ds;
this.level = level;
this.closeConnection = closeConnection;
}
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
if (this.connection == null) {
openConnection();
}
return this.connection;
}
public void commit() throws SQLException {
// Does nothing
}
public void rollback() throws SQLException {
// Does nothing
}
public void close() throws SQLException {
if (this.closeConnection && this.connection != null) {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Closing JDBC Connection [" + this.connection + "]");
}
this.connection.close();
}
}
protected void openConnection() throws SQLException {
if (log.isDebugEnabled()) {
log.debug("Opening JDBC Connection");
}
this.connection = this.dataSource.getConnection();
if (this.level != null) {
this.connection.setTransactionIsolation(this.level.getLevel());
}
}
}
可以看出这个事物的主要功能是将事物交给其他容器(如Spring)去处理,可以这么理解:如果我们使用MyBatis构建本地程序,即不是WEB程序,若将type设置成"MANAGED",那么,我们执行的任何update操作,即使我们最后执行了commit操作,数据也不会保留,不会对数据库造成任何影响。因为我们将MyBatis配置成了“MANAGED”,即MyBatis自己不管理事务,而我们又是运行的本地程序,没有事务管理功能,所以对数据库的update操作都是无效的。
TransactionFactory(事物工厂):
public interface TransactionFactory {
/**
* Sets transaction factory custom properties.
* @param props
*/
void setProperties(Properties props);
Transaction newTransaction(Connection conn);
/**
* Creates a {@link Transaction} out of a datasource.
* @param dataSource DataSource to take the connection from
* @param level Desired isolation level
* @param autoCommit Desired autocommit
* @return Transaction
* @since 3.1.0
*/
Transaction newTransaction(DataSource dataSource, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit);
}
我们此时来分析Mybatis解析config.xml文件内容为
private TransactionFactory transactionManagerElement(XNode context) throws Exception {
if (context != null) {
String type = context.getStringAttribute("type");
Properties props = context.getChildrenAsProperties();
//此时获取了一个TransactionFactory对象,并且调用该方法创建一个Transaction对象。
/*
如果type = "JDBC",则MyBatis会创建一个JdbcTransactionFactory.class 实例;
如果type="MANAGED",则MyBatis会创建一个MangedTransactionFactory.class实例
*/
TransactionFactory factory = (TransactionFactory) resolveClass(type).newInstance();
factory.setProperties(props);
return factory;
}
throw new BuilderException("Environment declaration requires a TransactionFactory.");
}
这个接口有三个实现类,我们来看JDBCTransactionFactory:
public class JdbcTransactionFactory implements TransactionFactory {
public void setProperties(Properties props) {
}
public Transaction newTransaction(Connection conn) {
//直接new了一个JdbcTransaction对象管理Connection对象
return new JdbcTransaction(conn);
}
public Transaction newTransaction(DataSource ds, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
return new JdbcTransaction(ds, level, autoCommit);
}
}
Connection连接对象的创建及方法实现
要理解这个java.sql.Connection对象,那就必须先看看我之前学习到的DBUtil.java这个工具类的代码
package com.edu.util;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.DriverManager;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class DBUtil {
//数据库连接基本信息
private static final String DRIVER_CLASS="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver";
private static final String DRIVER_URL="jdbc:mysql:///data?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8";
private static final String DRIVER_USER="root";
private static final String DRIVER_PWD="123456";
protected Connection conn ;
protected PreparedStatement pstmt ;
protected ResultSet rs ;
static {
try {
//注册驱动(com.mysql.jdbc.Driver这个类中的有一段静态代码块就是专门用于反射注册的)
Class.forName(DRIVER_CLASS);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 数据连接工具类
public Connection getConnection() {
try {
//我们来查看这个方法
return DriverManager.getConnection(DRIVER_URL, DRIVER_USER, DRIVER_PWD) ;
} catch (SQLException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
return null;
}
}
Driver注册驱动静态代码块:
//静态字段初始化器
// 向DriverManager注册驱动
static {
try {
java.sql.DriverManager.registerDriver(new Driver());
} catch (SQLException E) {
throw new RuntimeException("Can't register driver!");
}
}
public static synchronized void registerDriver(java.sql.Driver driver,
DriverAction da)
throws SQLException {
/* 注册尚未添加到我们的列表中的驱动程序*/
if(driver != null) {
registeredDrivers.addIfAbsent(new DriverInfo(driver, da));
} else {
// 不等于空,我就给你报错,为了兼容我原先的Drivermanager(你一个在列表中的驱动还添加进来,那肯定不行啊)
throw new NullPointerException();
}
println("registerDriver: " + driver);
}
DriverManager.getConnection(…) 方法具体事项:
public static Connection getConnection(String url,
String user, String password) throws SQLException {
java.util.Properties info = new java.util.Properties();
if (user != null) {
info.put("user", user);
}
if (password != null) {
info.put("password", password);
}
return (getConnection(url, info, Reflection.getCallerClass()));
}
//-----具体调用(getConnection(url, info, Reflection.getCallerClass())---------
// Worker method called by the public getConnection() methods.
private static Connection getConnection(
String url, java.util.Properties info, Class<?> caller) throws SQLException {
/*
当callerCl为null时,我们应该检查应用程序的(间接调用该类的)类加载器,
以便可以从此处加载rt.jar外的JDBC驱动程序类。
*/
ClassLoader callerCL = caller != null ? caller.getClassLoader() : null;
synchronized(DriverManager.class) {
// synchronize loading of the correct classloader.
if (callerCL == null) {
callerCL = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader();
}
}
if(url == null) {
throw new SQLException("The url cannot be null", "08001");
}
println("DriverManager.getConnection(\"" + url + "\")");
//遍历试图建立连接的已加载的注册驱动程序。请记住第一个引发的异常,以便我们重新提出。
SQLException reason = null;
for(DriverInfo aDriver : registeredDrivers) {
// 如果调用者没有该驱动调用权限,则跳过它(无视该驱动)
if(isDriverAllowed(aDriver.driver, callerCL)) {
try {
println(" trying " + aDriver.driver.getClass().getName());
Connection con = aDriver.driver.connect(url, info);
//开始尝试连接
if (con != null) {
// Success!
println("getConnection returning " + aDriver.driver.getClass().getName());
//连接成功直接返回(从这可以看出来,当有多个驱动类进行驱动注册,那么我们也只能获取到最开始获得连接的那个驱动类的连接conn对象)
return (con);
}
} catch (SQLException ex) {
if (reason == null) {
reason = ex;
}
}
} else {
println(" skipping: " + aDriver.getClass().getName());
}
}
//一个连接都没拿到啊,给你报个错
if (reason != null) {
println("getConnection failed: " + reason);
throw reason;
}
}
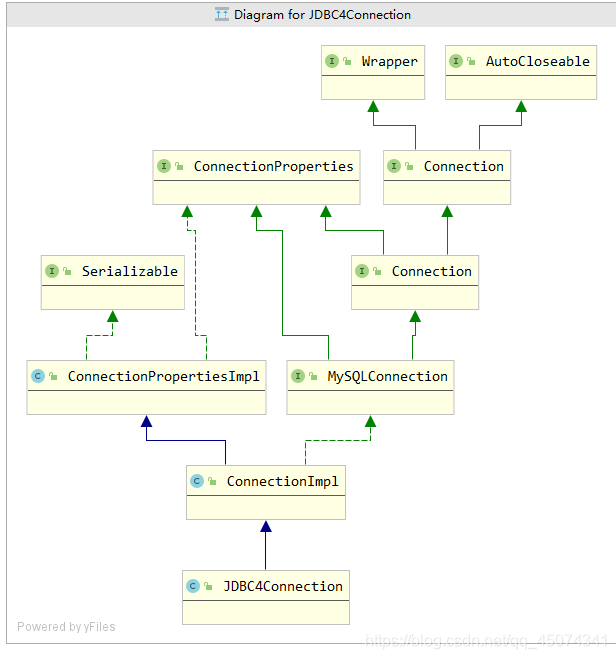
因为我最主要就是连接mysql数据库,所以我们来看看Jdbc驱动拿到的连接对象,具体方法详情请看com.mysql.jdbc.MySQLConnection接口,基本所有对数据库的操作api都在这个接口里。

可以看出它是com.mysql.jdbc.JDBC4Connection对象,可以从下图看出层级关系挺复杂的。