LeetCode算法:1578~1588道
目录
1578. 避免重复字母的最小删除成本
1579. 保证图可完全遍历
1582. 二进制矩阵中的特殊位置
1583. 统计不开心的朋友
1584. 连接所有点的最小费用
1588. 所有奇数长度子数组的和
1578. 避免重复字母的最小删除成本
English Version
题目描述
给你一个字符串 s 和一个整数数组 cost ,其中 cost[i] 是从 s 中删除字符 i 的代价。
返回使字符串任意相邻两个字母不相同的最小删除成本。
请注意,删除一个字符后,删除其他字符的成本不会改变。
示例 1:
输入:s = "abaac", cost = [1,2,3,4,5] 输出:3 解释:删除字母 "a" 的成本为 3,然后得到 "abac"(字符串中相邻两个字母不相同)。
示例 2:
输入:s = "abc", cost = [1,2,3] 输出:0 解释:无需删除任何字母,因为字符串中不存在相邻两个字母相同的情况。
示例 3:
输入:s = "aabaa", cost = [1,2,3,4,1]
输出:2
解释:删除第一个和最后一个字母,得到字符串 ("aba") 。
提示:
s.length == cost.length1 <= s.length, cost.length <= 10^51 <= cost[i] <= 10^4s中只含有小写英文字母
解法
Python3
Java
class Solution {
public int minCost(String s, int[] cost) {
int res = 0;
char[] word = s.toCharArray();
for(int i = 0;i < word.length;i++){
char c = word[i];
int max = cost[i];
int sum = max;
while(i + 1 < word.length && word[i + 1] == c){
sum += cost[++i];
max = Math.max(max,cost[i]);
}
if(sum != max){
res += sum - max;
}
}
return res;
}
}
…
1579. 保证图可完全遍历
English Version
题目描述
Alice 和 Bob 共有一个无向图,其中包含 n 个节点和 3 种类型的边:
- 类型 1:只能由 Alice 遍历。
- 类型 2:只能由 Bob 遍历。
- 类型 3:Alice 和 Bob 都可以遍历。
给你一个数组 edges ,其中 edges[i] = [typei, ui, vi] 表示节点 ui 和 vi 之间存在类型为 typei 的双向边。请你在保证图仍能够被 Alice和 Bob 完全遍历的前提下,找出可以删除的最大边数。如果从任何节点开始,Alice 和 Bob 都可以到达所有其他节点,则认为图是可以完全遍历的。
返回可以删除的最大边数,如果 Alice 和 Bob 无法完全遍历图,则返回 -1 。
示例 1:
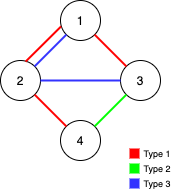输入:n = 4, edges = [[3,1,2],[3,2,3],[1,1,3],[1,2,4],[1,1,2],[2,3,4]] 输出:2 解释:如果删除 [1,1,2] 和 [1,1,3] 这两条边,Alice 和 Bob 仍然可以完全遍历这个图。再删除任何其他的边都无法保证图可以完全遍历。所以可以删除的最大边数是 2 。
示例 2:
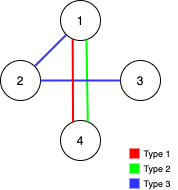输入:n = 4, edges = [[3,1,2],[3,2,3],[1,1,4],[2,1,4]] 输出:0 解释:注意,删除任何一条边都会使 Alice 和 Bob 无法完全遍历这个图。
示例 3:
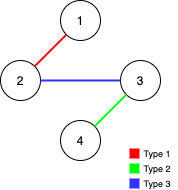输入:n = 4, edges = [[3,2,3],[1,1,2],[2,3,4]] 输出:-1 解释:在当前图中,Alice 无法从其他节点到达节点 4 。类似地,Bob 也不能达到节点 1 。因此,图无法完全遍历。
提示:
1 <= n <= 10^51 <= edges.length <= min(10^5, 3 * n * (n-1) / 2)edges[i].length == 31 <= edges[i][0] <= 31 <= edges[i][1] < edges[i][2] <= n- 所有元组
(typei, ui, vi)互不相同
解法
Python3
Java
class Solution {
// https://oi-wiki.org/ds/dsu/#_3
private boolean[] used;
public int maxNumEdgesToRemove(int n, int[][] edges) {
used = new boolean[edges.length];
// type 为倒序,3, 2, 1
Arrays.sort(edges, (a, b) -> Integer.compare(b[0], a[0]));
if (!unionFind(n, edges, 1)) return -1;
if (!unionFind(n, edges, 2)) return -1;
int result = 0;
for (boolean u : used) {
result += u ? 0 : 1;
}
return result;
}
private boolean unionFind(int n, int[][] edges, int excludedType) {
int[] union = new int[n + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
union[i] = i;
}
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < edges.length; i++) {
int[] edge = edges[i];
if (edge[0] == excludedType) continue;
int rootA = findRoot(union, edge[1]);
int rootB = findRoot(union, edge[2]);
if (rootA != rootB) {
cnt += 1;
union[rootA] = rootB;
used[i] = true;
}
if (cnt == n - 1) return true;
}
return false;
}
private int findRoot(int[] union, int idx) {
if (union[idx] != idx) {
int root = findRoot(union, union[idx]);
union[idx] = root;
return root;
}
return idx;
}
}
…
1582. 二进制矩阵中的特殊位置
English Version
题目描述
给你一个大小为 rows x cols 的矩阵 mat,其中 mat[i][j] 是 0 或 1,请返回 矩阵 mat 中特殊位置的数目 。
特殊位置 定义:如果 mat[i][j] == 1 并且第 i 行和第 j 列中的所有其他元素均为 0(行和列的下标均 从 0 开始 ),则位置 (i, j) 被称为特殊位置。
示例 1:
输入:mat = [[1,0,0], [0,0,1], [1,0,0]] 输出:1 解释:(1,2) 是一个特殊位置,因为 mat[1][2] == 1 且所处的行和列上所有其他元素都是 0
示例 2:
输入:mat = [[1,0,0], [0,1,0], [0,0,1]] 输出:3 解释:(0,0), (1,1) 和 (2,2) 都是特殊位置
示例 3:
输入:mat = [[0,0,0,1], [1,0,0,0], [0,1,1,0], [0,0,0,0]] 输出:2
示例 4:
输入:mat = [[0,0,0,0,0], [1,0,0,0,0], [0,1,0,0,0], [0,0,1,0,0], [0,0,0,1,1]] 输出:3
提示:
rows == mat.lengthcols == mat[i].length1 <= rows, cols <= 100mat[i][j]是0或1
解法
Python3
Java
class Solution {
public int numSpecial(int[][] mat) {
int rows = mat.length;
int cols = mat[0].length;
int[] rows1 = new int[rows];
int[] cols1 = new int[cols];
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
if (mat[i][j] == 1) {
rows1[i]++;
cols1[j]++;
}
}
}
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < cols; j++) {
if (mat[i][j] == 1 && rows1[i] == 1 && cols1[j] == 1) {
ans ++;
}
}
}
return ans;
}
}
…
1583. 统计不开心的朋友
English Version
题目描述
给你一份 n 位朋友的亲近程度列表,其中 n 总是 偶数 。
对每位朋友 i,preferences[i] 包含一份 按亲近程度从高到低排列 的朋友列表。换句话说,排在列表前面的朋友与 i 的亲近程度比排在列表后面的朋友更高。每个列表中的朋友均以 0 到 n-1 之间的整数表示。
所有的朋友被分成几对,配对情况以列表 pairs 给出,其中 pairs[i] = [xi, yi] 表示 xi 与 yi 配对,且 yi 与 xi 配对。
但是,这样的配对情况可能会是其中部分朋友感到不开心。在 x 与 y 配对且 u 与 v 配对的情况下,如果同时满足下述两个条件,x 就会不开心:
x与u的亲近程度胜过x与y,且u与x的亲近程度胜过u与v
返回 不开心的朋友的数目 。
示例 1:
输入:n = 4, preferences = [[1, 2, 3], [3, 2, 0], [3, 1, 0], [1, 2, 0]], pairs = [[0, 1], [2, 3]] 输出:2 解释: 朋友 1 不开心,因为: - 1 与 0 配对,但 1 与 3 的亲近程度比 1 与 0 高,且 - 3 与 1 的亲近程度比 3 与 2 高。 朋友 3 不开心,因为: - 3 与 2 配对,但 3 与 1 的亲近程度比 3 与 2 高,且 - 1 与 3 的亲近程度比 1 与 0 高。 朋友 0 和 2 都是开心的。
示例 2:
输入:n = 2, preferences = [[1], [0]], pairs = [[1, 0]] 输出:0 解释:朋友 0 和 1 都开心。
示例 3:
输入:n = 4, preferences = [[1, 3, 2], [2, 3, 0], [1, 3, 0], [0, 2, 1]], pairs = [[1, 3], [0, 2]] 输出:4
提示:
2 <= n <= 500n是偶数preferences.length == npreferences[i].length == n - 10 <= preferences[i][j] <= n - 1preferences[i]不包含ipreferences[i]中的所有值都是独一无二的pairs.length == n/2pairs[i].length == 2xi != yi0 <= xi, yi <= n - 1- 每位朋友都 恰好 被包含在一对中
解法
Python3
Java
class Solution {
public int unhappyFriends(int n, int[][] preferences, int[][] pairs) {
Map<Integer, Set<Integer>> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int[] pair : pairs) {
calcBetter(preferences[pair[0]], map, pair[0], pair[1]);
calcBetter(preferences[pair[1]], map, pair[1], pair[0]);
}
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
for (int i = 0; i < pairs.length; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < pairs.length; j++) {
if (unhappy(pairs[i][0], pairs[j][0], map)) {
set.add(pairs[i][0]);
set.add(pairs[j][0]);
}
if (unhappy(pairs[i][1], pairs[j][0], map)) {
set.add(pairs[i][1]);
set.add(pairs[j][0]);
}
if (unhappy(pairs[i][0], pairs[j][1], map)) {
set.add(pairs[i][0]);
set.add(pairs[j][1]);
}
if (unhappy(pairs[i][1], pairs[j][1], map)) {
set.add(pairs[i][1]);
set.add(pairs[j][1]);
}
}
}
return set.size();
}
private void calcBetter(int[] preference, Map<Integer, Set<Integer>> map, int from, int to) {
Set<Integer> betterSet = new HashSet<>();
for (int i : preference) {
if (i == to) {
break;
}
betterSet.add(i);
}
map.put(from, betterSet);
}
private boolean unhappy(int x, int y, Map<Integer, Set<Integer>> map) {
return map.get(x).contains(y) && map.get(y).contains(x);
}
}
…
1584. 连接所有点的最小费用
English Version
题目描述
给你一个points 数组,表示 2D 平面上的一些点,其中 points[i] = [xi, yi] 。
连接点 [xi, yi] 和点 [xj, yj] 的费用为它们之间的 曼哈顿距离 :|xi - xj| + |yi - yj| ,其中 |val| 表示 val 的绝对值。
请你返回将所有点连接的最小总费用。只有任意两点之间 有且仅有 一条简单路径时,才认为所有点都已连接。
示例 1:
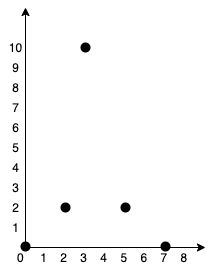输入:points = [[0,0],[2,2],[3,10],[5,2],[7,0]] 输出:20 解释: 我们可以按照上图所示连接所有点得到最小总费用,总费用为 20 。 注意到任意两个点之间只有唯一一条路径互相到达。
示例 2:
输入:points = [[3,12],[-2,5],[-4,1]] 输出:18
示例 3:
输入:points = [[0,0],[1,1],[1,0],[-1,1]] 输出:4
示例 4:
输入:points = [[-1000000,-1000000],[1000000,1000000]] 输出:4000000
示例 5:
输入:points = [[0,0]] 输出:0
提示:
1 <= points.length <= 1000-106 <= xi, yi <= 106- 所有点
(xi, yi)两两不同。
解法
Python3
Java
class Solution {
static class Edge {
int x;
int y;
int len;
Edge(int x, int y, int len) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.len = len;
}
}
public int minCostConnectPoints(int[][] points) {
Queue<Edge> heap = new PriorityQueue<>(Comparator.comparingInt((Edge e) -> e.len));
boolean[] marked = new boolean[points.length];
marked[0] = true;
addVertex(points, marked, 0, heap);
int count = 1;
int res = 0;
while (!heap.isEmpty()) {
Edge edge = heap.poll();
if (!marked[edge.y]) {
res += edge.len;
marked[edge.y] = true;
addVertex(points, marked, edge.y, heap);
count++;
if (count == points.length) {
break;
}
}
}
return res;
}
public void addVertex(int[][] points, boolean[] marked, int x, Queue<Edge> heap) {
for (int i = 0; i < marked.length; i++) {
if (marked[i]) {
continue;
}
heap.add(new Edge(x, i,
Math.abs(points[x][0] - points[i][0]) + Math.abs(points[x][1] - points[i][1])));
}
}
}
…
1588. 所有奇数长度子数组的和
English Version
题目描述
给你一个正整数数组 arr ,请你计算所有可能的奇数长度子数组的和。
子数组 定义为原数组中的一个连续子序列。
请你返回 arr 中 所有奇数长度子数组的和 。
示例 1:
输入:arr = [1,4,2,5,3] 输出:58 解释:所有奇数长度子数组和它们的和为: [1] = 1 [4] = 4 [2] = 2 [5] = 5 [3] = 3 [1,4,2] = 7 [4,2,5] = 11 [2,5,3] = 10 [1,4,2,5,3] = 15 我们将所有值求和得到 1 + 4 + 2 + 5 + 3 + 7 + 11 + 10 + 15 = 58
示例 2:
输入:arr = [1,2] 输出:3 解释:总共只有 2 个长度为奇数的子数组,[1] 和 [2]。它们的和为 3 。
示例 3:
输入:arr = [10,11,12] 输出:66
提示:
1 <= arr.length <= 1001 <= arr[i] <= 1000
解法
Python3
Java
class Solution {
public int sumOddLengthSubarrays(int[] arr) {
int[] sum = new int[arr.length];
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
sum[i] = (i != 0 ? sum[i - 1] : 0) + arr[i];
}
int ans = 0;
// sum[b] - sum[a] 为 (a,b] 的和
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
ans += arr[i];
for (int j = i + 2; j < arr.length; j += 2) {
// [i, j]
ans += sum[j] - sum[i] + arr[i];
}
}
return ans;
}
}
…
