Mybatis工作流程
1、解析配置文件,包括全局配置文件和映射器配置文件,把它们解析成一个 Configuration 对象。
2、创建会 话 工 厂 SqlSessionFactory
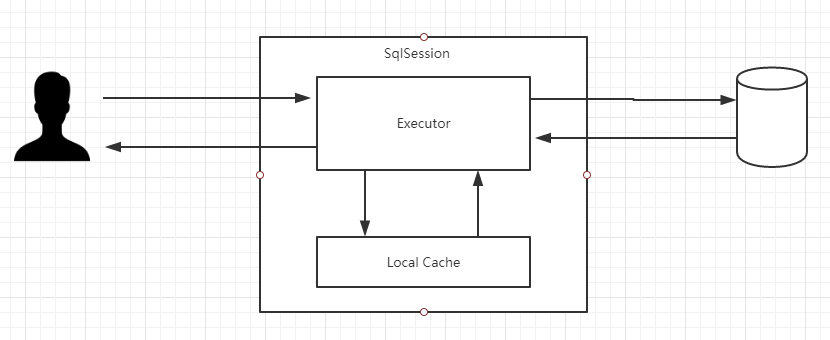
3、操作数据库的接口,它在应用程序和数据库中间,代表我们跟数据库之间的一次连接:创建 SqlSession 对象。
4、SqlSession 持有了一个 Executor 对象,用来封装对数据库的操作。
5、在执行器 Executor 执行 query 或者 update 操作的时候我们创建一系列的对象,来处理参数、执行 SQL、处理结果集。
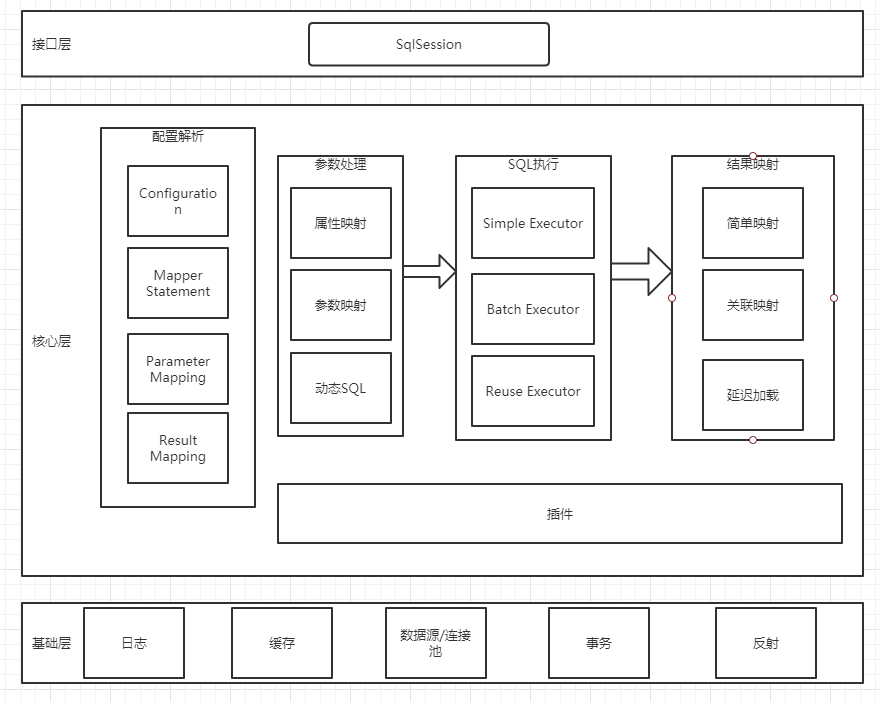
架构分层和模块划分
github代码
接口层
接口层是最重要的一层,核心对象是 SqlSession,它是上层应用和 MyBatis打交道的桥梁,SqlSession 上定义了非常多的对数据库的操作方法。接口层在接收到调用请求的时候,会调用核心处理层的相应模块来完成具体的数据库操作。
核心处理层
所有跟数据库操作相关的动作都是在这一层完成的,插件也属于核心层,这是由它的工作方式和拦截的对象决定的。
主要做的事情:
- 把接口中传入的参数解析并且映射成 JDBC 类型;
- 解析 xml 文件中的 SQL 语句,包括插入参数,和动态 SQL 的生成;
- 执行 SQL 语句;
- 处理结果集,并映射成 Java 对象。
基础支持层
基础支持层主要是一些抽取出来的通用的功能(实现复用),用来支持核心处理层的功能。比如数据源、缓存、日志、xml 解析、反射、IO、事务等等这些功能。
Mybatis缓存
缓存是一般的 ORM 框架都会提供的功能,目的就是提升查询的效率和减少数据库的压力。跟 Hibernate 一样,MyBatis 也有一级缓存和二级缓存,并且预留了集成第三方缓存的接口。
缓存体系结构
MyBatis 跟缓存相关的类都在 cache 包里面,其中有一个 Cache 接口,只有一个默认的实现类 PerpetualCache,它是用 HashMap 实现的。
这里用到了装饰器模式,通过这些装饰器可以额外实现很多的功能:回收策略、日志记录、定时刷新等等。
通过查看代码,缓存实现类总体可分为三类:基本缓存、淘汰算法缓存、装饰器缓存
| 缓存实现类 | 描述 | 作用 | 装饰条件 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 基本缓存 | 缓存基本实现类 | 默认是 PerpetualCache,也可以自定义比如RedisCache、EhCache 等,具备基本功能的缓存类 | 无 |
| LruCache | LRU 策略的缓存 | 当缓存到达上限时候,删除最近最少使用的缓存(Least Recently Use) | eviction="LRU"(默认) |
| FifoCache | FIFO 策略的缓存 | 当缓存到达上限时候,删除最先入队的缓存 | eviction="FIFO" |
| SoftCache、WeakCache | 带清理策略的缓存 | 通过 JVM 的软引用和弱引用来实现缓存,当 JVM内存不足时,会自动清理掉这些缓存,基于SoftReference 和 WeakReference | eviction="SOFT" eviction="WEAK" |
| LoggingCache | 带日志功能的缓存 | 比如:输出缓存命中率 | 基本 |
| SynchronizedCache | 同步缓存 | 基于 synchronized 关键字实现,解决并发问题 | 基本 |
| BlockingCache | 阻塞缓存 | 通过在 get/put 方式中加锁,保证只有一个线程操作缓存,基于 Java 重入锁实现 | blocking=true |
| SerializedCache | 支持序列化的缓存 | 将对象序列化以后存到缓存中,取出时反序列化 | readOnly=false(默认) |
| ScheduledCache | 定时调度的缓存 | 在进行 get/put/remove/getSize 等操作前,判断缓存时间是否超过了设置的最长缓存时间(默认是一小时),如果是则清空缓存--即每隔一段时间清空一次缓存 | flushInterval 不为空 |
| TransactionalCache | 事务缓存 | 在二级缓存中使用,可一次存入多个缓存,移除多个缓存 | 在TransactionalCacheManager 中用 Map维护对应关系 |
一级缓存
一级缓存也叫本地缓存,MyBatis 的一级缓存是在会话(SqlSession)层面进行缓存的。MyBatis 的一级缓存是默认开启的,不需要任何的配置。
如果要在同一个会话里面共享一级缓存,这个对象肯定是在 SqlSession 里面创建的,作为 SqlSession 的一个属性。而DefaultSqlSession实现了SqlSession,对应的要实现他的所有方法。
DefaultSqlSession 里面只有两个属性,Configuration 是全局的,所以缓存只可能放在 Executor 里面维护,SimpleExecutor /ReuseExecutor/BatchExecutor 的父类BaseExecutor 的构造函数中持有了 PerpetualCache。
在同一个会话里面,多次执行相同的 SQL 语句,会直接从内存取到缓存的结果,不会再发送 SQL 到数据库。但是不同的会话里面,即使执行的 SQL 一模一样(通过一个Mapper 的同一个方法的相同参数调用),也不能使用到一级缓存。
一级缓存的缺点
使用一级缓存的时候,因为缓存不能跨会话共享,不同的会话之间对于相同的数据可能有不一样的缓存。在有多个会话或者分布式环境下,会存在脏数据的问题。如果要解决这个问题,就要用到二级缓存。
二级缓存
二级缓存是用来解决一级缓存不能跨会话共享的问题的,范围是 namespace 级别的,可以被多个 SqlSession 共享(只要是同一个接口里面的相同方法,都可以共享),生命周期和应用同步。二级缓存是默认关闭的
一级缓存和二级缓存同时存在的时候,那个先执行?
二级缓存作为一个作用范围更广的缓存,他是在SqlSession的外层,否则不可能被多个SqlSession共享,而一级缓存是在SqlSession的内部的,所以在工作在一级缓存之前,也就是说只有取不到二级情况下才到会话中去取一级缓存
二级缓存在哪里维护的?
由于二级缓存是跨会话共享的,SqlSession本身和它里面的BaseExecutor已经满足不了需求了,所以需要用到CachingExecutor这个类,启用了二级缓存的话,CachingExecutor对于查询请求,会判断二级缓存中是否有缓存结果,如果有就直接返回,如果没有则委派交给真正的查询器Executor实现类
开启二级缓存
1、在 mybatis-config.xml 中配置了(可以不配置,默认是 true),只要没有显式地设置 cacheEnabled=false,都会用 CachingExecutor 装饰基本的执行器。
2、在 Mapper.xml 中配置
eviction ="LRU"
flushInterval ="120000"
readOnly =" false" "/>
cache属性介绍:
| 属性 | 含义 | 取值 |
|---|---|---|
| type | 缓存实现类 | 需要实现 Cache 接口,默认是 PerpetualCache |
| size | 最多缓存对象个数 | 默认1024 |
| eviction | 回收策略(缓存淘汰算法) | LRU – 最近最少使用的:移除最长时间不被使用的对象(默认)。FIFO – 先进先出:按对象进入缓存的顺序来移除它们。SOFT – 软引用:移除基于垃圾回收器状态和软引用规则的对象。WEAK – 弱引用:更积极地移除基于垃圾收集器状态和弱引用规则的对象。 |
| flushInterval | 定时自动清空缓存间隔 | 自动刷新时间,单位 ms,未配置时只有调用时刷新 |
| readOnly | 是否只读 | true:只读缓存;会给所有调用者返回缓存对象的相同实例。因此这些对象不能被修改。这提供了很重要的性能优势。false:读写缓存;会返回缓存对象的拷贝(通过序列化),不会共享。这会慢一些,但是安全,因此默认是 false。改为 false 可读写时,对象必须支持序列化。 |
| blocking | 是否使用可重入锁实现缓存的并发控制 | true,会使用 BlockingCache 对 Cache 进行装饰默认 false |
Mapper.xml 配置了
在单个 Statement ID 上显式关闭二级缓存(默认是 true)
验证二级缓存(需要先开启)
1、事务不提交,二级缓存不存在
因为二级缓存使用 TransactionalCacheManager(TCM)来管理,最后又调用了 TransactionalCache的getObject()、putObject和commit()方法,TransactionalCache里面又持有了真正的 Cache 对象,比如是经过层层装饰的 PerpetualCache。
在 putObject 的时候,只是添加到了 entriesToAddOnCommit 里面,只有它的commit()方法被调用的时候才会调用 flushPendingEntries()真正写入缓存。它就是在DefaultSqlSession 调用 commit()的时候被调用的。
2、使用不同的 session 和 mapper,二级缓存可以跨 session 存在
BlogMapper mapper1 = session1.getMapper(BlogMapper. class);
System. out .println(mapper1.selectBlogById(1));
// 事务不提交的情况下,二级缓存不会写入
session1.commit();
BlogMapper mapper2 = session2.getMapper(BlogMapper. class);
System. out .println(mapper2.selectBlogById(1));
3、在其他的 session 中执行增删改操作,验证缓存会被刷新(清空缓存)
在 CachingExecutor 的 update()方法里面会调用 flushCacheIfRequired(ms),isFlushCacheRequired 就是从标签里面渠道的 flushCache 的值。而增删改操作的flushCache 属性默认为 true。
二级缓存开启的时机
1、因为所有的增删改都会刷新二级缓存,导致二级缓存失效,所以适合在查询为主的应用中使用,比如历史交易、历史订单的查询。否则缓存就失去了意义。
2、如果多个 namespace 中有针对于同一个表的操作,比如 Blog 表,如果在一个namespace 中刷新了缓存,另一个 namespace 中没有刷新,就会出现读到脏数据的情况。所以,推荐在一个 Mapper 里面只操作单表的情况使用。
第三方缓存做二级缓存
可以通过实现 Cache 接口来自定义二级缓存。
MyBatis 官方提供了一些第三方缓存集成方式,比如 ehcache 和 redis:
操作步骤:
< groupId>org.mybatis.caches
< artifactId>mybatis-redis
< version>1.0.0-beta2
源码解读
分为四个步骤来分析:
1.配置解析
2.会话创建
3.获取Mapper对象
4.执行SQL
配置解析
配置解析的过 程全 部 只 解 析 了 两 种 文 件 。 一个是mybatis-config.xml 全局配置文件,一个是很多的Mapper.xml文件
//解析文件
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);
解析配置文件之后new了一个SqlSessionFactoryBuilder(建造者模式),返回了一个SqlSessionFactory对象(单例模式)
从SqlSessionFactoryBuilder#build()方法就是XMLConfigBuilder对象的解析
XMLConfigBuilder
这个类是抽象类BaseBuilder的一个子类,专门用来解析全局配置文件,针对不同的构建目标还有其他的子类,比如:
XMLMapperBuilder:解析 Mapper 映射器
XMLStatementBuilder:解析增删改查标签
解析文件流,创建了一个parser,返回了一个Configuration类,然后调用parser.parse()方法
public Configuration parse() {
if (parsed) {
throw new BuilderException("Each XMLConfigBuilder can only be used once.");
}
parsed = true;
parseConfiguration(parser.evalNode("/configuration"));
return configuration;
}
这个方法首先会检查是不是已经解析过,也就是说在应用的生命周期里面,config 配置文件只需要解析一次,生成的 Configuration 对象也会存在应用的整个生命周期中。
parseConfiguration这个方法就是加载 config 文件里面的所有一级标签。
private void parseConfiguration(XNode root) {
try {
//issue #117 read properties first
propertiesElement(root.evalNode("properties"));
Properties settings = settingsAsProperties(root.evalNode("settings"));
loadCustomVfs(settings);
loadCustomLogImpl(settings);
typeAliasesElement(root.evalNode("typeAliases"));
pluginElement(root.evalNode("plugins"));
objectFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectFactory"));
objectWrapperFactoryElement(root.evalNode("objectWrapperFactory"));
reflectorFactoryElement(root.evalNode("reflectorFactory"));
settingsElement(settings);
// read it after objectFactory and objectWrapperFactory issue #631
environmentsElement(root.evalNode("environments"));
databaseIdProviderElement(root.evalNode("databaseIdProvider"));
typeHandlerElement(root.evalNode("typeHandlers"));
mapperElement(root.evalNode("mappers"));
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error parsing SQL Mapper Configuration. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
一级标签解析
propertiesElement()
第一个是解析
这里面又有两种类型,一种是放在 resource 目录下的,是相对路径,一种是写的绝对路径的。
解析的最终结果就是我们会把所有的配置信息放到名为 defaults 的 Properties 对象里面,最后把XPathParser 和 Configuration 的 Properties 属性都设置成我们填充后的 Properties对象。
settingsAsProperties) ()
把
标签的子标签的处理在后面。
loadCustomVfs(settings)
loadCustomVfs 是获取 Vitual File System 的自定义实现类。
比如我们要读取本地文件,或者 FTP 远程文件的时候,就可以用到自定义的 VFS 类。我们根据
private void loadCustomVfs(Properties props) throws ClassNotFoundException {
String value = props.getProperty("vfsImpl");
if (value != null) {
String[] clazzes = value.split(",");
for (String clazz : clazzes) {
if (!clazz.isEmpty()) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Class vfsImpl = (Class)Resources.classForName(clazz);
configuration.setVfsImpl(vfsImpl);
}
}
}
}
loadCustomLogImpl(settings)
loadCustomLogImpl 是根据
typeAliasesElement()
有两种定义方式,一种是直接定义一个类的别名,一种就是指定一个包,那么这个 package 下面所有的类的名字就会成为这个类全路径的别名。
类的别名和类的关系,我们放在一个 TypeAliasRegistry 对象里面。
private void typeAliasesElement(XNode parent) {
if (parent != null) {
for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) {
if ("package".equals(child.getName())) {
String typeAliasPackage = child.getStringAttribute("name");
configuration.getTypeAliasRegistry().registerAliases(typeAliasPackage);
} else {
String alias = child.getStringAttribute("alias");
String type = child.getStringAttribute("type");
try {
Class clazz = Resources.classForName(type);
if (alias == null) {
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias(clazz);
} else {
typeAliasRegistry.registerAlias(alias, clazz);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
throw new BuilderException("Error registering typeAlias for '" + alias + "'. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
}
}
}
pluginElement()
插件标签,比如 Pagehelper 的翻页插件,或者我们自定义的插件。
标签解析完以后,会生成一个 Interceptor 对象,并且添加到 Configuration 的InterceptorChain 属性里面,它是一个 List。
objectFactoryElement() 、objectWrapperFactoryElement()
用来实例化对象,分 别 生 成 ObjectFactory 、ObjectWrapperFactory 对象,同样设置到 Configuration 的属性里面。
reflectorFactoryElement()
解析 reflectorFactory 标签,生成 ReflectorFactory 对象
settingsElement(settings)
对
private void settingsElement(Properties props) {
configuration.setAutoMappingBehavior(AutoMappingBehavior.valueOf(props.getProperty("autoMappingBehavior", "PARTIAL")));
configuration.setAutoMappingUnknownColumnBehavior(AutoMappingUnknownColumnBehavior.valueOf(props.getProperty("autoMappingUnknownColumnBehavior", "NONE")));
configuration.setCacheEnabled(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("cacheEnabled"), true));
configuration.setProxyFactory((ProxyFactory) createInstance(props.getProperty("proxyFactory")));
configuration.setLazyLoadingEnabled(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("lazyLoadingEnabled"), false));
configuration.setAggressiveLazyLoading(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("aggressiveLazyLoading"), false));
configuration.setMultipleResultSetsEnabled(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("multipleResultSetsEnabled"), true));
configuration.setUseColumnLabel(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("useColumnLabel"), true));
configuration.setUseGeneratedKeys(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("useGeneratedKeys"), false));
configuration.setDefaultExecutorType(ExecutorType.valueOf(props.getProperty("defaultExecutorType", "SIMPLE")));
configuration.setDefaultStatementTimeout(integerValueOf(props.getProperty("defaultStatementTimeout"), null));
configuration.setDefaultFetchSize(integerValueOf(props.getProperty("defaultFetchSize"), null));
configuration.setDefaultResultSetType(resolveResultSetType(props.getProperty("defaultResultSetType")));
configuration.setMapUnderscoreToCamelCase(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("mapUnderscoreToCamelCase"), false));
configuration.setSafeRowBoundsEnabled(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("safeRowBoundsEnabled"), false));
configuration.setLocalCacheScope(LocalCacheScope.valueOf(props.getProperty("localCacheScope", "SESSION")));
configuration.setJdbcTypeForNull(JdbcType.valueOf(props.getProperty("jdbcTypeForNull", "OTHER")));
configuration.setLazyLoadTriggerMethods(stringSetValueOf(props.getProperty("lazyLoadTriggerMethods"), "equals,clone,hashCode,toString"));
configuration.setSafeResultHandlerEnabled(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("safeResultHandlerEnabled"), true));
configuration.setDefaultScriptingLanguage(resolveClass(props.getProperty("defaultScriptingLanguage")));
configuration.setDefaultEnumTypeHandler(resolveClass(props.getProperty("defaultEnumTypeHandler")));
configuration.setCallSettersOnNulls(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("callSettersOnNulls"), false));
configuration.setUseActualParamName(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("useActualParamName"), true));
configuration.setReturnInstanceForEmptyRow(booleanValueOf(props.getProperty("returnInstanceForEmptyRow"), false));
configuration.setLogPrefix(props.getProperty("logPrefix"));
configuration.setConfigurationFactory(resolveClass(props.getProperty("configurationFactory")));
}
environmentsElement()
一个 environment 就是对应一个数据源,所以在这里我们会根据配
置的
databaseIdProviderElement()
解析 databaseIdProvider 标签,生成 DatabaseIdProvider 对象(用来支持不同厂商的数据库)。
typeHandlerElement()
TypeAlias 一样,TypeHandler 有两种配置方式,一种是单独配置一个类,一种是指定一个 package。最后我们得到的是 JavaType 和 JdbcType,以及用来做相互映射的 TypeHandler 之间的映射关系。
最后存放在 TypeHandlerRegistry 对象里面。
private void typeHandlerElement(XNode parent) {
if (parent != null) {
for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) {
if ("package".equals(child.getName())) {
String typeHandlerPackage = child.getStringAttribute("name");
typeHandlerRegistry.register(typeHandlerPackage);
} else {
String javaTypeName = child.getStringAttribute("javaType");
String jdbcTypeName = child.getStringAttribute("jdbcType");
String handlerTypeName = child.getStringAttribute("handler");
Class javaTypeClass = resolveClass(javaTypeName);
JdbcType jdbcType = resolveJdbcType(jdbcTypeName);
Class typeHandlerClass = resolveClass(handlerTypeName);
if (javaTypeClass != null) {
if (jdbcType == null) {
typeHandlerRegistry.register(javaTypeClass, typeHandlerClass);
} else {
typeHandlerRegistry.register(javaTypeClass, jdbcType, typeHandlerClass);
}
} else {
typeHandlerRegistry.register(typeHandlerClass);
}
}
}
}
}
mapperElement()
private void mapperElement(XNode parent) throws Exception {
if (parent != null) {
for (XNode child : parent.getChildren()) {
//包
if ("package".equals(child.getName())) {
String mapperPackage = child.getStringAttribute("name");
configuration.addMappers(mapperPackage);
} else {
//相对路径
String resource = child.getStringAttribute("resource");
//绝对路径
String url = child.getStringAttribute("url");
//单个接口
String mapperClass = child.getStringAttribute("class");
if (resource != null && url == null && mapperClass == null) {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(resource);
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, resource, configuration.getSqlFragments());
mapperParser.parse();
} else if (resource == null && url != null && mapperClass == null) {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(url);
InputStream inputStream = Resources.getUrlAsStream(url);
XMLMapperBuilder mapperParser = new XMLMapperBuilder(inputStream, configuration, url, configuration.getSqlFragments());
mapperParser.parse();
} else if (resource == null && url == null && mapperClass != null) {
Class mapperInterface = Resources.classForName(mapperClass);
configuration.addMapper(mapperInterface);
} else {
throw new BuilderException("A mapper element may only specify a url, resource or class, but not more than one.");
}
}
}
}
}
这个标签的解析主要做了几个事情:
1.判断
首先会判断是不是接口,只有接口才解析;然后判断是不是已经注册了,单个 Mapper重复注册会抛出异常。
2.注册
XMLMapperBuilder.parse()方法,是对 Mapper 映射器的解析。里面有两个方法:
public void parse() {
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {
configurationElement(parser.evalNode("/mapper"));
configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);
bindMapperForNamespace();
}
parsePendingResultMaps();
parsePendingCacheRefs();
parsePendingStatements();
}
configurationElement()—— 解析所有的子标签 , 其中
buildStatementFromContext()最终获得 MappedStatement 对象。
bindMapperForNamespace()——把 namespace(接口类型)和工厂类绑定起来。
无论是按 package 扫描,还是按接口扫描,最后都会调用到 MapperRegistry 的addMapper()方法。
MapperRegistry 里面维护的其实是一个 Map 容器,存储接口和代理工厂的映射关系。
3.注释处理
除了解析映射文件之外,还会去解析 Mapper 接口方法上的注解,在 addMapper()方法里面创建了一个 MapperAnnotationBuilder,调用parse()方法
public void parse() {
String resource = type.toString();
if (!configuration.isResourceLoaded(resource)) {
loadXmlResource();
configuration.addLoadedResource(resource);
assistant.setCurrentNamespace(type.getName());
parseCache();
parseCacheRef();
Method[] methods = type.getMethods();
for (Method method : methods) {
try {
// issue #237
if (!method.isBridge()) {
parseStatement(method);
}
} catch (IncompleteElementException e) {
configuration.addIncompleteMethod(new MethodResolver(this, method));
}
}
}
parsePendingMethods();
}
parseCache() 和 parseCacheRef() 方 法 其 实 是 对@CacheNamespace 和@CacheNamespaceRef 这两个注解的处理。
parseStatement()方法里面的各种 getAnnotation(),都是对注解的解析,比如@Options,@SelectKey,@ResultMap 等等。
最后同样会解析成 MappedStatement 对象,也就是说在 XML 中配置,和使用注解配置,最后起到一样的效果。
4.处理完成
如果注册没有完成,还要从 Map 里面 remove 掉。
if (!loadCompleted) {
knownMappers.remove(type);
}
MapperRegistry 也会放到 Configuration 里面去,最后调用另一个 build()方法,返回 DefaultSqlSessionFactory。
配置解析小结
1.主要完成了 config 配置文件、Mapper 文件、Mapper 接口上的注解的解析。
2.得到了一个最重要的对象 Configuration,这里面存放了全部的配置信息,它在属性里面还有各种各样的容器。
3.返回了一个 DefaultSqlSessionFactory,里面持有了 Configuration的实例。
创建会话
数据库的每一次连接,都需要创建一个会话,我们用openSession()方法来创建。
DefaultSqlSessionFactory#openSessionFromDataSource()
private SqlSession openSessionFromDataSource(ExecutorType execType, TransactionIsolationLevel level, boolean autoCommit) {
Transaction tx = null;
try {
final Environment environment = configuration.getEnvironment();
final TransactionFactory transactionFactory = getTransactionFactoryFromEnvironment(environment);
tx = transactionFactory.newTransaction(environment.getDataSource(), level, autoCommit);
final Executor executor = configuration.newExecutor(tx, execType);
return new DefaultSqlSession(configuration, executor, autoCommit);
} catch (Exception e) {
closeTransaction(tx); // may have fetched a connection so lets call close()
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error opening session. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
由源码可以得出:要先从 Configuration 里面拿到 Enviroment,Enviroment 获取事务工厂,最后通过执行器Executor 处理请求(sql)
1.创建Transaction
这里有2种方式获取:JDBC、MANAGED
1.1.JDBC(JdbcTransactionFactory-> JdbcTransaction)
如果配置的是 JDBC,则会使用 Connection 对象的 commit()、rollback()、close()管理事务。
1.2.MANAGED(ManagedTransactionFactory->ManagedTransaction)
如果配置成 MANAGED,会把事务交给容器来管理,比如 JBOSS,Weblogic。因为我们跑的是本地程序,如果配置成 MANAGE 不会有任何事务。
PS:如 果 是 Spring + MyBatis,则 没 有 必 要 配 置 , 因 为 我 们 会 直 接 在applicationContext.xml 里面配置数据源和事务管理器,覆盖 MyBatis 的配置。
2.创建Executor(执行器)
Executor 的基本类型有三种:SIMPLE、BATCH、REUSE,默认是 SIMPLE(settingsElement()读取默认值),他们都继承了抽象类 BaseExecutor。
三种执行器的区别:
SimpleExecutor:每执行一次 update 或 select,就开启一个Statement 对象,用完立刻关闭 Statement 对象。
ReuseExecutor:执行 update 或 select,以 sql 作为 key 查找 Statement 对象,存在就使用,不存在就创建,用完后,不关闭 Statement 对象,而是放置于 Map 内,供下一次使用。简言之,就是**重复使用 **Statement 对象。
BatchExecutor:执行 update(没有 select,JDBC 批处理不支持 select),将所有 sql 都添加到批处理中(addBatch()),等待统一执行(executeBatch()),它缓存了多个 Statement 对象,每个 Statement 对象都是 addBatch()完毕后,等待逐一执行executeBatch()批处理。与 JDBC 批处理相同。
小结
创建会话的过程,获得了一个DefaultSqlSession,里面包含了一个Executor,用来执行SQL
获取Mapper对象
获得DefaultSqlSession之后,必须找到 Mapper.xml 里面定义的Statement ID,才能执行对应的 SQL 语句。
找到Statement ID有2中方式:
1.直接调用session的方法,在参数里面传入Statement ID(硬编码),如果写错了很难调试,因为编译的时候不会报错,在用的时候才会说找不到
2.定义一个接口,在调用Mapper接口的方法,由于我们的接口名称跟 Mapper.xml 的 namespace 是对应的,接口的方法跟statement ID 也都是对应的,可以快速定位(Mybatis后面的版本默认用这种方式)
Mapper对象的获取?
在DefaultSqlSession#getMapper()方法,调用了 Configuration#getMapper()方法,Configuration 的 getMapper()方法,又调用了 MapperRegistry 的 getMapper()方法,在最后返回了一个mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession)
public T getMapper(Class type) {
return configuration.getMapper(type, this);
}
public T getMapper(Class type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
return mapperRegistry.getMapper(type, sqlSession);
}
public T getMapper(Class type, SqlSession sqlSession) {
final MapperProxyFactory mapperProxyFactory = (MapperProxyFactory) knownMappers.get(type);
if (mapperProxyFactory == null) {
throw new BindingException("Type " + type + " is not known to the MapperRegistry.");
}
try {
return mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new BindingException("Error getting mapper instance. Cause: " + e, e);
}
}
在解析 mapper 标签和 Mapper.xml 的时候已经把接口类型和类型对应的 MapperProxyFactory 放到了一个 Map Map中。获取 Mapper 代理对象,实际上是从Map 中获取对应的工厂类后mapperProxyFactory.newInstance(sqlSession)
在这里用到了动态代理,那Mybatis的动态代理和JDK的动态代理有什么区别?(这个就是面试很常问的一个问题)
用过JDK动态代理的都知道,在实现了 InvocationHandler 的代理类里面,需要传入一个被代理对象的实现类。
这里 不需要实现是因为:我们只需要根据 接口类型+方法的名称,就可以找到Statement ID了,而唯一要做的一件事情也是这件,所以不需要实现类。在MapperProxy里面直接执行逻辑(也就是执行 SQL)就可以。
小结
获得 Mapper 对象的过程,实质上是获取了一个 MapperProxy 的代理对象。MapperProxy 中有 sqlSession、mapperInterface、methodCache。
执行sql
上面提到的Mapper都是MapperProxy代理对象,所以所有的方法都值执行invoker方法
1.Mapper.invoke()
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
try {
//首先判断是否需要去执行 SQL,还是直接执行方法。
//Object 本身的方法和 Java 8 中接口的默认方法不需要去执行SQL
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} else if (method.isDefault()) {
if (privateLookupInMethod == null) {
return invokeDefaultMethodJava8(proxy, method, args);
} else {
return invokeDefaultMethodJava9(proxy, method, args);
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
throw ExceptionUtil.unwrapThrowable(t);
}
//获取缓存,保存了方法签名和接口方法的关系
//为了提升 MapperMethod 的获取速度
final MapperMethod mapperMethod = cachedMapperMethod(method);
return mapperMethod.execute(sqlSession, args);
}
2.MapperMethod.execute()
public Object execute(SqlSession sqlSession, Object[] args) {
Object result;
switch (command.getType()) {
case INSERT: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.insert(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case UPDATE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.update(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case DELETE: {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = rowCountResult(sqlSession.delete(command.getName(), param));
break;
}
case SELECT:
if (method.returnsVoid() && method.hasResultHandler()) {
executeWithResultHandler(sqlSession, args);
result = null;
} else if (method.returnsMany()) {
result = executeForMany(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsMap()) {
result = executeForMap(sqlSession, args);
} else if (method.returnsCursor()) {
result = executeForCursor(sqlSession, args);
} else {
Object param = method.convertArgsToSqlCommandParam(args);
result = sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param);
if (method.returnsOptional()
&& (result == null || !method.getReturnType().equals(result.getClass()))) {
result = Optional.ofNullable(result);
}
}
break;
case FLUSH:
result = sqlSession.flushStatements();
break;
default:
throw new BindingException("Unknown execution method for: " + command.getName());
}
if (result == null && method.getReturnType().isPrimitive() && !method.returnsVoid()) {
throw new BindingException("Mapper method '" + command.getName()
+ " attempted to return null from a method with a primitive return type (" + method.getReturnType() + ").");
}
return result;
}
MapperMethod里面主要有两个参数 ,一 个是SqlCommand , 一 个 是MethodSignature,这两个都是 MapperMethod 的内部类。
在execute方法中,根据不同的type和返回类型:
调用 convertArgsToSqlCommandParam()将参数转换为 SQL 的参数。
调用 sqlSession 的 insert()、update()、delete()、selectOne ()方法
以查询为例,会走到 selectOne()方法。
3.DefaultSqlSession.selectOne()
sqlSession.selectOne(command.getName(), param)最终调用了selectList()方法
public T selectOne(String statement, Object parameter) {
// Popular vote was to return null on 0 results and throw exception on too many.
List list = this.selectList(statement, parameter);
if (list.size() == 1) {
return list.get(0);
} else if (list.size() > 1) {
throw new TooManyResultsException("Expected one result (or null) to be returned by selectOne(), but found: " + list.size());
} else {
return null;
}
}
在 SelectList()中,我们先根据 command name(Statement ID)从 Configuration中拿到 MappedStatement,这个 ms 上面有我们在 xml 中配置的所有属性,包括 id、statementType、sqlSource、useCache、入参、出参等等。执行了 Executor 的 query()方法。
public List selectList(String statement, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds) {
try {
MappedStatement ms = configuration.getMappedStatement(statement);
return executor.query(ms, wrapCollection(parameter), rowBounds, Executor.NO_RESULT_HANDLER);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw ExceptionFactory.wrapException("Error querying database. Cause: " + e, e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
3.1.执行器的选择
除了SIMPLE/REUSE/BATCH,还有一种包装类型CachingExecutor。
如果启用了二级缓存,就会先调用 CachingExecutor 的 query()方法,里面有缓存相关的操作,然后才是再调用基本类型的执行器。
在没有开启二级缓存的情况下,先会走到 BaseExecutor 的 query()方法(否则会先走到 CachingExecutor)。
4.BaseExecutor.query()
4.1.创建CacheKey
从 Configuration 中获取 MappedStatement, 然后从 BoundSql 中获取 SQL 信息,创建 CacheKey。这个 CacheKey 就是缓存的 Key。
然后再调用另一个 query()方法。
public List query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameter);
CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameter, rowBounds, boundSql);
return query(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
public CacheKey createCacheKey(MappedStatement ms, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, BoundSql boundSql) {
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
CacheKey cacheKey = new CacheKey();
cacheKey.update(ms.getId());
cacheKey.update(rowBounds.getOffset());
cacheKey.update(rowBounds.getLimit());
cacheKey.update(boundSql.getSql());
List parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings();
TypeHandlerRegistry typeHandlerRegistry = ms.getConfiguration().getTypeHandlerRegistry();
// mimic DefaultParameterHandler logic
for (ParameterMapping parameterMapping : parameterMappings) {
if (parameterMapping.getMode() != ParameterMode.OUT) {
Object value;
String propertyName = parameterMapping.getProperty();
if (boundSql.hasAdditionalParameter(propertyName)) {
value = boundSql.getAdditionalParameter(propertyName);
} else if (parameterObject == null) {
value = null;
} else if (typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(parameterObject.getClass())) {
value = parameterObject;
} else {
MetaObject metaObject = configuration.newMetaObject(parameterObject);
value = metaObject.getValue(propertyName);
}
cacheKey.update(value);
}
}
if (configuration.getEnvironment() != null) {
// issue #176
cacheKey.update(configuration.getEnvironment().getId());
}
return cacheKey;
}
4.2.清空本地缓存
queryStack 用于记录查询栈,防止递归查询重复处理缓存。
flushCache=true 的时候,会先清理本地缓存(一级缓存):clearLocalCache();
如果没有缓存,会从数据库查询:queryFromDatabase()
如果 LocalCacheScope == STATEMENT,会清理本地缓存。
4.3.从数据库查询
4.3.1.缓存
先在缓存用占位符占位。执行查询后,移除占位符,放入数据。
4.3.2.查询
执行 Executor 的 doQuery();默认是 SimpleExecutor。
public List query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
ErrorContext.instance().resource(ms.getResource()).activity("executing a query").object(ms.getId());
if (closed) {
throw new ExecutorException("Executor was closed.");
}
//flushCache=true 的时候,会先清理本地缓存(一级缓存)
if (queryStack == 0 && ms.isFlushCacheRequired()) {
clearLocalCache();
}
List list;
try {
//用于记录查询栈,防止递归查询重复处理缓存
queryStack++;
list = resultHandler == null ? (List) localCache.getObject(key) : null;
if (list != null) {
handleLocallyCachedOutputParameters(ms, key, parameter, boundSql);
} else {
//如果没有缓存,会从数据库查询
list = queryFromDatabase(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
} finally {
queryStack--;
}
if (queryStack == 0) {
for (DeferredLoad deferredLoad : deferredLoads) {
deferredLoad.load();
}
// issue #601
deferredLoads.clear();
//如果 LocalCacheScope == STATEMENT,会清理本地缓存。
if (configuration.getLocalCacheScope() == LocalCacheScope.STATEMENT) {
// issue #482
clearLocalCache();
}
}
return list;
}
private List queryFromDatabase(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, CacheKey key, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
List list;
localCache.putObject(key, EXECUTION_PLACEHOLDER);
try {
list = doQuery(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
} finally {
localCache.removeObject(key);
}
localCache.putObject(key, list);
if (ms.getStatementType() == StatementType.CALLABLE) {
localOutputParameterCache.putObject(key, parameter);
}
return list;
}
5.SimpleExecutor.doQuery()
public List doQuery(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) throws SQLException {
Statement stmt = null;
try {
Configuration configuration = ms.getConfiguration();
StatementHandler handler = configuration.newStatementHandler(wrapper, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
stmt = prepareStatement(handler, ms.getStatementLog());
return handler.query(stmt, resultHandler);
} finally {
closeStatement(stmt);
}
}
5.1.创建StatementHandler
在 configuration.newStatementHandler()中,new 一个StatementHandler,先得到 RoutingStatementHandler。
public StatementHandler newStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
StatementHandler statementHandler = new RoutingStatementHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
statementHandler = (StatementHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(statementHandler);
return statementHandler;
}
RoutingStatementHandler 里 面 没 有 任 何 的 实 现 , 是 用 来 创 建 基 本 的StatementHandler 的。这里会根据 MappedStatement 里面的 statementType 决定StatementHandler 的 类 型 。 默 认 是 PREPARED ( STATEMENT 、 PREPARED 、CALLABLE)。
public RoutingStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
switch (ms.getStatementType()) {
case STATEMENT:
delegate = new SimpleStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
break;
case PREPARED:
delegate = new PreparedStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
break;
case CALLABLE:
delegate = new CallableStatementHandler(executor, ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
break;
default:
throw new ExecutorException("Unknown statement type: " + ms.getStatementType());
}
}
StatementHandler 里面包含了处理参数的 ParameterHandler 和处理结果集的ResultSetHandler。
这2个对象是在这里创建的
protected BaseStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
this.configuration = mappedStatement.getConfiguration();
this.executor = executor;
this.mappedStatement = mappedStatement;
this.rowBounds = rowBounds;
this.typeHandlerRegistry = configuration.getTypeHandlerRegistry();
this.objectFactory = configuration.getObjectFactory();
if (boundSql == null) { // issue #435, get the key before calculating the statement
generateKeys(parameterObject);
boundSql = mappedStatement.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
}
this.boundSql = boundSql;
this.parameterHandler = configuration.newParameterHandler(mappedStatement, parameterObject, boundSql);
this.resultSetHandler = configuration.newResultSetHandler(executor, mappedStatement, rowBounds, parameterHandler, resultHandler, boundSql);
}
这三个对象都是可以被插件拦截的四大对象之一,所以在创建之后都要用拦截器进行包装的方法。
public ParameterHandler newParameterHandler(MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, BoundSql boundSql) {
ParameterHandler parameterHandler = mappedStatement.getLang().createParameterHandler(mappedStatement, parameterObject, boundSql);
parameterHandler = (ParameterHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(parameterHandler);
return parameterHandler;
}
public ResultSetHandler newResultSetHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, RowBounds rowBounds, ParameterHandler parameterHandler,
ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
ResultSetHandler resultSetHandler = new DefaultResultSetHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterHandler, resultHandler, boundSql, rowBounds);
resultSetHandler = (ResultSetHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(resultSetHandler);
return resultSetHandler;
}
public StatementHandler newStatementHandler(Executor executor, MappedStatement mappedStatement, Object parameterObject, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler, BoundSql boundSql) {
StatementHandler statementHandler = new RoutingStatementHandler(executor, mappedStatement, parameterObject, rowBounds, resultHandler, boundSql);
statementHandler = (StatementHandler) interceptorChain.pluginAll(statementHandler);
return statementHandler;
}
5.2.创建Statement
用 new 出来的 StatementHandler 创建 Statement 对象的prepareStatement()方法对语句进行预编译,处理参数。
handler.query(stmt, resultHandler);
5.3.执行StatementHandler的query()方法
RoutingStatementHandler 的 query()方法,delegate 委派,最终执行 PreparedStatementHandler 的 query()方法。
5.4.执行PreparedStatement 的 execute() 方法
JDBC 包中的 PreparedStatement 的执行了。
5.5.ResultSetHandler处理结果集
resultSetHandler.handleResultSets(ps);
根据代码可知:我们会先拿到第一个结果集,如果没有配置一个查询返回多个结果集的情况,一般只有一个结果集。如果下面的这个 while 循环我们也不用,就是执行一次。然后会调用 handleResultSet()方法。
public List源码核心对象总结
| 对象 | 关联对象 | 作用 |
|---|---|---|
| Configuration | MapperRegistry TypeAliasRegistry TypeHandlerRegistry | 包含了 MyBatis 的所有的配置信息 |
| SqlSession | SqlSessionFactory DefaultSqlSession | 对操作数据库的增删改查的 API 进行了封装,提供给应用层使用 |
| Executor | BaseExecutor SimpleExecutor BatchExecutor ReuseExecutor | MyBatis 执行器,是 MyBatis 调度的核心,负责 SQL 语句的生成和查询缓存的维护 |
| StatementHandler | BaseStatementHandler SimpleStatementHandler PreparedStatementHandler CallableStatementHandler | 封装了 JDBC Statement 操作,负责对 JDBC statement 的操作,如设置参数、将 Statement 结果集转换成 List 集合 |
| ParameterHandler | DefaultParameterHandler | 把用户传递的参数转换成 JDBC Statement 所需要的参数 |
| ResultSetHandler | DefaultResultSetHandler | 把 JDBC 返回的 ResultSet 结果集对象转换成 List 类型的集合 |
| MapperProxy | MapperProxyFactory | 代理对象,用于代理 Mapper 接口方法 |
| MappedStatement | SqlSource BoundSql | MappedStatement 维护了一条 |