Spring依赖注入
常的java开发中,程序员在某个类中需要依赖其它类的方法,则通常是new一个依赖类再调用类实例的方法,这种开发存在的问题是new的类实例不好统一管理,spring提出了依赖注入的思想,即依赖类不由程序员实例化,而是通过spring容器帮我们new指定实例并且将实例注入到需要该对象的类中。依赖注入的另一种说法是“控制反转”,通俗的理解是:平常我们new一个实例,这个实例的控制权是我们程序员,而控制反转是指new实例工作不由我们程序员来做而是交给spring容器来做。
构造函数注入
在bean标签的内部使用constructor-arg标签就可以进行构造函数注入了。 constructor-arg标签的属性:
- type:用于指定要注入的数据的数据类型,该数据类型也是构造函数中某个或某些参数的类型
- index:用于指定要注入的数据给构造函数中指定索引位置的参数赋值,索引的位置从0开始
- name:用于给指定构造函数中指定名称的参数赋值
- value:用于提供基本类型和String类型的数据
- ref:用于指定其他的bean类型数据,就是在IOC容器中出现过的bean对象 bean.xml
AccountServiceImpl 类
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Date birthday;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
this.age = age;
}
public Date getBirthday() {
return birthday;
}
public void setBirthday(Date birthday) {
this.birthday = birthday;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "AccountServiceImpl{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", birthday=" + birthday +
'}';
}
public AccountServiceImpl(String name, Integer age, Date birthday) {
System.out.println("含参的构造方法被调用了");
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.birthday = birthday;
}
public AccountServiceImpl() {
System.out.println("构造方法调用");
}
@Override
public int addMoney(int money) {
System.out.println("向账户中加钱:" + money);
return 0;
}
@Override
public void saveAccount(Account account) {
System.out.println("saveAccount方法执行了");
}
}
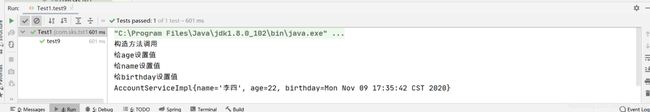
测试
/**
* 测试构造函数注入
*/
@Test
public void test8() {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:bean.xml");;
AccountService accountService = (AccountService) applicationContext.getBean("accountService");
System.out.println(accountService.toString());
}
优点:在获取bean对象时,注入数据是必须的操作,否则对象无法创建成功。 缺点:改变了bean对象的实例化方式,使我们在创建对象时,如果用不到这些数据也必须提供。
setter方法注入
在bean标签内部使用property标签进行配置。 property标签的属性:
- name:用于指定注入时所调用的set方法名称
- value:用于提供基本类型和String类型的数据
- ref:用于指定其他的bean类型数据
这里面我们注入了基本类型、包装类型、日期类型数据。 AccountServiceImpl 类
public class AccountServiceImpl implements AccountService {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private Date birthday;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
System.out.println("给name设置值");
this.name = name;
}
public Integer getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(Integer age) {
System.out.println("给age设置值");
this.age = age;
}
public Date getBirthday() {
return birthday;
}
public void setBirthday(Date birthday) {
System.out.println("给birthday设置值");
this.birthday = birthday;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "AccountServiceImpl{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", birthday=" + birthday +
'}';
}
public AccountServiceImpl(String name, Integer age, Date birthday) {
System.out.println("含参的构造方法被调用了");
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.birthday = birthday;
}
public AccountServiceImpl() {
System.out.println("构造方法调用");
}
@Override
public int addMoney(int money) {
System.out.println("向账户中加钱:" + money);
return 0;
}
@Override
public void saveAccount(Account account) {
System.out.println("saveAccount方法执行了");
}
}
bean.xml
测试
/**
* 测试setter方法注入
*/
@Test
public void test9() {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:bean.xml");;
AccountService accountService = (AccountService) applicationContext.getBean("accountService");
System.out.println(accountService.toString());
}
优势:创建对象时没有明确的限制,可以直接使用默认构造函数。 缺点:如果又某个成员必须有值,则获取对象有可能是set方法没有执行。
对集合类型数据进行注入
AccountService2Impl 类
public class AccountService2Impl implements AccountService2 {
private String[] myStrs;
private List myList;
private Set mySet;
private Map myMap;
private Properties myProps;
public String[] getMyStrs() {
return myStrs;
}
public void setMyStrs(String[] myStrs) {
this.myStrs = myStrs;
}
public List getMyList() {
return myList;
}
public void setMyList(List myList) {
this.myList = myList;
}
public Set getMySet() {
return mySet;
}
public void setMySet(Set mySet) {
this.mySet = mySet;
}
public Map getMyMap() {
return myMap;
}
public void setMyMap(Map myMap) {
this.myMap = myMap;
}
public Properties getMyProps() {
return myProps;
}
public void setMyProps(Properties myProps) {
this.myProps = myProps;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "AccountService2Impl{" +
"myStrs=" + Arrays.toString(myStrs) +
", myList=" + myList +
", mySet=" + mySet +
", myMap=" + myMap +
", myProps=" + myProps +
'}';
}
}
bean.xml
AAA
BBB
CCC
list1
list2
list3
set1
set2
set3
柯森
23
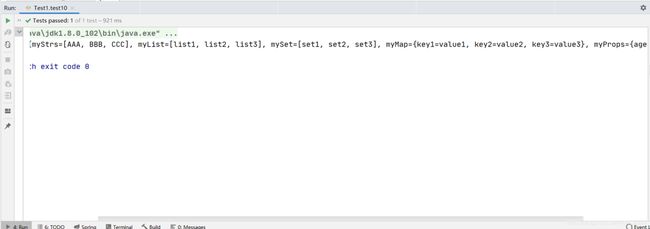
测试
/**
* 测试注入复杂类型/集合数据
*/
@Test
public void test10() {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:bean.xml");
AccountService2 accountService2 = (AccountService2) applicationContext.getBean("accountService2");
System.out.println(accountService2.toString());
}
这说明我们注入集合类型数据成功了。
注解注入
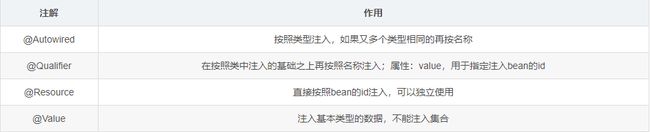
用于注入数据的注解
bean.xml文件
AccountService4Impl 类
@Component
public class AccountService4Impl implements AccountService3 {
@Autowired
private AccountDao accountDao;
@Override
public void addMoney(int money) {
System.out.println("向账户中加钱....AccountService3Impl");
}
}
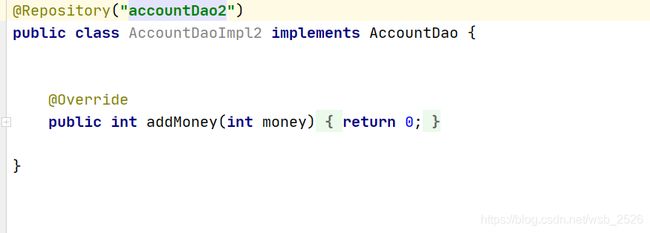
假设此时只有一个AccountDao的实现类,并且这个类也加上了@Repository注解,那么我们这样注入是可以成功的,但是如果容器中存在多个AccountDao的实现类,此时仅仅使用AccountDao是不能完成数据注入的,需要配合@Qualifier注解使用注入数据。
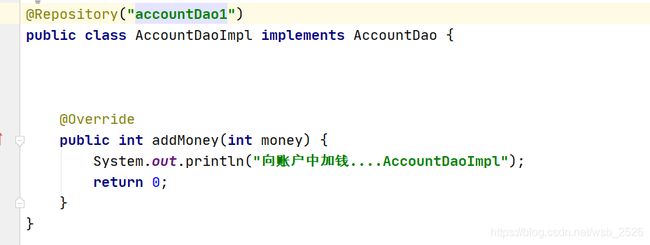
假设现有如下两个实现类,那我们应该怎么写才能成功注入数据?@Component
public class AccountService4Impl implements AccountService3 {
//错误写法,默认会去容器中查找名称为accountDao的bean
//@Autowired
//private AccountDao accountDao;
//正确写法
//@Autowired
//private AccountDao accountDao1
//正确写法
//@Autowired
//private AccountDao accountDao1;
//正确写法
@Autowired
@Qualifier("accountDao1")
private AccountDao accountDao;
@Override
public void addMoney(int money) {
System.out.println("向账户中加钱....AccountService3Impl");
}
}
测试
@Test
public void test2() {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:bean.xml");
AccountService4Impl accountService4 = (AccountService4Impl) applicationContext.getBean("accountService4Impl");
System.out.println("accountService4:" + accountService4);
}
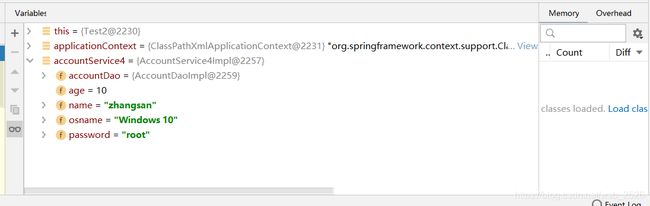
@Value注解的基本使用 在使用@Value注入基本类型和String类型的数据时使用"#“号;使用@Value读取配置文件的值时需要使用”$"符号,同时使用@PropertySource注解指定配置文件的位置。
@Component
@PropertySource("classpath:db.properties")
public class AccountService4Impl implements AccountService3 {
@Autowired
@Qualifier("accountDao1")
private AccountDao accountDao;
//使用SPEL表达式只注入值
@Value("#{19 - 9}")
private int age;
@Value("zhangsan")
private String name;
//读取操作系统的名称
@Value("#{systemProperties['os.name']}")
private String osname;
//读取数据库配置文件中的值
@Value("${password}")
private String password;
@Override
public void addMoney(int money) {
System.out.println("向账户中加钱....AccountService3Impl");
}
}
测试
@Test
public void test2() {
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("classpath:bean.xml");
AccountService4Impl accountService4 = (AccountService4Impl) applicationContext.getBean("accountService4Impl");
System.out.println("accountService4:" + accountService4 + " " + accountService4.getName() + " " + accountService4.getAge());
}
最后
大家看完有什么不懂的可以在下方留言讨论.
谢谢你的观看。
觉得文章对你有帮助的话记得关注我点个赞支持一下!
作者:前程有光
链接:https://juejin.cn/post/6897185998834008072