Pytorch搭建MobileNetV2
1、背景
深度学习发展过程中刚开始总是在增加网络深度,提高模型的表达能力,没有考虑实际应用中硬件是否能支持参数量如此之大的网络,因此有人提出了轻量级网络的概念,MobileNet是其中的代表,主要目的在保证网络模型性能的同时,减少模型参数量,提升模型速度和可移植性。
2、MobileNet
目前mobilenet系列经历的v1~v3的过程,在v1中的核心点是采用了深度可分离卷积,将提取空间特征和通道特征的过程分开,传统的卷积核可以认为是一个三维的filter,空间特征和通道特征是同时提取的,分离卷积中的deepwise卷积可以认为是一个二维的filter,在上层输出特征图的每个通道进行卷积,用于提取空间特征,再用1x1卷积(文中叫做pointwise卷积)进行结合,得到通道特征。经过计算参数变为正常卷积的~~额-->1/5。v2在v1的基础上参考残差结构,提出了invert residual,传统方法通常用1x1卷积降维后,用大的卷积核提出特征后又升维,因为深度可分离卷积的原因,v2变为了先升维,卷积,再降维。能够避免信息丢失,具有一定优势。v3利用到了神经网络架构搜索(nas),也提出了一个新的激活函数H-swise。虽然在v2中提到了遗传算法和强化学习得到的神经网络模型拓扑结构复杂,不适合轻量级网络,但是v3就“渐渐的”用上了。
3、MobileNet-V2
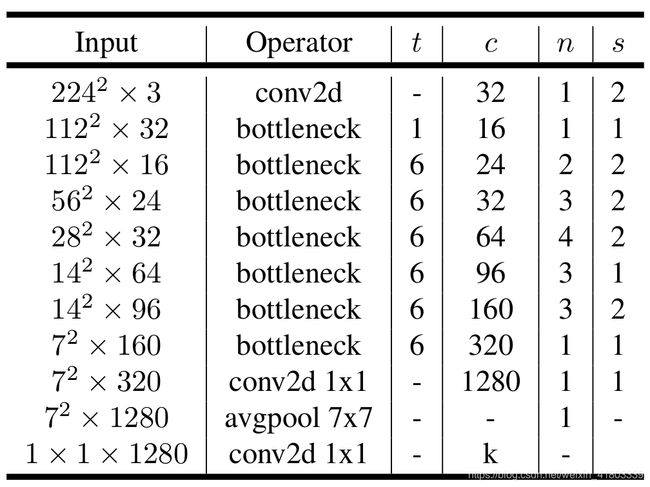
今天的主角依然是MobileNet-V2,V3虽然神奇,但是搜索的架构不一定适用于其他的目标任务。V2论文中的网络结构如下表所示:
首先导入需要的包
import torch
from torch import nn
import torch.nn.functional as F在网络的头部用的通用卷积:
class Head(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,inp_c,out_c):
super(Head,self).__init__()
self.conv2d=nn.Conv2d(inp_c,out_c,3,2,padding=1,bias=False)
self.bn=nn.BatchNorm2d(out_c)
self.relu6=nn.ReLU6(inplace=True)
def forward(self,x):
x=self.conv2d(x)
x=self.bn(x)
out=self.relu6(x)
return out接下来是网络结构的核心模块:
class InvertResidual(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,inp_c,out_c,stride,expand):
super(InvertResidual,self).__init__()
self.stride=stride
out_ce=out_c*expand
self.conv1_1=nn.Conv2d(inp_c,out_ce,1,bias=False)
self.conv1_2=nn.Conv2d(out_ce,out_c,1,bias=False)
self.bn1=nn.BatchNorm2d(out_ce)
self.bn2=nn.BatchNorm2d(out_c)
self.deepwide=nn.Conv2d(out_ce,out_ce,3,stride,padding=1,groups=out_c)
self.relu6=nn.ReLU6(inplace=True)
self.shortcut = nn.Sequential()
if stride == 1 and inp_c != out_c:
self.shortcut = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(inp_c,out_c,1,bias=False),
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_c))
def forward(self,x):
ori_x=x
x=self.conv1_1(x)
x=self.bn1(x)
x=self.relu6(x)
x=self.deepwide(x)
x=self.bn1(x)
x=self.relu6(x)
x=self.conv1_2(x)
y=self.bn2(x)
out=y + self.shortcut(ori_x) if self.stride==1 else y
return out最后是网络整体结构搭建:
class MobileNetv2(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,width_mult=1,num_classes=100):
super(MobileNetv2,self).__init__()
block = InvertResidual
input_channel = 32
interverted_residual_setting = [
# t, c, n, s
[1, 16, 1, 1],
[6, 24, 2, 2],
[6, 32, 3, 2],
[6, 64, 4, 2],
[6, 96, 3, 1],
[6, 160, 3, 2],
[6, 320, 1, 1]]
input_channel=int(input_channel * width_mult)
head_layer=Head(3,input_channel)
self.layers=[head_layer]
for t, c, n, s in interverted_residual_setting:
stride = s
output_channel = int(c * width_mult)
for i in range(n):
if i==0:
self.layers.append(block(input_channel,output_channel,stride,t))
else:
self.layers.append(block(input_channel,output_channel,1,t))
input_channel=output_channel
self.layers = nn.Sequential(*self.layers)
self.conv_end = nn.Conv2d(320,1280, kernel_size=1, stride=1,padding=0, bias=False)
self.bn_end = nn.BatchNorm2d(1280)
self.relu=nn.ReLU6(inplace=True)
self.AdaptiveAvgPool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1))
self.linear = nn.Linear(1280, num_classes)
def forward(self,x):
x=self.layers(x)
x=self.conv_end(x)
x=self.bn_end(x)
x=self.relu(x)
x=self.AdaptiveAvgPool(x)
x= x.view(x.size(0), -1)
out = self.linear(x)
return out测试:
if __name__=="__main__":
test_input=torch.rand(1, 3, 480, 640)
print(test_input.size())
model= MobileNetv2()
out=model(test_input )
print(out.size())结果为:
torch.Size([1, 3, 480, 640])
torch.Size([1, 100])
有错误的地方希望大家指出来,该文章供大家参考。