第十六课.基于K-means的图像分割
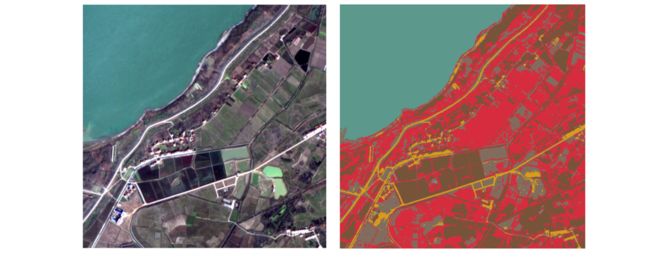
本实验基于图像,使用 K-means 算法进行像素聚类,将一幅图像分解成若干互不相交区域的集合,从而实现图像分割;本次实验分割的对象是遥感图像,图像来自GID(Gaofen Image Dataset)数据集;
首先加载必要的包和模块:
import numpy as np
from PIL import Image
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
PIL(Python Image Library)是 Python 的第三方图像处理库,在 Python3 中只需要安装 pillow 模块即可,安装命令:pip install pillow
加载图像:
image = Image.open('remote.jpg')
image
- 上图中的每个彩色像素点包含3个特征值,分别是:R(红色)、G(绿色)、B(蓝色) 三个颜色通道;
- 通过 RGB 三个颜色通道的变化以及它们相互之间的叠加可以得到各式各样的颜色。
获取图像的色彩模式:
image.mode
# 'RGB'
获取图像的像素值:
image.getpixel((0,0))
# (72, 139, 145)
加载图像的像素数据:
def load_data(image):
# 存放所有的像素数据
data = []
# 获取图片像素的行列数
row,col = image.size
# 遍历每个像素点的位置 (i,j)
for i in range(row):
for j in range(col):
# 获取 (i,j) 处的像素值,并添加到 data 列表中
data.append(image.getpixel((i,j)))
return data,row,col
获取 K 个类的像素值:
def get_color(k):
# 存放聚类中心的像素值
color = []
# 设置随机种子,使多次运行的结果保持一致
np.random.seed(2021)
# 为 k 个聚类中心生成随机像素值
for i in range(k):
# 生成包含三个随机数的序列,随机数范围:[0,255]
c = np.random.choice(a=range(255),size=3)
# 将随机数三元组添加到 color 列表中
color.append(tuple(c))
return color
get_color(5)
"""
[(116, 85, 57), (128, 109, 94), (214, 44, 62), (219, 157, 21), (93, 152, 140)]
"""
像素聚类:
# 聚类簇数
k = 5
# 获取像素数据、图片像素的行列数
data,row,col = load_data(image)
# 对图片像素进行聚类,获取每个像素的聚类编号
label = KMeans(k).fit_predict(data)
# 将 label 改成二维数组,且 shape = (row,col)
label = label.reshape(row,col)
聚类结果可视化:
# 获取 k 个类的像素值
color = get_color(k)
# 创建一张新的图片,色彩模式为 RGB,图片大小为(row,col)
image_new = Image.new("RGB", (row, col))
# 遍历新图片每个像素的位置:(i,j)
for i in range(row):
for j in range(col):
# 获取(i,j)处的聚类编号 x
x = label[i][j]
# 在(i,j)处添加类 x 的像素值的像素值 color[x]
image_new.putpixel((i,j), color[x])
image_new