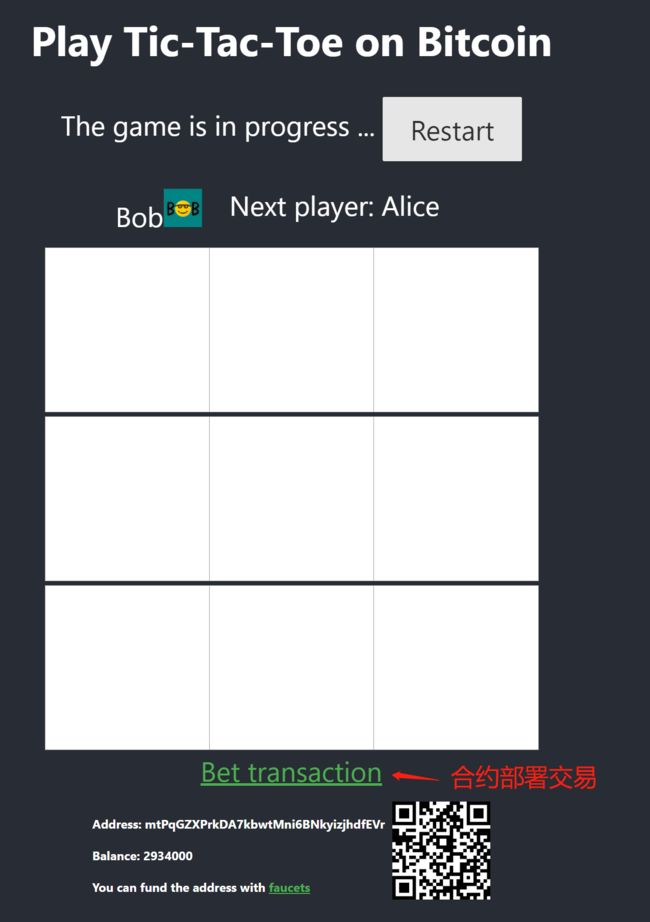
基于 sCrypt 合约开发一个完整的 dApp:井字棋游戏
在我们之前的博客中,介绍了如何使用 sCrypt 来编写比特币智能合约。但是作为刚入门的开发者,你可能对如何使用 sCrypt 来构建 dApp 更加感兴趣。接下来我们将教大家如何使用 sCrypt 一步一步地构建一个井字棋 dApp.
该应用程序非常简单,它所做的就是使用两个玩家(分别是 Alice 和 Bob)的公钥哈希,初始化合约,各自下注相同的金额锁定到合约中,只有赢得那个人可以取走合约里面的钱,如果最后没有人赢,则两个玩家各自可以取走一半的钱。目标不仅是对应用程序进行编码,主要是学习如何对其进行编译,测试,部署和交互的过程。
我们将逐步完成构建全栈去中心化应用程序的整个过程,包括:
- 编写合约
- 测试合约
- 将 web app 集成合约
搭建开发环境
- 安装 sCrypt IDE,见 sCrypt 开发工具篇 - Visual Studio Code 插件
- 安装 nodejs, version >= 12
- 安装 Typescript
搭建开发环境非常简单方便,接下来我们用 create-react-app 来创建一个 react app, 执行 npx create-react-app tic-tac-toe。然后用 vscode 打开我们刚刚创建的代码工程,并在根目录下创建一个contracts 目录,用来存放我们的合约代码,创建一个 test 目录,用来存放合约的测试代码。你将看到以下目录结构。
使用 sCrypt 编写 tic-tac-toe 合约
我们将使用 sCrypt 编程语言来编写一个名为 TicTacToe 的合约, TicTacToe 合约主要实现原理是将游戏的状态存储在合约中,这在之前的文章已经详细介绍过了
游戏状态由以下组成:
turn: 轮到谁下棋, 0 表示轮到 Alice, 1 表示轮到 Bob, 长度为 1 byteboard: 记录棋盘当前的状态,每个字节代表棋盘的一个位置,0 表示空,1 表示 ALICE,2 表示 BOB,长度为 9 byte
import "util.scrypt";
contract TicTacToe {
PubKey alice;
PubKey bob;
static const int TURNLEN = 1;
static const int BOARDLEN = 9;
static const bytes EMPTY = b'00';
static const bytes ALICE = b'01';
static const bytes BOB = b'02';
public function move(int n, Sig sig, int amount, SigHashPreimage txPreimage) {
require(Tx.checkPreimage(txPreimage));
require(n >= 0 && n < BOARDLEN);
bytes scriptCode = Util.scriptCode(txPreimage);
int scriptLen = len(scriptCode);
int boardStart = scriptLen - BOARDLEN;
// state: turn (1 byte) + board (9 bytes)
int turn = unpack(scriptCode[boardStart - TURNLEN : boardStart]);
bytes board = scriptCode[boardStart : ];
// not filled
require(Util.getElemAt(board, n) == EMPTY);
bytes play = turn == 0 ? ALICE : BOB;
PubKey player = turn == 0 ? this.alice : this.bob;
// ensure it's player's turn
require(checkSig(sig, player));
// make the move
board = Util.setElemAt(board, n, play);
bytes outputs = b'';
if (this.won(board, play)) {
// winner takes all
bytes outputScript = Util.pubKeyToP2PKH(player);
bytes output = Util.buildOutput(outputScript, amount);
outputs = output;
}
else if (this.full(board)) {
// draw: equally split, i.e., both outputs have the same amount
bytes aliceScript = Util.pubKeyToP2PKH(this.alice);
bytes aliceOutput = Util.buildOutput(aliceScript, amount);
bytes bobScript = Util.pubKeyToP2PKH(this.bob);
bytes bobOutput = Util.buildOutput(bobScript, amount);
outputs = aliceOutput + bobOutput;
} else {
// update state: next turn & next board
bytes scriptCode_ = scriptCode[ : scriptLen - BOARDLEN - TURNLEN] + num2bin(1 - turn, TURNLEN) + board;
bytes output = Util.buildOutput(scriptCode_, amount);
outputs = output;
}
require(hash256(outputs) == Util.hashOutputs(txPreimage));
}
// does play win after current move?
function won(bytes board, bytes play) : bool {
// three in a row, a column, or a diagnoal
int[8][3] lines = [
[0, 1, 2],
[3, 4, 5],
[6, 7, 8],
[0, 3, 6],
[1, 4, 7],
[2, 5, 8],
[0, 4, 8],
[2, 4, 6]
];
bool anyLine = false;
loop (8) : i {
bool line = true;
loop (3) : j {
line = line && Util.getElemAt(board, lines[i][j]) == play;
}
anyLine = anyLine || line;
}
return anyLine;
}
// is board full?
function full(bytes board) : bool {
bool full = true;
loop (BOARDLEN) : i {
full = full && Util.getElemAt(board, i) != EMPTY;
}
return full;
}
}
合约中有 3 个函数:
move爱丽丝(Alice)和鲍勃(Bob)各自将 X 个比特币锁定在包含上述合同的一个 UTXO 中。 接下来,他们通过调用公共函数move()交替玩游戏won检查是否有玩家已经赢得比赛,他将能取走所有合约锁定的赌注full如果棋盘,没人赢得比赛,则两个人平分赌注
测试合约
接下来我们用 Javascript 编写合约的单元测试,以确保合约在上线部署之前能够按预期工作。 通过sCrypt 测试框架,我们可以模拟调用 move() 并断言游戏状态
const Tictactoe = buildContractClass(runCompile('tictactoe.scrypt'));
game = new Tictactoe(new PubKey(toHex(publicKey1)), new PubKey(toHex(publicKey2)));
let state = new Bytes('00000000000000000000').toASM();
game.setDataPart(state)
describe('Test sCrypt contract Tictactoe In Javascript', () => {
let result, preimage, sig, prevLockingScript
it('Alice places an X at 0-th cell', () => {
prevLockingScript = game.lockingScript.toASM();
let newState = new Bytes('01010000000000000000').toASM();
const tx = newTx();
const newLockingScript = [game.codePart.toASM(), newState].join(' ');
tx.addOutput(new bsv.Transaction.Output({
script: bsv.Script.fromASM(newLockingScript),
satoshis: 10000
}))
preimage = getPreimage(tx, prevLockingScript, inputSatoshis);
sig = signTx(tx, privateKey1, prevLockingScript, inputSatoshis)
const context = {
tx, inputIndex, inputSatoshis }
result = game.move(0, new Sig(toHex(sig)), 10000, preimage).verify(context)
expect(result.success, result.error).to.be.true;
game.setDataPart(newState)
});
}
集成合约
1. 部署合约
我们将复用 官方 React 教程 中现有的 tic-tac-toe 项目。如果您有前端开发的经验,这应该看起来很熟悉。我们将专注于集成 dApp 的智能合约部分。对于与比特币区块链的所有交互,我们使用 whatsonchain 提供的 API。
-
通过右键单击 编译 来编译我们的合约。将会输出
tictactoe_desc.json,这包含有关我们合约的所有内容,将其拷贝到public目录中,以便我们的能从前端页面加载到该文件。

-
我们需要先实现一个测试网的钱包。我们将钱包的接口定义在wallet.ts 中, 包括以下接口:
//Dapp use this api to connect to the wallet. abstract requestAccount(name: string, permissions: string[]): Promise<Account>; //get wallet balance abstract getbalance(): Promise<number>; //sign raw transaction, returns unlockscript of the p2pkh input if success abstract signRawTransaction(tx: Tx, inputIndex: number, sigHashType: SignType ): Promise<string>; //get signature for special input abstract getSignature(tx: Tx, inputIndex: number, sigHashType: SignType ): Promise<string>; //send raw transaction, returns transaction hash if success abstract sendRawTransaction(rawTx: string): Promise<string>; //returns array of unspent transaction outputs, which total amount is more than the minAmount argument. abstract listUnspent(minAmount: number, options?: { purpose?: string }): Promise<UTXO[]>; //returns a new Bitcoin address, for receiving change. abstract getRawChangeAddress(options?: { purpose?: string }): Promise<string>; //returns a public key abstract getPublicKey(options?: { purpose?: string }): Promise<string>;localwallet.ts 则是我们的具体实现。
我们创建 wallet.js react 组件,并在页面中绘制出来

这样 Bob 和 Alice 就能往 dApp 充比特币了。
-
资金准备就绪后,就能使用步骤 1 中的
tictactoe_desc.json以及 Alice 和 Bob 的公钥来实例化合约了。async function fetchContract(alicePubKey, bobPubKey) { let { contractClass: TictactoeContractClass } = await web3.loadContract( "/tic-tac-toe/tictactoe_desc.json" ); let instance = newCall(TictactoeContractClass, [ new PubKey(toHex(alicePubKey)), new PubKey(toHex(bobPubKey)), ]); instance.setDataPart("00000000000000000000"); updateContractInstance(instance); console.log("fetchContract successfully"); return instance; } -
合约实例化后,可以通过合约实例来构建交易了,Alice 和 Bob 分别提供一个 Input,同时我们给他添加一个对应的 Output 用于找零,最后我们构建出来一个包含 2 个 Input 和 3 个 Output 的交易。
static async buildDeployTx(contract: AbstractContract, amountInContract: number, alicePrivateKey: string, bobPrivateKey: string): Promise<Tx> { let aliceWallet = new LocalWallet(NetWork.Testnet, alicePrivateKey); let bobWallet = new LocalWallet(NetWork.Testnet, bobPrivateKey); const aliceChangeAddress = await aliceWallet.getRawChangeAddress(); const bobChangeAddress = await bobWallet.getRawChangeAddress(); const tx: Tx = { inputs: [], outputs: [] }; tx.outputs.push({ script: contract.lockingScript.toHex(), satoshis: amountInContract * 2 }); const minAmount = amountInContract + FEE; return aliceWallet.listUnspent(minAmount, { purpose: 'change' }).then(async (utxos: UTXO[]) => { if (utxos.length === 0) { throw new Error('no utxos'); } //add input which using utxo from alice tx.inputs.push( { utxo: utxos[0], script: '', sequence: 0 } ); const changeAmount = utxos[0].satoshis - amountInContract - FEE; if (changeAmount <= 0) { throw new Error('fund is not enough'); } //add alice change output tx.outputs.push( { script: bsv.Script.buildPublicKeyHashOut(aliceChangeAddress).toHex(), satoshis: changeAmount } ); return tx; }).then(tx => { return bobWallet.listUnspent(minAmount, { purpose: 'change' }).then(async (utxos: UTXO[]) => { if (utxos.length === 0) { throw new Error('no utxos'); } //add input which using utxo from bob tx.inputs.push( { utxo: utxos[0], script: '', sequence: 0 } ); const changeAmount = utxos[0].satoshis - amountInContract - FEE; if (changeAmount <= 0) { throw new Error('fund is not enough'); } //add bob change output tx.outputs.push( { script: bsv.Script.buildPublicKeyHashOut(bobChangeAddress).toHex(), satoshis: changeAmount } ); return tx; }) }).then(tx => { //alice sign return aliceWallet.signRawTransaction(tx, 0, SignType.ALL).then(unlockscript => { tx.inputs[0].script = unlockscript; return tx; }) }).then(tx => { //bob sign return bobWallet.signRawTransaction(tx, 1, SignType.ALL).then(unlockscript => { tx.inputs[1].script = unlockscript; return tx; }) }) } -
交易构建完成后,分别由 Alice 和 Bob 进行签名,然后广播,从而完成合约的部署。我们尝试运行
npm start,并用浏览器打开http://localhost:3000, 尝试开始游戏,如果顺利,我们将会看到部署成功的交易,尝试打开浏览一下交易:
2. 调用合约
接下来就是开始下棋了,每下一步棋,就是对合约的一次调用,并触发合约状态的改变。调用合约需要构建一个符合合约规则的交易。首先需要计算合约的新状态,同时,我们可以在 dApp 通过棋盘状态推演出来谁输谁赢,这样就能根据结果来构建交易的输出。下面就是推演结果和构建调用合约交易的代码。
-
计算合约的新状态
calculateNewState(squares) { return (!this.state.xIsNext ? '00' : '01') + squares.map(square => { if (square && square.label === 'X') { return '01' } else if (square && square.label === 'O') { return '02' } else { return '00'; } }).join(''); } -
构建调用合约的交易
async buildCallContractTx(i, newState, squares, history) { let newLockingScript = ""; let winner = calculateWinner(squares).winner; const FEE = 3000; let outputs = []; let amount = this.props.game.lastUtxo.satoshis - FEE; if (winner) { // winner is current player let address = await web3.wallet.getRawChangeAddress(); newLockingScript = bsv.Script.buildPublicKeyHashOut(address).toHex(); outputs.push({ satoshis: amount, script: newLockingScript }) } else if (history.length >= 9) { const aliceAddress = new bsv.PublicKey(this.props.game.alicePubKey, { network: bsv.Networks.testnet }); const bobAddress = new bsv.PublicKey(this.props.game.bobPubKey, { network: bsv.Networks.testnet }); //no body win const aliceLockingScript = bsv.Script.buildPublicKeyHashOut(aliceAddress.toAddress(bsv.Networks.testnet)).toHex(); const bobLockingScript = bsv.Script.buildPublicKeyHashOut(bobAddress.toAddress(bsv.Networks.testnet)).toHex(); amount = (this.props.game.lastUtxo.satoshis - FEE) / 2; outputs.push({ satoshis: amount, script: aliceLockingScript }) outputs.push({ satoshis: amount, script: bobLockingScript }) } else { //next newLockingScript = [this.props.contractInstance.codePart.toHex(), bsv.Script.fromASM(newState).toHex()].join(''); outputs.push({ satoshis: amount, script: newLockingScript }) } if (outputs[0].satoshis <= 0) { alert(`fund in contract is too low `) return undefined; } let tx = { inputs: [{ utxo: this.props.game.lastUtxo, sequence: 0, script: "" }], outputs: outputs } let preimage = getPreimage(tx); let sig = await web3.wallet.getSignature(tx, 0, SignType.ALL, true); let unlockScript = this.props.contractInstance.move(i, new Sig(toHex(sig)), amount, preimage).toHex(); tx.inputs[0].script = unlockScript; return tx; }上面 Input 对应的
script默认是空的,也就是构建的交易并没包含解锁脚本,我们需要计算并填充解锁脚本,才能构成一个完整的交易。 我们知道 sCrypt 合约 的public方法的参数就是对应的解锁脚本。TicTacToe合约的 move 函数有 4 个参数:n棋盘位置amount合约花费后剩下的余额txPreimage交易原象, 如果您对这个参数不了解,可以查看深入学习比特币脚本之 OP_PUSH_TXsig对交易的签名
前面 2 个参我们都可以在 dApp 端计算,
txPreimage由于未签名的交易模板已经构建好,我们也可以直接在 dApp 端直接调用getPreimage方法计算。sig的计算涉及到私钥,我需要使用钱包的getSignature方法。当 4 个解锁参数我们都计算好之后,我们可以调用合约实例的
move方法来组装解锁脚本得到unlockScript... let unlockScript = this.props.contractInstance.move(i, new Sig(toHex(sig)), amount, preimage).toHex(); tx.inputs[0].script = unlockScript; // 填充解锁脚本后,交易才算是构建完整了 ... -
交易构建完成了,接下来通过 API 将交易广播到区块链上。同时我们更新合约最新的 UTXO, 以便下次调用合约时候可以直接使用。
web3.sendTx(tx).then(txid => { squares[i].tx = txid; squares[i].n = history.length; let gameState = { history: history.concat([ { squares, currentLocation: getLocation(i), stepNumber: history.length, }, ]), xIsNext: !this.state.xIsNext, currentStepNumber: history.length, }; server.saveGame(Object.assign({ }, this.props.game, { gameState: gameState, lastUtxo: { txHash: txid, outputIndex: 0, satoshis: tx.outputs[0].satoshis, script: tx.outputs[0].script } }), 'next') this.setState(gameState); }).catch(e => { ... })注意,由于这里我们使用的 localstorage 来模拟服务器通信,所以 alice 更新 UTXO 后,bob 也就能获取到对应的最新的 UTXO,在实际的生产环境中,合约的最新的 utxo 需要通过其它方法来获取。
至此,我们完成了 TicTacToe 小游戏下棋动作和合约调用的绑定,玩家的每个下棋动作,都产生一个区块链上对应的 transaction 与之对应。
总结
恭喜你! 您刚刚在比特币上构建了第一个全栈 dApp。 现在,您可以玩井字游戏或在比特币上构建您自己喜欢的游戏。现在是时候喝些香槟了,或者打开下方连接和小伙伴来一场比赛!
- 本文演示的游戏可以在 这里试玩(注意仅支持测试网,请勿使用主网上的钱包)
- 本文使用的所有代码均源自这个 Github Repo ,欢迎大家加星收藏。