01 | python环境管理与pip依赖管理
安装python环境
- 官网:https://www.python.org/
pip
pip install xxpip install xx == versionpip uninstall xxpip install xx -i 国内pip源pip install xx -i http://pypi.douban.com/simple/ --trusted-host pypi.douban.com国内pip源
1.阿里云:https://mirrors.aliyun.com/pypi/simple
2.清华:https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
3.豆瓣:http://pypi.douban.com/simple/
02 | python语法
官方文档:https://docs.python.org/3/tutorial/index.html
变量
命名规则
1.数字、字母、下划线组成,数字不能开头
2.大小写敏感
3.不要跟关键字和系统保留字冲突PEP8要求
1.用小写字母拼写,多个单词用下划线链接
2.受保护的实例属性用单个下滑线开头
3.私有的实例属性用两个下划线开头
数字
- int:
int_a = 1 - float:
float_a =2.1 - complex:
complex_a = 2j
字符串
- 转义符:
\ - 忽略转义:
r - 多个字符串连接:
+ - 引用语法:
"{}".format
列表
- 切片:
a[0:3] 开闭区间,即包含起始位,不包含结束位
for-in 循环
- range函数
1.产生一个0-100的整数序列:range(101)
2.产生一个1-99的整数序列:range(1,100)
3.产生一个1-99的奇数序列:range(1,100,2)
while循环
- 如果不知道具体循环次数,推荐使用while循环
while a==1:
print("a == 1")
else:
print("a != 1")
- 若while循环体中只有1条语句,可以将该语句与while写在同一行
flag = 1
while(flag): print("你好")
break和continue
- break:结束所有循环
- continue:结束当前循环,进入下次循环
练习
- 猜字游戏
1.电脑计算出一个1-100的随机数由人来猜
2.电脑根据根据人猜的数字给出提示“大一点,小一点,猜对了”
import random
computer_number = random.randint(1,100)
while True:
person_number = int(input("请输入一个数字:"))
if computer_number < person_number:
print("小一点")
elif computer_number > person_number:
print("大一点")
else:
print("猜对了")
break
函数参数
- *args:接收元组
def method(*a):
print(a[0])
print(a[1])
print(a[2])
method(1,2,3)
- **kwargs:接收字典
def method(**a):
print(a.keys())
method(a=1,b=2,c=3)
- 仅限关键字参数
def method(*,a):
print(a)
method(a=1)
- 解包参数列表
1.解包字典
def method(a,b,c):
print(a)
print(b)
print(c)
dic1 = {"a":1,"b":2,"c":3}
method(**dic1)
相当于把字典拆成3个,即a=1,b=2,c=3
2.解包元组
print(list(range(3,6)))
tuple_a = (3,6)
list(range(*tuple_a))
相当于把元组拆成 3和6
lambda表达式
- 定义:
1.用lambda关键字创建一个小的匿名函数
2.lambda的主体是一个表达式,而不是一个代码块。仅在lambda表达式中封装有限的逻辑。 - 示例
z = lambda x,y:x+y
print(z(1,2))
03 | python常用数据结构
列表
list.append(x):在列表的末尾添加一个元素
list.insert(i,x):在给定的位置插入一个元素。第一个参数是要插入的元素的索引,a.insert(0,x)插入列表头部,a.insert(len(a),x)等同于a.append(x)
list.remove(x):移除列表中第一个值为x的元素。若没有这样的元素,则抛出ValueError异常。
list.pop([i]):删除列表中给定位置的元素并返回它。若没有给定位置,a.pop()将会删除并返回列表中的最后一个元素
list.sort(key=None,reverse=False):对列表中的元素进行排序(参数可用于自定义排序,解释参见sorted())
list.reverse():反转列表中的元素
list.clear():删除列表中所有元素,相当于del a[:]
list.extend(iterable):使用可迭代对象中所有元素来扩展列表,相当于a[len(a):]=iterable
list.index(x[,start[,end]])
1.返回列表中第一个值为x的元素的索引,若没有这样的元素将会抛出ValueError异常
2.start,end可指定搜索的范围list.count(x):返回元素x在列表中出现的次数
list.copy():返回列表的一个浅拷贝,相当于a[:]
列表推导式
1.概念:更简单的创建列表的方法。
2.练习:生成一个平方列表,如[1,4,9......]
list_a = []
#方式一:
for i in range(4):
list_a.append(i**2)
#方式二:
list_a = [ i**2 for i in range(4)]
#扩展
list_a = [ i**2 for i in range(4) if i !=1]
元组
- 特点
1.使用()进行定义
2.不可变,可通过解包、索引访问 - tuple.index(x)
- tuple.count(x)
- 元组中的列表可修改,比列表占用内存空间要小
集合
- 特点
1.集合是由不重复元素组成的无序的集
2.基本用法包括成员监测和消除重复元素
3.使用{}或set()函数创建集合
4.创建空集合只能用set(),不能用{},如set({""}) - 去重:
set("aaa") - 推导式:
{i for in "aaabbcccc"}
字典
- 定义方法
1.dict_a = {"a":1,"b":2}
2.dict_b = dict(a=1,b=2) dict.pop(key)-
dict.popitem()随机删除 dict.keys()dict.values()- 推导式:
{i: i**2 for i in range(1,4)}
04 | python面向对象编程
类、方法、类变量的定义
类:具有相同属性和方法的对象的集合,对象是类的实例。
方法:类中定义的函数。类方法和普通的函数只有一个区别,即类方法必须有一个参数self
类变量:在整个实例化的对象中是共用的,定义在类中且在函数体外,类变量通常不作为实例变量使用
示例
class Person():
name = "xiaoming"
def get_name(self):
return self.name
print(Person.name)
p = Person()
print(p.name)
print(p.get_name())
p.name = "xiaohong"
Person.name = "xiaohei"
print(p.name)
实例引用、实例变量
- 实例:类的具体对象,例如车是一个类,摩托车或自行车是车的实例,类是抽象的,实例是具体的
- 实例引用:给对象起个别名,比如a是对象,b是对象的引用,则a和b的地址空间是一样的,修改b则a也被同事修改
- 实例变量:实例属性,在方法内部以“self.变量名”方式定义的变量。实例变量只能通过对象名访问,不能通过类名访问
- 示例
class Person():
def __init__(self,name,age,gender):
self.name = name
self.age = age
self.gender = gender
def set_att(self,value):
self.value = value
p = Person("xiaoming",12,"male")
p.set_att("shengao")
print(p.value)
05 | Pytest测试框架
pytest介绍
- pytest是一个非常成熟的全功能的python测试框架,有以下特点:
1.简单灵活,容易上手
2.支持参数化
3.测试用例skip和xfail,自动失败重试等处理
4.支持简单的单元测试和复杂的功能测试,还可以与selenium/appium/requests结合做自动化测试
5.pytest有很多第三方插件,也可自定义扩展,如allure(生成html测试报告)、xdist(多cpu分发)
6.可很好的与Jenkins集成 - 文档:https://docs.pytest.org/en/latest/contents.html#toc
- 第三方库:https://pypi.org/search/?q=pytest
pytest安装与依赖
pip install -U pytest-
pip install pytest-sugar:美化运行过程界面 -
pip install pytest-rerunfailures:重新运行出错的测试用例
pytest --reruns 3 -v -s test_pytest.py
pytest -v --reruns 5 --reruns-delay 1
pip install pytest-xdist:多任务并发执行测试用例
1.pytest -n 3pip install pytest-assume:执行1个测试用例里的所有断言
def test_one():
pytest.assume(1 == 2)
pip install pytest-html:生成测试报告
1.pytest -v -s --html=report.html --self-contained-htmlpytest -h
pytest测试用例的识别与运行
测试文件名必须以test_.py或_test.py命名
用例识别
1.测试类以大写T开头(Test*),测试类包含所有test_的方法,测试类不能带有__init__方法
2.不在class中所有的test_方法pytest也可执行unittest框架写的用例和方法
终端执行
1.pytest -v(--verbose)打印详细运行日志信息
2.pytest -v -s 文件-s打印所有print的内容
3.pytest 文件名.py
4.pytest 文件名.py::类名
5.pytest 文件名.py::类名::方法名
6.pytest -v -k "类名 and not 方法名"跳过运行某个用例
7.pytest -k "add or div" --collect-only模糊匹配用例名中包含add和div的用例数
8.pytest -m [标记名]@pytest.mark.[标记名]将运行有这个标记的测试用例
pytest -m "not xxx"
9.pytest -x 文件名一旦运行到报错就停止运行
10.pytest --maxfail=[num]当运行错误达到num时就停止运行
11.pytest --pyargs pkg.testing指定包下所有用例
12.pytest --junitxml=path生成junitxml报告-
在pycharm中用pytest执行用例
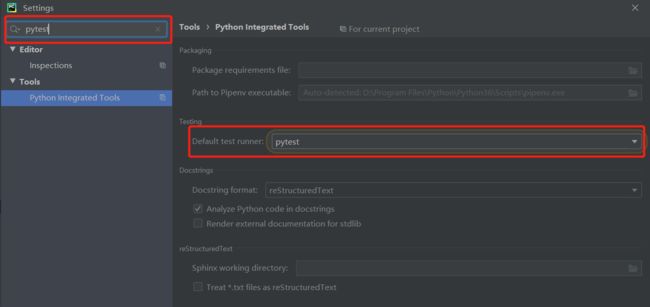
1.设置:File->Settings->搜素pytest->Default test runner(见下图)
2.示例
import pytest
class TestDemo():
def test_one(self):
print("开始执行test_one方法")
x = "this"
assert "h" in x
def test_two(self):
print("开始执行test_two方法")
y = "that"
assert "s" in y
if __name__ == '__main__':
pytest.main("-v -s TestDemo::test_two")
pytest.main("-v -s TestDemo")
setup/teardown
1.模块级(setup_module/teardown_module)模块始末,全局的(优先最高)
2.函数级(setup_function/teardown_function)只对函数用例生效(不在类中)
3.类级(setup_class/teardown_class)只在类中前后运行一次(在类中)
4.方法级(setup_method/teardown_method)开始于方法始末(在类中)
5.类里面(setup/teardown)运行在调用方法前后
pytest-fixture的用法
参考资料:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_30457465/article/details/101827541
- @pytest.fixture()
import pytest
@pytest.fixture()
def login():
print("这是个登录方法")
def test_case1(login):
print("test_case1,要登录")
def test_case2():
print("test_case2,不需要登录")
def test_case3(login):
print("test_case3,需要登录")
if __name__ == '__main__':
pytest.main("-v -s TestDemo::test_two")
pytest.main("-v -s TestDemo")
- @pytest.fixture(scope="module")
import pytest
@pytest.fixture(scope="module")
def open_and_close():
print("打开浏览器")
yield # 第1次调用执行yield前的代码,第2次调用执行yield后的代码
print("关闭浏览器")
def test_one(open_and_close):
print("test_one")
def test_two(open_and_close):
print("test_two")
if __name__ == '__main__':
pytest.main()
- @pytest.fixture(autouse=True)
所有用例自动应用
import pytest
@pytest.fixture(autouse=True)
def open():
print("打开浏览器")
def test_one():
print("test_one")
def test_two():
print("test_two")
if __name__ == '__main__':
pytest.main()
- @pytest.mark.parametrize(params=)
import pytest
@pytest.mark.parametrize("test_input,expected",[("3+5",8),("2+5",7),("7*5",30)])
def test_eval(test_input,expected):
assert eval(test_input) == expected
@pytest.mark.parametrize("x",[1,2])
@pytest.mark.parametrize("y",[3,4,5])
def test_foo(x,y):
print(f"测试数据组合x:{x},y:{y}")
# 方法名作为参数
test_user_data = ['Tome','Jerry']
@pytest.fixture(scope="module")
def login_r(request):
# 这是接受兵传入的参数
user = request.param
print(f"\n 打开首页准备登陆,登陆用户:{user}")
return user
# indirect=True,可以把穿过来的参数当函数来执行
@pytest.mark.parametrize("login_r",test_user_data,indirect=True)
def test_login(login_r):
a = login_r
print(f"测试用例中login的返回值:{a}")
assert a != ""
if __name__ == '__main__':
pytest.main()
- @pytest.mark.skip("跳过")
使用场景:
1.调试时不想运行这个用例
2.标记无法在某些平台上运行的测试功能
3.在某些版本中执行,其他版本跳过
4.外部资源不可用时跳过(若测试数据是从数据库中取的,数据库返回结果成功就跳过)
@pytest.mark.skip("跳过")
def test_login():
print("登陆")
@pytest.mark.skipif(sys.platform == "darwin",reason="不在macos上执行")
def test_login()
print("登陆")
- @pytest.mark.xfail
使用场景
1.功能测试尚未实施或尚未修复的错误
2.希望测试由于某种情况就应该失败
@pytest.mark.xfail
def test_login()
print("登陆")
- @pytest.mark.
自定义标记
@pytest.mark.search
def test_search():
print("test_search")
@pytest.mark.login
def test_login():
print("test_login")
# 在conftest.py文件中添加函数
def pytest_configure(config):
marker_list = ["search","login"]
for markers in marker_list:
config.addinivalue_line(
"markers",markers
)
# 命令行执行
pytest xx.py -m login
- conftest.py
1.pytest为我们提供了公共方法存放的位置
2.在用例里直接使用即可,无需import引用
3.conftest.py与运行的用例要在同一个package下,且有init.py文件
4.全局配置和前期工作都可写在这里
05 | 参数化使用
格式
@pytest.mark.parametrize(argnames,argvalues)
1.argnames:要参数化的变量,string,list,tuple
2.argvalues:参数化的值,list,list[tuple]示例
import pytest
@pytest.mark.parametrize("a,b",[(10,20),(10,30)])
def test_one(a,b):
print(a+b)
@pytest.mark.parametrize(["a","b"],[(10,20),(10,30)])
def test_two(a,b):
print(a+b)
@pytest.mark.parametrize(("a","b"),[(10,20),(10,30)])
def test_three(a,b):
print(a+b)
yaml数据参数化
- 安装pyyaml:
pip install pyyaml - list
list
- 10
- 20
- 30
- dict
by: id
locator: name
action: click
- 嵌套
-
- by: id
- locator: name
- action: click
compannies:
-
id: 1
name: company1
price: 200w
-
id: 2
name: company2
price: 500w
- 加载yaml文件
yaml.safe_load(open("./data.yaml"))
@pytest.mark.parametrize(["a","b"],yaml.safe_load(opne("./data.yaml")))
def test_param(a,b):
print(a+b)
06 | 测试报告定制
allure安装
- windows
1.https://github.com/allure-framework/allure2/releases下载allure2.7.zip包
2.解压->进入bin目录->运行allure.bat
3.把bin目录加入PATH环境变量 - mac:
brew install allure - 官网:http://allure.qatools.ru/
- 文档:https://docs.qameta.io/allure/#
- 安装allure-pytest:
pip install allure-pytest
生成报告
- 运行收集结果:
pytest --alluredir=/tmp/my_allure_results - 查看报告
1.方式一:直接打开默认浏览器在线看报告
allure serve /tmp/my_allure_results
2.方式二:启动tomcat服务,从结果生成报告
# 生成报告
allure generate ./result/ -o ./report/ --clean(注:覆盖路径加--clean)
# 打开报告
allure open -h 127.0.0.1 -p 8883 ./report/
allure常用特性
@allure.feature('功能名称')@allure.story('子功能名称')@allure.step('步骤细节')@allure.attach('具体文本信息'),附加信息(数据、文本、图片、视频、网页)pytest 文件名 --allure-features '购物车功能' --allure-stories '加入购物车'示例
import allure
@allure.feature("登录模块")
class TestLogin():
@allure.story("登录成功")
def test_login_success(self):
print("登录成功")
@allure.story("登录失败")
def test_login_fail(self):
print("登录失败")
@allure.story("密码缺失")
def test_input_pwd(self):
with allure.step("输入用户名"):
print("输入用户名")
with allure.step("点击登录按钮"):
print("点击登录按钮")
关联
- 关联用例
import allure
@allure.link("http://www.baidu.com",name="百度")
def test_with_link():
print("加了测试用例链接")
TEST_CASE_LINK = "http://www.baidu.com"
@allure.link(TEST_CASE_LINK,name="百度")
def test_with_link():
print("加了测试用例链接")
- 关联bug
@allure.issue("140","这是个bug")
def test_with_link():
print("加了BUG链接")
执行:pytest test_case.py --allure-link-pattern=issue:http://www.mytestissue/issue/{} --alluredir=result
按用例的优先级测试
级别划分
1.Trivial(不重要,必填项无提示,或提示不规范)
2.Minor(不太重要,界面错误或UI需求不符)
3.Normal(普通,数值计算错误)
4.Critical(严重,功能点缺失)
5.Blocker(阻塞,中断缺陷,程序无响应,无法执行下一步操作)示例
@allure.severity(allure.severity_level.TRIVIAL)
def test_with_link():
print("something")
执行:pytest -s -v case.py --alluredir=result --allure-severities normal,critical
添加文本、图片、网页
def test_attach_text():
allure.attach("这是一个纯文本",attachment_type=allure.attachment_type.TEXT)
def test_attach_html():
allure.attach("这是一段htmlbody块","html测试块",attachment_type=allure.attachment_type.HTML)
def test_attach_photo():
allure.attach.file("./tupian.png",name="这是一个图片",attachment_type=allure.attachment_type.PNG)
练习
@allure.link("http://www.baidu.com")
@allure.feature("百度搜索")
@pytest.mark.parametrize('test_data1',['allure','pytest','unitest'])
def test_steps_demo(test_data1):
with allure.step("打开百度网页"):
driver = webdriver.Chrome()
driver.get("http://www.baidu.com")
driver.maximize_window()
with allure.step(f"输入关键词:{test_data1}"):
driver.find_element_by_id("kw").send_keys(test_data1)
time.sleep(2)
driver.find_element_by_id("su").click()
time.sleep(2)
with allure.step("保存图片"):
driver.save_screenshot("report/xx.png")
with allure.step("关闭浏览器"):
driver.quit()
07 | python测试实践
参考文档
- 入门教程
https://docs.python.org/zh-cn/3/tutorial/index.html - 安装 https://docs.python.org/3/using/index.html 3
pycharm
-
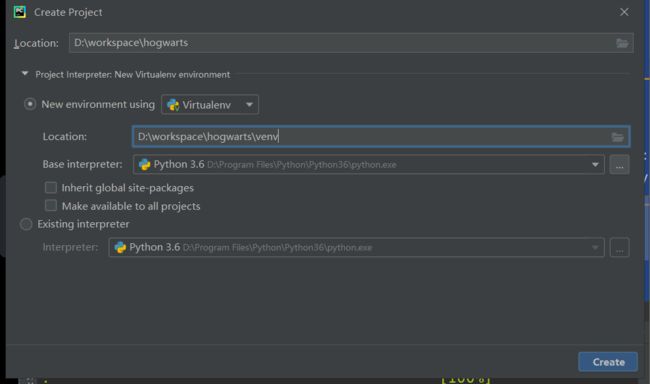
创建项目
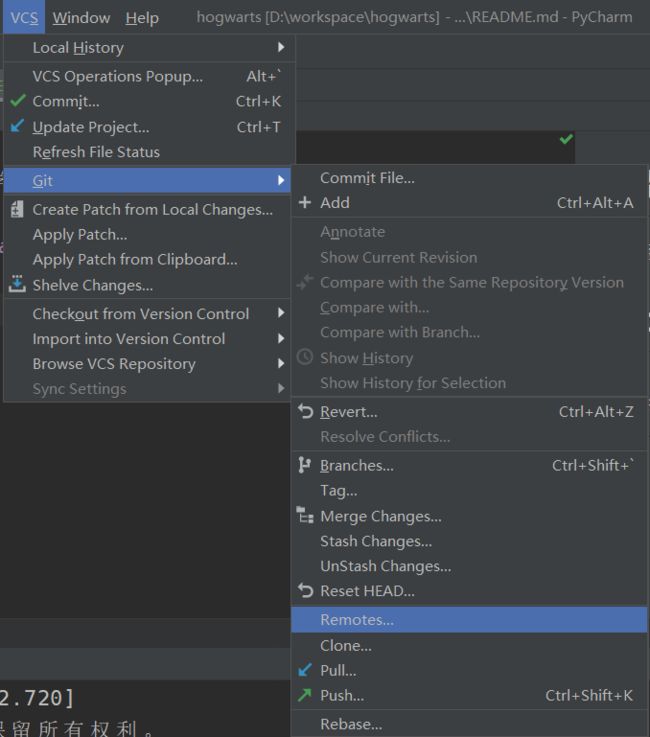
- 创建git仓库
1.在项目目录下执行:git init
2.点击右上角绿色对勾
3.Add to .gitignore
4.常用命令
echo "# something" >> README.md
git init
git add README.md
git commit -m "first commit"
git remote add origin [email protected]:seveniruby/HogwartsLagouTesting1.git
git push -u origin master
5.也可以通过pycharm操作
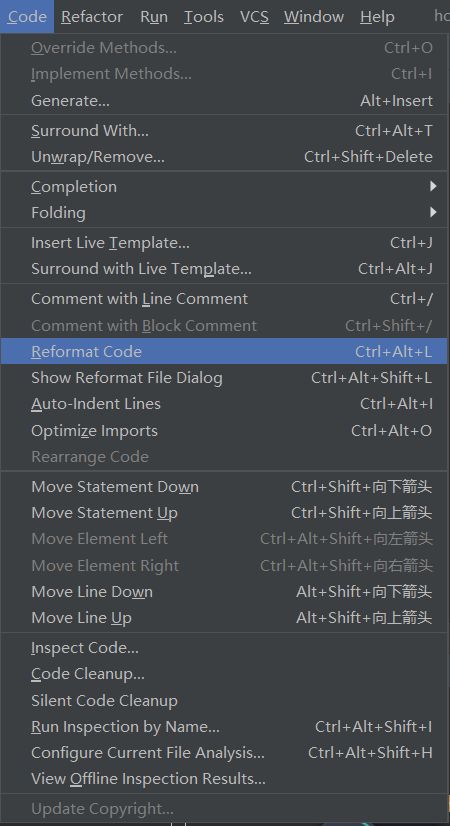
6.格式化代码
unittest介绍
参考资料:https://docs.python.org/zh-cn/3/library/unittest.html
calc.py
class Calc:
def add(self, a, b):
return a + b
def div(self, a, b):
return a / b
- test_calc.py
import unittest
from python.calc import Calc
class TestCalc(unittest.TestCase):
def setUp(self) -> None:
self.calc = Calc()
def test_add_1(self):
self.assertEqual(3, self.calc.add(1, 2))
def test_add_2(self):
self.assertEqual(0.03, self.calc.add(0.01, 0.02))
pytest介绍
- 参考资料:https://docs.pytest.org/en/5.4.1/contents.html
类型提示(python3.5以后的特性)
- 便于IDE识别类型,不影响代码运行
- calc.py
class Calc:
def add(self, a: int, b: int) -> int:
return a + b
def div(self, a, b):
return a / b
-
调用此方法时,IDE可智能识别
08 | pytest实战
测试装置
- setup & teardown
- setup_class & teardown_class
- setup_module & teardown_module
def setup_module():
pass
def teardown_module():
pass
class TestCase:
@classmethod
def setup_class(cls):
pass
@classmethod
def teardown_class(cls):
pass
def setup(self):
pass
def teardown(self):
pass
测试用例顺序
- 不要让测试用例有顺序依赖
实例方法可以访问类变量
class TestCase:
@classmethod
def setup_class(cls):
cls.calc = Calc()
def test_case(self):
# 这里的self.calc其实调用的是类变量cls.calc
assert (self.calc.add(1, 2), 3)
设置标签
class TestCase:
@classmethod
def setup_class(cls):
cls.calc = Calc()
@pytest.mark.demo1
def test_case(self):
assert (self.calc.add(1, 2), 3)
@pytest.mark.demo2
def test_case1(self):
assert (self.calc.div(1, 2), 0.5
运行:
pytest -m "demo1 or demo2"
断言
def test_zero_division():
with pytest.raise(ZeroDivisionError):
1/0
def test_recursion_depth():
with pytest.raises(RuntimeError) as excinfo:
def f():
静态方法、实例方法、类方法
- 静态方法
1.用@staticmethod装饰
2.可用类名直接调用
3.示例
class Demo:
@staticmethod
def class_method(a,b):
pass
- 类方法
1.用@classmethod装饰
2.可用类或实例调用
3.示例
class Demo:
@classmethod
def class_method(cls,a,b):
pass
调用类方法时,类作为第一个参数传入
- 实例方法
1.无需装饰
2.只能实例调用
3.示例
class Demo:
def class_method(self,a,b):
pass
调用类方法时,实例作为第一个参数传入
09 | pytest实战3
数据驱动
- 测试数据的数据驱动
test_pyteset_data.yaml
- [0, 2, 3]
- [3, 4, 7]
test_pytest.py
def data():
with open("test_pyteset_data.yaml") as f:
return yaml.load(f)
class TestCalc:
def setup(self):
self.calc = Calc()
@pytest.mark.parametrize("a,b,result", data())
def test_add(self, a, b, result):
assert (self.calc.add(a, b), result)
- 测试步骤的数据驱动
test_pyteset_data.yaml
- add
- add2
- add
- add2
test_pytest.py(代码是有问题的)
def data():
with open("test_pyteset_data.yaml") as f:
return yaml.load(f)
class TestCalc:
def setup(self):
self.calc = Calc()
@pytest.mark.parametrize("a,b,result", data())
def test_add(self, a, b, result):
assert (self.calc.add(a, b), result)
def steps(self,data,r):
test_steps=steps()
for step in test_steps:
if step=="add":
assert self.calc.add(*data) == r
elif step=="add2":
assert self.calc.add2(data) == r
- 数据格式的选择
| 格式 | 优点 | 缺点 |
|---|---|---|
| excel | 生成数据方便 | 二进制文件不利于版本管理 |
| csv | 可使用excel编辑 | 文本格式方便版本管理 |
| yaml | 格式完备,可读性好 | 格式简单 |
| xml | 格式完备 | 冗长复杂 |
| json | 格式完备,可读性一般 | 不能编写注释,格式死板 |
yaml语法
- 参考资料
1.http://www.ruanyifeng.com/blog/2016/07/yaml.html
2.https://yaml.org/spec/1.1/#id857168
3.https://pyyaml.org/wiki/PyYAMLDocumentation