TensorFlow--Chapter03编程基础知识总结,TensorBoard可视化初步
TensorFlow1.8编程基础知识总结
TensorFlow–Chapter03编程基础知识总结,TensorBoard可视化初步
TensorFlow 是一个端到端开源机器学习平台。它拥有一个全面而灵活的生态系统,其中包含各种工具、库和社区资源,可助力研究人员推动先进机器学习技术的发展,并使开发者能够轻松地构建和部署由机器学习提供支持的应用。
由于课程教了1.8版本的操作,所以在这里我会总结TensorFlow1.8版本的编程基础知识
作者:北山啦
地址:https://beishan.blog.csdn.net
文章目录
- TensorFlow1.8编程基础知识总结
- 1 变量与常量
- 2 会话
-
- 2.1 会话的模式1
- 2.2 会话的模式2
- 2.3 指定默认的会话
- 3 变量的赋值
- 4 占位符、Feed、Fetch
- 4.1 占位符
-
- 4.2 fedd_dict传入值
- 4.3 多个操作可以通过一次feed完成
- 4.4 一次返回多个值分别赋给多个变量
- 5 TensorBoard可视化
-
- 5.2 产生日志文件
- 5.2 启动TensorBoard
import tensorflow as tf
tf.__version__
'1.8.0'
1 变量与常量
变量创建采用tf.Variable类:例如创建w1、w2变量,初始值分别为3和1
w1 = tf.Variable(initial_value=3, name="w1")
w2 = tf.Variable(initial_value=1, name="w2")
当创建一个变量时,可以将一个张量作为初始值传入构造函数Variable()
weights = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(
[784, 200], stddev=0.35), name="weights")
biases = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([200]), name="biases")
变量初始化:tf.global_variables_initializer()
必须在模型的其他操作运行之前先明确地完成变量初始化,最简单的方法是添加一个给所有变量初始化的操作,并在模型使用前首先运行该操作
Int_ops = tf.global_variables_initializer()
sess = tf.Session()
sess.run(Int_ops)
常量是不能修改的张量,用constant类定义
con1 = tf.constant(100)
2 会话
在TensorFlow的Python API中,张量对象a、b和c是操作结果的字符别名,他其实并不存储输出结果的值

2.1 会话的模式1
需要明确调用Session.close()函数来关闭会话并释放资源
tens1 = tf.constant([1, 2, 3]) # 定义计算图
sess = tf.Session() # 创建一个会话
try:
print(sess.run(tens1)) # 得到张量的取值
except:
print("Exception")
finally:
sess.close() # 关闭会话使得本次运行中使用到的资源可以被释放
[1 2 3]
2.2 会话的模式2
不需要调用Session.close()函数来关闭会话
# 定义计算图
node1 = tf.constant(3.0, tf.float32, name="node1")
node2 = tf.constant(4.0, tf.float32, name="node2")
result = tf.add(node1, node2)
# 创建一个会话,并通过Python中的上下文管理器来管理这个会话
with tf.Session() as sess:
print(sess.run(result))
7.0
2.3 指定默认的会话
TensorFlow不会自动生成默认的会话,需要手动指定,当默认的会话被指定之后可以通过tf.Tensor.eval函数来计算一个张量的取值
node1 = tf.constant(3.0, tf.float32, name="node1")
node2 = tf.constant(4.0, tf.float32, name="node2")
result = tf.add(node1, node2)
sess = tf.Session()
with sess.as_default():
print(result.eval())
7.0
3 变量的赋值
与传统编程语法不同,TensorFlow中的变量定义之后,一般五福人工赋值,系统会根据算法模型,训练优化过程中自动调整变量对应的数值
通过变量赋值输出1、2、3……10
value = tf.Variable(0, name="value")
one = tf.constant(1)
new_value = tf.add(value, one)
update_value = tf.assign(value, new_value)
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
for _ in range(10):
sess.run(update_value)
print(sess.run(value))
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
4 占位符、Feed、Fetch
4.1 占位符
tf.placeholder(dtype, shape=None, name=None)

"""此代码生成一个2*3的二维数组,矩阵中每个元素的类型都是tf.float32,内部对应的符号名称都是tx"""
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,[2,3],name="tx")
如果构建了一个包含placeholder操作的计算图,但在session中调用run方法时,placeholder占用的变量必须通过feed_dict参数传递进去
4.2 fedd_dict传入值
a = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,name="a")
b = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,name="b")
c = tf.multiply(a,b,name="c")
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
"""通过feed_dict的参数传值,按字典格式"""
result = sess.run(fetches=c, feed_dict={
a:8.0,b:3.5})
print(result)
28.0
4.3 多个操作可以通过一次feed完成
a = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,name="a")
b = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,name="b")
c = tf.multiply(a,b,name="c")
d = tf.subtract(a,b,name="d")
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
"""通过feed_dict的参数传值,按字典格式"""
result = sess.run(fetches=[c,d], feed_dict={
a:8.0,b:3.5})
print(result)
28.0 4.5
4.4 一次返回多个值分别赋给多个变量
# 作者:北山啦
# 地址:https://beishan.blog.csdn.net
a = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,name="a")
b = tf.placeholder(tf.float32,name="b")
c = tf.multiply(a,b,name="c")
d = tf.subtract(a,b,name="d")
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(init)
"""通过feed_dict的参数传值,按字典格式"""
rc,rd = sess.run(fetches=[c,d], feed_dict={
a:8.0,b:3.5})
print("value of c = ",rc,"\nvalue of d = ",rd)
value of c = 28.0
value of d = 4.5
5 TensorBoard可视化
- TensorBoard是TensorFlow的可视化工具
- 通过Tensor Flow程序运行过程中输出的日志文件可视化TensorFlow程序的运行状态
- TensorBoard和TensorFlow程序跑在不同的进程中
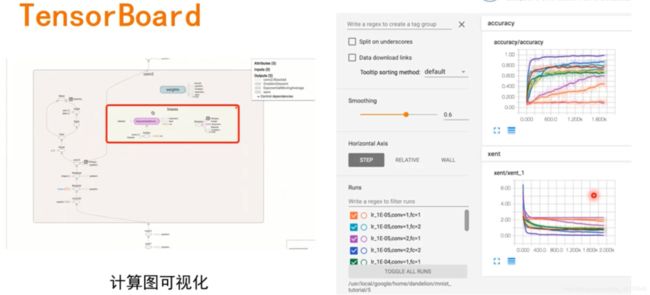
5.2 产生日志文件
- tf.reset_default_graph():清除default graph和不断增加的节点
# 作者:北山啦
# 地址:https://beishan.blog.csdn.net
tf.reset_default_graph()
logdir = "D:/log"
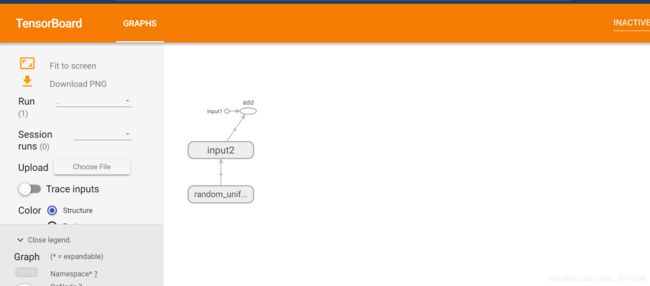
"""定义一个简单的计算图,实现向量加法的操作"""
input1 = tf.constant([1.0, 2.0, 3.0], name="input1")
input2 = tf.Variable(tf.random_uniform([3]), name="input2")
output = tf.add_n([input1, input2], name="add")
"""生成一个写日志的writer,并将当前的TensorFlow计算图写入日志"""
writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(logdir, tf.get_default_graph())
writer.close()
5.2 启动TensorBoard
tensorboard --logdir=D:\log
到这里就结束了,如果对你有帮助,欢迎点赞关注评论,你的点赞对我很重要
![]()