【笔记】医学图像配准综述(2014年以前)
本博文是阅读几篇医学图像配准综述的笔记,主要是2014年前。本博文也按照模型,策略,算法三个层面总结医学图像配准的相关内容。内容繁多,故用大纲形式以做概览,不涉及具体,详见文末参考文献。另外,之后会推出另外一篇博文,关于深度学习技术,如CNN,GAN等在医学配准任务中的相关工作。平台上有很多优秀的配准类笔记,拙记实在是狗尾续貂,如有任何意见请评论留言,帮助我写出好的博文,以飨读者!
概念及基础
什么是图像配准
对于一组图像数据集中的两幅图像,通过寻找一种空间变换把一幅图像(浮动图像,moving image)映射到另一幅图像(参考图像,fixed image)上,使得两图中对应于空间同一位置的点一一对应起来,从而达到信息融合的目的。
这个配准
的过程包括
建立不同图像获取之间的空间对应关系。
可变形配准与光流估计紧密相关,两者都是建立两张图像之间的联系。前者
寻找空间匹配, 而光流估计是寻找与不同时间点相关的空间匹配。光流估计可以看作是小形变单模态可变形的配准问题。
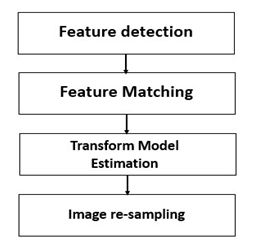
配准的通用流程
图像配准技术包括四个方面:变换模型、特征空间、相似性测度、搜索空间和搜索策略
配准的五个步骤
-
根据实际应用场合选取适当的变换模型;
-
选取合适的特征空间,基于灰度或基于特征;
-
根据变换模型的参数配置以及所选用的特征,确定参数可能变化的范围,并选用最优的搜索策略;
-
应用相似性测度在搜索空间中按照优化准则进行搜索,寻找最大相关点,从而求解出变换模型中的未知参数;
-
将待配准图像按照变换模型对应到参考图像中,实现图像间的匹配。
基本变换
-
刚体变换:距离不变,旋转和平移
-
仿射变换: 直线平行
-
投影变换:直线不平行
-
非线性变换:曲线
根据配准模式分类
-
单模态:待配准的两幅图象是用同一种成像设备获取
-
多模态:待配准的两幅图象来源于两种不同的成像设备
根据受试对象分类
-
对象间
-
对象内部
图像配准质量评估标准
-
单模图像配准常使用 相关性(Correlation Coefficient, CC) 来衡量效果,
-
而多模图像配准常使用 互信息(Mutual Information, MI) 衡量。
-
DICE loss
-
熵相关系数(Entropy Corrleation Coefficient,ECC)
两种常用的配准范例
-
Demons算法及其扩展
-
块匹配和HAMMER
模型
常用的弹性形变模型:
-
非参数模型:图像被看成是一片有弹性的薄膜, 在外力和内力的作用下达到平衡, 外力由参考图像和变形图像的差异确定;内力由薄膜的强度和平滑程度确定
-
如:流体模型,扩散模型,光流模型
-
-
参数模型:模型由基函数及其参数来表示, 模型的计算过程也就是参数的计算过程
-
仿射变换、B-spline based FFD
-
基函数如:多项式、谐波函数、分级基函数、小波、B样条
-
形变模型
-
来源于物理模型的几何变换
-
elastic body models
-
Linear Models: the image under deformation is modeled as an elastic body
-
Nonlinear Models: linear elastic models cannot cope with large deformations, to account for large deformations
-
-
viscous fluid flow models
-
diffusion models
-
curvature registration
-
flows of diffeomorphisms
-
Large Deformation Diffeomorphic Metric Mapping (LDDMM)
-
-
-
来源于插值的几何变换
-
Radial Basis Functions
-
Elastic Body Splines
-
Free-Form Deformations
-
basis functions from signal processing
-
Locally Affine Models
-
piecewise affine models
-
poly-affine
-
-
-
基于知识的几何变换
-
Statistically-Constrained Geometric Transformations:
-
Statistical deformation
models (SDMs) capture statistical information about deformation fields across a population
-
of subjects
-
PCA
-
-
Geometric Transformations Inspired by Biomechanical/Biophysical Models
more
informed priors regarding the biomechanical properties of the tissues will allow the reliable
estimation of complex deformation fields with the use of few degrees of freedom
-
-
Tumor growth models
-
Biomechanical models of the breast
-
Biomechanical models of the prostate
-
Miscellaneous
-
-
特定任务约束
-
Topology Preservation
-
Volume Preservation
-
Rigidity Constraints
-
生物医学图像中应用于变换的约束:
-
inverse consistency
-
symmetry
-
topology preservation
-
diffeomorphism
-
asymmetric
基于特征的配准流程
匹配方法(策略)
根据利用可得到信息进行匹配过程的方式可将配准方法分为3组
-
几何法( Geometric Methods): 在landmarks之间建立对应联系. 这方面的兴趣今年减少了.
-
仅仅推断对应关系:这种方法当与基于插值的变换模型结合预测密集位移是有用的.使用稀疏几何法和图标准则可提高空间变换
-
Matching by descriptor distance: 描述子包含的信息用于确定两图像间的对应关系
-
a spectral technique to solve the matching problem
-
Pairwise constraints were used to preserve pairwise geometry
-
graph matching problem with higher order constraints
-
-
Matching through geometric constraints:结构约束把对应关系问题构建为图匹配
-
-
仅仅推断空间变换:不直接建立两个lanmarks集之间的对应关系, 而实预测一个空间变换使得两个lanmarks集合对齐. 根据对应关系是否已知分为两类
-
Known correspondences
-
Procrustes analysis
-
Given the correspondences, one may estimate non-rigid transformations by adopting an interpolation strategy
-
Radial basis functions are able to produce dense deformation fields for any spatial distribution of points
-
approximating splines are able to account for the uncertainty in the estimated correspondences
-
-
Unknown correspondences: estimate the transformation without concerning itself with the establishment of correspondences
-
through the use of alternative representations of the geometric information. One possibility is to represent the point sets as probability distributions
-
establish correspondences is by adopting a representation of the geometric information based on the use of signed distance functions
-
-
-
两者都进行推断: estimate the correspondences and the transformation at the same time, This is usually performed in an iterative way
-
Iterative Closest Point (ICP) has drawn a lot of attention
-
multiscale EM-ICP
-
dual-bootstrap ICP
-
Thin-Plate Spline Robust Point Matching (TPS-RPM)
-
-
-
标记法(Iconic Methods): 通常指的是voxel-based 或者 intensity-based 方法, 量化对齐效果. 与几何法相比, it has the potential to better quantify and represent the accuracy of the estimated dense deformation field.
-
Mono-Modal Registration
-
Intensity-based methods:两个图像之间的灰度值是线性关系
-
Cross Correlation (CCor)
-
Correlation Coefficient (CCoef)
-
-
Attribute-based methods: 通过使用能表示潜在解剖的集合结构, 引入局部信息进行特征空间增广.
-
-
Multi-Modal Registration
-
reduction of the multimodal problem to a mono-modal problem
-
simulating one modality from another, simulate one modality from another so that at the end both images come from the same modality. achieved by taking advantage of the available knowledge regarding the physical properties of the imaging device
-
mapping both modalities to a common domain, one can map both images to a third domain where the registration will take place
-
-
use of information theoretic measures
-
Mutual Information (MI): An important property of MI is its generality. The way of estimating entropy: a) non-parametric estimator
-
Local evaluation of mutual information: Regional Mutual Information (RMI)
-
NMI
-
Correlation Ratio (CR)
-
f-information measures
-
divergence measures: Kullback-Leibler Divergence (KLD), Jensen-Shannon Divergence (JSD)
-
Jensen-Renyi divergence(based on Renyi Entropy (RE))
-
-
-
-
组合法(Hybrid Methods):将上面两种方式杂糅, 根据几何信息的使用方式分为
-
as initialization:通过几何法先粗配准,然后使用标志法refine。
-
Exploiting landmarks information
-
Exploiting surface information
-
-
as constraint:用一种类型的信息初始化通常会使得配准过程的鲁棒性增加,但是不能保证此前建立的对应关系被保存下来。因此,在第一步预测的对应关系被用作后续步骤的约束。
-
Additional information used as soft constraint
-
Additional information used as hard constraint
-
Coupled approaches:标志法能受益于几何法的初始化或者通过几何法建立的初始对应关系,但是反过来却不行,因为几何发的解是独立获得的。通过一个目标函数,将两者统一起来。
-
-
in a coupled fashion
-
算法
对于一个目标函数(包括匹配项和正则项),通过优化算法求解,得到一个最优的变换。
-
连续
-
梯度下降(GD),随机梯度下降(SGD)
-
共轭梯度法( Conjugate gradient)
-
拟牛顿法( Quasi-Newton)
-
高斯牛顿法( Gauss-Newton)
-
约束优化方法: 拉格朗日转化为无约束问题,再使用上述无约束优化方法。
-
-
离散
-
基于图方法: 最大流最小割
-
变分推断, Belief propagation methods
-
线性规划
-
资源
医学图像配准数据集
数据集2
[1] Sotiras, Aristeidis, Davatzikos,et al. Deformable Medical Image Registration: A Survey.[J].IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2013 July ; 32(7): 1153–1190.
[2] 罗述谦, 吕维雪. 医学图像配准技术[J]. 国际生物医学工程杂志, 1999(01):1-8.
[3] Oliveira, Francisco P.M, Tavares,et al. Medical image registration: a review.[J]. Computer Methods in Biomechanics & Biomedical Engineering, 2014.
[4] 白小鱼 图像配准综述 https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/80985475