散列表(Hash Table)概念、散列冲突、开散列模拟实现散列表
散列表提供了一种完全不同的存储和搜索方式,通过将关键码映射到表中某个位置上来存储元素,然后根据关键码用同样的方式直接访问。
理想的搜索方法是可以不经过任何比较,一次直接从表中拿到搜索的元素,如果在元素的存储位置与它的关键码之间建立一个确定的对应函数关系Hash(),使得每个关键码与结构中的一个唯一的存储位置相对应Adderss = Hash(Key)。
插入元素:根据待插入元素的关键码,以此函数计算该元素的存储位置并按此位置进行存放;
搜索元素:对元素的关键码进行计算,将求得的函数值作为元素的存储位置,在表中按此位置取元素比较,若关键码相等,则搜索成功。
这种方法就叫做散列方法,使用的转换函数称为散列函数,构建的表又称为散列表。
对于不同的关键码,通过散列函数计算得到了同一散列地址,称这些散列地址相同的不同关键码为同义词。按照这样的地址加入散列表时就产生了冲突,冲突太多会降低搜索效率。
冲突是不可避免的,只能尽量避免、减少冲突。
1. 散列函数
在构造散列函数需要注意:
- 散列函数的定义域必须包括需要存储的全部关键码,而如果散列表允许有m个地址,其值域必须在0到m - 1之间;
- 散列函数计算出来的地址应能均匀分布在整个地址空间中;
- 散列函数应该比较简单,能在较短时间内计算出来。
常见散列函数:
- 除留余数法(常用)
设表中允许的地址数为m,取一个不大于m,但最接近于或等于m的质数p作为除数,散列函数为:
hash(key) = key % p (p ≤ m)
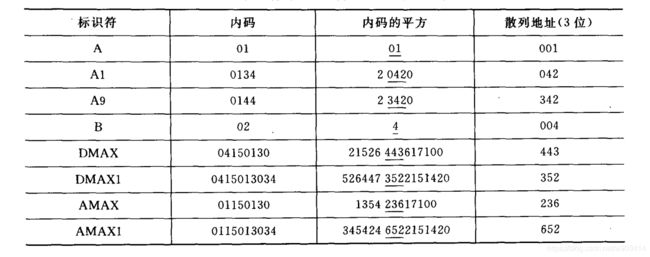
- 平方取中法
先计算构成关键码的标识符的内码的平方,然后按照散列表的大小取中间的若干位作为散列地址,设标识符可以用一个计算机字长的内码表示,内码平方数的中间几位一般是由标识符所有字符决定,所以对不同的标识符计算出的散列地址大多不相同,即使可能有些字符相同。
- 折叠法
将关键码自左向右分成位数相等的几部分,每一部分的位数应与散列表地址位数相同,只有最后一部分的位数可以短一些,将这些部分叠加起来,就可以得到具有该关键码记录的散列地址,两种叠加方法:
(1)移位法:把各部分的最后移位对齐相加;
(2)分界法:各部分不折断,沿各部分的分界来回折叠,然后对其相加,将相加的结果作为散列地址。
例:key = 23938587841,存储空间为3位,则划分结果分为每段3位,则
239 385 878 41
将超出地址位数的最高位删除,保留最低的3位。
2. 解决散列冲突办法
最常见的两种方法:闭散列和开散列。
2.1 闭散列
闭散列:**又称开放定址法,当发送散列冲突时,如果散列表未被装满,说明在散列表中还有空位置,那么就可以把key存放到冲突位置中的下一个空位置中去。**寻找下一个空位置
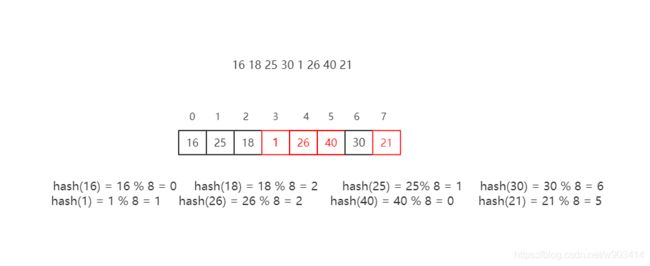
- 线性探测:从发起冲突的位置开始,依次向后探测,直到寻找到下一个空位置为止。
散列表的大小为8,红色方格代表了产生了散列冲突,依次寻找下一个空位置。
删除时:闭散列解决散列冲突时,不能随便物理删除散列表已有的元素,若是直接删除元素会影响其它元素的搜索,则线性探测需要采用标记的伪删除法删除一个元素。
线性探查方法容易产生“堆积”问题,即不同探查序列的关键码占据了可利用的空桶,使得为寻找某一关键码需要经历不同的探查序列的元素。
- 二次探查法
二次探查法寻找下一个空位置公式为: H i H_i Hi = ( H 0 H_0 H0 + i 2 i^2 i2) % m,或者 H i H_i Hi = ( H 0 H_0 H0 - i 2 i^2 i2) % m,其中i = 1,2,3…, H 0 H_0 H0是通过散列函数计算得到的位置,m为散列表的大小。
H i H_i Hi = ( H 0 H_0 H0 + i 2 i^2 i2) % m 则 H i + 1 H_{i + 1} Hi+1 = ( H 0 H_0 H0 + ( i + 1 ) 2 {(i+1)}^2 (i+1)2) % m,则 H i + 1 − H i = 2 i + 1 H_{i+1} - H_i = 2i + 1 Hi+1−Hi=2i+1,则 H i + 1 = H 0 + 2 i + 1 H_{i+1} = H_0 + 2i + 1 Hi+1=H0+2i+1。
当表的长度为质数且表中装载因子不超过0.5时,新的关键码一定能够插入,而且任意位置不会被探查两次。如果装在因子超出0.5时,需要考虑对表进行扩容。
在删除时,也只能做逻辑删除,不能将该位置进行删除。
2.2 开散列
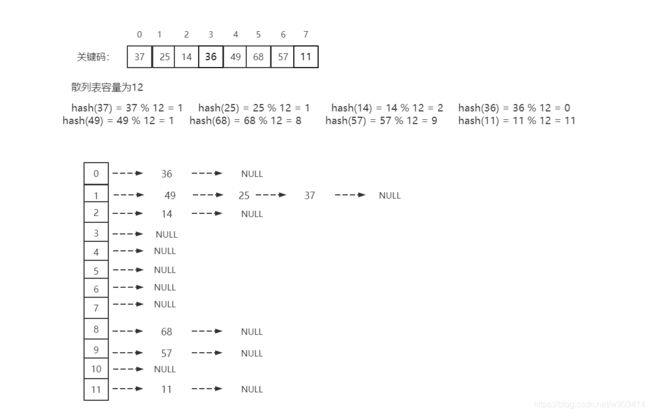
开散列:又称为链地址法,首先对关键码集合用散列函数计算散列地址,具有相同地址的关键码归于同一子集合,每一个子集合称为一个桶,各个桶中的元素通过一个单链表链接起来,各链表的头节点存储在散列表中。
如图:
开散列桶中,每个桶存放的都是发送散列冲突的关键码。
随着元素的插入,散列表中每一个桶中的元素都会增加,当某些桶中的链表节点非常多时,会影响散列表的性能,因此则考虑为散列表进行扩容。
最优的情况:一个桶中只放一个元素,则当前元素个数等于散列表桶的个数时,对散列表进行扩容。
3. 开散列模拟实现散列表
代码:
#pragma once
#include newHT(table.capacity() * 2);
vector<Node*> newHT(GetNextPrime(table.capacity()));
for (size_t i = 0; i < table.capacity(); ++i)
{
Node* cur = table[i];
while (cur)
{
table[i] = cur->next;
size_t tablenumber = HashFunc(cur->val, newHT.capacity());
cur->next = newHT[tablenumber];
newHT[tablenumber] = cur;
cur = table[i];
}
}
table.swap(newHT);
}
}
unsigned long GetNextPrime(size_t capacity)//stl容器中使用的方法,lower_bound
{
const unsigned long* first = Prime_list;
const unsigned long* last = Prime_list + (int)num_primes;
const unsigned long* pos = std::lower_bound(first, last, capacity);
return pos == last ? *(last - 1) : *pos;
}
void clear()
{
for (size_t i = 0; i < capacity(); ++i)
{
Node* cur = table[i];
while (cur)
{
table[i] = cur->next;
delete cur;
cur = table[i];
}
cur = nullptr;
}
}
};
测试用例:
int main()
{
HashTable<string, KOFV<string>> ht;
ht.InsertUnique("小王");
ht.InsertUnique("小刘");
ht.InsertUnique("小李");
ht.InsertUnique("小张");
ht.PrintHashTable();
ht.InsertEqual("小张");
ht.InsertEqual("小李");
ht.PrintHashTable();
ht.PrintHashTable();
cout << ht.capacity() << endl;
cout << ht.Size() << endl;
cout << ht.Find("小五") << endl;
auto it = ht.begin();
cout << *it << endl;
cout << it->data() << endl;
ht.PrintHashTable();
return 0;
}