前言
- 上篇博客spring 5.0.x源码学习系列四: AnnotationConfigApplicationContext类register方法作用主要介绍了register方法的作用。下面我们将进入初始化spring环境最重要的一步:refresh方法
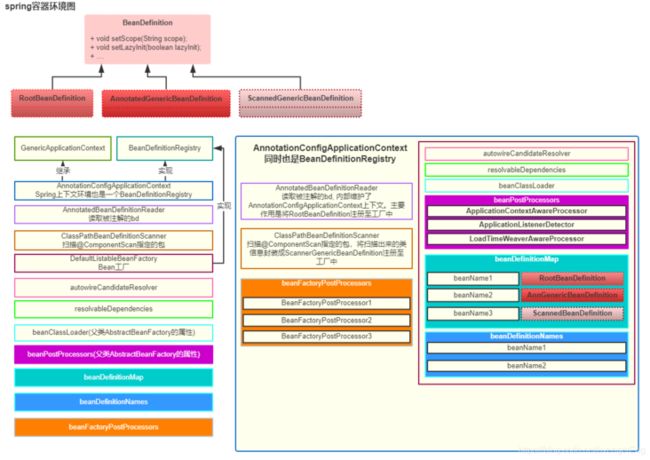
一、refresh源码黑箱理论
- 在此篇章中,咱们先把源码中每个方法的执行流程先列出来, 再根据每一个具体的方法进行解析
源码
@Override public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException { synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) { // Prepare this context for refreshing. prepareRefresh(); // 获取spring bean工厂 ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory(); // Prepare the bean factory for use in this context. // 这个方法执行完成, spring的bean单例容器中会存在三个bean, // 分别是systemEnvironment, environment, systemProperties // 同时会添加ApplicationContextAwareProcessor的后置处理器, 这个处理器没有走 // spring的bean初始化, 是在内部直接new出来的, 该处理器是用来处理实现了 // ApplicationContextAware接口的bean, 调用重写的set方法, 所以可以利用 // 这种方法获取spring的上下文对象 prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory); try { // 该方法没有做任何事, 内部无任何逻辑 postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory); // 调用后置处理器, 此方法太重要了, 在后续的源码解读系列中会解析它 // 先大致总结下它做了什么事 // 1. 处理手动添加的BeanFactoryPostProcessor // 1.1 调用手动添加的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor, 并添加到存储它的集合中, // 该集合名字为: registryProcessors // 1.2 存储手动添加的BeanFactoryPostProcessor, // 该集合名字为: regularPostProcessors // 注意: 上面这个步骤是if else逻辑, 存了一个另外一个就不会存了 // 2. 执行BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor类型且实现了PriorityOrdered接 // 口的后置处理器. 默认执行spring内置BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor // 后置处理器(ConfigurationClassPostProcessor), 这个后置处理器执行完之后, // 所有能被扫描出来的bean都以BeanDefinition的方式注册到bean工厂了 // 3. 执行BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor类型且实现了 // Ordered接口的后置处理器 // 4. 执行以@Component方式添加的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor类型没实现 // Ordered和PriorityOrdered接口的后置处理器 // 5. 执行regularPostProcessors和registryProcessors数据结构中 // BeanFactoryPostProcessor类型的后置处理器(在此处执行 // ConfigurationClassPostProcessor类的postProcessBeanFactory方法, 主要是 // 为全配置类生成了cglib代理类的Class对象, 并修改它的beanDefinition信息为代 // 理类的信息 // 6. 执行以@Component形式添加并实现了PriorityOrdered接口的BeanFactoryPost // Processor后置处理器 // 7. 执行以@Component形式添加并实现了Ordered接口的BeanFactoryPost // Processor后置处理器 // 8. 执行以@Component形式添加并未实现PriorityOrdered和Ordered接口的Bean // FactoryPostProcessor后置处理器 invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory); // 注册spring bean工厂的BeanPostProcessor // 其中包括spring内置的、扫描出来的(eg: 使用ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar, AOP的实现方式)、 // 自己手动添加的(手动添加BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor, // 并在其中注册一个BeanPostProcessor的bean) // // 默认情况下, spring内置的3个BeanPostProcessor分别为: // org.springframework.context.annotation.internalAutowiredAnnotationProcessor => 处理@Autowired注解的 // org.springframework.context.annotation.internalRequiredAnnotationProcessor => 处理@Required注解的 // org.springframework.context.annotation.internalCommonAnnotationProcessor => 处理Common注解的后置处理器 // 以及各种实现了PriorityOrdered接口、Ordered接口的BeanPostProcessor处理 // 最主要的就是把这些bean通过spring bean工厂创建出来, 并添加到一个存放BeanPostProcessor的list中, 再利用广播 // 机制调用 // 我觉得这里用list而不用set的原因有两个 // 1. list是有序的, 因为有些BeanPostProcessor会实现PriorityOrdered接口、Ordered接口, 所以要按照一定的顺序执行 // 2. 广播机制时要遍历集合, list遍历速度快一些 registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory); // Initialize message source for this context. // 国际化 initMessageSource(); // Initialize event multicaster for this context. // 初始化spring事件驱动模型的执行者 initApplicationEventMulticaster(); // 该方法没有做任何事, 内部无任何逻辑 onRefresh(); // 注册自己手动添加的监听器和spring扫描出来的监听器 // 手动添加的监听器: 调用spring上下文的addApplicationListener方法, eg: AnnotationConfigApplicationContext上下文的方法 // spring扫描出来的监听器: 有@Component注解标识的监听器 // 这里有人会问: 万一我一个监听器同时加了@Component注解也手动调用了addApplicationListener添加呢? // 没关系, 那就执行两次呗, 因为spring处理手动添加的和扫描出来的监听器是不一样的, 手动添加的是一个java 对象, 而spring扫描出来 // 的监听器是一个bean, 所以这两个监听器是同一类型的不同对象 // 但要注意的是, 手动添加的监听器是一个java object, 而spring扫描出来的是一个bean registerListeners(); // 开始创建非抽象、非原型、非懒加载的bean 以及处理bean的自动装配 finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); // 完成刷新, 发布相应的事件 finishRefresh(); } catch (BeansException ex) { if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) { logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " + "cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex); } // Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources. destroyBeans(); // Reset 'active' flag. cancelRefresh(ex); // Propagate exception to caller. throw ex; } finally { // Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we // might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore... resetCommonCaches(); } } }总结
二、本篇博客的主角: invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessor方法
- 流程图
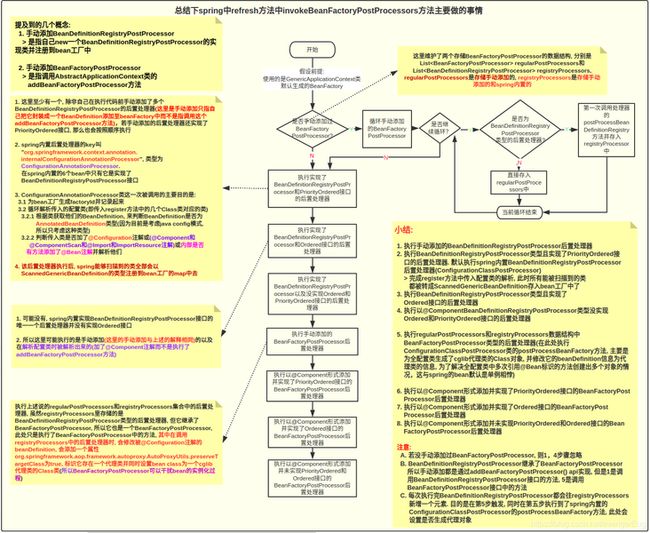
源码注释
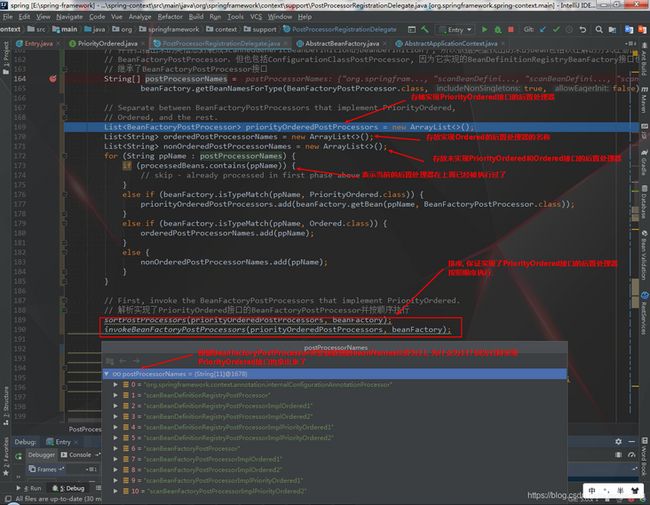
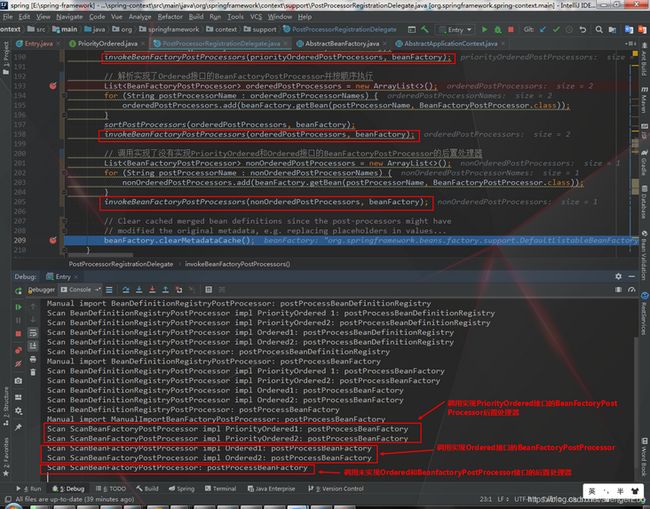
public static void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors( ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, ListbeanFactoryPostProcessors) { // Invoke BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors first, if any. Set processedBeans = new HashSet<>(); // 传入的bean工厂DefaultListableBeanFactory也是一个BeanDefinitionRegistry, 它实现了这个接口 if (beanFactory instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistry) { BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = (BeanDefinitionRegistry) beanFactory; // 用来存储手动添加BeanFactoryPostProcessor的处理器, // eg: context.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(new MyBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor()); // 其中context是AnnotationConfigApplicationContext对象, 但是它只是执行到了父类AbstractApplicationContext的方法 List regularPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(); // 用来存储手动添加BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的处理器, 也是执行上述注释中说的方法 // 因为BeanFactoryPostProcessor有一个子类叫BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor // regularPostProcessors和registryProcessors这两个list只是为了存储手动添加的BeanFactoryPostProcessor List registryProcessors = new ArrayList<>(); for (BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor : beanFactoryPostProcessors) { if (postProcessor instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) { BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor registryProcessor = (BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) postProcessor; // 对于手动添加的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor会在这里第一次被调用, 所以这里是后置处理器第一次被调用的地方 registryProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry); // 存储手动添加的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor, 后续会用到 registryProcessors.add(registryProcessor); } else { // 存储手动添加的BeanFactoryPostProcessor, 后续会用到 regularPostProcessors.add(postProcessor); } } // 这个list是用来存储spring内置的BeanFactoryPostProcessor List currentRegistryProcessors = new ArrayList<>(); // 这里是调用实现了PriorityOrdered接口的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor后置处理器 // 这里只是获取, 调用是在下面的invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);完成的 String[] postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false); for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) { if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) { currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class)); processedBeans.add(ppName); } } sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory); registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors); // 这里首先调用的类是spring内置beanName叫org.springframework.context.annotation.internalConfigurationAnnotationProcessor, // 类名叫ConfigurationClassPostProcessor的bean // 因为在spring内置的6个bean中只有它是实现了BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor接口 // 所以ConfigurationClassPostProcessor类这一次被调用的主要目的是: // 1. 为bean工厂生成factoryId并记录起来 // 2. 循环解析传入的配置类(即传入register方法中的几个Class类对应的类) // 2.1 根据类获取他们的BeanDefinition, 来判断BeanDefinition是否为AnnotatedBeanDefinition类型(因为目前是考虑java config模式, 所以只考虑这种类型) // 2.2 判断传入类是否加了@Configuration注解或者(@Component和@ComponentScan和@Import和ImportResource注解)或者内部是否有方法添加了@Bean注解并解析他们 invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry); currentRegistryProcessors.clear(); // Next, invoke the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement Ordered. postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false); for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) { if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName) && beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) { currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class)); processedBeans.add(ppName); } } sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory); registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors); invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry); currentRegistryProcessors.clear(); // Finally, invoke all other BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors until no further ones appear. boolean reiterate = true; while (reiterate) { reiterate = false; postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false); for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) { if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName)) { currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class)); processedBeans.add(ppName); reiterate = true; } } sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory); registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors); invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry); currentRegistryProcessors.clear(); } // Now, invoke the postProcessBeanFactory callback of all processors handled so far. // 这里是第一次调用手动添加到spring的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的重写BeanFactoryPostProcessors接口的(postProcessBeanFactory)方法 // 因为BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor是继承BeanFactoryPostProcessor类。所以也重写了BeanFactoryPostProcessor的方法 // 在第一次调用时只调用了BeanDefinitionRegisterPostProcessor中的方法 invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(registryProcessors, beanFactory); // 这里是第一次调用手动添加到spring的BeanFactoryPostProcessor invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(regularPostProcessors, beanFactory); } else { // Invoke factory processors registered with the context instance. invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactoryPostProcessors, beanFactory); } // Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans // uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them! // 这里是调用非手动添加的BeanFactoryPostProcessor后置处理器, 即使用了@Component注解 // 因为在上一步调用ConfigurationClassPostProcessor这种类型(BeanDefinitionRegistryBeanFactory)的后置处理器时, 对包已经扫描成功, // 并将扫描出来的类信息封装成ScannedGenericBeanDefinition的BeanDefinition了, 所以根据类型找出的来的bean包括以注解的方式注册的 // BeanFactoryPostProcessor,但也包括ConfigurationClassPostProcessor, 因为它实现的BeanDefinitionRegistryBeanFactory接口也 // 继承了BeanFactoryPostProcessor接口 String[] postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class, true, false); // Separate between BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered, // Ordered, and the rest. List priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(); List orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>(); List nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>(); for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) { if (processedBeans.contains(ppName)) { // skip - already processed in first phase above } else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) { priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class)); } else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) { orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName); } else { nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName); } } // First, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered. // 解析实现了PriorityOrdered接口的BeanFactoryPostProcessor并按顺序执行 sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); // 解析实现了Ordered接口的BeanFactoryPostProcessor并按顺序执行 List orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(); for (String postProcessorName : orderedPostProcessorNames) { orderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class)); } sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); // 调用实现了没有实现PriorityOrdered和Ordered接口的BeanFactoryPostProcessor的后置处理器 List nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>(); for (String postProcessorName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) { nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class)); } invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(nonOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory); // Clear cached merged bean definitions since the post-processors might have // modified the original metadata, e.g. replacing placeholders in values... beanFactory.clearMetadataCache(); }
三、项目测试demo
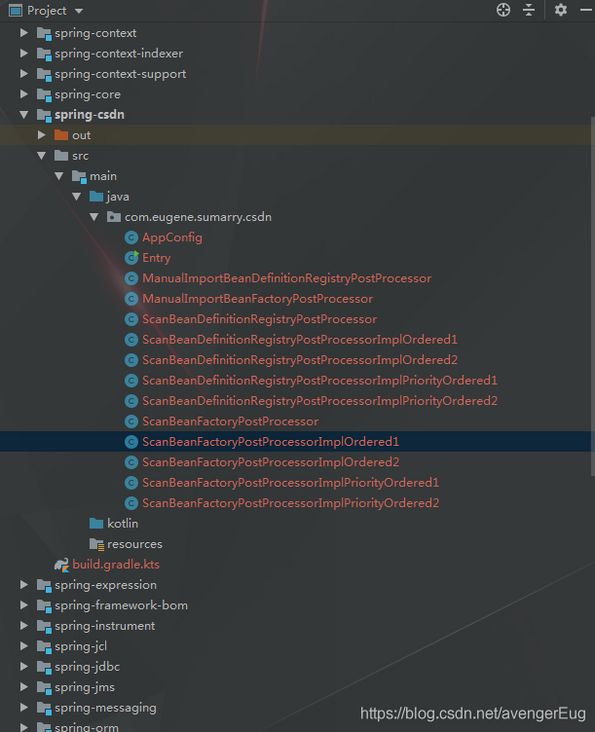
3.1 项目结构
3.1.1 结构全景图
3.1.2 各类详情与作用
- 项目入口(启动spring环境的入口)
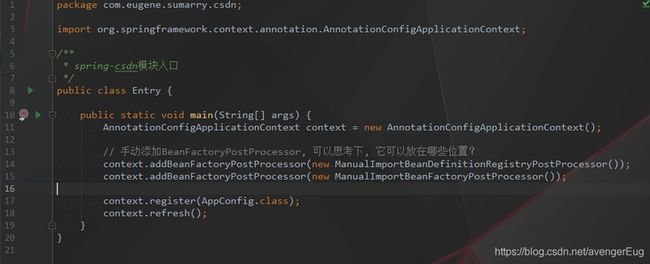
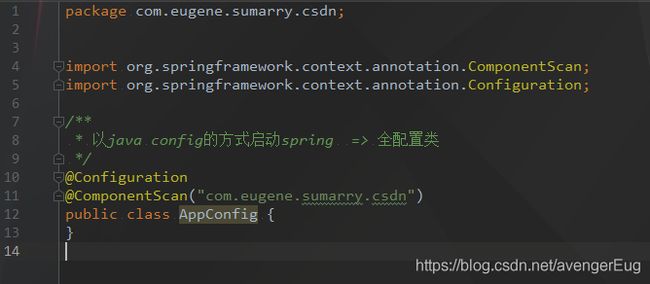
- 全配置类, 定义扫描的包
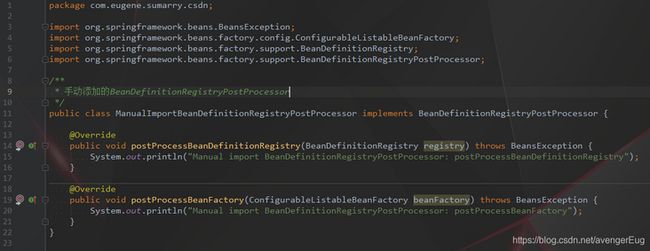
- 手动添加的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor
- 手动添加的BeanFactoryPostProcessor
- 由spring扫描出来的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor但无实现Ordered和PriorityOrdered接口

- 由spring扫描出来的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor实现了Ordered接口, 且权重为1 => 权重低, 优先执行
- 由spring扫描出来的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor实现了Ordered接口, 且权重为2 => 权重低, 优先执行
- 由spring扫描出来的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor实现了PriorityOrdered接口, 且权重为1 => 权重低, 优先执行
- 由spring扫描出来的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor实现了PriorityOrdered接口, 且权重为2 => 权重低, 优先执行
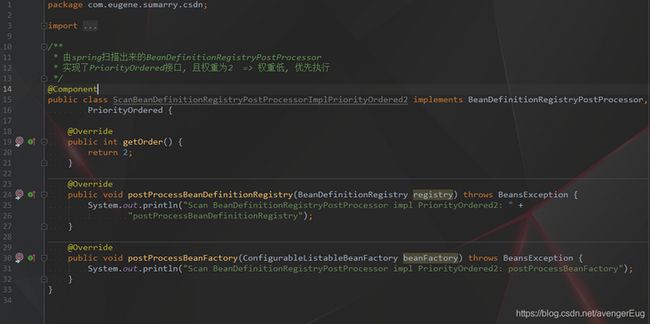
- 由spring扫描出来的BeanFactoryPostProcessor
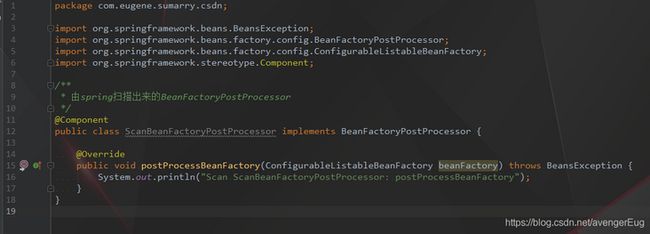
- 由spring扫描出来的BeanFactoryPostProcessor实现了Ordered接口, 且权重为1 => 权重越低, 越优先执行
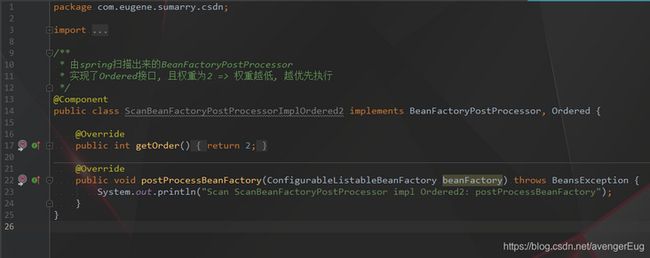
- 由spring扫描出来的BeanFactoryPostProcessor实现了Ordered接口, 且权重为2 => 权重越低, 越优先执行
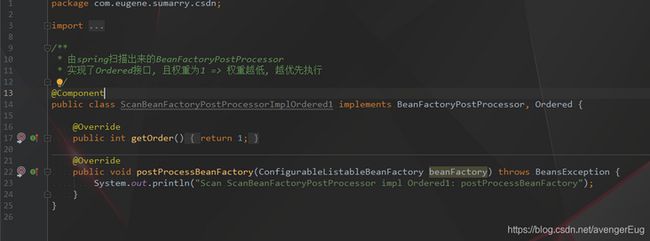
- 由spring扫描出来的BeanFactoryPostProcessor实现了PriorityOrdered接口, 且权重为1 => 权重越低, 越优先执行
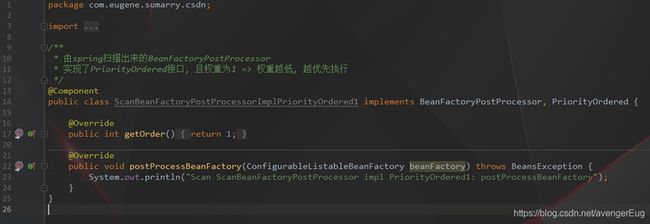
- 由spring扫描出来的BeanFactoryPostProcessor实现了PriorityOrdered接口, 且权重为2 => 权重越低, 越优先执行

3.2 执行流程及原理
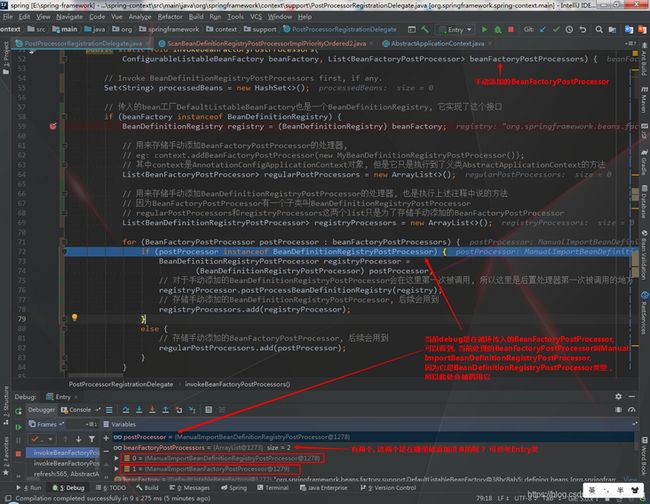
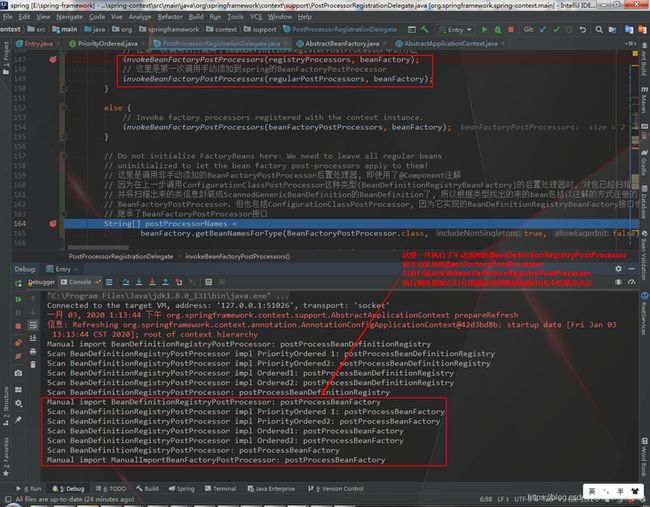
3.2.1 处理手动添加的BeanFactoryPostProcessor(包含BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor和BeanFactoryPostProcessor)
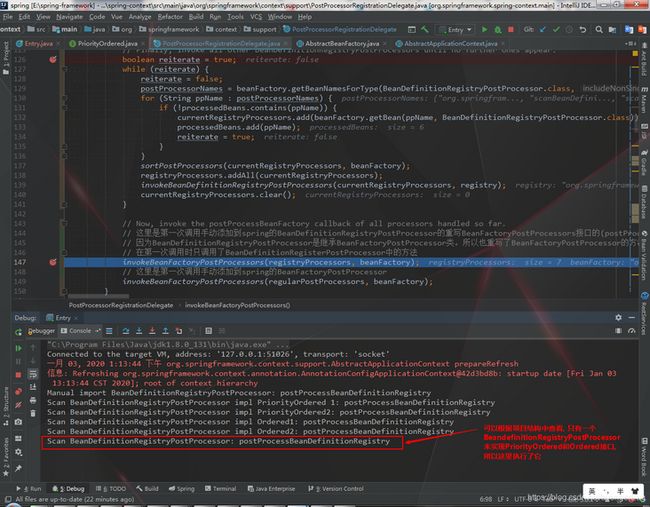
3.2.2 执行BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor类型且实现了PriorityOrdered接口的后置处理器
此步骤非常重要,后续将专门为此步骤总结一篇博客, 来具体描述它做了些什么事
3.2.3 执行BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor类型且实现了Ordered接口的后置处理器, 执行过程与第二步大同小异
3.2.4 执行BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor类型且未实现Ordered接口和PriorityOrdered接口的后置处理器, 执行过程与第三步大同小异
3.2.5 处理BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor类型的BeanFactoryPostProcessor
上述4步都是调用BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor类型的后置处理器, 后面将开始调用BeanFactoryPostProcessor类型的后置处理器。因为还有手动添加BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor也是BeanFactoryPostProcessor类型的后置处理器(继承), 所以此步骤将开始调用手动添加的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor后置处理器的BeanFactoryPostProcessor中的方法以及手动添加的BeanFactoryPostProcessor
// Now, invoke the postProcessBeanFactory callback of all processors handled so far. // 这里是第一次调用手动添加到spring的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor的重写BeanFactoryPostProcessors接口的(postProcessBeanFactory)方法 // 因为BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor是继承BeanFactoryPostProcessor类。所以也重写了BeanFactoryPostProcessor的方法 // 在第一次调用时只调用了BeanDefinitionRegisterPostProcessor中的方法 invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(registryProcessors, beanFactory); // 这里是第一次调用手动添加到spring的BeanFactoryPostProcessor invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(regularPostProcessors, beanFactory);
3.2.6 执行以@Component形式添加并实现了PriorityOrdered接口的BeanFactoryPostProcessor后置处理器
3.2.7 执行以@Component形式添加并实现了Ordered接口的BeanFactoryPostProcessor后置处理器
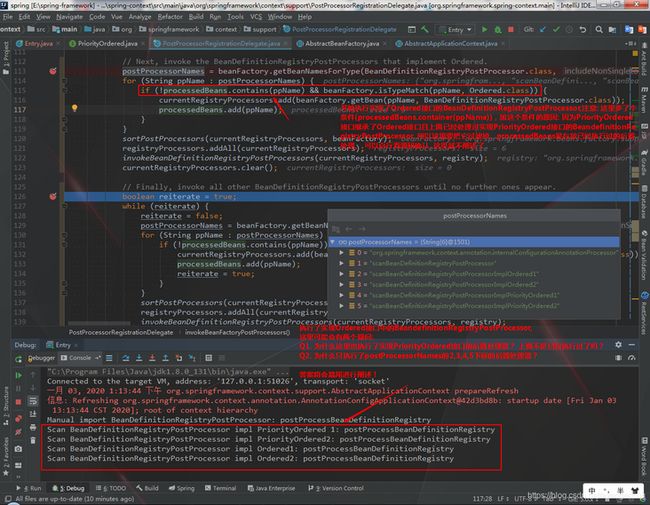
3.3 关于"3.2.3 执行BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor类型且实现了Ordered接口的后置处理器, 执行过程与第二步大同小异"的两个疑问
| 问题 | 答案 |
|---|---|
| Q1: 为什么这里也执行了实现PriorityOrdered接口的后置处理器?上面不是已经执行过了吗? | 因为PriorityOrdered接口继承了Ordered接口, 所以在处理实现Ordered类型的接口时, 也会把实现PriorityOrdered接口的后置处理器也拿出来。同时之前的确已经执行过了实现了PriorityOrdered接口的后置处理器(ConfigurationClassPostProcessor), 但这是一个特殊的后置处理器, 因为它,我们才能在后面获取@Component注解形式添加的后置处理器。最重要的是在执行它的时候, bean工厂中只有一个实现了PriorityOrdered接口的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor类型的后置处理器, 所以spring才用了processedBeans的set集合来存储已经执行过的后置处理器 |
| Q2: 为什么只执行了postProcessorNames的2,3,4,5下标的后置处理器? | 因为它们都实现了Ordered接口, 尽管有些后置处理器实现的是PriorityOrdered接口, 但PriorityOrdered接口继承了Ordered接口 |
三、小结
- invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessor方法的主要作用就是调用后置处理器, 这里最需要主要到的一个后置处理器就是ConfigurationClassPostProcessor, 它不仅做了扫描工作还做了为全配置类生成cglib代理对象的工作(因为它有两个身份: 一个是BeandefinitionRegistryPostProcessor另一个是BeanFactoryPostProcessor)
关于BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor和BeanFactoryPostProcessor后置处理器的区别和作用
类型 提供api 作用 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor BeanDefinitionRegistry 是一个beanDefinition的注册器, 一般用它来注册一个beanDefinition BeanFactoryPostProcessor ConfigurableListableBeanFactory 其实就是spring的bean工厂, 只不过是用父类来接收。 bean工厂都可以拿到了, 我们可以对bean做不可描述的事情了,比如改变bean的class为它创建代理对象, 使用 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor和BeanFactoryPostProcessor后置处理器的注意事项
- 得明白每个后置处理器的执行顺序 eg:手动添加的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor类型的后置处理器, 比spring内置和以@Component方式添加的后置处理器都先执行
- 熟悉实现不同接口的后置处理器的执行顺序, eg: BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor和BeanFactoryPostProcessor类型的后置处理器都是优先处理实现PriorityOrdered接口
- spring源码学习对应GitHub 地址https://github.com/AvengerEug/spring/tree/develop/resourcecode-study
- I am a slow walker, but I never walk backwards.